present perfect tense: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
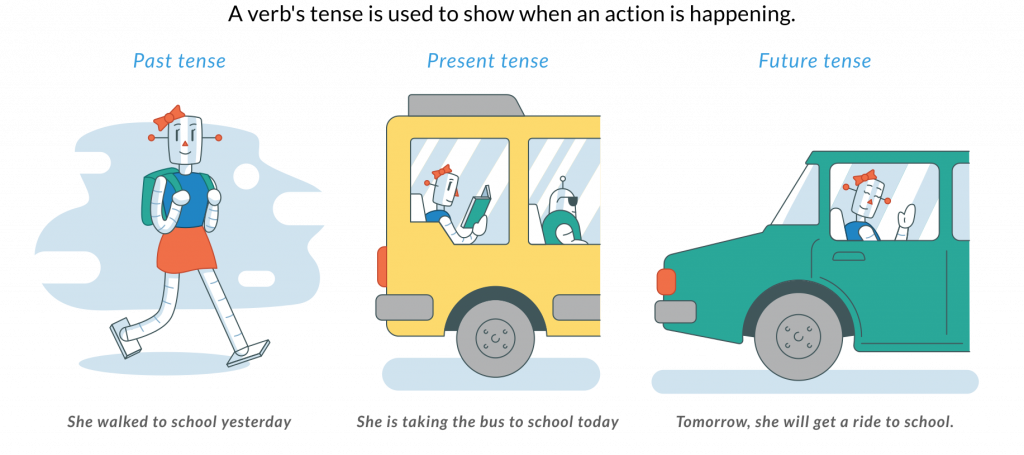
We know that verb tense is essential in understanding the action of the sentence was performed, but did you know that there are more ways to express tense than just past, present, and future?
While simple verb tense describes when an action or, perfect verb tense expresses when an action or. Although this is a small difference, it is an important one. Simple verb tense expresses the possibility of an action happening while perfect verb tense expresses with absolute certainty that the action will be completed.
There are some simple verb tenses and progressive verb tenses, as well as some irregular verbs, that do not follow the rules when changing tense. While this blog post focuses on perfect verb tenses, these other verb tenses can be explored in other blog posts on Albert.
When you’re ready, test yourself with a quiz and practice with our high-quality, standards-aligned questions here.
Table of Contents
The Basics of Perfect Verb Tense
What is Perfect Verb Tense?
Perfect verb tense is used to show an action that is complete and finished, or . This tense is expressed by adding one of the auxiliary verbs — or to the past participle form of the main verb.
For example:
-
I
have seen
the movie that was nominated for an Academy Award.
This sentence expresses that the speaker watching a particular movie and did not fall asleep halfway through.
How is Past Perfect Verb Tense Used in Writing?
Past perfect verb tense is created by adding or to the past participle form of the verb and is used in four distinct ways:
1. To show completed actions
For example:
-
I
had just finished
brushing my cat when she tore across the yard and jumped into a mud puddle.
In this example, the writer wants to emphasize the quick sequence of events as her cat went from clean to dirty within a matter of seconds.
2. To express conditional statements
For example:
-
If she
had studied
for her exam, she would have passed.
In this example, it is clear that the subject of the sentence did not study for her exam, as she did not pass. This sentence proposes a different outcome the subject a better decision.

3. In the form of a question
For example:
-
“
Have
you
seen
my hairbrush?” Larry asked Bob anxiously.
In this example, Larry is hopeful that Bob saw his hairbrush recently and can help him find it.
4. As a negative
For example:
He had not missed a single free-throw since the beginning of the season.
In this example, “negative” simply means that the word is added to the past perfect verb phrase. The use of this negative implies that the subject has a perfect free-throw average since he has never missed a shot.
How is Present Perfect Verb Tense Used in Writing?
Present perfect verb tense expresses an action that occurred at an indefinite (or unknown) time in the past or an action that started in the past and is continuing in the present time.
While past perfect verb tense is created by adding or to the past participle form of the verb, present perfect verb tense is created by adding or to the past participle form of the main verb.
For example:
-
The close bond between humans and dogs
has continued
to be a common theme in both literature and movies.
In this example, the writer implies that the theme of dogs as “man’s best friend” started at an indefinite or unknown time and is still relevant today.

How is Future Perfect Verb Tense Used in Writing?
Future perfect verb tense is formed by combining the auxiliary verbs will+have with the past participle form of the verb. This tense is used to show actions that either will be completed at some point in the future or will continue into the future.
It is similar to a situation. Here’s how: essentially when we talk in future perfect tense, we are speaking about the future as if we have already experienced it and we are looking back on it.
In the antagonist travels to the future and learns the results of every major sporting event. When he returns to the present day, he builds enormous wealth and power because he can bet with absolute certainty on the outcome of each game throughout his life.
Here is a real life example:
-
When I turn 21, I
will have visited
all fifty states.
This is a pretty bold statement, but when we use the future perfect tense, we are speaking with the authority of someone who knows the future to be true. Maybe the speaker has already planned a nationwide road trip or already visited 49 states with only one to go. Or, maybe the speaker is simply overconfident and should have used a simple future verb tense instead!
Either way, the future perfect verb tense should only be used when the speaker or writer has absolute confidence that something will be completed or will continue into the future.
What is Perfect Progressive Verb Tense?
The main difference between perfect verb tense and perfect progressive verb tense is the form of the main verb that is used.
While perfect verb tense pairs an auxiliary verb with a , perfect progressive verb tense combines the same auxiliary verb with the word and aending in .
Here are some helpful definitions and examples:
Past Perfect Progressive: This verb tense describes a past, ongoing action that occurred before another past action in time.
For example:
-
Before her family moved, she
had been attending
a private school.
Present Perfect Progressive: This verb tense describes an action that started in the past, is continuing now in the present, and may continue into the future.
For example:
-
He
has been dating
her for several months.
Future Perfect Progressive: This verb tense describes a future, ongoing action that will occur before a specified future time.
For example:
-
In the next few years, we
will have been wearing
masks
and
washing
our hands more often than ever before.
Return to the Table of Contents
3 Tips for Understanding Perfect Verb Tense
Here are some important tips to help you understand perfect verb tense:

Tip #1. Perfect verb tense is created when the auxiliary verb , , or is paired with the past participle form of the main verb
For example:
-
Past Perfect: Robin Hood
had outwitted
the Sheriff of Nottingham on countless occasions.
-
Present Perfect: Maid Marian
has loved
Robin Hood ever since they first met.
-
Future Perfect: Prince John
will have cried
for his mommy when things do not go his way.
Tip #2. If the auxiliary verbs or are used without a main verb, they are considered linking verbs and do not express perfect verb tense
For example:
-
Perfect Verb Tense: I
have watched
over twenty times.
-
Linking Verb (
not
perfect verb tense): I
have
a lovely bunch of coconuts.

Tip #3. Perfect progressive verb tense is a combination of the auxiliary verb phrase , , or and the -ing form of the main verb
For example:
-
Past Perfect: Aladdin
had been lying
to Jasmine about his true identity.
-
Present Perfect: Jafar
has been manipulating
the king for some time.
-
Future Perfect: The Genie
will have been helping
his friend, Aladdin, even after being freed.
Return to the Table of Contents
Applying the Basics: Perfect Verb Tense Review & Practice
Now that you understand how perfect verb tense functions in sentences, review the anchor chart below and complete the review to fully understand how to use and recognize perfect verb tense as well as how to differentiate it from other verb tenses.
The Ultimate List of Verb Tenses
Refer to the graphic below to learn the different types of Verb Tenses, including perfect verb tense:
This list, obviously, does not include all possible verbs and their tenses; however, it is meant to be used as a guide while identifying different types of verb tenses.
Perfect Verb Tense Exercises and Review
Now that you understand perfect verb tense, test your ability to recognize which verb tense is needed in the sentences below.
Select the correct verb tense in the sentences below. Remember, past perfect verb tense describes events that have happened in the past, present perfect verb tense describes events that have happened currently, and future perfect verb tense describes events will have happened.
1. Although Charlie dreamed of finding a golden ticket, he has/had/have never expected to actually find one.
In this sentence, is the correct auxiliary to use to express past perfect tense. You know that past perfect tense is needed because the other verb in this sentence, , is also in past tense, and verbs must always agree with one another in tense.
2. No one was surprised when Augustus Gloop fell into the chocolate river; he has/had/have been drinking greedily from it just moments earlier.
In this sentence, is the correct verb to use to express past perfect progressive tense. This verb does a perfect job describing how a continual action in the past led to the current action of Augustus falling into the river.
3. When he accompanies Charlie to Wonka’s chocolate factory, Grandpa George will has/had/have walked for the first time in twenty years.
In this sentence, is the correct verb to use to express future perfect tense. Grandpa George insists on accompanying Charlie to the factory, and he is so confident in his decision that he is miraculously able to walk again.
4. Slugworth has/had/have been searching unsuccessfully for the secret behind Wonka’s Everlasting Gobstopper candy.
In this sentence, is the correct use of the present perfect progressive verb tense. It would not be past perfect progressive tense because Slugworth has not been successful in his search, meaning, the search must be ongoing. Slugworth has searched for this recipe in the past, he has been searching in the present, and he will continue to search for this elusive recipe in the future.
5. The Oompa Loompas were a mysterious tribe of people who has/had/have left their home to work for Mr. Wonka in his chocolate factory.
In this sentence, is the correct past perfect verb tense since the Oompa Loompas left their home for good in the past.
Pro Tip:
- Perfect verb tense
always expresses an action that has either been completed, is being completed, or will be completed.
- Perfect progressive verb tense
expresses an ongoing action that was completed in the past, an ongoing action that started in the past, continues in the present, and will be continued in the future, and an ongoing action that will be completed in the future.
For additional practice, check out Perfect Verb Tense content on Albert.
Return to the Table of Contents
Try for Yourself: Perfect Verb Tense Quiz

Feeling confident in your understanding of Perfect Verb Tense?
Take this short six-question quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Which three auxiliary verbs are used before the main verb to show perfect verb tense?
-
Answer: has, have, and had
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right!
Perfect verb tense
is shown through the pairing of the auxiliary verb
or
with the main verb.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
perfect verb tense
is shown through the pairing of the auxiliary verb
or
with the main verb.
2. What ending does the main verb use to show perfect progressive tense?
-
Answer: -ing
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right!
Perfect progressive tense
is shown through the combination of the auxiliary verbs have been, has been, or had been and the -ing form of the main verb.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
perfect progressive tense
is shown through the combination of the auxiliary verbs have been, has been, or had been and the -ing form of the main verb, while
perfect verb tense
is shown through the combination of the auxiliary verb have, has, or had with the past participle form of the main verb.
3. In this sentence, is the future tense verb, “will have been barking” simple, perfect, or perfect progressive tense?
If he keeps this up, the neighbor’s dog will have been barking all night.
-
Answer: Perfect Progressive Tense
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verb
is
future perfect progressive tense
, meaning that the speaker believes that the dog will continue the ongoing action of barking into the next morning.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
perfect progressive verb tenses
express a future, ongoing action and consist of the auxiliary verb phrase “
combined with the -ing form of the main verb, which in this case, is “
”.
4. In this sentence, is the present tense verb, , simple, perfect, or perfect progressive tense?
She has witnessed her start-up company evolve from a few employees in a single room to a multi-million dollar business with employees stationed around the world.
-
Answer: Perfect Verb Tense
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verb phrase,
, implies an action that started in the past and continues in the present day. Therefore, this verb is
present perfect tense
.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
present perfect tense
implies an action that started in the past and continues in the present day and is shown by the combination of the auxiliary verb,
or
, and the past participle form of the main verb.
5. In this sentence, is the past participle verb, simple, perfect, or perfect progressive tense?
They will be attending the awards ceremony this evening.
-
Answer: Progressive verb tense
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right! In this sentence, the phrase
implies an ongoing activity that will occur in the future; therefore, a
future progressive verb
is required.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
future progressive verb tense
implies an ongoing activity that will occur in the future, such as,
6. In this sentence, is a past perfect or past perfect progressive tense verb needed?
Four years ago I had graduated/had been graduating from my alma mater.
-
Answer: bumped: Past Perfect Tense
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right! Since graduating is an accomplishment that takes place during the span of only a few hours on a single day, a
past perfect tense verb
is needed to show that this action has been completed. A
past perfect progressive tense verb
would be incorrect because it implies that the speaker has been graduating from college every day for the past four years.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
past perfect tense verbs
are used to show that an action has been completed in the past, like graduating. A
past perfect progressive tense verb
would be incorrect because it implies that the speaker has been graduating from college every day for the past four years.
For additional practice with Perfect Verb Tense, check out our completely free practice on Albert: Perfect Verb Tense.
Return to the Table of Contents
Teacher’s Corner for Perfect Verb Tenses
Even if students understand that verb tense can be expressed as an action happening in the past, present, or future, it is possible that students may not realize the many other ways to express tense that goes beyond the simplest categories. Perfect verb tense is a great example in showing students how subtle changes in verb tense can affect a writer’s tone.
For example, a writer stating in simple future tense that “” does not give the reader much of a sense of when, or even if, this will happen in the story!
However, if the author uses future perfect tense, the tone of the sentence and possibly the entire story changes: “”
Suddenly, the story has intrigue because the writer has established an unwavering timeline. Instead of getting annoyed at Elizabeth in the first sentence for not thinking to look under the rocks, the second sentence invests the reader in learning what leads Elizabeth to eventually uncover this hidden hoard.
While the Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart provides a broad look at where students should ideally land in their understanding of grammatical concepts, for specific standards on the many different types of verb tense including perfect verb tense, refer to the Common Core State Standards website.
Albert provides a variety of verb tense practice assignments, including a Perfect Verb Tense Practice. Albert has also created ready-to-use assessments and quizzes on a range of grammatical topics that can be used by educators to track student understanding and progress.
Summary for Perfect Verb Tense
Whenever you want to express with certainty that an action was completed, is being completed, or will be completed, use perfect verb tense.
Whenever you want to express an ongoing action that was completed, an ongoing, perpetual action that started in the past, continues in the present, and will continue in the future, or an ongoing action that will be completed in the future, use perfect progressive verb tense.
Be sure to check out our free grammar course for more Perfect Verb Tense practice.
You can also access over 3,400 free, high-quality questions that address nearly every grammatical concept.
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.
[Update] Present Perfect Tense – настоящее совершенное время в английском языке ‹ engblog.ru | present perfect tense – NATAVIGUIDES
Present Perfect (Present Perfect Simple) – настоящее совершенное время. Ему нет соответствий в русском языке. Нам может быть трудно понять Present Perfect, потому что англоговорящие люди иначе воспринимают понятие времени. С точки зрения русского языка действие в настоящем времени не может закончиться, на то оно и настоящее. Если действие завершилось (прошло), значит, время должно быть прошедшее. Английский язык придерживается другой логики: в нем действие в настоящем может закончиться, и пример этому – Present Perfect.
Как образуется Present Perfect
Утверждение
Сказуемое в Present Perfect состоит из вспомогательного глагола have (has) и основного глагола. С местоимениями I, you, we, they и существительными во множественном числе мы используем have, с местоимениями he, she, it и существительными в единственном числе – has.
В качестве основного глагола в Present Perfect мы используем третью форму глагола. Получить ее можно двумя способами: если глагол правильный, мы добавляем окончание -ed к основе. Если глагол неправильный, мы берем форму из третьей колонки таблицы неправильных глаголов.
I/We/You/They + have + 3-я форма глагола
He/She/It + has + 3-я форма глагола
I have started. – Я начал.
We have gone. – Мы ушли.
You have finished. – Вы закончили.
They have come. – Они пришли.
He has decided. – Он решил.
She has done. – Она сделала.
It has turned off. – Оно выключилось.
Отрицание
Для того чтобы построить отрицательное предложение в Present Perfect, нам надо поставить между вспомогательным глаголом и основным отрицательную частицу not.
I/We/You/They + have not + 3-я форма глагола
He/She/It + has not + 3-я форма глагола
I have not started. – Я не начал.
We have not gone. – Мы не ушли.
You have not finished. – Вы не закончили.
They have not come. – Они не пришли.
He has not decided. – Он не решил.
She has not done. – Она не сделала.
It has not turned off. – Оно не выключилось.
Глагол to have (has) может принимать сокращенные формы. В утвердительном предложении have (has) объединяется с местоимением, в сокращенном виде have выглядит как ‘ve, has как ‘s:
- We’ve gone.
- He’s decided.
В отрицательном предложении have (has) объединяется с not, сокращенные формы выглядят как haven’t, hasn’t:
- I haven’t started.
- She hasn’t done.
В разговорной речи чаще встречаются сокращенные формы, чем полные.
Вопрос
Have + I/we/you/they + 3-я форма глагола
Has + he/she/it + 3-я форма глагола
Have I started? – Я начал?
Have we gone? – Мы ушли?
Have you finished? – Вы закончили?
Have they come? – Они пришли?
Has he decided? – Он решил?
Has she done? – Она сделала?
Has it turned off? – Оно выключилось?
Изучить сразу все функции времени Present Perfect практически невозможно, поэтому мы решили разделить все функции на 3 удобные группы согласно уровню владения английским языком: начальный (зеленая рамка), средний (желтая рамка), высокий (красная рамка).
Употребление Present Perfect
Начальный уровень
- Мы используем Present Perfect, когда хотим показать результат действия, которое уже совершилось. С помощью Present Perfect мы акцентируем внимание именно на результате и по нему видим, что действие уже выполнено. Гораздо легче понять, что значит результат, на примере глаголов «делать» и «сделать»:
- Я делал это – I did it. (Past Simple – действие было в прошлом)
- Я сделал это – I have done it. (действие закончилось, значит, есть результат)
К действию с результатом относится:
- Действие с наречиями already (уже), just (только что), yet (уже, еще). Они указывают на то, что действие произошло недавно и в результате что-то изменилось.
I know Jane. We have already met. – Я знаком с Джейн, мы уже встречались. (мы встречались в прошлом, поэтому, как результат, сейчас я ее знаю)
I don’t want to go to the café, I’ve just eaten. – Я не хочу идти в кафе, я только что поел. (я не голодный, это результат того, что я недавно ел)
Наречие yet используется в вопросах и отрицаниях. В отрицательном предложении yet переводится как «еще», в вопросе – «уже». Yet обычно стоит в конце предложения.
– Is Jim here? – Джим здесь?
– No, he hasn’t arrived yet. – Нет, он еще не приехал.Have you been to the new supermarket yet? – Ты уже была в новом супермаркете?
- Действие, которое произошло в прошлом, неважно когда, но в настоящем виден результат.
I have bought a new car. – Я купил новую машину. (я уже совершил покупку, мы не знаем, когда это произошло, но видим результат – новую машину)
They aren’t at home, they have gone shopping. – Их нет дома, они ушли за покупками. (неважно, когда они ушли, важно, что сейчас их нет)
Еще результат действия может влиять на настоящее:
She has lost her keys, she can’t get home now. – Она потеряла ключи, теперь она не может попасть домой. (из-за того, что она потеряла ключи в прошлом, она не может открыть дверь в настоящем)
- Действие, которое произошло в незаконченный период времени. На незаконченный период нам указывают слова today (сегодня), this morning/week/month/year (этим утром / на этой неделе / в этом месяце / в этом году). У нашего действия уже есть результат, но сегодня, эта неделя / этот месяц / этот год еще не закончились, то есть мы успеем выполнить действие или повторить его еще раз за этот период.
Today he has visited two galleries. – Сегодня он побывал в двух галереях. (сегодня еще не закончилось, и он может отправиться в третью галерею)
I haven’t been at work this week because of sickness. – Я не был на работе на этой неделе из-за болезни. (но неделя еще не закончилась, и я могу выйти на работу на этой неделе)
- Present Perfect используется, когда мы говорим о нашем личном опыте. Эту функцию часто называют «жизненный опыт».
I’ve been to England but I haven’t been to Scotland. – Я был в Англии, но не был в Шотландии. (на данный момент моей жизни я посетил Англию и не успел посетить Шотландию, но я все еще надеюсь там побывать)
- В таких предложениях не указывают точное время. Но вы можете подчеркнуть, сколько раз действие происходило:
– Have you read this book? – Ты прочитал эту книгу?
– Yes, I have read this book twice already. – Да, я прочитал эту книгу уже дважды.I have eaten in this restaurant many times. – Я ел в этом ресторане много раз.
А можете говорить в целом, не указывая точное количество раз:
– Have you read this book? – Ты прочитал эту книгу?
– Yes, I have read this book. – Да, я прочитал эту книгу.I have eaten in this restaurant. – Я ел в этом ресторане.
- Наречия ever (когда-нибудь) и never (никогда) часто встречаются, когда мы говорим о жизненном опыте. Они показывают, что мы делали или не делали в нашей жизни. Обратите внимание, что never замещает частицу not.
– Have you ever seen this film? – Ты видел когда-нибудь этот фильм?
– No, I have never seen this film before. – Нет, я никогда не видел этот фильм раньше.– Has he ever been abroad? – Он когда-нибудь был за границей?
– No, he hasn’t. – Нет, не был.I have never eaten mango. – Я никогда не ел манго.
- В таких предложениях не указывают точное время. Но вы можете подчеркнуть, сколько раз действие происходило:
- Здесь представлен далеко не самый полный список слов и выражений, употребляемых в Present Perfect. У этого времени очень много спутников – читайте о них в нашей статье «Наречия с Present Perfect: слова-маркеры».
Когда еще употребляется Present Perfect
Средний уровень
- Помимо результата, Present Perfect показывает длительное действие, которое все еще актуально: оно началось в прошлом, но продолжается в настоящем и, возможно, будет продолжаться в будущем. Обычно в этих случаях стоят предлоги for (в течение) и since (с тех пор как, начиная с). For указывает на то, сколько действие длится, since показывает, что действие началось в определенный момент в прошлом и сейчас все еще длится. Возможно, вы скажете, что это функция времени Present Perfect Continuous. Так и есть, но Present Perfect также употребляется в этом значении в нескольких случаях:
- C глаголами состояния, которые почти не используются с временами группы Continuous.
We’ve known each other since school years. – Мы знаем друг друга со школы.
She has wanted to become an actress since her childhood. – Она мечтает стать актрисой с детства.
- С глаголами, которые сами по себе передают длительное действие (to live – жить, to work – работать, to study – учиться, to sleep – спать, to wait – ждать). В этом случае мы можем использовать как Present Perfect, так и Present Perfect Continuous, при этом смысл предложения не поменяется.
I’ve studied English for 5 years. – Я учу английский в течение 5 лет. (я начал 5 лет назад, продолжаю сейчас и, возможно, буду учить в будущем)
I’ve lived in the suburbs since childhood. – Я живу в пригороде с детства. (я начал жить еще в детстве и продолжаю жить в пригороде сейчас)
- В отрицательных предложениях, когда мы сообщаем о том, чего не делали в течение какого-то времени.
I haven’t heard of him for the last 3 years. – Я о нем ничего не слышал последние три года.
We haven’t been to Rome since our honeymoon. – Мы не были в Риме с нашего медового месяца.
У глаголов to be и to go в Present Perfect есть дополнительные оттенки значения: have been означает, что говорящий где-то был, куда-то ходил или ездил и сейчас оттуда вернулся. А has gone означает, что говорящий куда-то ушел или уехал и пока не вернулся.
She has been to Madrid. – Она была в Мадриде. (но сейчас она дома)
She has gone to Madrid. – Она уехала в Мадрид. (она все еще в Мадриде)
- C глаголами состояния, которые почти не используются с временами группы Continuous.
- Мы употребляем Present Perfect, когда хотим подчеркнуть, сколько раз выполнялось действие. Для этого используется конструкция it is (that is) the first/second/third time something has happened – это первый/второй/третий раз, как что-то произошло.
It is the first time I have driven a car. = I have never driven a car before. – Я в первый раз водил машину.
That is the fifth time Bill has phoned his girlfriend this evening. = He has called his girlfriend five times this evening. – Билл позвонил своей девушке уже пятый раз за вечер.
Сложные случаи употребления Present Perfect
Высокий уровень
- Present Perfect используется вместе с Past Simple в сложных предложениях. Для того чтобы показать точное время, когда действие началось, мы используем придаточное времени с союзом since / ever since (с тех пор как). Это придаточное будет в Past Simple, главное предложение – в Present Perfect.
He hasn’t played the cello since he broke his bow. – Он не играет на виолончели с тех пор, как сломал смычок.
I’ve lived like this ever since I moved to London. – Я так живу с тех пор, как переехал в Лондон.
Мы можем употреблять Present Perfect в придаточном предложении, если действие в придаточном началось в прошлом и продолжается в настоящем.
Have you invited any of your friends since you’ve lived in your new apartment? – Ты приглашал кого-нибудь из друзей с тех пор, как живешь в новой квартире?
- Время Present Perfect очень часто путают со временем Past Simple. О том, как избежать подобной путаницы, вы можете узнать из статьи «Present Perfect и Past Simple: разница между временами»
After he graduates from Harvard, he will find a promising job. = After he has graduated from Harvard, he will find a promising job. – После того как он окончит Гарвард, он устроится на перспективную работу.
Present Perfect предпочтительнее Present Simple:
- Когда мы хотим показать, что действие в главном может быть выполнено, только если выполнить действие в придаточном.
As soon as I’ve got to the station I’ll buy the tickets. – Как только я приеду на станцию, я куплю билеты. (я смогу купить билеты, когда буду на станции, раньше не смогу)
You can’t write the article on the subject until you’ve read this book. – Ты не можешь писать статью по этой теме, пока не прочтешь эту книгу. (в книге написано что-то важное, без чего нельзя написать статью)
- Если мы хотим логически выделить или эмоционально подчеркнуть, что одно действие произойдет раньше другого.
I’ll call you when I’ve got home. – Я позвоню тебе, когда попаду домой. (я хочу подчеркнуть, что сначала я приду домой и только потом позвоню)
Let’s have a farewell party before you’ve gone to Paris. – Давай устроим прощальный ужин, прежде чем ты уедешь в Париж. (мы хотим подчеркнуть, что в Париже не сможем устроить тебе прощальный ужин)
A pony has escaped from the zoo. Zookeepers were looking for it in the neighbourhood, but with no luck. The police found the pony at the far end of the city. It was walking in the park and was asking the passers-by for some treat. – Пони сбежал из зоопарка. Работники зоопарка искали его в окрестностях, но безуспешно. Полиция обнаружила пони на другом конце города. Он гулял в парке и просил угощения у прохожих.
Как видите, Present Perfect не кажется таким уж нелогичным и непонятным, если в нем разобраться. Кроме того, у этого времени очень много слов-спутников – наречий, которые помогают нам распознать настоящее совершенное время. Да, Present Perfect можно назвать самой сложной темой в изучении английских времен, но если вы его освоили, то все остальные времена вам покажутся сущим пустяком.
Для того чтобы закрепить полученные знания, рекомендуем пройти тест и скачать табличку-шпаргалку с правилами образования Present Perfect.
↓ Скачать таблицу употребления времени Present Perfect (*.pdf, 186 Кб)
Тест
Present Perfect Tense
1. Выберите правильный вариант ответа
Задание 1.
They …
-
has just arrived.
-
have just arrived.
-
have arrived just.
Задание 2.
She … .
-
has already gone
-
have already gone
-
has already go
Задание 3.
… the new book yet?
-
You have read
-
Have you read
-
Has you read
Задание 4.
I … here for 6 years.
-
have live
-
have liven
-
have lived
Задание 5.
He … a teacher of English since 2009.
-
has be
-
have been
-
has been
Задание 6.
I … this film eight times.
-
‘ve seen
-
‘ve saw
-
‘s seen
Задание 7.
… to Disneyland?
-
Has you been ever
-
Has you ever been
-
Have you ever been
Задание 8.
He … the bike.
-
has never fallen off
-
haven’t ever fallen off
-
have never fallen off
Задание 9.
He … to India, but he will go there soon.
-
not has been
-
haven’t been
-
hasn’t been
Задание 10.
It is the first time he … a mountain.
-
has climbed
-
has climbt
-
has climbing
2. Исправьте ошибки в предложениях, используя, где необходимо, Present Perfect
Задание 1.
He just left the party.
Задание 2.
We has not seen each other ever since he got married.
Задание 3.
You will not come out until you finished tidying up.
Задание 4.
I will call as soon as I will arrive at the airport.
Задание 5.
I have not play tennis since I have broke my arm in 1996.
Тест недоступен для мобильных устройств.
Тест недоступен для мобильных устройств.
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Present Perfect
In this video, students learn two common uses of the present perfect tense. They also learn the difference between regular and irregular past participles. For more videos and lessons, visit us at https://esllibrary.com.
Link to lesson: https://esllibrary.com/courses/88/lessons/1597
Subscribe to ESL Library’s YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/c/Esllibrary
Follow us for more great content!
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/esllibrary/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ESLlibrary/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/esllibrary/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ESLlibrary/
Pinterest: https://ar.pinterest.com/esllibrary/
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

Learn English Tenses: PRESENT PERFECT
It’s time to learn the PRESENT PERFECT. What does it mean to say “I have worked” or “I have understood”? Many students are confused by the PRESENT PERFECT TENSE, because it combines the past and the present. Yet this advanced verb tense can lead to success in a job interview or on your IELTS! In this complete English class, I’ll show you how to use this tense, when to use it, and what mistakes to avoid. You will move forward stepbystep, to master this tense by learning structure, usage, pronunciation, spelling, contractions, questions, short answers, past participles, regular verbs, and irregular verbs. Then, continue your progress through my complete English Tenses series by watching the next lesson, which compares the present perfect and past simple tenses: https://youtu.be/UmdGwttUfKU
Introduction to Present Perfect 0:00
When to use the Present Perfect tense 5:19
Present Perfect: Common Expressions 9:42
When not to use the Present Perfect tense 15:19
How to use the Present Perfect tense: Regular Verbs 20:33
How to use the Present Perfect tense: Irregular Verbs 26:51
Present Perfect: Contractions 32:02
Present Perfect: Short Answers 37:27
Present Perfect: Practice 40:26
Present Perfect: Common Errors 46:12
Present Perfect: Conclusion 54:53
After the lesson, take the quiz: https://www.engvid.com/presentperfecttense/

Introduction to Present Perfect Tense | EasyTeaching
Learn when to use the present perfect tense in English and how to form present perfect. Understand the difference between present perfect and past simple. Check out our Present Perfect Activity Video https://youtu.be/S6CnTCRXvkc
Like us on Facebook at https://www.facebook.com/easyteachingnet/ for more free downloads!
Find more resources at https://easyteaching.net

The Present Perfect Tense in English | Structuring Sentences
The present perfect is formed, in the affirmative, as follows
Subject + have + past participle + object.
I + have + climbed + the mountain!
Example: have climbed the mountain!
The past participle is, often, the same as the past simple form of the verb (although not always so be sure to learn them!), except it has a different function here. The auxiliary verb is the one linked to the subject; the past participle simply denotes the action while the I have…, You have…, etc. denotes who had the experience.
Conjugating the Present Perfect (affirmative)
I have climbed the mountain
You have climbed the mountain
He/She has climbed the mountain
We have climbed the mountain
They have climbed the mountain
As is quite common in English, all these conjugations are the same except for one: the third person. One must be careful to remember this exception. Apart from this, the present perfect is quite simple; now you can go forth fully equipped to brag about your experiences in any conversation!
Forming the Present Perfect (negative)
The present perfect (negative) is formed as follows:
Subject + have + not + past participle + object.
We + have + not + eaten + Thai food.
We have not eaten Thai food.
Conjugating the Present Perfect (affirmative)
I have not eaten Thai food
You have not eaten Thai food
He/She has not eaten Thai food
We have not eaten Thai food
They have not eaten Thai food
It is important to keep in mind the order of the various parts of these phrases. Remember always that the negation (not) goes between the auxiliary verb and the past participle.
We can also employ a contraction here which will make conversation easier. In this case there are two contractions to be learned
have not ⇒ haven’t
has not ⇒ hasn’t
With our newly learned contractions, the conjugations become
I haven’t eaten Thai food
You haven’t eaten Thai food
He/She hasn’t eaten Thai food
We haven’t eaten Thai food
They haven’t eaten Thai food
Forming the Present Perfect (interrogative)
The present perfect (interrogative) is formed as follows
Have + subject + past participle + object?
Have + you + visited + South Carolina?
Have you visited South Carolina?
Conjugating the Present Perfect
Have I visited South Carolina ?
Have you visited South Carolina ?
Has he/she visited South Carolina ?
Have we visited South Carolina ?
Have they visited South Carolina ?
Again, we can add negation in order to affect emphasis. For example
Robert: Do you know much about Elvis Presley?
John: Haven’t I visited Memphis?
John answers Robert’s question with another question, which he believes should suffice as an answer. In this case, John means that he indeed knows much about Elvis Presley and has even visited his home in Memphis.
With the negation (and contraction), our interrogative conjugations become:
Haven’t I visited Memphis?
Haven’t you visited Memphis?
Hasn’t he/she visited Memphis?
Haven’t we visited Memphis?
Haven’t they visited Memphis?

8- شرح زمن المضارع التام في اللغه الانجليزيه Present Perfect
شرح زمن المضارع التام في اللغه الانجليزيه Present Perfect .عندنا في اللغه العربيه الموضوع بسيط جدا فيما يتعلق بالازمنه هم 3 ازمنه اما ماضي او مضارع او مستقبل
لكن في اللغه الانجليزيه الموضوع مختلف بعض الشئ كل زمن له 4 صور
واصعبهم بالنسبه للكثير هي الصور التامه
ولكن الموضوع اسهل مما تتخيل 🙂
كما يمكنك مشاهدة الدروس السابقه من هنا :
شرح زمن الماضي البسيط Past Simple
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rlbFDiuwlF0
شرح زمن المضارع البسيط Present Simple
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5TjpEcrNbCc
شرح زمن المستقبل البسيط Future Simple
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TDhm2xLyg8
شرح زمن الماضي المستمر Past Continuous
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZqQG54ydsY
شرح زمن المضارع المستمر Present Continuous
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oBzkMfEXj1s
شرح زمن المستقبل المستمر Future Continuous
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q2Vkhcvq9uw
شرح زمن الماضي التام في اللغه الانجليزيه Past Perfect
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8QehpHhgN04
وهذا رابط صفحتنا علي فيسبوك:
http://www.facebook.com/droosonline
وهذا الايميل الشخصي لي:
[email protected]
وهذا هو موقعنا:
http://www.droosonline.com

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่LEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ present perfect tense