passive voice present simple: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
Advertisement

The passive is a grammatical voice that moves an object of a sentence in the active voice into the subject position. The simple present passive is an English verb form that refers to verbs in the present tense, simple aspect, indicative mood, and passive voice.
Formation of the Simple Present Passive
Like most other verb forms in the English language, the simple present passive is periphrastic meaning that that “a phrase of two or more words performs a single grammatical function that would otherwise be expressed by the inflection of a single word.” Verbs in the simple present passive are formed by the present tense form of the verb plus a past participle (regular or irregular). Only transitive verbs (verbs that can take objects) and verbs with verb phrase complements may be conjugated in the passive voice. The verb phrase patterns for the simple present passive are as follows:
- first person singular – am + past participle – I to work by my boss every day.
- second person singular – are + past participle – You easily by loud noises.
- third person singular – is + past participle – The wind chime by even a light breeze.
- first person plural – are + past participle – We to wash our hands frequently.
- second person plural – are + past participle – you by your neighbors a lot?
- third person plural – are + past participle – Bagels to the office each Monday.
Some Englishes also allow for the simple present passive to be formed by the present tense form of the verb plus a past participle in declarative sentences. The use of as a passive auxiliary requires the addition of the operator in interrogative sentences. The verb phrase patterns for the simple present passive with the auxiliary verb are as follows:
Advertisement
- first person singular – get + past participle – I always by my brother.
- second person singular – get + past participle – you ever at work?
- third person singular – gets + past participle – The bathroom once a week.
- first person plural – get + past participle – We to few parties.
- second person plural – get + past participle – You easily.
- third person plural – get + past participle – Cookies quickly at my office.
Notice that the present tense of the verb is irregular in all persons and numbers but that the present tense of the verb is identical in all persons and numbers except for the third person singular.
Uses of the Simple Present Passive
Like the simple present in the active voice, the simple present passive expresses a discrete action or event in the present or near future. Also like the simple present active, the simple present passive occurs most often in sentences that (1) express discrete actions in the present, (2) describe habits and routines, (3) state general facts and truths, (4) express thoughts and feelings, and (5) describe events in the near future. For example:
- The misbehaving child is scolded by her mother.
- Our mail carrier is barked at every afternoon.
- Crops are destroyed by insects.
- His lover is whisked away by train this evening.
The main grammatical and semantic difference between the simple present in the active voice and the simple present in the passive voice is that the simple present passive allows an object of an active sentence to appear in the subject position. For example, the use of the active voice in means that the subject is the noun phrase and the direct object is the noun phrase . By changing the same sentence into the passive voice — — the original direct object moves into the subject position. Using the passive voice thus allows a speaker to emphasize an object from an active sentence and/or to de-emphasize the subject from an active sentence.
The following visual illustrates the uses of the simple present of English verbs:
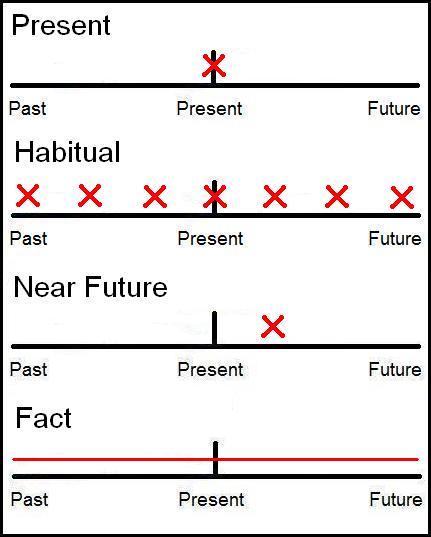
The simple present passive expresses discrete actions or states in the present or near future while moving an object from an active sentence into the subject position.
Summary
The simple present is defined as a verb form that expresses a discrete action or event in the present or near future.
The simple present passive is periphrastic, which means consisting of a “phrase of two or more words that perform a single grammatical function that would otherwise be expressed by the inflection of a single word.”
The simple present passive is formed by the present tense form of the verb plus a past participle.
Only transitive verbs and verbs with verb phrase complements may be conjugated into the passive voice.
The main grammatical and semantic difference between the simple present in the active voice and the simple present in the passive voice is that the simple present passive allows an object of an active sentence to appear in the subject position.
Hopper, Paul J. 1999. . New York: W. W. Norton & Company.
Kilby, David. 1984. . Dover, New Hampshire: Croom Helm.
Leech, Geoffrey N. 2004. . Harlow, English: Pearson Longman.
Pin
3
Share
17
Shares
Advertisement
Advertisement
Table of Contents
[Update] Examples of Active and passive voice simple present tense | passive voice present simple – NATAVIGUIDES
By Prof. Fazal Rehman Shamil
Last modified on September 11th, 2021
Formula, Structure, Rules for simple present tense
Formula
Active voice
Passive voice
(auxiliary verb- is/are+by)
Simple
subject+verb+object
object+is/are+past participle(V3)+ by+subject
Negative
subject+do/does not+verb+object
object+is/are+not+past participle(V3)+by+suject
Interrogative
do/does+subject+verb+object
is/are+object+past participle(V3)+by+subject
Interrogative+Negative
do/does+subject+not+verb+object
is/are+object+not+past participle(V3)+by+subject
Examples:
Active: He plays football.
Passive: Football is played by him.
Active: He does not play football.
Passive: Football is not played by him.
Active: Does he play football?
Passive: Is football played by him?
Active: Does he not play football?
Passive: Is he not play football?
Active: She writes a book.
Passive: A book is written by her.
Active: She does not write a book.
Passive: A book is not written by her.
Active: Does she write a book?
Passive: Is a book written by her?
Active: Does she not write a book?
Passive: Is a book not written by her?
Active: Hewlett-Packard types a document.
Passive: A document is written by Hewlett-Packard.
Active: Hewlett-Packard does not type a document.
Passive: A document is not typed by Hewlett-Packard.
Active: Does Hewlett-Packard type a document?
Passive: Is a document typed by Hewlett-Packard?
Active: Does Hewlett-Packard not type a document?
Passive: Is a document not typed by Hewlett-Packard?
Active: A cat drinks milk.
Passive: Milk is drunk by a cat.
Active: A cat does not drink milk.
Passive: Milk is not drunk by a cat.
Active: Does a cat drink milk?
Passive: Is milk drunk by a cat?
Active: Does a cat not drink milk?
Passive: Is milk not drunk by a cat?
Active: They enjoy a picnic.
Passive: A picnic is enjoyed by them.
Active: They do not enjoy a picnic.
Passive: A picnic is not enjoyed by them.
Active: Do they enjoy a picnic?
Passive: Is a picnic enjoyed by them?
Active: Do they not enjoy a picnic?
Passive: Is a picnic not enjoyed by them?
Active: Tim Berners-Lee enters the gate.
Passive: The gate is entered by Tim Berners-Lee.
Active: Tim Berners-Lee does not enter the gate.
Passive: The gate is not entered by Tim Berners-Lee.
Active: Does Tim Berners-Lee enter the gate?
Passive: Is the gate entered by Tim Berners-Lee?
Active: Does Tim Berners-Lee enter the gate?
Passive: Is the gate not entered by Tim Berners-Lee?
Active: I plant flowers.
Passive: Flowers are planted by me.
Active: I do not plant flowers.
Passive: Flowers are not planted by me.
Active: Do I plant flowers?
Passive: Are flowers not planted by me?
Active: Do I not plant flowers?
Passive: Are flowers not planted by me?
Active: James Gosling takes breakfast.
Passive: Breakfast is taken by James Gosling.
Active: James Gosling does not take breakfast.
Passive: Breakfast is not taken by James Gosling.
Active: Does James Gosling take breakfast?
Passive: Is breakfast taken by James Gosling.
Active: Does James Gosling not take breakfast?
Passive: Is breakfast not taken by James Gosling?
Active: we eat mangoes.
Passive: Mangoes are eaten by us.
Active: We do not eat mangoes.
Passive: Mangoes are not eaten by us.
Active: Do we eat mangoes?
Passive: Are mangoes eaten by us?
Active: Do we not eat mangoes?
Passive: Are mangoes not eaten by us?
Active: I make noodles.
Passive: Noodles are made by me.
Active: I do not make noodles.
Passive: Noodles are not made by me.
Active: Do I make noodles?
Passive: Are noodles made by me?
Active: Do I not make noodles?
Passive: Are noodles not made by me?
Active: Linus joins an office.
Passive: An office is joined by Steve Jobs.
Active: Linus does not join an office.
Passive: An office is joined by Linus.
Active: Does Linus join an office?
Passive: Is an office joined by Linus?
Active: Does Linus not join an office?
Passive: Is an office not join by Linus?
Active: Torvalds water plants.
Passive: Plants are watered by Torvalds.
Active: Torvalds does not water plants.
Passive: Plants are not watered by Torvalds.
Active: Does Torvalds water plants?
Passive: Are plants watered by Torvalds?
Active: Does Torvlds not water plants?
Passive: Are plants not watered by Torvalds?
Active: Bill Gates earns money.
Passive: Money is earned by Bill Gates.
Active: Bill Gates does not earn money.
Passive: Money is not earned by Bill Gates.
Active: Does Bill Gates earn money?
Passive: Is money earned by Bill Gates?
Active: Does Bill Gates not earn money?
Passive: Is money not earned by Bill Gates?
Active: You eat pasta.
Passive: Pasta is eaten by you.
Active: You do not eat pasta.
Passive: Pasta is not eaten by you.
Active: Do you eat pasta?
Passive: Is pasta eaten by you?
Active: Do you not eat pasta?
Passive: Is pasta not eaten by you?
Active: They play a game.
Passive: A game is played by them.
Active: They do not play a game.
Passive: A game is not played by them.
Active: Do they play a game?
Passive: Is a game played by them?
Active: Do they not play a game?
Passive: Is a game not played by them?
Active: Steve Jobs paints a picture.
Passive: A picture is painted by Steve Jobs.
Active: Steve Jobs does not paint a picture.
Passive: A picture is not painted by Steve Jobs.
Active: Does Steve Jobs paint a picture?
Passive: Is a picture painted by Does Steve?
Active: Does Does Steve paint a picture?
Passive: Is a picture painted by Does Steve?
Learn More About Active & Passive Voice
1. Message on Facebook page for discussions,2. Video lectures on Youtube3. Email is only for Advertisement/business enquiries.
Passive Voice in English: Active and Passive Voice Rules and Useful Examples
Passive Voice Rules for All Tenses | Examples of Active \u0026 Passive Voice: https://7esl.com/passivevoice/
The passive is used:
• When the agent (= the person who does the action) is unknown, unimportant or obvious from the context.
• To make more polite or formal statements.
• When the action is more important than the agent, as in processes, instructions, events, reports,
• To put emphasis on the agent.
…
WATCH MORE:
★ Grammar: https://goo.gl/pK8eBC
★ Vocabulary: https://goo.gl/d4dJfR
★ Expressions: https://goo.gl/mNKvAB
★ Phrasal Verbs: https://goo.gl/Riw1r6
★ Idioms: https://goo.gl/KrEMRx
★ Conversations: https://goo.gl/MxQEnV
★ Kids Vocabulary: https://goo.gl/K96toU
★ English Writing: https://goo.gl/3zxuQB
★ IELTS: https://goo.gl/5fi2Sk
★ TOEFL: https://goo.gl/3rdyML
★ British vs. American English: https://goo.gl/ySYPWp
★ Pronunciation: https://goo.gl/UXYD2M
★ Business English: https://goo.gl/xpVNkr
OUR SOCIAL MEDIA:
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/7english/
Facebook: https://www.fb.com/7ESLLearningEnglish/
For more videos and lessons visit:
https://7esl.com/
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่

Describing Animals with Simple Present Tense
Learn how to describe pets and wild animals using verbs in Simple Present Tense.

Cartoon Descriptions Activity – Past Simple Passive Voice
Practise your English with this fun video activity. Use the past simple passive to describe what happens in each clip. Download the worksheet from here: https://en.islcollective.com/resources/printables/worksheets_doc_docx/past_simple_passive_video_activity__describing_cartoons/passivevoiceor/114465

Past Passive . Learn English
Learn how to use the past passive.

The Passive Voice
Passive Voice is used when the focus is on the action, and not on the person who does it. Learn how to use it correctly in more tenses in this video. There are many examples that will make it easy for you to understand.

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆLEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ passive voice present simple