relative clause คือ: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
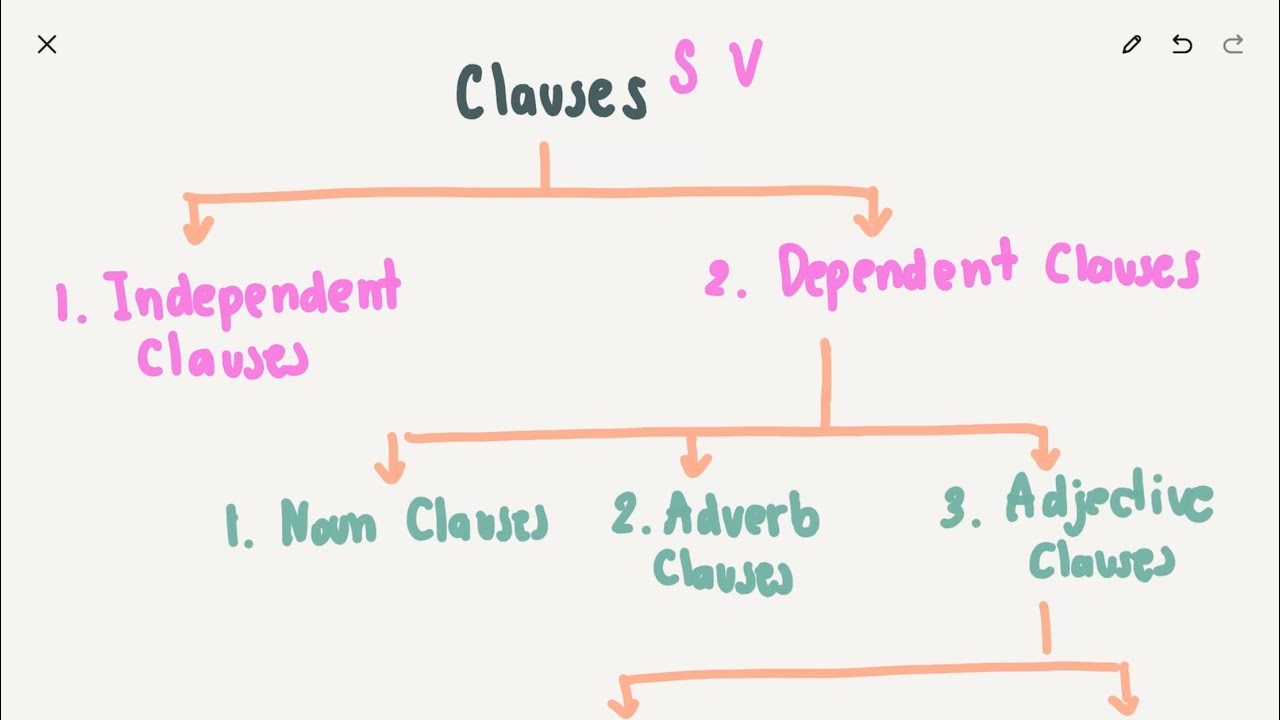
Complex
Sentences
��ͻ���¤����Сͺ���»���¤��ѡ
(main clause) �Ѻػ���¤ (subordinate
clause) ����������ö���������Ӿѧ
���ͧ����»���¤��ѡ����
ػ���¤�
complex sentences ����ö��ṡ�͡�� 3 ���������
1) adjective clauses
(relative clause)
2) noun
clauses
3) adverb
clauses
1. Adjective
Clauses (Relative Clauses)���ػ���¤����˹�ҷ�������Ӥس�Ѿ��
��͢��¤ӹ�� ���Ҩ����Фӹ����������������������������ǡѺ�ӹ�����
adjective clauses ������Ѻ����¤��ѡ���� relative pronoun (�� who,
whom, whose, + whom, which, of which, +
which, that) ��� relative adverb (�� where,
when, why) ��觷�˹�ҷ���иҹ ���� ������ǹ����� adjective
clause ����
adjective
clauses �Ҩ���͡�� 3 ���������
1.1 �繻���¤�س�Ѿ�������Фӹ�����١����
�ҡ����ջ���¤�س�Ѿ�����й�����
��з����ӹ��㹻���¤��ѡ�դ��������ա���ҧ˹�� ��
Students
who get grade A in all subjects will be sent for special training in the
U.S.
[ػ���¤ who get grade A in all subjects �� restrictive
relative clause ���������ҹѡ���¹������ͺ���ô A �ء�Ԫ� (����Ǥ�� �����ѡ���¹�ء��) �ж١�������Ѻ���ͺ������ɷ���������Ѱ����ԡ�
����ҡ����ջ���¤�س�Ѿ�����й����¤ӹ�� students ��еդ������������ ���¶֧�ѡ���¹�ء��]
People
who do such silly things are fools.
[ػ���¤ who do such silly things �� restrictive
relative clause ���������Ҥ��������������� ��� �
Ẻ��� (����Ǥ��
����褹�ء��) �繤��� �һѭ��
����ҡ����ջ���¤�س�Ѿ�����й����¤ӹ�� people ��еդ������������
���¶֧���ء��]
Tell me the
reason why you didn�t
do your homework.
[ػ���¤ why you didn�t
do your homework �� restrictive relative clause ������� �˵ؼ���ҷ����س�֧���ӡ�ú�ҹ (����Ǥ��
������˵ؼ�����ͧ㴡���) ����ҡ����ջ���¤�س�Ѿ�����й����¤ӹ�� reason ���Ҩ�դ������������ ���¶֧�˵ؼ�����ͧ㴡��� �����˵ؼ���� � ]
1.2 �繻���¤�س�Ѿ�����������������������ǡѺ�ӹ�������� ���������
�����������������¢ͧ����¤��ѡ�Դ�
��
Soonthorn
Phu, who wrote �Phra
Aphaimanee,�
was one of the most famous poets in Thailand.
[ػ���¤ who wrote �Phra
Aphaimanee� �� non-restrictive relative clause ���������������������
�ع���������繤����������ͧ���������� ��������բ�ͤ���������������� ������ö������ç�ѹ������¶֧�ع�����
����͡�ͧ��]
Her
parents, who left her with her grandmother, came back.
[ػ���¤ who left her with her grandmother �� non-restrictive
relative clause ��������������������� ������ͧ����觷�������Ѻ��� ��������բ�ͤ���������������� ������ö������ç�ѹ������¶֧
������ͧ�� (����褹���) ��Ѻ������]
�������㨤���ᵡ��ҧ�����ҧ
��� �ҡ��觢�� ��������º��º������ҧ����������Ф��
���仹��
The
l (whom) Suchart is going to marry is over twenty-five.
,
whom Suchart is going to marry, is over
twenty-five.
The
which runs through Bangkok is now polluted.
,
which runs through Bangkok, is now
polluted.
He
works at where radios are produced.
He
works at , where radios are produced.
They
visited me when I did not go to work.
They
visited me , when I did not go to work.
1.3 �繻���¤�س�Ѿ������������ which
��������᷹�Фӹ������Ң�ҧ˹��
����᷹����¤���͢�ͤ�������Ң�ҧ˹�ҷ����� which ����˹�ҷ���繻�иҹ
�����ç ���͡��������ѧ�ؾ��� adjective clauses �¨��� comma
��������ҧ��ͤ����á�Ѻ��ͤ�����ѧ ��
He is a kind,
gentle, and well-behaved person, which made his parents very proud of him.
She came very
late, with which I was very dissatisfied.
She
considered them all fools, to which they replied with angry cries.
2. Noun
Clauses���ػ���¤����˹�ҷ�������Ӥӹ��
����������͡Ѻ����¤��ѡ���¤���������仹����
2.1 ��˹�һ���¤�͡����
����Ҩ���¡ noun clause ��Դ������ �that�
clause ��觷�˹�ҷ�����������ҧ㹻���¤ �� �� subject,
object, complement ���
apposition �ѧ������ҧ���仹��
That he failed the final exam .
Subj.
Predicate
I know that she will arrive here tonight.
Subj. V.
Obj.
His excuse was that the traffic jam was so congested.
Subj. V.
Complement
She made the announcement that they were married.
Subj. V.
Obj.
Apposition
����¤�����
noun clause �� subject ����ö����¹�繻���¤����鹵鹴���
�It� �� �ѧ������ҧ���仹��
That he
passed the course .
Subj,
Predicate
It is a miracle that he passed the
course.
2.2 ���� what, whatever, who, whoever,
whom, whomever, whose, which, whichever, where, when, why ��� how ��觤����Фӡ��դ�����������Ըա����ᵡ��ҧ�ѹ�͡� �ѧ������ҧ���仹��
Tell me what
your name is.
John told me who
rang me yesterday.
I don�t like whomever he goes out with.
Could you
tell me whose car this is?
You can take whichever
you like.
She told me where
I should buy a diamond ring.
He wanted to
know when Ploy would come back from Ireland.
I don�t understand why Paul and Jenny
broke up.
How you won
the scholarship was a bit surprising to me.
2.3 ���˹�� noun
clause 㹤���������� ��������� �ѧ������ҧ���仹��
Whether Nancy
will come here (or not) is not important.
Do you know whether
/ if John is coming here again this year?
3. Adverb
Clauses��ػ���¤����˹�ҷ�������ӡ��������ɳ�
��͢��¤ӡ���� �Ӥس�Ѿ�� ��Фӡ��������ɳ�㹻���¤��ѡ
�����ʴ���������ѹ�������ҧ��ͤ���㹻���¤��ѡ�Ѻػ���¤��������ѡɳ�� �� �͡�������ҡ�� (manner)
ʶҹ��� (place) ���� (time) �˵ؼ� (reason) �ѵ�ػ��ʧ�� (purpose) �Ţͧ��á�з� (result) ��âѴ��駡ѹ (concession/contrast)
������º��º (comparison) ���� (condition)
�繵� �ѧ������ҧ���仹��
·
�͡�������ҡ��
(manner) ����
ػ���¤����� as, in a way that, in the way that, like, as if, as
though
She always
practices conversation with English speaking people as her teacher told her
to.
She
dances in a way that I like.
She speaks
English as if she were a native speaker.
He acts as
though he were my boss.
·
�͡ʶҹ���
(place) ���� ػ���¤����� where, wherever
Put this book
where it belongs.
Wherever you
go in Bangkok, you can find places to eat.
·
�͡����
(time) ����
ػ���¤����� as, while, as soon as, before, after, since, until,
when, whenever
While he was
studying, his sister was listening to
classical music.
When I was
young, I loved to go to the temple fair.
I will call
you as soon as I finish.
·
�͡�˵ؼ�
(reason) ����
ػ���¤����� because, since, as
Some of us
study English because it may help us get a good job.
Since Jane
was not a Thai citizen, she could not apply for
the scholarship.
As English is
one of the international languages, it is
worthwhile to spend time studying it.
·
�͡�ѵ�ػ��ʧ��
(purpose) ����
ػ���¤����� in order
that, so that
We took a sky
train (BTS) to Silom so that we could get there in time.
She takes a
writing class in order that she can write well.
·
�͡�Ţͧ��á�з�
(result) ��
ػ���¤����� so, so (adj./adv.) that
She has
failed the English test many times, so she plans to get a tutor.
Ann speaks so
clearly that every student understands very well.
·
�͡��âѴ��駡ѹ
(concession/contrast) ����
ػ���¤����� while,
whereas, although, though, even though
Kim wants to
go to Hua Hin her husband wants to go to Phuket.
he is only 10 years old,
he understands calculus very well.
·
�͡������º��º
(comparison) ����
ػ���¤�������ʴ�������º��º������������ҡѹ �ҡ���������¡���
Michael is taller
than David (is).
Pim sings more
beautifully than Prang (does).
Dao does not
speak Italian as fast as a native speaker (does).
·
�͡����
(condition) ����
ػ���¤����� if, unless (= if �
not)
If you
blue and yellow, you green. (�����䢷���繢���稨�ԧ����)
If Mr. Smith
me to his party himself, I . (�����䢻��Է�������)
Unless I
my work, I to the party. (�����䢻��Է�������)
If I
a bird, I all over the sky.
(�����䢷��������������������ҡ)
If he me yesterday, I
the party. (�����䢷��ç�����Ѻ����稨�ԧ�ʹյ)
Table of Contents
[NEW] Relative Clauses | relative clause คือ – NATAVIGUIDES
Relative clauses
What is a relative clause?
(See a list of all the exercises about relative clauses here.)
We can use relative clauses to join two English sentences, or to give more information about something.
I bought a new car. It is very fast.
→ I bought a new car that is very fast.
She lives in New York. She likes living in New York.
→ She lives in New York, which she likes.
Defining and Non-defining
A defining relative clause tells which noun we are talking about:
- I like the woman who lives next door.
(If I don’t say ‘who lives next door’, then we don’t know which woman I mean).
A non-defining relative clause gives us extra information about something. We don’t need this information to understand the sentence.
- I live in London, which has some fantastic parks.
(Everybody knows where London is, so ‘which has some fantastic parks’ is extra information).
Defining relative clauses:
1: The relative pronoun is the subject:
First, let’s consider when the relative pronoun is the subject of a defining relative clause.
We can use ‘who’, ‘which’ or ‘that’. We use ‘who’ for people and ‘which’ for things. We can use ‘that’ for people or things.
The relative clause can come after the subject or the object of the sentence. We can’t drop the relative pronoun.
For example (clause after the object of the sentence):
- I’m looking for a secretary who / that can use a computer well.
- She has a son who / that is a doctor.
- We bought a house which / that is 200 years old.
- I sent a letter which / that arrived three weeks later.
More examples (clause after the subject of the sentence):
- The people who / that live on the island are very friendly.
- The man who / that phoned is my brother.
- The camera which / that costs £100 is over there.
- The house which / that belongs to Julie is in London.
Try an exercise where the relative pronoun is the subject here.
2: The relative pronoun is the object:
Next, let’s talk about when the relative pronoun is the object of the clause. In this case we can drop the relative pronoun if we want to. Again, the clause can come after the subject or the object of the sentence. Here are some examples:
(Clause after the object)
(Clause after the object)
- She loves the chocolate (which / that) I bought.
- We went to the village (which / that) Lucy recommended.
- John met a woman (who / that) I had been to school with.
- The police arrested a man (who / that) Jill worked with.
(Clause after the subject)
(Clause after the subject)
- The bike (which / that) I loved was stolen.
- The university (which / that) she likes is famous.
- The woman (who / that) my brother loves is from Mexico.
- The doctor (who / that) my grandmother liked lives in New York.
Non-defining relative clauses:
We don’t use ‘that’ in non-defining relative clauses, so we need to use ‘which’ if the pronoun refers to a thing, and ‘who’ if it refers to a person. We can’t drop the relative pronoun in this kind of clause, even if the relative pronoun is the subject of the clause.
(Clause comes after the subject)
- My boss, who is very nice, lives in Manchester.
- My sister, who I live with, knows a lot about cars.
- My bicycle, which I’ve had for more than ten years, is falling apart.
- My mother’s house, which I grew up in, is very small.
(Clause comes after the object)
- Yesterday I called our friend Julie, who lives in New York.
- The photographer called to the Queen, who looked annoyed.
- Last week I bought a new computer, which I don’t like now.
- I really love the new Chinese restaurant, which we went to last night.
Prepositions and relative clauses
If the verb in the relative clause needs a preposition, we put it at the end of the clause:
For example:
- listen to
The music is good. Julie listens to the music.
→ The music (which / that) Julie listens to is good.
- work with
My brother met a woman. I used to work with the woman.
→ My brother met a woman (who / that) I used to work with.
- go to
The country is very hot. He went to the country.
→ The country (which / that) he went to is very hot.
- come from
I visited the city. John comes from the city.
→ I visited the city (that / which) John comes from.
- apply for
The job is well paid. She applied for the job.
→ The job (which / that) she applied for is well paid.
Whose
‘Whose’ is always the subject of the relative clause and can’t be left out. It replaces a possessive. It can be used for people and things.
The dog is over there. The dog’s / its owner lives next door.
→ The dog whose owner lives next door is over there.
The little girl is sad. The little girl’s / her doll was lost.
→ The little girl whose doll was lost is sad.
The woman is coming tonight. Her car is a BMW.
→ The woman whose car is a BMW is coming tonight.
The house belongs to me. Its roof is very old.
→ The house whose roof is old belongs to me.
Where / when / why
We can sometimes use these question words instead of relative pronouns and prepositions.
I live in a city. I study in the city.
→ I live in the city where I study.
→ I live in the city that / which I study in.
→ I live in the city in which I study.
The bar in Barcelona is still there. I met my wife in that bar.
→ The bar in Barcelona where I met my wife is still there.
→ The bar in Barcelona that / which I met my wife in is still there.
→ The bar in Barcelona in which I met my wife is still there.
The summer was long and hot. I graduated from university in the summer.
→ The summer when I graduated from university was long and hot.
→ The summer that / which I graduated from university in was long and hot.
→ The summer in which I graduated was long and hot.
(See a list of all the exercises about relative clauses here.)
Need more practice? Get more Perfect English Grammar with our courses.
ติว TOEIC ครูดิว : Relative Pronouns ที่ออกสอบ TOEIC บ่อยที่สุด !!!!
✿ ถ้าพื้นฐานน้อย แนะนำหาคอร์สติวดีกว่าค่ะ! ✿
👉 สมัครคอร์ส KruDew ติว New TOEIC 2020 (ทดลองติวฟรี!) ➡️ https://bit.ly/2wR4Gmu
✿ คอร์ส KruDew ติว TOEIC มีอะไรให้บ้าง? ✿
✅Grammar ที่ใช้สอบ TOEIC ให้ครบ เริ่มสอนจากพื้นฐาน เรียนได้ทุกคนแน่นอน
✅เทคนิคช่วยจำต่างๆ จำง่าย เอาไปใช้กับข้อสอบได้จริงๆ
✅เก็งศัพท์ TOEIC ออกข้อสอบบ่อยๆ ให้ครบ ไม่ต้องเสียเวลาไปนั่งรวบรวมเอง
✅ อัพเดทข้อสอบ New TOEIC ล่าสุด ครบ 200 ข้อ
✅สามารถสอบถามข้อหรือจุดที่สงสัยได้ตลอด
✅การันตี 750+ (ถ้าสอบแล้วไม่ถึง สามารถทวนคอร์สได้ฟรี)
📣 ถ้าไม่อยากพลาดคลิปดีๆแบบนี้ อย่าลืมกด ❤️ Subscribe ❤️กันนะคะ
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

Relative Clauses: The Grammar Gameshow Episode 11
Welcome to the Grammar Gameshow! Test your knowledge in this crazy quiz! The presenter is a bit strange, the points don’t make sense and the prizes could use some improvement, but at least the grammar is correct!
Levington already has one win under his belt, but Kate is hard on his heels. In this episode, our contestants test themselves against defining relative clauses! Those useful, noun modifying phrases that make complex sentences! Will Levington win through, or can Kate take him down? And what’s this big surprise at the end? Find out in this episode of the Grammar Gameshow!
Watch and see! Learn more here: http://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish/english/course/tgg/
Do you want to learn how to speak English? Then join us here on YouTube for great grammar, drama, news, study, pronunciation, vocabulary, music, interviews and celebrity videos. Every day we have a new video to help you with English. We also produce regular ‘extra’ videos across the week so come back every day to see what’s new.
MONDAY: The English We Speak
TUESDAY: News Review
TUESDAY: English At Work
WEDNESDAY: The Grammar Gameshow and LingoHack
THURSDAY: 6 Minute English
FRIDAY: The Experiment (watch this space for new and exciting content that we are trying out!)
For more videos and content that will help you learn English, visit our website: http://www.bbclearningenglish.com

Clauses คืออะไร มีกี่ประเภท
จัดทำขึ้นเพื่อเป็นส่วนหนึ่งในการเรียนรู้
ติดตาม Facebook และ Instagram : The Happy Time with Q
หากผิดพลาดประการใด ผู้จัดทำขออภัยมานะที่นี้ด้วยค่ะ 😀
If – Clause ในภาษาอังกฤษใช้อย่างไร
ตามไปเรียนภาษาอังกฤษกับครูหวานต่อที่
https://www.facebook.com/kruwhanenglishonair
https://www.instagram.com/english_kruwhan

Defining relative clauses – 6 Minute Grammar
In English, defining relative clauses give us important information about the person, thing or place that we are talking about. We use ‘who’ for people, ‘that’ and ‘which’ for things and ‘where’ for places. Watch the programme to hear examples of how these words are used and take the quiz at the end of the video to test your understanding!
You’ll find a quiz on our website: http://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish/english/course/lowerintermediate/unit15/session2/activity2
0:00 Introduction
0:29Defining Relative Clauses
3:46 Defining Relaltive Clauses Quiz:
If you liked this lesson, then you’ll love the following lessons:
Defining and Nondefining Relative Clauses: https://youtu.be/ppyws3GdZ2E
Phrasal Verbs Type 1, 2, 3 \u0026 4: https://youtu.be/FBmjH6nh5k
Reported Speech: https://youtu.be/LwTVCByxzk
6MinuteGrammar BBCLearningEnglish LearnEnglish

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆLEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ relative clause คือ