present perfect tense examples: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
We know that verb tense is essential in understanding the action of the sentence was performed, but did you know that there are more ways to express tense than just past, present, and future?
While simple verb tense describes when an action or, perfect verb tense expresses when an action or. Although this is a small difference, it is an important one. Simple verb tense expresses the possibility of an action happening while perfect verb tense expresses with absolute certainty that the action will be completed.
There are some simple verb tenses and progressive verb tenses, as well as some irregular verbs, that do not follow the rules when changing tense. While this blog post focuses on perfect verb tenses, these other verb tenses can be explored in other blog posts on Albert.
When you’re ready, test yourself with a quiz and practice with our high-quality, standards-aligned questions here.
Table of Contents
The Basics of Perfect Verb Tense
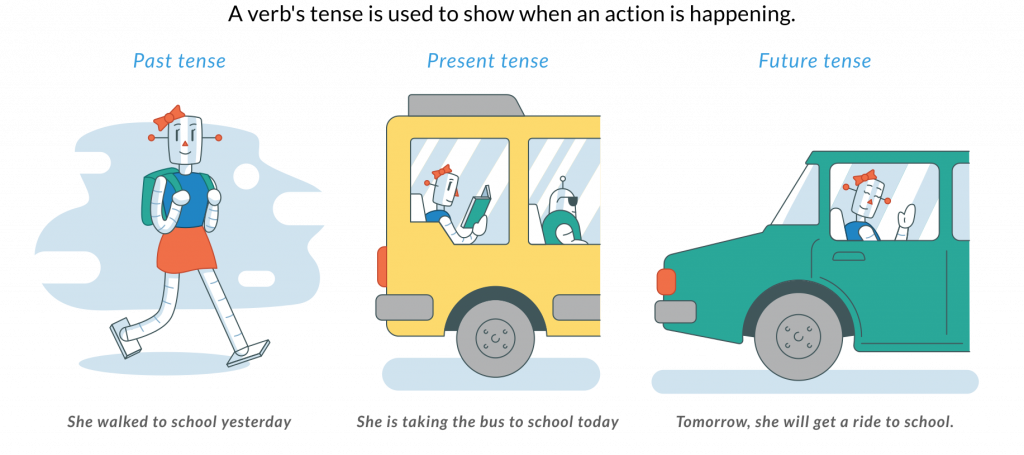
What is Perfect Verb Tense?
Perfect verb tense is used to show an action that is complete and finished, or . This tense is expressed by adding one of the auxiliary verbs — or to the past participle form of the main verb.
For example:
-
I
have seen
the movie that was nominated for an Academy Award.
This sentence expresses that the speaker watching a particular movie and did not fall asleep halfway through.
How is Past Perfect Verb Tense Used in Writing?
Past perfect verb tense is created by adding or to the past participle form of the verb and is used in four distinct ways:
1. To show completed actions
For example:
-
I
had just finished
brushing my cat when she tore across the yard and jumped into a mud puddle.
In this example, the writer wants to emphasize the quick sequence of events as her cat went from clean to dirty within a matter of seconds.
2. To express conditional statements
For example:
-
If she
had studied
for her exam, she would have passed.
In this example, it is clear that the subject of the sentence did not study for her exam, as she did not pass. This sentence proposes a different outcome the subject a better decision.

3. In the form of a question
For example:
-
“
Have
you
seen
my hairbrush?” Larry asked Bob anxiously.
In this example, Larry is hopeful that Bob saw his hairbrush recently and can help him find it.
4. As a negative
For example:
He had not missed a single free-throw since the beginning of the season.
In this example, “negative” simply means that the word is added to the past perfect verb phrase. The use of this negative implies that the subject has a perfect free-throw average since he has never missed a shot.
How is Present Perfect Verb Tense Used in Writing?
Present perfect verb tense expresses an action that occurred at an indefinite (or unknown) time in the past or an action that started in the past and is continuing in the present time.
While past perfect verb tense is created by adding or to the past participle form of the verb, present perfect verb tense is created by adding or to the past participle form of the main verb.
For example:
-
The close bond between humans and dogs
has continued
to be a common theme in both literature and movies.
In this example, the writer implies that the theme of dogs as “man’s best friend” started at an indefinite or unknown time and is still relevant today.

How is Future Perfect Verb Tense Used in Writing?
Future perfect verb tense is formed by combining the auxiliary verbs will+have with the past participle form of the verb. This tense is used to show actions that either will be completed at some point in the future or will continue into the future.
It is similar to a situation. Here’s how: essentially when we talk in future perfect tense, we are speaking about the future as if we have already experienced it and we are looking back on it.
In the antagonist travels to the future and learns the results of every major sporting event. When he returns to the present day, he builds enormous wealth and power because he can bet with absolute certainty on the outcome of each game throughout his life.
Here is a real life example:
-
When I turn 21, I
will have visited
all fifty states.
This is a pretty bold statement, but when we use the future perfect tense, we are speaking with the authority of someone who knows the future to be true. Maybe the speaker has already planned a nationwide road trip or already visited 49 states with only one to go. Or, maybe the speaker is simply overconfident and should have used a simple future verb tense instead!
Either way, the future perfect verb tense should only be used when the speaker or writer has absolute confidence that something will be completed or will continue into the future.
What is Perfect Progressive Verb Tense?
The main difference between perfect verb tense and perfect progressive verb tense is the form of the main verb that is used.
While perfect verb tense pairs an auxiliary verb with a , perfect progressive verb tense combines the same auxiliary verb with the word and aending in .
Here are some helpful definitions and examples:
Past Perfect Progressive: This verb tense describes a past, ongoing action that occurred before another past action in time.
For example:
-
Before her family moved, she
had been attending
a private school.
Present Perfect Progressive: This verb tense describes an action that started in the past, is continuing now in the present, and may continue into the future.
For example:
-
He
has been dating
her for several months.
Future Perfect Progressive: This verb tense describes a future, ongoing action that will occur before a specified future time.
For example:
-
In the next few years, we
will have been wearing
masks
and
washing
our hands more often than ever before.
Return to the Table of Contents
3 Tips for Understanding Perfect Verb Tense
Here are some important tips to help you understand perfect verb tense:

Tip #1. Perfect verb tense is created when the auxiliary verb , , or is paired with the past participle form of the main verb
For example:
-
Past Perfect: Robin Hood
had outwitted
the Sheriff of Nottingham on countless occasions.
-
Present Perfect: Maid Marian
has loved
Robin Hood ever since they first met.
-
Future Perfect: Prince John
will have cried
for his mommy when things do not go his way.
Tip #2. If the auxiliary verbs or are used without a main verb, they are considered linking verbs and do not express perfect verb tense
For example:
-
Perfect Verb Tense: I
have watched
over twenty times.
-
Linking Verb (
not
perfect verb tense): I
have
a lovely bunch of coconuts.

Tip #3. Perfect progressive verb tense is a combination of the auxiliary verb phrase , , or and the -ing form of the main verb
For example:
-
Past Perfect: Aladdin
had been lying
to Jasmine about his true identity.
-
Present Perfect: Jafar
has been manipulating
the king for some time.
-
Future Perfect: The Genie
will have been helping
his friend, Aladdin, even after being freed.
Return to the Table of Contents
Applying the Basics: Perfect Verb Tense Review & Practice
Now that you understand how perfect verb tense functions in sentences, review the anchor chart below and complete the review to fully understand how to use and recognize perfect verb tense as well as how to differentiate it from other verb tenses.
The Ultimate List of Verb Tenses
Refer to the graphic below to learn the different types of Verb Tenses, including perfect verb tense:
This list, obviously, does not include all possible verbs and their tenses; however, it is meant to be used as a guide while identifying different types of verb tenses.
Perfect Verb Tense Exercises and Review
Now that you understand perfect verb tense, test your ability to recognize which verb tense is needed in the sentences below.
Select the correct verb tense in the sentences below. Remember, past perfect verb tense describes events that have happened in the past, present perfect verb tense describes events that have happened currently, and future perfect verb tense describes events will have happened.
1. Although Charlie dreamed of finding a golden ticket, he has/had/have never expected to actually find one.
In this sentence, is the correct auxiliary to use to express past perfect tense. You know that past perfect tense is needed because the other verb in this sentence, , is also in past tense, and verbs must always agree with one another in tense.
2. No one was surprised when Augustus Gloop fell into the chocolate river; he has/had/have been drinking greedily from it just moments earlier.
In this sentence, is the correct verb to use to express past perfect progressive tense. This verb does a perfect job describing how a continual action in the past led to the current action of Augustus falling into the river.
3. When he accompanies Charlie to Wonka’s chocolate factory, Grandpa George will has/had/have walked for the first time in twenty years.
In this sentence, is the correct verb to use to express future perfect tense. Grandpa George insists on accompanying Charlie to the factory, and he is so confident in his decision that he is miraculously able to walk again.
4. Slugworth has/had/have been searching unsuccessfully for the secret behind Wonka’s Everlasting Gobstopper candy.
In this sentence, is the correct use of the present perfect progressive verb tense. It would not be past perfect progressive tense because Slugworth has not been successful in his search, meaning, the search must be ongoing. Slugworth has searched for this recipe in the past, he has been searching in the present, and he will continue to search for this elusive recipe in the future.
5. The Oompa Loompas were a mysterious tribe of people who has/had/have left their home to work for Mr. Wonka in his chocolate factory.
In this sentence, is the correct past perfect verb tense since the Oompa Loompas left their home for good in the past.
Pro Tip:
- Perfect verb tense
always expresses an action that has either been completed, is being completed, or will be completed.
- Perfect progressive verb tense
expresses an ongoing action that was completed in the past, an ongoing action that started in the past, continues in the present, and will be continued in the future, and an ongoing action that will be completed in the future.
For additional practice, check out Perfect Verb Tense content on Albert.
Return to the Table of Contents
Try for Yourself: Perfect Verb Tense Quiz

Feeling confident in your understanding of Perfect Verb Tense?
Take this short six-question quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Which three auxiliary verbs are used before the main verb to show perfect verb tense?
-
Answer: has, have, and had
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right!
Perfect verb tense
is shown through the pairing of the auxiliary verb
or
with the main verb.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
perfect verb tense
is shown through the pairing of the auxiliary verb
or
with the main verb.
2. What ending does the main verb use to show perfect progressive tense?
-
Answer: -ing
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right!
Perfect progressive tense
is shown through the combination of the auxiliary verbs have been, has been, or had been and the -ing form of the main verb.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
perfect progressive tense
is shown through the combination of the auxiliary verbs have been, has been, or had been and the -ing form of the main verb, while
perfect verb tense
is shown through the combination of the auxiliary verb have, has, or had with the past participle form of the main verb.
3. In this sentence, is the future tense verb, “will have been barking” simple, perfect, or perfect progressive tense?
If he keeps this up, the neighbor’s dog will have been barking all night.
-
Answer: Perfect Progressive Tense
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verb
is
future perfect progressive tense
, meaning that the speaker believes that the dog will continue the ongoing action of barking into the next morning.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
perfect progressive verb tenses
express a future, ongoing action and consist of the auxiliary verb phrase “
combined with the -ing form of the main verb, which in this case, is “
”.
4. In this sentence, is the present tense verb, , simple, perfect, or perfect progressive tense?
She has witnessed her start-up company evolve from a few employees in a single room to a multi-million dollar business with employees stationed around the world.
-
Answer: Perfect Verb Tense
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verb phrase,
, implies an action that started in the past and continues in the present day. Therefore, this verb is
present perfect tense
.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
present perfect tense
implies an action that started in the past and continues in the present day and is shown by the combination of the auxiliary verb,
or
, and the past participle form of the main verb.
5. In this sentence, is the past participle verb, simple, perfect, or perfect progressive tense?
They will be attending the awards ceremony this evening.
-
Answer: Progressive verb tense
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right! In this sentence, the phrase
implies an ongoing activity that will occur in the future; therefore, a
future progressive verb
is required.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
future progressive verb tense
implies an ongoing activity that will occur in the future, such as,
6. In this sentence, is a past perfect or past perfect progressive tense verb needed?
Four years ago I had graduated/had been graduating from my alma mater.
-
Answer: bumped: Past Perfect Tense
-
Correct Explanation: That’s right! Since graduating is an accomplishment that takes place during the span of only a few hours on a single day, a
past perfect tense verb
is needed to show that this action has been completed. A
past perfect progressive tense verb
would be incorrect because it implies that the speaker has been graduating from college every day for the past four years.
-
Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember,
past perfect tense verbs
are used to show that an action has been completed in the past, like graduating. A
past perfect progressive tense verb
would be incorrect because it implies that the speaker has been graduating from college every day for the past four years.
For additional practice with Perfect Verb Tense, check out our completely free practice on Albert: Perfect Verb Tense.
Return to the Table of Contents
Teacher’s Corner for Perfect Verb Tenses
Even if students understand that verb tense can be expressed as an action happening in the past, present, or future, it is possible that students may not realize the many other ways to express tense that goes beyond the simplest categories. Perfect verb tense is a great example in showing students how subtle changes in verb tense can affect a writer’s tone.
For example, a writer stating in simple future tense that “” does not give the reader much of a sense of when, or even if, this will happen in the story!
However, if the author uses future perfect tense, the tone of the sentence and possibly the entire story changes: “”
Suddenly, the story has intrigue because the writer has established an unwavering timeline. Instead of getting annoyed at Elizabeth in the first sentence for not thinking to look under the rocks, the second sentence invests the reader in learning what leads Elizabeth to eventually uncover this hidden hoard.
While the Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart provides a broad look at where students should ideally land in their understanding of grammatical concepts, for specific standards on the many different types of verb tense including perfect verb tense, refer to the Common Core State Standards website.
Albert provides a variety of verb tense practice assignments, including a Perfect Verb Tense Practice. Albert has also created ready-to-use assessments and quizzes on a range of grammatical topics that can be used by educators to track student understanding and progress.
Summary for Perfect Verb Tense
Whenever you want to express with certainty that an action was completed, is being completed, or will be completed, use perfect verb tense.
Whenever you want to express an ongoing action that was completed, an ongoing, perpetual action that started in the past, continues in the present, and will continue in the future, or an ongoing action that will be completed in the future, use perfect progressive verb tense.
Be sure to check out our free grammar course for more Perfect Verb Tense practice.
You can also access over 3,400 free, high-quality questions that address nearly every grammatical concept.
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.
[Update] Present Perfect Tense With Examples | present perfect tense examples – NATAVIGUIDES
There are
many parts of tenses but unlike the present
indefinite tense, the present perfect tense itself is perfect and
keeps its significance alone. This tense is used when the action is perfectly
acted out recently. When you have done any action recently, which tense is to
be used in such a case? There are several positions where the present perfect
tense must be used. In our today’s article, we would surely learn Present perfect tense rules and its
uses with detailed examples.
Formation of the tense with various subjects
Subject
Helping Verb
Action verb
I
Have
V3
We, You, They
Have
V3
She, He, It
Has
V3
Singular
Has
V3
Plural
Have
V3
In this tense we often speak of
the actions that has taken place recently,
Types of sentences wherein the
present perfect tense is used. We use certain adverbs to indicate them in the
sentences that leave a recognizable impact for the beginners to catch them.
Note :- We always use the past
participle in the present perfect tense which is also commonly known as V3. In
case you have no idea about the types of verbs, here are a few to show you. The
last V3 you need to use in this tense.
V1 V2 V3
Go went gone
Come came come
Cut cut cut
Study studied studied
Buy bought bought
Adverbs For Present Perfect Tense
(Yet,
as yet, just, just now, already, recently, lately, frequently, so far, for
since, this morning, ever, never, once, twice, thrice, always, several times,
up to now, and up to the present etc.)
These
are the adverbs that you can see in the sentences or can use in your own
sentences. These adverbs are very crucial for the competitive exams whomsoever
is preparing for these exams, must take these Rules down for further practice or
revision.
Here are the types of sentences wherein these
different uses are going to be used.
1. Affirmative: the affirmative are austere
sentences used as a statement to give an answer or describe something.
(Subject + Has / Have +
V3 + object)
Example -:
A.P.J. Kalam has amalgamated a great name and fame in the field of aeronautics
engineering as a rocket scientist.
2. Negative: the
negative sentences show a disagreement from a speaker’s end for something.
These sentences contain adverbs to show negation in the sentences so that the
reader can easily find out it. These are not, never, seldom, rarely,
barely, or neither nor, few etc.
[Subject + Has / Have +
Not + V3 + object]
Example -:
I have not understood this theory even after being explained several times in
the class.
3. Interrogative:
you can answers with an affirmation or a negation but when it comes to asking
something to something. How can you raise questions? for this task you need
question formation that comes under the interrogative sentences. The questions
are formed using type of pronoun which interrogative pronoun words such as
What, When, Why … etc.
(Interrogative
pronoun + Has / Have + Subject +V3 + object?)
Example -:
How many grammar lessons
have you learnt completely?
4. Negative
Interrogative: The negative interrogative
questions consist of two types of sentences one is a negative sentence and
another is an interrogative sentences come together to form a sentence. This
requires an exact answer with a bit explanation for a question.
(W.H.F. words +
Has / Have + Subject + not + V3+ Object?)
Example -: Why hasn’t she finished her work and slept by now?
Present perfect tense rules
1.
Recent
action -: the first and foremost use of present perfect tense is that it
describes a recent action that has been completed recently.
Example
:- Neeraj Chopra has won the gold
medal in the Olympics in men’s javelin throw and created an adamant record for
others.
:– The
Taliban attack has made the Afghanistan army surrender and give
them the charge of the country.
2.
Past
action -: In this use we describe actions that took place in the past but
can be defined with the sources available at the time.
Examples
:– I have worked for this company for several months.
:- The Defence research and development organization (DRDO) has
provide the county a vivid recognition amongst the world countries.
3.
Untimely
actions -: there are certain actions that don’t have any
specific time period hence these are used in the present perfect tense.
Examples
:- We have already applied for our enrollment in the master of arts
in the high demanding colleges.
:– Some employees have not received their salary yet due to
covid19.
4.
Significant
actions -: some actions took place in the past but still have importance.
Examples
:- My family has visited one of the
seven wonders The Taj Mahal.
:– They have helped their
domestic helper innumerous times.
5.
Past
started actions till now -: we have several actions that we
started doing in the past and still continue them. These types of sentences are
used in the present perfect tense.
Examples
:- I have taught at the Success
Mirror more for than 4 years.
:– She has known more for almost
3 years.
:– Millions of people have been
ill due to Coronavirus across the world.
6.
With
after / When -: We often use after / when to make an
antecedent assumption of a future action wherein the present perfect tense is
used.
Examples
:- After he has finished his course at the Harvard University, he
will apply for the post of a data analytic.
:– When she has finished her work, she will talk to me.
7.
With
Since or For :- these actions are also used with since and
for adverbs of time. These words help them show the actions that took place in
the past but still manage their continuity anyhow.
Use of For
For
is used for a period of time and shows unspecific starting time for the
actions.
For
four hours For several days
For
some weeks For three years
Use of Since
Since
is used to show a point of time and shows a specific beginning time for the
actions.
Since 6’ o clock since
childhood
Since morning since
15th August 1947
Since Monday since
February
Examples
:- The boys have been practicing for the Indian army physical for
several months.
:– The teacher has been educating us since 1st Nov,
2019.
:- I have been working in this company for more than 1 year and 9
months.
:- The children have been going to schools since their childhood.
I hope that you have surely learnt the multiple uses of the
present perfect tense by now. For a personal introspection, here is the Present Perfect tense Exercise
for you to examine your learning progress yourself and comment the answers for
the same.
1.
Rahul _______ (finish) his work by now.
2.
They ________ (watch) DDLJ
movie several times.
3.
The children ______ (leave) studying
after school closing.
4.
I ___ not ____ (eat) anything
since morning.
5.
She ____ just ____ (start) working in this
company.
In case you don’t the verbs,
kindly take help from the below help box.
V1 V2 V3
Finish Finished Finished
Watch Watched Watched
Leave Left Left
Eat Ate Eaten
Start Started Started
What have you done lately? Present Perfect Tense
Learn how to use the present perfect tense through a short story and pay attention to the time expressions used like ever, never, just, always, already, yet.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

The Present Perfect Tense in English | Structuring Sentences
The present perfect is formed, in the affirmative, as follows
Subject + have + past participle + object.
I + have + climbed + the mountain!
Example: have climbed the mountain!
The past participle is, often, the same as the past simple form of the verb (although not always so be sure to learn them!), except it has a different function here. The auxiliary verb is the one linked to the subject; the past participle simply denotes the action while the I have…, You have…, etc. denotes who had the experience.
Conjugating the Present Perfect (affirmative)
I have climbed the mountain
You have climbed the mountain
He/She has climbed the mountain
We have climbed the mountain
They have climbed the mountain
As is quite common in English, all these conjugations are the same except for one: the third person. One must be careful to remember this exception. Apart from this, the present perfect is quite simple; now you can go forth fully equipped to brag about your experiences in any conversation!
Forming the Present Perfect (negative)
The present perfect (negative) is formed as follows:
Subject + have + not + past participle + object.
We + have + not + eaten + Thai food.
We have not eaten Thai food.
Conjugating the Present Perfect (affirmative)
I have not eaten Thai food
You have not eaten Thai food
He/She has not eaten Thai food
We have not eaten Thai food
They have not eaten Thai food
It is important to keep in mind the order of the various parts of these phrases. Remember always that the negation (not) goes between the auxiliary verb and the past participle.
We can also employ a contraction here which will make conversation easier. In this case there are two contractions to be learned
have not ⇒ haven’t
has not ⇒ hasn’t
With our newly learned contractions, the conjugations become
I haven’t eaten Thai food
You haven’t eaten Thai food
He/She hasn’t eaten Thai food
We haven’t eaten Thai food
They haven’t eaten Thai food
Forming the Present Perfect (interrogative)
The present perfect (interrogative) is formed as follows
Have + subject + past participle + object?
Have + you + visited + South Carolina?
Have you visited South Carolina?
Conjugating the Present Perfect
Have I visited South Carolina ?
Have you visited South Carolina ?
Has he/she visited South Carolina ?
Have we visited South Carolina ?
Have they visited South Carolina ?
Again, we can add negation in order to affect emphasis. For example
Robert: Do you know much about Elvis Presley?
John: Haven’t I visited Memphis?
John answers Robert’s question with another question, which he believes should suffice as an answer. In this case, John means that he indeed knows much about Elvis Presley and has even visited his home in Memphis.
With the negation (and contraction), our interrogative conjugations become:
Haven’t I visited Memphis?
Haven’t you visited Memphis?
Hasn’t he/she visited Memphis?
Haven’t we visited Memphis?
Haven’t they visited Memphis?

The easiest way to learn English
Learning English is not easy, but if you know the right way to learn, it will be very effective. In this lesson, there are methods and tricks for learning English in the best way.

Past Perfect Tense
Learn how to use correctly the past perfect tense in this video. You’re going to see several situations where we need to use this tense. Words like already, when, after, before, never can indicate that Past Perfect could be used.

Present Perfect Tense – English grammar tutorial video lesson
The present perfect tense might be a hard tense for learners of English and students often have a hard time keeping the present perfect tense apart from the past simple tense. In this English grammar lesson I am going to show you how to form a present perfect tense, and when to use a present perfect tense. But before we get started it’s good to know how to conjugate the verb ‘to have’.
For the singular forms:
I have
you have
he has
she has
it has.
For the plural forms:
we have
you have
they have.
It’s also good to know that in the English language there are regular and irregular verbs. And it is advisable that you study the most commonly used irregular verbs.
Now let’s get started. Take a look at these sentences:
I have painted the door yellow.
They have paid for dinner themselves.
Both these sentences are in the present perfect tense.
How to form a present perfect tense. Let’s have a look at the regular verbs. For the regular verbs we use the auxiliary verb ‘to have’ and the past participle. You can make the past participle by adding ‘ed’ to the infinitive form of the verb.
Now let’s have a look at the singular forms.
I have worked there.
You have listened carefully.
He has cleared the table.
She has placed it on the floor.
It has snowed.
For the plural forms:
We have walked to school.
You have watched the tennis match.
They have marked the tests.
Now we need to pay extra attention to verbs that end in an ‘e’.
Such as live, close and wipe. For these verbs we use the auxiliary verb to
have and the past participle. But the past participle is made by simply adding a ‘d’ to the verb.
Look at the examples:
I have lived here for quite some time now.
He has closed the window.
They have wiped the floor.
We also need to pay attention to verbs that end in a ‘y’, especially those preceded by consonant such as spy and study because we change the ‘y’ into an ‘i’.
For example:
He has spied on his neighbours.
We have studied hard.
Now let’s have a look at the irregular verbs. For the irregular verbs we also use the auxiliary verb to have and the past participle.
But for the irregular verbs the past participle has a unique present perfect form. Take a look at the examples:
I have built that shed with my own two hands. (The infinitive form of the verb is to build.)
She has bought some flowers at the market.(The infinitive form of the verb is ‘to buy’.)
We have run the marathon. (The infinitive form of the verb is to run.)
Now let’s have a look at the present perfect tense in questions.
First for the regular verbs. Again we use the auxiliary verb ‘to
have’ and the past participle.
Has she talked to him yet?
Have you kicked the ball?
Have they ever worked on a farm?
For the irregular verbs we also use the auxiliary verb ‘to have’
and the past participle, but now the unique present perfect tense form.
For example
Has she quit her job yet?
Have you ever driven a car?
Have they ever paid for dinner?
Let’s have a look at the present perfect tense in negations.
For the regular verbs the auxiliary verb ‘to have’ and we add ‘not’,
contracting it into haven’t or hasn’t and the past participle.
I haven’t listened to the news.
It hasn’t rained since Friday
They haven’t closed the window.
For the irregular verbs we also use the verb ‘to have’, and not contracting it into haven’t and hasn’t and the past participle.
For example:
She hasn’t quit her job. (The infinitive form is ‘to quit’.)
You haven’t ever driven a car. (The infinitive form is ‘to drive’.)
They haven’t paid for dinner. (The infinitive form of the verb is ‘to pay’.)
Let’s have a look at the present perfect tense in use. We use the present perfect tense for things that happened in the past, but it is not important when they
happened.
I have been to Scotland. It’s not important when I’ve been there, it’s important that I’ve been to Scotland.
They’ve decided to buy a car. It’s not important when they decided it, the decision alone is important.
We also use the present perfect tense for things that started in the past,
that have continued in the present.
For example:
Bob and Jack have known each other for ages. (For example they met in the 1970s, and they are still friends.)
They have lived there since 2011. (So they moved there in 2011 and they’ve continued to live there.)
We also use the present perfect tense, when the following words are in a sentence:
for, yet, never, ever, just, already, since.
Here are some examples:
I have lived here for three years.
We haven’t seen that film yet.
Have you ever watched a football game?
www.englishgrammarspot.com

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆLEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ present perfect tense examples