fixed asset คือ: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
Table of Contents
What Is a Fixed Asset?
The term fixed asset refers to a long-term tangible piece of property or equipment that a firm owns and uses in its operations to generate income. The general assumption about fixed assets is that they are expected to last, be consumed, or converted into cash after at least one year. As such, companies are able to depreciate the value of these assets to account for natural wear and tear. Fixed assets most commonly appear on the balance sheet as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E).
Key Takeaways:
- Fixed assets are items that a company plans to use over the long term to help generate income.
- Fixed assets are most commonly referred to as property, plant, and equipment.
- Current assets are any assets that are expected to be converted to cash or used within a year.
- Noncurrent assets, in addition to fixed assets, include intangibles and long-term investments.
- Fixed assets are subject to depreciation to account for the loss in value as the assets are used, whereas intangibles are amortized.
1:34
Fixed Asset
Understanding Fixed Assets
A company’s balance sheet statement includes its assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity. Assets are divided into current assets and noncurrent assets, the difference for which lies in their useful lives. Current assets are typically liquid, which means they can be converted into cash in less than a year. Noncurrent assets refer to assets and property owned by a business that are not easily converted to cash and include long-term investments, deferred charges, intangible assets, and fixed assets.
The term alludes to the fact that these assets won’t be used up or sold within the accounting period. A fixed asset typically has a physical form and is reported on the balance sheet as PP&E. Companies purchase fixed assets for any number of reasons including:
- the production or supply of goods or services
- rental to third parties
- use in an organization
Fixed assets lose value as they age. Because they provide long-term income, these assets are expensed differently than other items. Tangible assets are subject to periodic depreciation while intangible assets are subject to amortization. A certain amount of an asset’s cost is expensed annually. The asset’s value decreases along with its depreciation amount on the company’s balance sheet. The corporation can then match the asset’s cost with its long-term value.
How a business depreciates an asset can cause its book value (the asset value that appears on the balance sheet) to differ from the current market value (CMV) at which the asset could sell. Land is one fixed asset that cannot be depreciated.
A fixed asset does not necessarily have to be fixed (i.e. stationary or immobile) in all senses of the word.
Special Considerations
The acquisition or disposal of a fixed asset is recorded on a company’s cash flow statement under the cash flow from investing activities. The purchase of fixed assets represents a cash outflow (negative) to the company while a sale is a cash inflow (positive). If the asset’s value falls below its net book value, the asset is subject to an impairment write-down. This means that its recorded value on the balance sheet is adjusted downward to reflect that it is overvalued compared to the market value.
When a fixed asset reaches the end of its useful life, it is usually disposed of by selling it for a salvage value. This is the asset’s estimated value if it was broken down and sold in parts. In some cases, the asset may become obsolete and will, therefore, be disposed of without receiving any payment in return. Either way, the fixed asset is written off the balance sheet as it is no longer in use by the company.
Some companies refer to their fixed assets as capital assets.
Fixed Assets vs. Current Assets and Noncurrent Assets
Both current assets and fixed assets appear on the balance sheet, with current assets meant to be used or converted to cash in the short term (less than one year) and fixed assets meant to be used over the longer term (more than one year). Current assets include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable (AR), inventory, and prepaid expenses. Fixed assets are depreciated, while current assets are not.
Fixed assets are a form of noncurrent assets. Other noncurrent assets include long-term investments and intangibles. Intangible assets are fixed assets to be used over the long term, but they lack physical existence. Examples of intangible assets include goodwill, copyrights, trademarks, and intellectual property. Meanwhile, long-term investments can include bond investments that will not be sold or mature within a year.
Benefits of Fixed Assets
Information about a corporation’s assets helps create accurate financial reporting, business valuations, and thorough financial analysis. Investors and creditors use these reports to determine a company’s financial health and decide whether to buy shares in or lend money to the business.
Because a company may use a range of accepted methods for recording, depreciating, and disposing of its assets, analysts need to study the notes on the corporation’s financial statements to find out how the numbers are determined.
Fixed assets are particularly important to capital-intensive industries, such as manufacturing, which require large investments in PP&E. When a business is reporting persistently negative net cash flows for the purchase of fixed assets, this could be a strong indicator that the firm is in growth or investment mode.
Examples of Fixed Assets
Fixed assets can include buildings, computer equipment, software, furniture, land, machinery, and vehicles. For example, if a company sells produce, the delivery trucks it owns and uses are fixed assets. If a business creates a company parking lot, the parking lot is a fixed asset.
What Is the Difference Between Fixed Assets and Current Assets?
Fixed assets, which are noncurrent assets, are long-term tangible pieces of property or equipment that a firm owns and uses in its operations to generate income. They are not expected to be consumed or converted into cash within one year, are subject to depreciation, and are illiquid.
Fixed assets are particularly important to capital-intensive industries, such as manufacturing, which require large investments in property, plant, and equipment.
Current assets are meant to be used or converted to cash in the short term, defined as less than one year, and are not depreciated. Current assets include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenses.
Fixed assets are depreciated, while current assets are not. Both current assets and fixed assets appear on the balance sheet,
What Are Examples of Fixed Assets?
Fixed assets can include buildings, computer equipment, software, furniture, land, machinery, and vehicles. For example, if a company sells produce, the delivery trucks it owns and uses are fixed assets.
What Are Other Types of Noncurrent Assets?
Other noncurrent assets include long-term investments and intangibles. Intangible assets are fixed assets to be used over the long term, but they lack physical existence. Examples of intangible assets include goodwill, copyrights, trademarks, and intellectual property. Meanwhile, long-term investments can include bond investments that will not be sold or mature within a year.
[NEW] fixed asset แปลว่าอะไร ดูความหมาย ตัวอย่างประโยค หมายความว่า พจนานุกรม Longdo Dictionary แปลภาษา คำศัพท์ | fixed asset คือ – NATAVIGUIDES
บริการเปิดพจนานุกรมอัตโนมัติ ติดโพย (PopThai)
บริการ ติดโพย (PopThai)
เป็นบริการเปิดพจนานุกรมอัตโนมัติ โดยผู้ใช้สามารถป้อนข้อความ ทีละประโยค หรือ เป็นหน้าเลยก็ได้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องทีละคำสองคำ
ระบบจะทำการแนบความหมายของคำหรือวลีภาษาต่างประเทศ
(ปัจจุบันสนับสนุน ภาษาอังกฤษ, ญี่ปุ่นและเยอรมัน)
ติดกับเนื้อหานั้นๆ และจะแสดงผลความหมายเมื่อเอาเมาส์ไปวางเหนือคำหนึ่งๆ
ช่วยให้สามารถเข้าใจเนื้อหาของเวบภาษาต่างประเทศได้สะดวกและรวดเร็วยิ่งขึ้น
ความหมายของคำจะปรากฏขึ้นมาเมื่อท่านเอาเมาส์ไปวางบนคำหรือวลีที่มีอยู่ในพจนานุกรม
โดยไม่จำเป็นต้องกดปุ่มใดๆ
ดังตัวอย่างในรูปข้างล่างนี้
คุณสมบัติ / Features
- แสดงความหมายของคำโดยอัตโนมัติ เพียงวางเมาส์ไว้บนคำที่ต้องการทราบความหมาย
- สนับสนุนเวบหลากภาษา (ปัจจุบัน ภาษาอังกฤษ ญี่ปุ่น และเยอรมัน)
- ค้นหาความหมายจากพจนานุกรมหลายชุดพร้อมๆกัน ในฐานข้อมูลของ Longdo ได้แก่
Lexitron2, Hope, Nontri, Longdo อังกฤษ-ไทย, Longdo เยอรมัน-ไทย เป็นต้น - แสดงได้ทั้งความหมายของคำเดี่ยว และคำผสม ได้อย่างถูกต้อง
เช่น Secretary of State=รัฐมนตรีต่างประเทศของสหรัฐฯ (ในภาพตัวอย่าง),
High school=โรงเรียนมัธยมปลาย - แสดงความหมายของคำที่แปรรูปจากคำในพจนานุกรมได้ เช่น
เมื่อวางเมาส์ไว้บนคำว่า executed/abusing ซึ่งไม่มีในพจนานุกรม
เครื่องจะแสดงความหมายของคำว่า execute/abuse ให้โดยอัตโนมัติ - เรียกใช้งานได้ง่ายเพียงกดปุ่ม PopThai บน
Longdo Toolbar
เพื่อแนบความหมายหน้าจอที่เปิดชมอยู่ในขณะนั้น - แก้ไข Link ในหน้าที่แสดง เพื่อให้สามารถเปิดชม Link เหล่านั้นผ่านบริการ PopThai
ได้ทันทีเช่นเดียวกัน - สนับสนุนบราวเซอร์ชั้นนำทั่วไป เช่น Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Safari, Konqueror, etc.
- แสดง Link ให้ผู้ใช้ช่วยป้อนความหมายสำหรับคำที่ยังไม่มีอยู่ในพจนานุกรม
- ใหม่: บริการ Vocabulary แสดงสรุปรายการคำศัพท์พร้อมความหมาย สำหรับพิมพ์ออกมาอ่านได้สะดวก
วิธีใช้งาน ให้เลือกตรงตัวเลือกบริการด้านบน ให้เป็น Vocabulary แทน PopThai. (PopThai ในโหมดปกติ จะเหมาะกับการใช้งาน on-line
หน้าจอคอมพิวเตอร็ ส่วนบริการ Vocabulary เหมาะสำหรับท่านที่ต้องการพิมพ์รายการคำศัพท์และความหมายออกมาบนกระดาษไว้อ่าน off-line) - ใหม่: บริการ Pronunciation Guide แสดงคำอ่านของคำใน เว็บ หรือ text ที่ป้อนให้ ข้างบนคำนั้นๆ, นอกเหนือไป
จากการแสดง pop-up ความหมาย. วิธีใช้งาน ให้เลือกตรงตัวเลือกบริการด้านบน ให้เป็น Pronunciation.
ขณะนี้ใช้ได้กับภาษาอังกฤษ (แสดงคำอ่านภาษาอังกฤษ) และภาษาญี่ปุ่น (แสดง hiragana เหนือคันจิ). บริการนี้
ใช้ extension ของ browser ที่ชื่อ Ruby ปัจจุบันมีแค่ IE browser ที่สนับสนุน ถ้าเป็น browser อื่นๆ จะเห็นคำอ่านปรากฎในวงเล็บแทน
วิธีใช้
ท่านสามารถป้อนเนื้อหาหรือ URL ของเว็บไซต์ที่ต้องการให้แนบความหมายนี้ ในช่องใส่ข้อความค้นหาปกติ
หลังจากนั้นเลือกบริการที่ต้องการ (เช่น ถ้าป้อนข้อความ ให้เลือก PopThai (text) ถ้าป้อน URL ให้เลือก PopThai (URL)) ถ้าท่านไม่เลือกบริการ
ระบบจะเดาบริการที่ท่านต้องการ จากข้อความที่ท่านใส่เข้ามา (ว่าเป็นข้อความหรือเป็น URL) โดยอัตโนมัติ,
จากนั้นกด Submit เป็นอันเสร็จ
ในกรณีที่ท่านใส่ URL ระบบจะไปทำการดาวน์โหลดเนื้อหาของหน้านั้นๆ มาและแนบความหมาย พร้อมแก้ไขลิงค์ต่างๆ ให้เป็นผ่านบริการ PopThai เ
พื่อที่ว่าเมื่อท่านกดที่ลิงค์ใดๆ ต่อไปจากเพจนั้นๆ ก็จะมีการแนบความหมายมาให้ด้วยในทันที
เพื่อเพิ่มความสะดวกในการใช้ท่านสามารถใช้ PopThai ผ่าน Longdo Toolbar โดยเมื่อท่านเปิดดูเว็บไซต์ใดๆ อยู่ตามปกติ และต้องการใช้บริการ PopThai สำหรับ
หน้านั้นๆ สามารถทำได้ทันที โดยคลิกที่ปุ่ม PopThai บน Toolbar รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมโปรดอ่านที่ Longdo Toolbar
คำเตือน ในกรณีของ URL นี้ ถึงแม้ทางผู้ดูแลระบบลองดูจะได้ทำการทดสอบกับหลายเว็บไซต์
แล้วก็ตาม ยังมีบางเว็บไซต์ที่ข้อมูลเวลาที่ระบบไปโหลดมาจะแตกต่างจากที่ท่านเปิดดูโดยใช้ browser โดยตรง โปรดระวังด้วย และไม่ควรใช้กับหน้าเว็บไซต์ที่
ต้องการความถูกต้องสูง)
Problems & TODO
- inflected word support (German)
- support HTTP POST
- other foreign language support (Japanese, French)
How to calculate depreciation using the straight line method in Excel
Our Excel training videos on YouTube cover formulas, functions and VBA. Useful for beginners as well as advanced learners. New upload every Thursday.
For details you can visit our website:
http://www.familycomputerclub.com
Depreciation is an important aspect in any business. Businesses calculate the depreciation of their assets, deduct the depreciation amount from their net incmome and then pay taxes on the final income after depreciation. We describe here the straight line method of depreciation calculation in Microsoft Excel.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่

Introduction to Fixed Assets Process
Http://www.technofunc.com presents another Functional Capsule on Fixed Asset process area. In these functional capsules; \”Technofunc\” provides you with compressed knowledge; to learn key business processes in the context of Information Technology systems. In this video, we will explore the business process area known as; Fixed Assets; Also known as FA.Learning objectives for this lesson are:
Meaning of Fixed Assets Process;Sub Processes under Fixed Assets;Process Flow for Fixed Assets;Key Transactions Fields \u0026 Key Roles;Key Setups \u0026 Master Data Requirements

Fixed Asset Module in Dynamics 365 Business Central
The fixed asset module in Dynamics 365 Business Central is highly intuitive, and at the same time very userfriendly.
In this video, we will go over the following:
Fixed asset setup windows – 0:30
How to add new fixed assets – 4:30
How to run monthly depreciation – 7:45
Some of the features you can do with fixed assets include:
Being able to project fixed asset depreciation easily when needed with userfriendly reporting
Being able to add/manage multiple assets (with differing classes and depreciation setups) that make up a main asset
For each asset you can manage maintenance costs as well as the next date of service. This provides visibility on budgeting for fixed assets and deciding whether to replace an asset
Ability to link assets to one or more insurance policies, making it easy to manage the annual insurance premiums associated with fixed assets
Ability to seamlessly run fixed asset transactions without the need for manual posting to GL
Ability to add fixed assets via the purchasing module (i.e. via invoice or purchase order)

Fixed Asset Manager and Fixed Asset Items in QuickBooks Desktop
QuickBooks 30day free trial + 30% off for 12 months:
https://quickbooks.intuit.com/partners/irp/?cid=irp4337pricing
Using Fixed Asset Manager and Fixed Asset Items in QuickBooks Desktop to book depreciation.
00:00:00 – Intro (QuickBooks Desktop)
00:00:42 – Traditional way that we manage fixed assets (Reports, Company \u0026 Financial, Balance Sheet Standard) (example) (how it works)
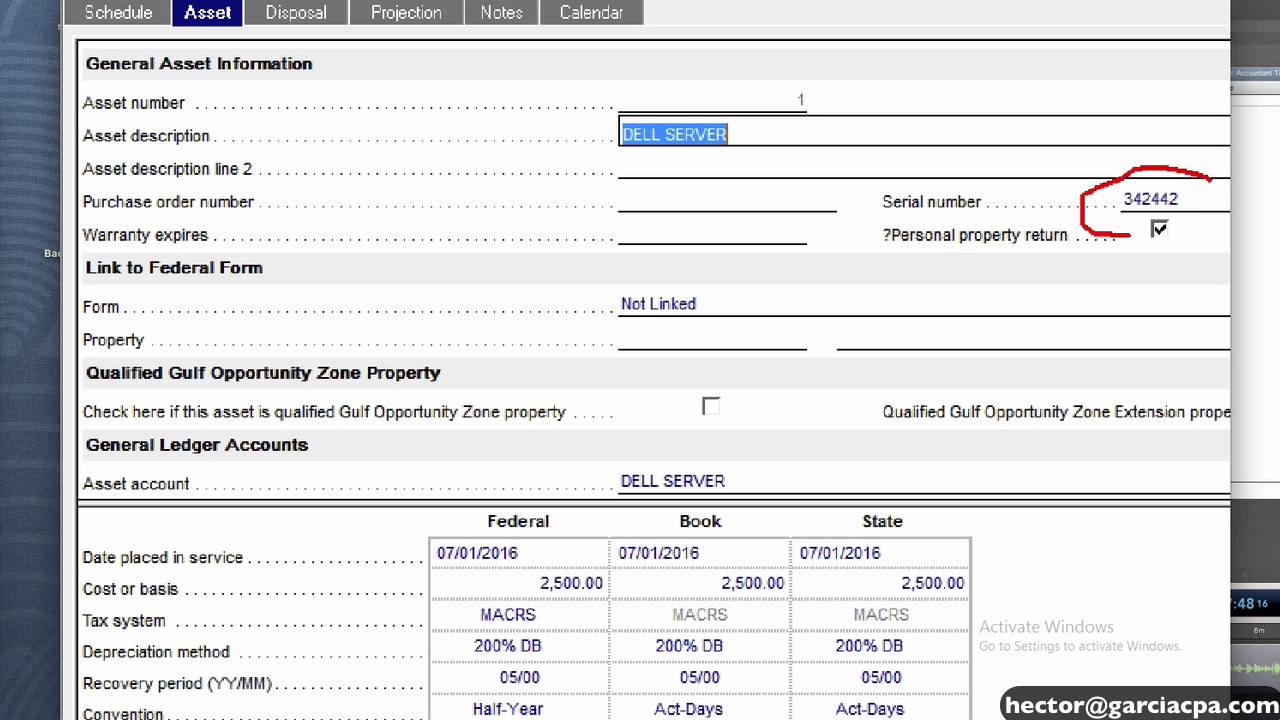
00:03:01 – How to access the fixed asset manager (company, manage fixed assets or accountant, manage fixed assets)
00:03:21 – QuickBooks Fixed Asset Manager (how it works)
00:05:43 – Chart of accounts (it should match chart of accounts of QuickBooks Desktop with QuickBooks fixed asset manager)
00:06:17 – QuickBooks Fixed Asset Manager tabs (Schedule, Asset, Disposal, Projection, Notes, Calendar)
00:07:32 – Fixed assets lists (lists, fixed asset item list)
00:08:33 – How to add new fixed asset in fixed assets lists (step by step) (example)
00:10:59 – Open QuickBooks Fixed Asset Manager (update assets from QuickBooks) (asset tab) (general ledger accounts)
00:13:37 – Groupings (federal, book, state) (methods of depreciation) (report) (client information) (asset tools) (how it works, example)
00:25:42 – Asset tools
00:27:06 – Display tax worksheet (reports) (creates tax form for you)
00:28:02 – Post journal entry to QuickBooks (how it works)
00:30:11 – Display journal entry list
00:31:38 – Write check (example) (book the purchase)
00:33:13 – Reports (list, fixed asset listing) (customize report
What is FIXED ASSETS MANAGEMENT? What does FIXED ASSETS MANAGEMENT mean?
✪✪✪✪✪ http://www.theaudiopedia.com ✪✪✪✪✪
What is FIXED ASSETS MANAGEMENT? What does FIXED ASSETS MANAGEMENT mean? ASSETS MANAGEMENT meaning ASSETS MANAGEMENT definition ASSETS MANAGEMENT explanation.
Source: Wikipedia.org article, adapted under https://creativecommons.org/licenses/bysa/3.0/ license.
Fixed assets management is an accounting process that seeks to track fixed assets for the purposes of financial accounting, preventive maintenance, and theft deterrence.
Organizations face a significant challenge to track the location, quantity, condition, maintenance and depreciation status of their fixed assets. A popular approach to tracking fixed assets uses serial numbered asset tags, which are labels often with bar codes for easy and accurate reading. The owner of the assets can take inventory with a mobile bar code reader and then produce a report.
Offtheshelf software packages for fixed asset management are marketed to businesses small and large. Some enterprise resource planning systems are available with fixed assets modules.
Some tracking methods automate the process, such as by using fixed scanners to read bar codes on railway freight cars or by attaching a radiofrequency identification (RFID) tag to an asset.
Tracking assets is an important concern of every company, regardless of size. Fixed assets are defined as any ‘permanent’ object that a business uses internally including but not limited to computers, tools, software, or office equipment. While employees may use a specific tool or tools, the asset ultimately belongs to the company and must be returned. And therefore without an accurate method of keeping track of these assets it would be very easy for a company to lose control of them.
With advancements in technology, asset tracking software is now available that will help any size business track valuable assets such as equipment and supplies. According to a study issued in December, 2005 by the ARC Advisory Group, the worldwide market for enterprise asset management (EAM) was then at an estimated $2.2 billion and was expected to grow at about 5.0 percent per year reaching $2.8 billion in 2010.

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่LEARN TO MAKE A WEBSITE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ fixed asset คือ