simple present: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
Devemos utilizar o tempo verbal simple present para descrever ações em geral. Precisamos ter cuidado quando pensamos sobre ações que acontecem no tempo de fala, isto é, como se elas estivessem acontecendo agora, pois as ações em progressão referem-se, na verdade, a outro tempo verbal: o present continuous. Dito isso, podemos nos concentrar no simple present, formado pelo verbo principal no infinitivo sem a preposição to, quando falamos de algo que acontece frequentemente.
Ao contrário da língua portuguesa, em inglês, os verbos no simple present não são flexionados em todas as pessoas, exceto na terceira pessoa do singular (he/ele, she/ela, it/ele, ela) |1| em frases afirmativas. Outra peculiaridade é o uso dos verbos auxiliares do e does em frases interrogativas e negativas. Nos tópicos a seguir, explicaremos o uso desse tempo verbal, abordando a sua estrutura e conjugando alguns verbos. Vamos lá!

Usamos o simple present para falar de nossa rotina.
Table of Contents
Quando usar o simple present?
→ What time do you have breakfast every day?
- Que horas você toma café da manhã todos os dias?
→ Do you go to work by car or by bicycle?
- Você vai para o trabalho de carro ou de bicicleta?
Pelas perguntas, podemos perceber o interesse naquilo que fazemos no nosso dia a dia. O simple present é empregado justamente para descrever o que as pessoas fazem no cotidiano. Além disso, podemos utilizá-lo para retratar fatos ou verdades em geral, caracterizar alguns estados emocionais ou características físicas e pessoais, narrar ou sintetizar histórias ou eventos, entre outros usos|2|. No quadro seguinte, exploraremos nos exemplos cada uso que podemos fazer do simple present:
- Daily Routine, Habits, Customs
(Rotina diária, hábitos, costumes)
1- They always wake up at 7 am.
(Eles sempre acordam às 7:00 da manhã.)
2- Clara has cereals for breakfast.
(Clara come cereais no café da manhã.)
3- She doesn’t study in the library on Mondays.
(Ela não estuda na biblioteca nas segundas-feiras.)
- General Facts and Truths
(Fatos e verdades gerais)
1- The sun rises in the east.
(O sol nasce no leste.)
2- The water boils at 100 degree Celsius.
(A água ferve a 100 graus Celsius.)
- Emotional States, Physical and Personal Chracteristics
(Estados emocionais, características físicas e pessoais)
1- Denis is a happy person.
(Denis é uma pessoa feliz.)
2- He is tall.
(Ele é alto.)
3- They don’t seem to be very comfortable.
(Eles não parecem estar confortáveis.)
4- Jack hates chocolate
(Jack odeia chocolate.)
5- Is Carlos a good teacher?
(Carlos é um bom professor?)
- Narration/Summary of Stories and Events
(Narração ou resumo de histórias ou eventos)
1- Ana goes to school after lunch. She studies in the afternoon. Then, she goes home with her friend and they study and play together.
(Ana vai para a escola depois do almoço. Ela estuda à tarde. Depois, ela vai para casa com os amigos e eles estudam e brincam juntos.)
2- According to the author, this paper is very important to define the composition of modern bands in Brazil. He affirms that people really love to mix genres.
(Segundo o autor, este artigo é muito importante para definir a composição das bandas modernas brasileiras. Ele afirma que as pessoas realmente gostam de misturar os gêneros).
Para não esquecer os diferentes empregos do simple present, que tal você elaborar uma lista, segundo cada uso, com seus próprios exemplos?!
Veja mais: Simple past: tempo verbal que indica uma ação do passado já concluída
Não pare agora… Tem mais depois da publicidade 😉
Principais regras do simple present
Nesta parte do texto, observaremos a estrutura do simple present em inglês, focando nas regras gramaticais. Primeiramente, destacamos que a frase é composta pelo sujeito + verbo + complemento:
I. I dance with you.
- (Eu danço com você.)
É importante dizer que a ordem sintática (das palavras) segue uma regra diferente da nossa língua em frases interrogativas (você verá nos tópicos a seguir). Além disso, a conjugação do verbo principal diferencia-se do português, uma vez que o verbo só se modifica na terceira pessoa do singular: he (ele), she (ela), it (ele/ela), na forma afirmativa, facilitando – de certa forma – a nossa aprendizagem no que diz respeito à conjugação de verbos.
Por último, o inglês utiliza verbos auxiliares (do/does) em frases tanto negativas quanto interrogativas. Abordaremos cada uma dessas peculiaridades separadamente nas seções seguintes.
-
Forma afirmativa
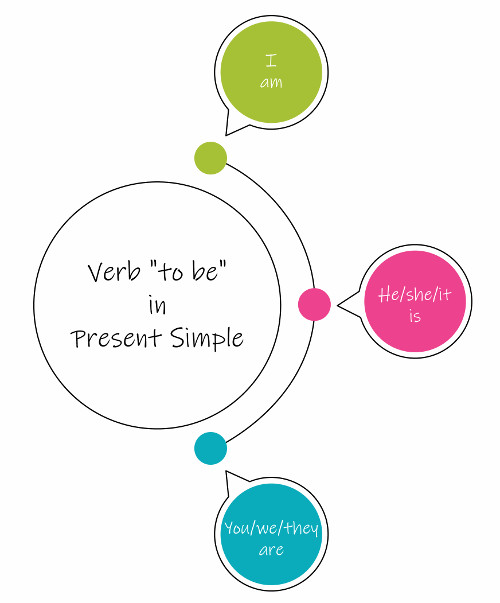
O verbo “to be” é um dos verbos irregulares no simple present.
A língua tem seus artifícios para marcar alguns aspectos de tempo, pessoa e lugar. Percebemos em frases afirmativas o acréscimo do –s ao verbo principal, indicando-nos de que se trata da 3ª pessoa do singular (he, she, it). Por exemplo:
I. Alice goes to the gym.
- (Alice vai para a academia.)
II. It’s a beautiful day.
- (É um dia bonito.)
Os dois exemplos apresentam dois outros aspectos importantes das frases afirmativas:
- As regras de ortografia para a 3ª pessoa do singular;
- Os verbos irregulares no simple present.
Na conjugação do verbo na terceira pessoa do singular, existem regras ortográficas:
Maioria dos verbos: acrescenta-se –s.
I feel (Eu sinto)
They live (Eles moram)
We talk (Nós falamos)
You read (Você lê)
She feels
He lives
He talks
She reads
Verbos que terminam em –ss, –sh, –ch, –o, –x: acrescenta-se –es.
We pass (Nós passamos)
They wash (Eles/elas lavam)
You watch (Vocês assistem)
I go (Eu vou)
I relax (Eu relaxo)
He passes
She washes
It watches
He goes
She relaxes
Verbos que terminam em consoante + y: retira-se o –y e, depois, acrescenta-se –ies.
I study (Eu estudo)
You copy (Você copia)
They cry (Eles/elas choram)
He studies
She copies
He cries
Verbos que terminam em vogal + y: acrescenta-se –s.
You play (Você brinca)
They say (Eles/elas dizem)
He plays
She says
Quanto à conjugação das outras pessoas, o verbo permanece da mesma forma. Por exemplo: I/you/we/they read. (Eu leio, você lê/vocês leem, nós lemos, eles/elas leem).
No simple present, há apenas dois verbos irregulares: o verbo to be (ser/estar) e to have (ter). A conjugação é diferente. Confira no final do texto, em tabela com exemplos de verbos conjugados, a conjugação completa deles!
-
Forma negativa
Na forma negativa do simple present, é necessário o uso do verbo auxiliar do/does. Enquanto verbo auxiliar, isto é, quando ele ocupa uma posição na frase com o objetivo de sinalizar que a frase é negativa, o verbo auxiliar do/does não tem sentido semântico. Mas se ele ocupa a posição de verbo principal na frase, o seu sentido semântico é de fazer. Por exemplo:
I. I don’t (do not) speak Italian.
⇒ Eu não falo italiano. (O verbo do indica que a frase é negativa. O verbo principal dessa frase é speak).
II. I do my Italian homework.
⇒ Eu faço minha tarefa de italiano. (O verbo do ocupa a posição de verbo principal. Possui o sentido de fazer).
Como apontamos sobre os aspectos ortográficos para a 3ª pessoa do singular, o auxiliar do também deve seguir as mesmas regras. Logo, devemos dizer:
I. She doesn’t (does not) have lunch at home.
⇒ Ela não almoça em casa.
-
Forma interrogativa
Para fazer uma pergunta no simple present, devemos utilizar o verbo auxiliar do/does tanto na pergunta quanto na resposta curta. O verbo auxiliar deve sempre vir no começo da pergunta. Além disso, o verbo auxiliar também não possui sentido semântico, apenas ocupa uma posição na frase para nos indicar que estamos diante de uma pergunta em inglês. Por exemplo:
Question: Do you go out with your friends? / Você sai com seus amigos?
O verbo do indica que a frase é interrogativa. O verbo principal dessa frase é go.
Short answers (respostas curtas)
Complete answers (respostas completas)
Yes, I do.
(Sim, eu saio.)
ou
No, I don’t.
(Não, eu não saio.)
Yes, I go out with my friends.
(Sim, eu saio com meus amigos.)
ou
No, I don’t go out with my friends.
(Não, eu não saio com meus amigos.)
Se for uma pergunta na 3ª pessoa do singular, utiliza-se does, por exemplo:
Question: Does he study English at school? / Ele estuda inglês na escola?
O verbo auxiliar é does. O verbo principal da frase é study.
Short answers (respostas curtas)
Complete answers (respostas completas)
Yes, he does.
(Sim, ele estuda.)
ou
No, he doesn’t.
(Não, ele não estuda.)
Yes, he studies English at school.
(Sim, ele estuda inglês na escola.)
ou
No, he doesn’t study English at school.
(Não, ele não estuda inglês na escola.)
Observe que o verbo na 3ª pessoa do singular, tanto na frase negativa quanto na interrogativa, precisa do auxiliar does. Consequentemente, o verbo principal não precisa ser marcado com –s, –es ou –ies (como na afirmativa), porque o verbo auxiliar já nos mostra que o sujeito da frase está na terceira pessoa.
Saiba mais: Question words: quais são e como usá-las
Tabela com exemplos de verbos conjugados
Have (Ter)
Go (Ir)
Affirmative
Negative
Interrogative
Affirmative
Negative
Interrogative
I
(eu)
I have
I don’t have
Do I have?
I go
I don’t go
Do I go?
You
(você)
You have
You don’t have
Do you have?
You go
You don’t go
Do you go?
He/she/it (ele/ela)
He has
He doesn’t have
Does he have?
She goes
She doesn’t go
Does she go?
We
(nós)
We have
We don’t have
Do we have
We go
We don’t go
Do we go?
You (vocês)
You have
You don’t have
Do you have?
You go
You don’t go
Do you go?
They (eles/elas)
They have
They don’t have
Do they have?
They go
They don’t go
Do they go?
→ Não se esqueça de que no inglês podemos usar a forma contraída: don’t/doesn’t ou completa: do not/does not.
Leia também: Contracted forms: formas abreviadas em inglês
Exercícios resolvidos
Questão 1
Sublinhe as alternativas corretas:
Hi! My name am/is/are David and I am/is/are 25 years old. I live/lives in Sydney, Australia. I am/is/are a biologist and I work/works in a zoo with my sister Alice. She am/is/are 27 years old and she am/is/are a veterinarian. She help/helps the animals there. I go/goes to work at 7 am and she go/goes to work at 8 am. I don’t/doesn’t work on Saturdays and she don’t/doesn’t work on Sundays.
Resolução:
Hi! My name am/is/are (terceira pessoa do singular) David and I am/is/are (primeira pessoa do singular) 25 years old. I live/lives (primeira pessoa do singular) in Sydney, Australia. I am/is/are (primeira pessoa do singular) a biologist and I work/works (primeira pessoa do singular) in a zoo with my sister Alice. She am/is/are (terceira pessoa do singular) 27 years old and she am/is/are (terceira pessoa do singular) a veterinarian. She help/helps (terceira pessoa do singular) the animals there. I go/goes (primeira pessoa do singular) to work at 7 am and she go/goes (terceira pessoa do singular) to work at 8 am. I don’t/doesn’t (primeira pessoa do singular) work on Saturdays and she don’t/doesn’t (terceira pessoa do singular) work on Sundays.
Notas
|1| “It” é um pronome sujeito da terceira pessoa do singular (ele, ela) para se referir a objetos, animais, situações, ideias etc.
|2| Outro uso do simple present é para falar da frequência que fazemos algo.
Por Patricia Veronica Moreira
Professora de Inglês
[NEW] Simple Present Tense | simple present – NATAVIGUIDES
What Is the Simple Present Tense? (with Examples)
The simple present tense is used:
- To describe facts and habits. For example:
- He
plays
chess.
- To describe scheduled events in the future. For example:
- The plane
lands
in 5 minutes.
- To tell stories (particularly jokes). For example:
- He
asks
the policeman for directions.
(This use of the simple present tense is quite rare.)
The simple present tense is quite easy to form, but it quite difficult to use. In fact, it’s complicated. (There’s more on this below.)
A Video Summary
Here is a short video summarizing the simple present tense:
Theis used:The simple present tense is quite easy to form, but it quite difficult to use. In fact, it’s complicated. (There’s more on this below.)Here is a short video summarizing the simple present tense:
Infographic for the Simple Present Tense
Here is an infographic explaining the simple present tense:
More Examples of the Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense is used:
(1) To describe facts and habits:
- I
like
chocolate. (Fact)
- Angela
runs
a youth club full of glue-sniffers. (Fact)
- I
ride
horses in the summer. (Fact and habit)
- It always
snows
here in January. (Fact and habit)
- Dawn
plays
chess in the evenings. (Fact and habit)
(NB: These activities do not have to be happening right now.)
This type of sentence, especially if it’s describing a habit, will usually include a time expression like “always,” “every year,” “never,” “often,” “on Mondays,” “rarely,” “sometimes,” or “usually.”
(2) To describe scheduled events in the future
- The train
arrives
at 5 o’clock.
- It
is
low tide at 0234.
(Yes, we know! It’s supposed to be the present tense!)
(3) To tell stories (particularly jokes) to make your listener or reader feel more engaged with the story.
- A horse
walks
into a bar, and the barman
says
, “why the long face?”
- We heard the helicopter overhead. Suddenly, the radio
bursts
into life.
(Compare to: A horse walked into a bar, and the barman said, “why the long face?”)
(This is sometimes called the fictional present or the historic present.)
Forming the Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense is quite easy to form.
Here is an infographic explaining the simple present tense:Theis used:(NB: These activities do not have to be happening right now.)This type of sentence, especially if it’s describing a habit, will usually include a time expression like “always,” “every year,” “never,” “often,” “on Mondays,” “rarely,” “sometimes,” or “usually.”(Yes, we know! It’s supposed to be the present tense!)(This is sometimes called the fictional present or the historic present.)Theis quite easy to form.
base form
or
or
base form
+
“s”
Let’s look at the verb to run (whose run). In the simple present tense, run looks like this:
PersonExample
First person singularI run
Second person singularYou run
Third person singularHe/She/It runs
First person pluralWe run
Second person pluralYou run
Third person pluralThey run
In other words, it only changes in the third person singular (he / she / it). It adds either s, es or ies.
The Negative Version
To create a negative sentence, use “do not” + [base form of the verb]. (Use “does not” with third person singular (he / she / it).)
Let’s look at the verb(whose base form is). In the simple present tense,looks like this:In other words, it only changes in the third person singular (he / she / it). It adds eitherorTo create a negative sentence, use. (Usewith third person singular (he / she / it).)
“do not” or “does not”
+
[base form of the verb]
- I
do not like
chocolate.
- Angela
does not run
a youth club full of glue-sniffers.
- I
do not ride
horses in the summer.
- It
does not always snow
here in January.
- Dawn
does not play
chess in the evenings.
In speech and writing (especially informal writing), “do not” is often shortened to “don’t,” and “does not” is often shortened to “doesn’t.” If you want to add some emphasis, use one of the long versions (i.e., “do not” or “does not”), and emphasize the word “not.”
The Question Version
If you need to ask a question, you can use the following word order for a yes/no question:
In speech and writing (especially informal writing), “do not” is often shortened to “don’t,” and “does not” is often shortened to “doesn’t.” If you want to add some emphasis, use one of the long versions (i.e., “do not” or “does not”), and emphasize the word “not.”If you need to ask a question, you can use the following word order for a yes/no question:
“do” or “does”
+
[subject]
+
base form of verb
-
Do you like
chocolate?
-
Does Angela run
the youth club?
You can use the following word order for a
You can use the following word order for a question-word question
[question word]
+
“do” or “does”
+
[subject]
+
base form of verb
-
Why does Tony talk
so quickly?
-
When do the farmers plant
the corn?
You can use the following word order for a choice question:
You can use the following word order for a choice question:
“do” or “does”
+
[subject]
+
base form of verb
+
choice A
+
or
+
choice B
- Does Mark sing or dance?
- Do they want hamburger or sausages?
The Spelling Rules
For regular verbs, just add s:
- talk > talks
- improve > improves
For verbs that end in s, ss, sh, ch, x and o, add es:
- guess > guesses
- mash > mashes
- fix > fixes
- go > goes
For verbs ending , change the y to i and add es:
- fly > flies
- study > studies
Verb Tense Widget
Use this widget to learn about the different tenses. How do you use this widget? Well, if there’s a button, a drop-down menu, or a , then you can click it!
to
base form
(
verb)
verb)
Select the tenses.
Present Tenses
Present Progressive Tense
The present progressive tense is used for an ongoing action in the present.
More…(opens new tab)
I am present participle
you are present participle
he/she/it is present participle
we are present participle
you are present participle
they are present participle
Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is used for actions that began in the past. (Often, the actions continue into the present.)
More…(opens new tab)
I have past participle
you have past participle
he/she/it has past participle
we have past participle
you have past participle
they have past participle
Present Perfect Progressive Tense
The present perfect progressive tense is used for a continuous activity that began in the past and continues into the present, or a continuous activity that began in past but has now finished (usually very recently).
More…(opens new tab)
I have been present participle
you have been present participle
he/she/it has been present participle
we have been present participle
you have been present participle
they have been present participle
Past Tenses
Past Progressive Tense
The past progressive tense is used to describe an ongoing activity in the past. Often, it is used to set the scene for another action.
More…(opens new tab)
I was present participle
you were present participle
he/she/it was present participle
we were present participle
you were present participle
they were present participle
Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense is used to emphasize that an action was completed before another took place.
More…(opens new tab)
I had past participle
you had past participle
he/she/it had past participle
we had past participle
you had past participle
they had past participle
Past Perfect Progressive Tense
The past perfect progressive tense is used to show that an ongoing action in the past has ended.
More…(opens new tab)
I had been present participle
you had been present participle
he/she/it had been present participle
we had been present participle
you had been present participle
they had been present participle
Future Tenses
Future Progressive Tense
The future progressive tense is used for an ongoing action that will occur in the future.
More…(opens new tab)
I will be present participle
you will be present participle
he/she/it will be present participle
we will be present participle
you will be present participle
they will be present participle
Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will have been completed at some point in the future.
More…(opens new tab)
I will have past participle
you will have past participle
he/she/it will have past participle
we will have past participle
you will have past participle
they will have past participle
Future Perfect Progressive Tense
The future perfect progressive tense is used for an ongoing action that will be completed at some specified time in the future.
More…(opens new tab)
I will have been present participle
you will have been present participle
he/she/it will have been present participle
we will have been present participle
you will have been present participle
they will have been present participle
The Other Present Tenses
The simple present tense is one of four present tenses. They are:
Slider Showing All the Tenses
The following slider shows all 12
For regular verbs, just addFor verbs that end inand, addFor verbs ending, change thetoand addUse this widget to learn about the different tenses. How do you use this widget? Well, if there’s a button, a drop-down menu, or a, then you can click it!Theis one of four present tenses. They are:The following slider shows all 12 tenses . The simple present tense is highlighted with a yellow background.
Describing Animals with Simple Present Tense
Learn how to describe pets and wild animals using verbs in Simple Present Tense.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

Listen and Speak English Story For Simple Present Tense
Short stories are perfect to practise English listening and speaking. You can use English grammar correctly and automatically by listening to the English story in the simple present tense. You can download our audio short stories here 👉 https://www.powerenglish.net/realenglishconversations/easypracticeenglishspeaking.html
In order to speak English fluently, you must practice grammar and vocabulary repeatedly so that you can use them automatically. That is where the short stories come in. Just listen to our English stories and answer the easy questions out loud.
Learn English by speaking to a native now 👉 https://www.gr8english.com/realenglishlessons/learnenglishbyspeakingitalki.html
In this story, we used a lot of simple present tense sentences. So you will hear many present simple examples to exercise. There are positive sentences, negative sentences, questions, and answers.
Our English Easy Practice course is very powerful to improve English listening skills and speaking skills. These are very useful short stories for kids as well.
Repetition is very important to speak English. So repeat that story with simple present tense exercises and you will become fluent eventually.
⭐ The Best English Courses ⭐
Effortless English 👉 https://www.powerenglish.net/effortlessenglish/powerenglish/powerenglishlessonset.html
English Easy Practice 👉 https://englisheasypractice.com/
Learn English Online 👉 https://tinyurl.com/englishrocket
Story For Past Continuous Tense 👉 https://youtu.be/QJ2x20GmUTs
Short Stories In English 👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O1iknZFsk0\u0026list=PLpODSd__yLPVVlSZo3RpAOiRZWHaUAoDb
Another great channel on Youtube, thanks to @Rahatingilizce
We would be happy if you like this video and subscribe to our channel. Now enjoy the English listening and speaking practice video here and write your comments below.
learnenglishthroughstory speakEnglish Englishlistening

10-DARS | Present Simple (INGLIZ TILIDA HOZIRGI ZAMON)
Assalamu alaykum!
00:00 Kirish
01:35 Present Simple nima?
02:05 Present Simple formulasi
03:20 Inkor gap yasash (negative)
04:49 Savol gap yasash (question)
05:20 Present Simple qoidasi
06:20 Sketch misol
07:10 JUDA KUCHLI MOTIVATSIYA
General English: https://clck.ru/QMX2B
Ingliz tili 0 dan Grammatika: https://clck.ru/QMXCf
Ingliz tili 0 dan Amaliyot: https://clck.ru/QMXur
Elementary: https://clck.ru/QMhEy
English Consultant: https://clck.ru/QMhLh
Savollarga Javoblar: https://clck.ru/QMhRr
Video sizga yoqdi degan umiddamiz. Agar shunday bo’lsa, kanalimizga obuna(подписаться, subscribe) bo’ling hamda \”Like\”ni bosing.
Savol yoki takliflaringiz bo’lsa, komentariyda qoldirsangiz bo’ladi. Hammasiga javob berishga harakat qilamiz.
Online darslar:
https://www.leapenglish.uz
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/leapenglish
Online kutubxona:
https://t.me/Leaplibrary
Biz bilan bog’lanish:
https://t.me/Leapeng
Englishonline Ingliz_tili Present_Simple
KEEP MOVING AND LEAP FORWARD!

Learn Present Simple Tense | English Grammar Course 1
QUIZ: https://shawenglish.com/quizzes/presenttensequiz/
Esther is teaching grammar videos again. In this video, Esther will teach the Present Simple Tense.
0:00 Introduction
0:24 Present Simple Tense | Facts, Truths, Generalizations
2:15 Present Simple Tense | Habits and Routines
4:07 Present Simple Tense | NonContinuous Verbs (Stative Verbs)
5:26 Present Simple Tense | Near Future, Scheduled Events
6:47 Present Simple Tense | Negative Usage
8:19 Present Simple Tense | Question Form
❤️✩Support Us! ✩
✭ Channel Membership: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC_OskgZBoS4dAnVUgJVexcw/join
✭ PayPal: https://paypal.me/shawenglish
✭ Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/ShawEnglish
👉✩ Connect With Us✩
✭ Website: http://www.shawenglish.com
✭ Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/shawenglish/
✭ Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/162048911162706/
✭ WhatsApp: http://shawenglish.com/whatsapplearnenglishwithrobin/
✭ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/shawenglishonline/
✭ Twitter: https://twitter.com/ShawEnglishNow
✭ Line: https://line.me/R/ti/g/5AJpLqlaln
✭ Telegram: https://t.me/ShawEnglish
✭ KakaoTalk: https://open.kakao.com/o/gcIHXP1
✭ Naver Café (네이버 카페): http://cafe.naver.com/shawenglish
🧔Learn English With Robin Shaw: http://shawenglish.com/learnenglishwithrobin/
👩🏫 Learn English with a live teacher NOW!
https://www.youtube.com/LearnEnglishLive
EnglishCourse BasicEnglish LearnEnglishGrammar

Simple Present
In this video, students learn when to use the simple present verb tense. They also learn how different subject pronouns and nouns affect the verb form. For more videos and lessons, visit us at https://esllibrary.com.
Link to lesson: https://esllibrary.com/courses/88/lessons/2403
Subscribe to ESL Library’s YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/c/Esllibrary
Follow us for more great content!
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/esllibrary/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ESLlibrary/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/esllibrary/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ESLlibrary/
Pinterest: https://ar.pinterest.com/esllibrary/

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่LEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ simple present