type1: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
Cloud computing wouldn’t be possible without virtualization. Virtualization wouldn’t be possible without the hypervisor. This thin layer of software supports the entire cloud ecosystem.
Table of Contents
What are hypervisors?
Before hypervisors hit the mainstream, most physical computers could only run one operating system (OS) at a time. This made them stable because the computing hardware only had to handle requests from that one OS. The downside of this approach was that it wasted resources because the operating system couldn’t always use all of the computer’s power.
A hypervisor solves that problem. It is a small software layer that enables multiple operating systems to run alongside each other, sharing the same physical computing resources. These operating systems come as virtual machines (VMs)—files that mimic an entire computing hardware environment in software.
The hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM), manages these VMs as they run alongside each other. It separates VMs from each other logically, assigning each its own slice of the underlying computing power, memory, and storage. This prevents the VMs from interfering with each other; so if, for example, one OS suffers a crash or a security compromise, the others survive.
To explore more about virtualization and virtual machines, check out “Virtualization: A Complete Guide” and “What is a Virtual Machine?”
For more information on how hypervisors manage VMs, check out this video, “Virtualization Explained” (5:20):
Characteristics of Hypervisors
There are different categories of hypervisors and different brands of hypervisors within each category. The market has matured to make hypervisors a commodity product in the enterprise space, but there are still differentiating factors that should guide your choice. Here’s what to look for:
- Performance: Look for benchmark data that show how well the hypervisor performs in a production environment. Ideally, bare-metal hypervisors should support guest OS performance close to native speeds.
- Ecosystem: You will need good documentation and technical support to implement and manage hypervisors across multiple physical servers at scale. Also, look for a healthy community of third-party developers that can support the hypervisor with their own agents and plugins that offer capabilities, such as backup and restore capacity analysis and fail-over management.
- Management tools: Running VMs isn’t the only thing you must manage when using a hypervisor. You must provision the VMs, maintain them, audit them, and clean up disused ones to prevent “VM sprawl.” Ensure that the vendor or third-party community supports the hypervisor architecture with comprehensive management tools.
- Live migration: This enables you to move VMs between hypervisors on different physical machines without stopping them, which can be useful for both fail-over and workload balancing.
- Cost: Consider the cost and fee structure involved in licensing hypervisor technology. Don’t just think about the cost of the hypervisor itself. The management software that makes it scalable to support an enterprise environment can often be expensive. Lastly, examine the vendor’s licensing structure, which may change depending on whether you deploy it in the cloud or locally.
Type 1 vs. Type 2
There are two broad categories of hypervisors: Type 1 and Type 2.
Type 1 hypervisor
A Type 1 hypervisor runs directly on the underlying computer’s physical hardware, interacting directly with its CPU, memory, and physical storage. For this reason, Type 1 hypervisors are also referred to as bare-metal hypervisors. A Type 1 hypervisor takes the place of the host operating system.
- Pros: Type 1 hypervisors are highly efficient because they have direct access to physical hardware. This also increases their security, because there is nothing in between them and the CPU that an attacker could compromise.
- Cons: A Type 1 hypervisor often needs a separate management machine to administer different VMs and control the host hardware.
Type 2 hypervisor
A Type 2 hypervisor doesn’t run directly on the underlying hardware. Instead, it runs as an application in an OS. Type 2 hypervisors rarely show up in server-based environments. Instead, they’re suitable for individual PC users needing to run multiple operating systems. Examples include engineers, security professionals analyzing malware, and business users that need access to applications only available on other software platforms.
Type 2 hypervisors often feature additional toolkits for users to install into the guest OS. These tools provide enhanced connections between the guest and the host OS, often enabling the user to cut and paste between the two or access host OS files and folders from within the guest VM.
- Pros: A Type 2 hypervisor enables quick and easy access to an alternative guest OS alongside the primary one running on the host system. This makes it great for end-user productivity. A consumer might use it to access their favorite Linux-based development tools while using a speech dictation system only found in Windows, for example.
- Cons: A Type 2 hypervisor must access computing, memory, and network resources via the host OS, which has primary access to the physical machine. This introduces latency issues, affecting performance. It also introduces potential security risks if an attacker compromises the host OS because they could then manipulate any guest OS running in the Type 2 hypervisor.
Examples
VMware hypervisors
- ESXi hypervisor: VMware ESXi (Elastic Sky X Integrated) is a Type 1 (or bare-metal) hypervisor targeting server virtualization in the data center. ESXi manages collections of VMware virtual machines.
- VSphere hypervisor: Customers can use VMware ESXi for free as part of the free vSphere hypervisor, which is a basic server virtualization offering. Companies with enterprise cloud environments will license vSphere, a more complete system that includes a license for VMware’s vCenter Server. This is a separate server used to administer vSphere environments running on physical hosts. VSphere can run in a private on-premiss cloud environment or in a hosted cloud configuration.
VMware also offers two main families of Type 2 hypervisor products for desktop and laptop users:
- VMware Fusion: This is the company’s MacOS-focused offering, which lets Mac users run a large range of guest operating systems.
- Workstation: VMware’s Linux- and Windows-focused platform comes in two flavors: Pro, which is a paid version, and Player, which is free for personal use. The Pro version allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single PC and also connects to VMware vSphere, just like Fusion. Workstation Player only supports a single guest OS.
- VirtualBox: A Type 2 hypervisor running on Linux, Mac OS, and Windows operating systems. Oracle inherited the product when it bought Sun Microsystems in 2010.
“VMware: A Complete Guide” goes into much more depth on all of VMware’s offerings and services.
Hyper-V hypervisor
Hyper-V is Microsoft’s hypervisor designed for use on Windows systems. It shipped in 2008 as part of Windows Server, meaning that customers needed to install the entire Windows operating system to use it. Microsoft subsequently made a dedicated version called Hyper-V Server available, which ran on Windows Server Core. This enabled administrators to run Hyper-V without installing the full version of Windows Server. Hyper-V is also available on Windows clients.
Microsoft designates Hyper-V as a Type 1 hypervisor, even though it runs differently to many competitors. Hyper-V installs on Windows but runs directly on the physical hardware, inserting itself underneath the host OS. All guest operating systems then run through the hypervisor, but the host operating system gets special access to the hardware, giving it a performance advantage.
Citrix XenServer
XenServer, now known as Citrix Hypervisor, is a commercial Type 1 hypervisor that supports Linux and Windows operating systems. XenServer was born of the Xen open source project (link resides outside IBM).
Open source hypervisors
Some hypervisors, such as KVM, come from open source projects. Red Hat’s ties to the open source community have made KVM the core of all major OpenStack and Linux virtualization distributions.
Open source hypervisors are also available in free configurations. KVM is downloadable on its own or as part of the oVirt open source virtualization solution, of which Red Hat is a long-term supporter.
Another is Xen, which is an open source Type 1 hypervisor that runs on Intel and ARM architectures. It began as a project at the University of Cambridge and its team subsequently commercialized it by founding XenSource, which Citrix bought in 2007.
In 2013, the open source project became a collaborative project under the Linux Foundation. Many cloud service providers use Xen to power their product offerings.
Xen supports several types of virtualization, including hardware-assisted environments using Intel VT and AMD-V. It also supports paravirtualization, which tweaks the guest OS to work with a hypervisor, delivering performance gains.
Hypervisor KVM
Linux also has hypervisor capabilities built directly into its OS kernel. The kernel-based virtual machine (KVM) became part of the Linux kernel mainline in 2007 and complements QEMU, which is a hypervisor that emulates the physical machine’s processor entirely in software.
KVM supports virtualization extensions that Intel and AMD built into their processor architectures to better support hypervisors. These extensions, called Intel VT and AMD-V respectively, enable the processor to help the hypervisor manage multiple virtual machines. Where these extensions are available, the Linux kernel can use KVM. Otherwise, it falls back to QEMU.
Find out more about KVM (link resides outside IBM) from Red Hat.
Red Hat Hypervisor
Red Hat bases its Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization Hypervisor on the KVM hypervisor. Its virtualization solution builds extra facilities around the hypervisor. This includes a virtualization manager that provides a centralized management system with a search-driven graphical user interface and secure virtualization technologies that harden the hypervisor against attacks aimed at the host or at virtual machines. Red Hat’s hypervisor can run many operating systems, including Ubuntu.
Virtual desktop integration (VDI)
Type 1 hypervisors can virtualize more than just server operating systems. They can also virtualize desktop operating systems for companies that want to centrally manage their end-user IT resources.
Virtual desktop integration (VDI) lets users work on desktops running inside virtual machines on a central server, making it easier for IT staff to administer and maintain their OSs.
In this environment, a hypervisor will run multiple virtual desktops. Each desktop sits in its own VM, held in collections known as virtual desktop pools. Each VM serves a single user who accesses it over the network.
The user’s endpoint can be a relatively inexpensive thin client, or a mobile device. This gives them the advantage of consistent access to the same desktop OS. They can get the same data and applications on any device without moving sensitive data outside a secure environment.
Users don’t connect to the hypervisor directly. Instead, they access a connection broker that then coordinates with the hypervisor to source an appropriate virtual desktop from the pool.
Products like VMware Horizon provide all this functionality in a single product delivered from your own on-premises service or via a hosted cloud service provider.
Troubleshooting
Because there are so many different makes of hypervisor, troubleshooting each of them will involve a visit to the vendor’s own support pages and a product-specific fix. However, some common problems include not being able to start all of your VMs. This can happen when you have exhausted the host’s physical hardware resources. To fix this problem, you can either add more resources to the host computer or reduce the resource requirements for the VM using the hypervisor’s management software.
Another common problem for hypervisors that stops VMs from starting is a corrupt checkpoint or snapshot of a VM. This is why VM backups are an essential part of an enterprise hypervisor solution, but your hypervisor management software may allow you to roll back the file to the last valid checkpoint and start it that way. However, this may mean losing some of your work.
Hypervisors and IBM
IBM invented the hypervisor in the 1960s for its mainframe computers. Today, IBM z/VM, a hypervisor for IBM z Systems mainframes, can run thousands of Linux virtual machines on a single mainframe. IBM PowerVM provides AIX, IBM i, and Linux operating systems running on IBM Power Systems.
IBM supports a range of virtualization products in the cloud. IBM Cloud Virtual Servers are fully managed and customizable, with options to scale up as your compute needs grow.
If you’re currently running virtualization on-premises, check out the solutions in the IBM VMware partnership.
Get started by creating your own IBM Cloud account today.
[Update] Type 1 Diabetes: Symptoms, Vs. Type 2, Causes, and More | type1 – NATAVIGUIDES
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic disease. In people with type 1 diabetes, cells in the pancreas that make insulin are destroyed, so the body is unable to make insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that helps your body’s cells use glucose (sugar) for energy. Your body gets glucose from the food you eat. Insulin allows the glucose to pass from your blood into your body’s cells.
When the cells have enough, your liver and muscle tissues store the extra glucose in the form of glycogen. It’s broken down into blood sugar and released when you need energy between meals, during exercise, or while you sleep.
With type 1 diabetes, your body is unable to process glucose due to the lack of insulin.
Glucose from your food can’t make its way into your cells. This leaves too much glucose circulating in your blood. High blood sugar levels can lead to both short- and long-term problems.
Type 1 vs. type 2 diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. They have similar symptoms and over time, they can lead to many of the same complications. However, they are very different diseases.
Type 1 diabetes is the result of a person’s body not producing insulin on its own. Taking insulin is necessary for survival, to move glucose from the bloodstream into the body’s cells.
For people with type 2 diabetes, the cells have stopped responding well to insulin. The body struggles to move glucose from the blood into the cells, despite having adequate levels of the hormone. Eventually, their bodies may stop making adequate insulin entirely.
Type 1 diabetes develops very quickly and symptoms are obvious. For people with type 2 diabetes, the condition can develop over many years. In fact, a person with type 2 diabetes may not know they have it until they have a complication.
The two types of diabetes are caused by different things. They also have unique risk factors.
Read about similarities and differences between the types of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes risk factors
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes are poorly understood. In many ways, they are similar to causes of diabetes.
This is because the factors that may trigger type 1 diabetes for some people may not trigger it for others.
Researchers have identified some potential risk factors:
Race
Race may be a risk factor for type 1 diabetes. People who are white may have more genetic predisposition to type 1 diabetes, since the condition is more common in this group.
Environmental factors
Some viruses may trigger type 1 diabetes as well. It’s unclear which ones might do this, however.
Likewise, people from cold climates are more likely to have type 1 diabetes. Doctors also diagnose more cases of type 1 in winter than they do in summer.
Several other components may influence who develops type 1 diabetes.
Read about these possible risk factors and the research underway to better understand why some people develop the disease.
Genetic factors
Researchers don’t understand exactly what causes type 1 diabetes. However, they believe that your genes may play a role, both in terms of the genes you inherit and your family’s history of diabetes.
People who have type 1 diabetes are born with a greater likelihood of developing the disease. It does appear to be passed down through generations of a family. It’s unclear how the pattern works and why some people in a family will develop diabetes while others will not.
Researchers have identified certain gene variants that may increase a person’s risk. These variants can be shared between parent and child, generation after generation. However, not everyone who has these genes develops type 1 diabetes.
That’s why researchers believe genes are only one part of the equation. They think something triggers the condition in people who have the inherited genes. A virus is one suspected trigger.
For example, identical twins, who have all the same genes, may not both develop the condition. If one twin has type 1 diabetes, the other twin develops the condition half of the time or less. This suggests that genes aren’t the only factor.
Type 1 diabetes treatment
If you receive a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, your body can’t make its own insulin. You’ll need to take insulin to help your body use the sugar in your blood.
Other treatments may also hold some promise for controlling symptoms of type 1 diabetes.
Insulin
People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin every day. You usually take the insulin through an injection.
Some people use an insulin pump. The pump injects insulin through a port in the skin. This can be easier for some people than sticking themselves with a needle. It may also help level out blood sugar highs and lows.
The amount of insulin you need varies throughout the day. People with type 1 diabetes regularly test their blood sugar to figure out how much insulin they need. Both diet and exercise can affect blood sugar levels.
Several insulin types exist. Your doctor may have you try more than one to find what works best for you.
Read about the differences in insulin and how it’s administered.
Metformin
Metformin is a type of oral diabetes medication. For many years, it was approved only for people with type 2 diabetes.
However, some people with type 1 diabetes can develop insulin resistance. That means the insulin they get from injections doesn’t work as well as it should. These days, doctors sometimes prescribe Metformin for type 1 patients.
Metformin helps lower sugar in the blood by reducing sugar production in the liver. Your doctor may advise you to take Metformin in addition to insulin.
Recall of metformin extended release
In May 2020, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommended that some makers of metformin extended release remove some of their tablets from the U.S. market. This is because an unacceptable level of a probable carcinogen (cancer-causing agent) was found in some extended-release metformin tablets. If you currently take this drug, call your doctor. They will advise whether you should continue to take your medication or if you need a new prescription.
Vaccines
The tuberculosis vaccine may possibly have some benefit as a treatment for people with type 1 diabetes but the data is very limited.
One 2012 study found that the bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) may have some impact on the autoimmune response that may be triggering type 1 diabetes. Since then, there’s been more research into the BCG vaccine and its potential use as a treatment tool for diabetes and other conditions.
The evidence for the vaccine’s use in diabetes remains controversial, though. A 2018 study suggests some promise, but at least one 2020 study does not.
Other medications
There is a new oral medication for people with type 1 diabetes. This drug will be the first oral medication designed to be used alongside insulin in people with type 1 diabetes, according to a 2019 research review.
It works to lower glucose levels in the blood by forcing the body to expel it in urine and by reducing glucose absorption in the gut. Similar medications already exist for people with type 2 diabetes, but none are approved for people with type 1.
However, Sotagliflozin (Zynquista) was denied by the FDA in 2019 due to some concerns about the medication as it’s currently produced.
On the other hand, the medication has been approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA). This raises the possibility that FDA may at some point still approve it in the United States.
Diagnosis of type 1 diabetes
Healthcare professionals usually diagnose type 1 diabetes through a series of tests. Some can be conducted quickly, while others require hours of preparation or monitoring.
Type 1 diabetes often develops quickly. According to the CDC, a healthcare professional can make a diabetes diagnosis if:
- Fasting blood sugar is greater than 126 mg/dL on two separate tests.
- Random blood sugar is greater than 200 mg/dL, along with symptoms of diabetes.
- Hemoglobin A1c is greater than 6.5 on two separate tests.
Doctors also use the same criteria to diagnose type 2 diabetes. In fact, people with type 1 diabetes are sometimes misdiagnosed as having type 2.
A doctor may not realize you’ve been misdiagnosed until you begin developing complications or worsening symptoms despite treatment.
When blood sugar gets so high that diabetic ketoacidosis occurs, you become very ill. This is often the reason people end up in the hospital or their doctor’s office, and type 1 diabetes is then diagnosed.
If you have any of the symptoms of diabetes, your doctor will likely order tests.
Learn how each of these tests is performed and what they show.
Complications
The two most common complications are hypoglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Hypoglycemia happens when your blood sugar is too low, usually when your body has too much insulin. It can happen if you wait too long to eat or have a snack, or if you exercise too much.
Ketoacidosis can be a life threatening condition. This when your body doesn’t have enough insulin. Symptoms of this condition include:
- rapid breathing
- dry skin and mouth
- flushed face
- fruity breath odor
- nausea
- vomiting or stomach pain
In addition, high blood sugar levels can cause damage to various parts of the body. Symptoms can include:
- increased heart attack risk
- eye problems, including blindness
- nerve damage
- infections on the skin, especially the feet, that could require amputation in serious cases
- kidney damage
Diabetes can also damage your nerves and lead to a condition called diabetic neuropathy. This is common in the feet.
Small cuts, especially on the bottom of your feet, can quickly turn into severe ulcers and infections, especially if blood sugar levels aren’t controlled. This is because you can’t feel or see the cuts, so you don’t treat them.
That is why it’s important to check your feet regularly if you have diabetes. If you happen to notice any foot injuries, let your doctor know right away.
People with type 1 diabetes should also pay attention to other changes to their bodies. Read more about the possible effects diabetes can have on your body.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy presents unique challenges for people who have type 1 diabetes. However, it’s possible to have a healthy pregnancy and baby despite having this condition.
The most important thing to remember if you are expecting or trying to become pregnant and have type 1 diabetes is that everything you do for your body, you do for your baby. People who have high blood sugar levels have babies with high blood sugar.
According to the CDC, high blood sugar levels during pregnancy can lead to complications such as:
- a high birth weight
- complicated cesarean delivery, commonly referred to as a C-section
- preterm birth
- low blood sugar
- high blood pressure
- stillbirth
If you have type 1 diabetes and want to become pregnant or find out that you’re pregnant, talk with your doctor immediately. They can discuss any changes you may need to make to guarantee your blood sugar levels remain stable and safe for you and your baby.
It’s best to plan ahead for a pregnancy and discuss your diabetes and blood sugar goals with your doctor.
During your pregnancy, you will likely need to see a healthcare professional more frequently. You may also need to adjust medication and insulin throughout the pregnancy.
Doctors and patients share their tips for managing pregnancy with diabetes.
Drinking alcohol
For people with type 1 diabetes, alcohol can have a big impact on blood sugar levels in the short term. Over time, excessive alcohol use can contribute to complications of diabetes.
The liver is responsible for processing and removing alcohol from the body. The liver is also involved in managing blood sugar levels. If you have type 1 diabetes and drink alcohol, your body slows the management of blood sugar in order to deal with the alcohol.
This can lead to low blood sugar, immediately and for several hours after drinking. It’s important to test your blood sugar before drinking alcohol and to continue to monitor it afterward.
Read more about drinking alcohol with diabetes.
Lifestyle tips
Living with type 1 diabetes means maintaining consistent lifestyle strategies that include both a change to your diet and a safe exercise routine.
Diet
Try to eat regular meals and snacks to keep your blood sugar stable. If you have access to one, a dietitian who is also a certified diabetes educator can help you establish an eating plan.
Some tips to consider when developing your nutrition plan include:
- Eat a balanced diet that includes vegetables, nonfat dairy, lean meats, plant proteins, whole grains, healthy fats, and fruits.
- Eat small meals. It’s better to eat more often in smaller portions and space your meals evenly throughout the day to keep your glucose level from spiking.
- Never skip meals.
Exercising safely
Exercise helps lower your blood sugar levels, and it is a vital part of the balanced lifestyle important for anyone with type 1 diabetes.
But, exercise can also be tricky for people with this condition. This is because your insulin amounts need to be adjusted according to your level of exercise.
Try to aim to exercise at least 150 minutes per week. Also, try to have no more than 2 consecutive days without exercise. Aerobic exercise is good for people with type 1 diabetes, as are strength training and resistance training.
What’s unclear, however, is the best practice for managing blood glucose during exercise. That’s because blood sugar levels can spike or even crash during and after exercise, as your body’s cells begin using insulin or moving glucose more effectively.
Still, experts suggest people with diabetes get regular exercise for optimal health. This may require working with your doctor or other expert to find a plan that is right for you.
This guide to blood sugar target levels and ranges for insulin may help you get started.
Learn more about managing day-to-day life, symptoms, and preventing complications.
Takeaway
Type 1 diabetes is a condition that causes the body to be unable to process glucose due to a lack of insulin.
The cause is likely an autoimmune process. Experts believe it is influenced by genetics and environmental factors, and possibly by viral infections.
Type 1 diabetes is a different disease than type 2 diabetes.
But just like with the other form of diabetes, you can typically manage it with insulin, medications, and a balanced diet and exercise routine.
It’s important to consult with a doctor and to monitor your glucose regularly, as well as to be aware of potential complications and their symptoms.
Why I’m glad I was diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes.
www.sebinspires.com
Already a veteran inspirational \u0026 motivational Keynote speaker with over 300 presentations throughout North America, including a TEDx talk, Sébastien Sasseville worked for large companies during the first 10 years of his career. He now speaks to organisations and corporations globally on the topics of peak performance, change and agility in the corporate environment and leadership. His inner fortitude, key insights and authenticity come from an ability to draw from lessons provided by seeking great personal challenges and to apply them to today’s most pressing and complex business concerns. His message connects with audiences worldwide from his exceptional storytelling, energy and humour.
For more information on Sebastien’s journey or to book him as a guest speaker, please visit www.sebinspires.com
@sebinspires
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

Thế nào là Tiểu đường Type 1 và Type 2

หลักการใช้ conditional sentence type 1 l ประโยคเงื่อนไขแบบที่ 1l ไวยากรณ์ภาษาอังกฤษพื้นฐาน
คลิปนี้จะมาสอนหลักการใช้ conditional sentence type 1 เริ่มจากโครงสร้างประโยค if clause และ main clause พร้อมทั้งวิธีการใช้งาน
เรียนภาษาอังกฤษฟรีกับปาป๊าอี๊ดได้โดยติดตามเราได้ที่
Youtube:https://goo.gl/Svd65u
Twitter:http://bit.ly/2Yt2lqH
Blog:https://goo.gl/JthDFX
Facebook:http://bit.ly/2CIaLBa

Diabetes Type 1 and Type 2, Animation.
This video and more updated versions of similar videos are available for instant download licensing https://www.alilamedicalmedia.com//galleries/narratedvideosbytopics/diabetes
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
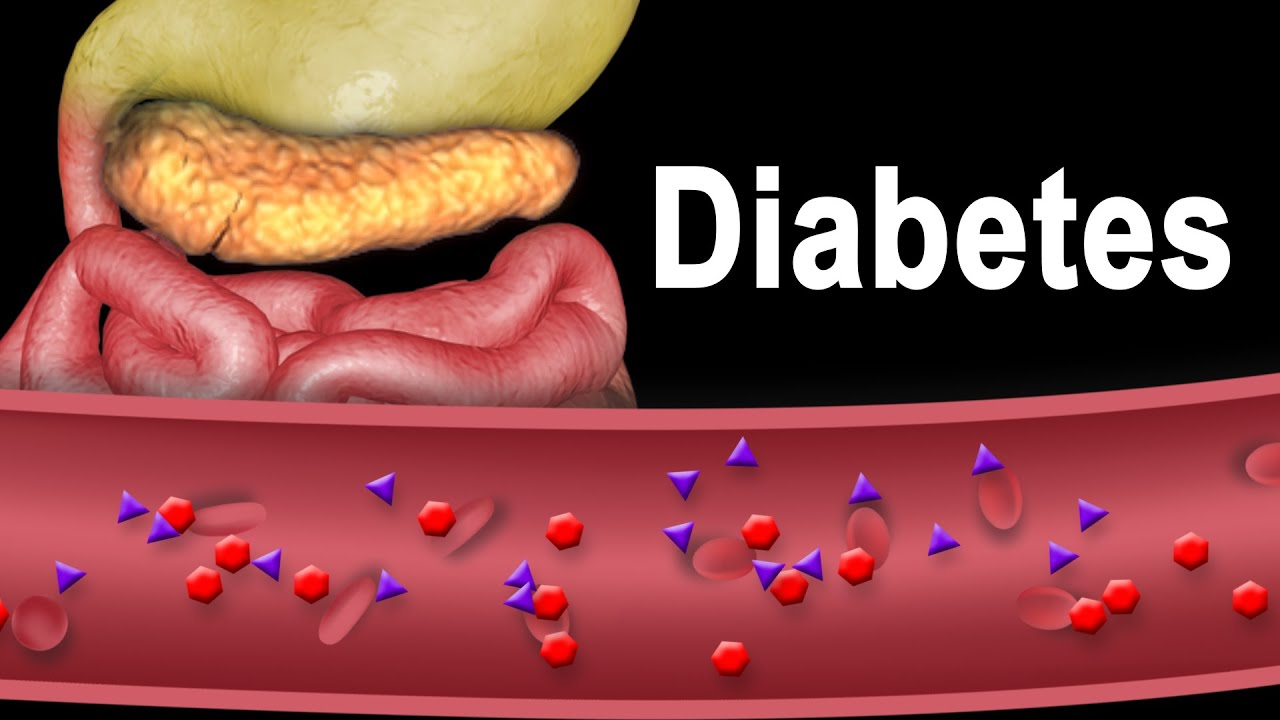
Diabetes refers to a group of conditions characterized by a high level of blood glucose, commonly referred to as blood sugar. Too much sugar in the blood can cause serious, sometimes lifethreatening health problems.
There are two types of chronic diabetic conditions: type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Pregnant women may acquire a transient form of the disease called “gestational diabetes” which usually resolves after the birth of baby. Prediabetes is when the blood sugar level is at the borderline: higher than normal, but lower than in diabetics. Prediabetes may or may not progress to diabetes.
During food digestion, carbohydrates or carb break down into glucose which is carried by the bloodstream to various organs of the body. Here, it is either consumed as an energy source in muscles for example or is stored for later use in the liver. Insulin is a hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreas and is necessary for glucose intake by target cells. In other words, when insulin is deficient, muscle or liver cells are unable to use or store glucose, and as a result, glucose accumulates in the blood.
In healthy people, beta cells of the pancreas produce insulin; insulin binds to its receptor on target cells and induces glucose intake.
In type 1 diabetes, beta cells of the pancreas are destroyed by the immune system by mistake. The reason why this happens is unclear, but genetic factors are believed to play a major role. Insulin production is reduced; less insulin binds to its receptor on target cells; less glucose is taken into the cells, more glucose stays in the blood. Type 1 is characterized by early onset, symptoms commonly start suddenly and before the age of 20. Type 1 diabetes is normally managed with insulin injection. Type 1 diabetics are therefore “insulin dependent”.
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas produces enough insulin but something goes wrong either with receptor binding or insulin signaling inside the target cells. The cells are not responsive to insulin and therefore cannot import glucose; glucose stays in the blood. In other words, type 2 diabetics are “insulin resistant”. Here again, genetic factors predispose susceptibility to the disease, but it is believed that lifestyle plays a very important role in type 2. Typically, obesity, inactive lifestyle, and unhealthy diet are associated with higher risk of type 2 diabetes. Type 2 is characterized by adult onset; symptoms usually appear gradually and start after the age of 30. Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 80 to 90% of all diabetics. Management focuses on weight loss and includes a lowcarb diet.
Pilipinas Got Talent 2018 Auditions: Type 1 Dance Company – Dance
Now on its 6th season, Pilipinas Got Talent showcases worldclass pinoy talents and phenomenal performances! See all the latest updates and exclusives here.
Watch the full episodes every Saturday (7PM) and Sunday (7:30PM)
Subscribe to the ABSCBN Piliipinas Got Talent channel! http://bit.ly/1REigeY
Visit our official website!
http://pilipinasgottalent.abscbn.com
Follow our social media accounts:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/PilipinasGotTalent.PGT/
Twitter: hhttps://twitter.com/ABSCBNPGT
Instagram: hhttps://www.instagram.com/abscbnpgt/

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆLEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ type1