had + v3: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
Để có thể tiếp cận những kiến thức nâng cao hơn, bạn buộc phải sử dụng thành thạo những thì trong tiếng Anh. Cần ghi nhớ rằng, nếu bạn muốn chinh phục các kì thi trong nước hay quốc tế như IELTS, TOEFL, TOEIC, SAT thì nhất định bạn phải thuộc lòng 12 thì trong tiếng Anh cơ bản. Hiểu được điều đó, TOPICA Native đã tổng hợp 12 thì tiếng Anh: công thức, cách dùng và dấu hiệu nhận biết.
Download Now: Trọn bộ Ebook ngữ pháp FREE
Xem thêm:
Có bao nhiêu thì trong tiếng Anh? Câu trả lời là có 12 thì trong tiếng Anh, quả là không phải con số nhỏ đúng không nào? Cùng tìm hiểu tổng hợp các công thức 12 thì và dấu hiệu nhận biết các thì trong tiếng Anh nhé!
Table of Contents
1. THÌ HIỆN TẠI ĐƠN – Simple Present tens
1.1. Khái niệm
Thì hiện tại đơn (Simple present tense) dùng để diễn tả một sự thật hiển nhiên hay một hành động diễn ra lặp đi lặp lại theo thói quen, phong tục, khả năng.
1.2. Công thức thì hiện tại đơn
Loại câu
Đối với động từ thường
Đối với động từ “to be”
Khẳng định
S + V(s/es) + O
S + be (am/is/are) + O
Phủ định
S + do not /does not + V_inf
S + be (am/is/are) + not + O
Nghi vấn
Do/Does + S + V_inf?
Am/is/are + S + O?
Ví Dụ
-
She gets up at 6 o’clock.
(Cô thức dậy lúc 6 giờ)
-
She doesn’t eat chocolate.
(Cô ấy không ăn sô cô la.)
-
Does she eat pastries?
(Cô ấy có ăn bánh ngọt không?)
-
She is a student.
(Cô ấy là học sinh)
-
She is not a teacher
(Cô ấy không phải là giáo viên)
-
Is she a student?
(Cô ấy có phải là học sinh không)
1.3. Cách dùng thì hiện tại đơn
- Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả một sự thật hiển nhiên, một chân lý.
Ex: The sun rises in the East and sets in the West (Mặt trời mọc ở hướng Đông và lặn ở hướng Tây)
- Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả 1 hành động xảy ra thường xuyên, một thói quen ở hiện tại.
Ex: He gets up early every morning.(Anh dậy sớm mỗi sáng.)
Lưu ý: Quy tắc thêm s/es tại bài viết về bài tập thì hiện tại đơn.
- Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả một năng lực của con người
Ex: He plays badminton very well (Anh ấy chơi cầu lông rất giỏi)
- Ngoài ra, thì hiện tại đơn còn diễn tả một kế hoạch đã được sắp xếp trong tương lai, đặc biệt là trong việc di chuyển.
Ex: The train leaves at 9 am tomorrow (Tàu khởi hành lúc 9 giờ sáng ngày mai)
1.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì hiện tại đơn
Trong câu có chứa các trạng từ chỉ tần suất như:
-
Every day/ week/ month…: mỗi ngày/ tuần/ tháng
-
Often, usually, frequently: thường
-
Sometimes, occasionally: thỉnh thoảng
-
Always, constantly: luôn luôn
-
Seldom, rarely: hiếm khi
1.5. Video hướng dẫn cách tự học dạng Câu Hỏi Yes/No trong thì hiện tại đơn
2. Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn – Present Continuous
2.1. Khái niệm
Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn (Present continuous tense) dùng để diễn tả những sự việc xảy ra ngay lúc chúng ta nói hay xung quanh thời điểm chúng ta nói, và hành động đó vẫn chưa chấm dứt (còn tiếp tục diễn ra).
2.2. Công thức thì hiện tại tiếp diễn
-
Khẳng định: S + am/is/are + V_ing
Ex: She is watching TV now. (Cô ấy đang xem ti vi)
-
Phủ định: S + am/is/are + not + V_ing
Ex: She is not doing his homework now. (Cô ấy không đang làm bài tập)
-
Nghi vấn: Am/Is/Are + S + V_ing?
Ex: Is she studying English? (Có phải cô ấy đang học tiếng Anh? )
2.3. Cách dùng thì hiện tại tiếp diễn
- Diễn tả một hành động đang diễn ra và kéo dài tại một thời điểm ở hiện tại.
Ex: The children are playing football now. (Bọn trẻ đang chơi bóng đá bây giờ.)
- Thường tiếp theo sau mệnh lệnh, câu đề nghị.
Ex: Look! The child is crying. (Nhìn xem! Đứa trẻ đang khóc.)
- Diễn tả 1 hành động xảy ra lặp đi lặp lại, dùng phó từ ALWAYS :
Ex: She is always borrowing our books and then she doesn’t remember. (Cô ấy luôn mượn sách của chúng tôi và sau đó cô ấy không nhớ.)
- Diễn tả một hành động sắp xảy ra (ở trong tương lai gần)
Ex: Tomorrow, I am taking to the train to ohio to visit a relative (ngày mai, tôi sẽ đi tàu tới Ohio để thăm người thân)
2.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết
Trong câu có chứa các các từ sau:
-
Now: bây giờ
-
Right now
-
Listen!: Nghe nào!
-
At the moment
-
At present
-
Look!: nhìn kìa
-
Watch out!: cẩn thận!
-
Be quiet!: Im lặng
* Lưu ý: Không dùng thì này với các động từ chỉ nhận thức, tri giác như: be, understand (hiểu), know (biết), like (thích) ,want (muốn), see (nhìn), hear (nghe), glance (liếc qua), feel (cảm thấy), think (nghĩ), smell (ngửi), love (yêu), hate (ghét), realize (nhận ra), seem (dường như), remember (nhớ), forget (quên), etc.
Với các động từ này, sử dụng Thì hiện tại đơn.
2.5. Video hướng dẫn tự học thì hiện tại tiếp diễn
Tự học thì hiện tại tiếp diễn
Cách Dùng Thì Hiện Tại Tiếp Diễn Và Be Going To
Để test trình độ và cải thiện kỹ năng tiếng Anh bài bản để đáp ứng nhu cầu công việc như viết Email, thuyết trình,…Bạn có thể tham khảo khóa học tiếng Anh giao tiếp cho người đi làm tại TOPICA Native để được trao đổi trực tiếp cùng giảng viên bản xứ.
3. Thì hiện tại hoàn thành – Present Perfect
3.1. Khái niệm
Thì hiện tại hoàn thành (Present perfect tense) dùng để diễn tả một hành động, sự việc đã bắt đầu từ trong quá khứ, kéo dài đến hiện tại và có thể tiếp tục tiếp diễn trong tương lai.
3.2. Công thức thì hiện tại hoàn thành
-
Khẳng định: S + have/has + V3/ed + O
Ex: I have done my homework. (Tôi hoàn thành xong bài tập)
She has had dinner with her family (Cô ấy đã ăn tối với gia đình)
-
Phủ định: S + have/has + not + V3/ed + O
Ex: I haven’t done my homework. (Tôi chưa làm xong bài tập)
She hasn’t completed the assigned work (Cô ấy không hoàn thành công việc được giao)
-
Nghi vấn: Have/has + S + V3/ed + O?
Ex: Have you done your homework? (Em đã làm xong bài tập về nhà chưa ?)
Has she visited the children at the orphanage? (Cô ấy đã đi thăm các bạn nhỏ tại trại trẻ mồ côi chưa?)
3.3. Cách dùng thì hiện tại hoàn thành
- Diễn tả hành động đã xảy ra hoặc chưa bao giờ xảy ra ở 1 thời gian không xác định trong quá khứ.
- Diễn tả sự lặp đi lặp lại của 1 hành động trong quá khứ.
- Được dùng với since và for.
-
Since + thời gian bắt đầu (1995, I was young, this morning etc.). Khi người nói dùng since, người nghe phải tính thời gian là bao lâu.
-
For + khoảng thời gian (từ lúc đầu tới bây giờ). Khi người nói dùng for, người nói phải tính thời gian là bao lâu.
Ex: I’ve done all my homework (Tôi đã làm tất cả bài tập về nhà)
She has lived in Liverpool all her life (Cô ấy đã sống ở Liverpool cả đời)
3.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì hiện tại hoàn thành
Trong câu thường chứa các các từ sau:
-
Just, recently, lately: gần đây, vừa mới
-
Already : đã….rồi , before: đã từng
-
Not….yet: chưa
-
Never, ever
-
Since, for
-
So far = until now = up to now: cho đến bây giờ
-
So sánh nhất
Download Now: Trọn bộ Ebook ngữ pháp miễn phí
4. Thì hiện tại hoàn thành tiếp diễn – Present Perfect Continuous
4.1. Khái niệm
Thì hiện tại hoàn thành tiếp diễn (Present perfect continuous tense) là thì diễn tả sự việc bắt đầu trong quá khứ và tiếp tục ở hiện tại có thể tiếp diễn ở tương lai sự việc đã kết thúc nhưng ảnh hưởng kết quả còn lưu lại hiện tại.
4.2. Công thức thì hiện tại hoàn thành tiếp diễn
-
Khẳng định: S + have/has + been + V_ing
Ex: She has been running all day. (Cô ấy đã chạy liên tục cả ngày)
-
Phủ định: S + have/has + not + been + V_ing
Ex: She has not been running all day. (Cô ấy không chạy liên tục cả ngày)
-
Nghi vấn: Has/ Have + S + been+ V_ing?
Ex: Has she been running all day? (Có phải cô ấy đã chạy liên tục cả ngày? )
4.3. Cách dùng thì hiện tại hoàn thành tiếp diễn
- Dùng để nhấn mạnh tính liên tục của một sự việc bắt đầu từ quá khứ và tiếp diễn đến hiện tại.
Ex: She has been learning English for 6 years. (Cô ấy đã học tiếng Anh được 6 năm)
- Diễn tả hành động vừa kết thúc với mục đích nêu lên tác dụng và kết quả của hành động ấy.
Ex: I am exhausted because I have been working all day. (Tôi kiệt sức bởi vì tôi đã làm việc cả ngày)
4.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì hiện tại hoàn thành tiếp diễn
Các từ để nhận biết:
-
All day, all week, all month: cả ngày/ tuần/tháng
-
Since, for

5. Thì quá khứ đơn– Simple Past
5.1. Khái niệm
Thì quá khứ đơn (Past simple tense) dùng để diễn tả một hành động, sự việc diễn ra và kết thúc trong quá khứ.
5.2. Công thức thì quá khứ đơn
Khẳng định
S + V2/ed + O
S + was/were + O
Phủ định
S + didn’t + V_inf + O
S + was/were + not + O
Nghi vấn
Did + S + V_inf + O?
Was/were + S + O?
Ví Dụ
-
I saw Peter yesterday.
(Ngày hôm qua tôi đã nhìn thấy Peter)
-
I didn’t go to school yesterday.
(Ngày hôm qua tôi đã không đi học)
-Did you visit Mary last week? (Tuần trước bạn đến thăm Mary phải không ?)
-
I was tired yesterday. (Ngày hôm qua tôi đã rất mệt)
-
The supermarket was not full yesterday. (Ngày hôm qua, siêu thị không đông)
-
Were you absent yesterday? (Hôm qua bạn vắng phải không?
5.3. Cách dùng thì quá khứ đơn
- Diễn tả hành động đã xảy ra và chấm dứt trong quá khứ.
Ex: I went to the “Trang Quynh” movie with my boyfriend 3 days ago (tôi đi xem phim “Trạng Quỳnh” với bạn trai vào 3 ngày trước)
- Diễn tả thói quen trong quá khứ.
Ex: I used to go swimming with neighbor friends when I was young. (Lúc nhỏ tôi đã từng đi bơi với các bạn hàng xóm)
- Diễn tả chuỗi hành động xảy ra liên tiếp
Ex: I got up, brushed my teeth and then had breakfast. (Tôi thức dậy, đánh răng rồi ăn sáng)
- Dùng trong câu điều kiện loại 2
Ex: If you studied hard, you could pass the entrance examination. (Nếu bạn học hành chăm chỉ, thì bạn đã đậu kỳ thi đại học)
5.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì quá khứ đơn
Các từ thường xuất hiện:
-
Ago: cách đây…
-
In…
-
Yesterday: ngày hôm qua
-
Last night/month…: tối qua, tháng trước
6. Thì quá khứ tiếp diễn – Past Continuous
6.1. Khái niệm
Thì quá khứ tiếp diễn (Past continuous tense) dùng để diễn tả một hành động, sự việc đang diễn ra xung quanh một thời điểm trong quá khứ.
6.2. Công thức thì quá khứ tiếp diễn
-
Khẳng định: S + was/were + V_ing + O
Ex: She was watching TV at 8 o’clock last night. (Tối hôm qua lúc 8 giờ cô ấy đang xem tv)
-
Phủ định: S + was/were + not + V_ing + O
Ex: She wasn’t watching TV at 8 o’clock last night. (Tối hôm qua lúc 8 giờ cô ấy không xem tv)
-
Nghi vấn: Was/were + S + V_ing + O?
Ex: Was she watching TV at 8 o’clock last night? (Có phải tối hôm qua lúc 8 giờ cô ấy đang xem TV?)
6.3. Cách dùng thì quá khứ tiếp diễn
- Diễn tả hành động đang xảy ra tại một thời điểm xác định trong quá khứ.
Ex: I was having dinner at 7 o’clock last night. (Tôi đang ăn tối lúc 7 giờ tối hôm qua)
- Diễn tả một hành động đang xảy ra trong quá khứ thì một hành động khác xen vào (hành động xen vào thường được chia ở quá khứ đơn).
Ex: I was watching TV when she called. (Trong khi đang xem TV thì cô ấy gọi)
- Diễn tả những hành động xảy ra song song với nhau.
Ex: While Ellen was reading book, Tom was watching television. (Trong khi Ellen đang đọc sách thì Tom đang xem TV)
6.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì quá khứ tiếp diễn
Trong câu xuất hiện các từ:
-
At 5pm last Sunday
-
At this time last night
-
When/ while/ as
-
From 4pm to 9pm…
7. Thì quá khứ hoàn thành – Past Perfect
7.1. Khái niệm
Thì quá khứ hoàn thành (Past perfect tense) dùng để diễn tả một hành động xảy ra trước một hành động khác trong quá khứ. Hành động nào xảy ra trước thì dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành. Hành động xảy ra sau thì dùng thì quá khứ đơn.
7.2. Công thức thì quá khứ hoàn thành
-
Khẳng định: S + had + V3/ed + O
Ex: By 4pm yesterday, he had left his house (Đến 4 giờ chiều ngày hôm qua, anh đã rời khỏi nhà.)
-
Phủ định: S + had + not + V3/ed + O
Ex: By 4pm yesterday, he had not left his house (Đến 4 giờ chiều ngày hôm qua, anh vẫn chưa rời khỏi nhà.)
-
Nghi vấn: Had + S + V3/ed + O?
Ex: Had he left his house by 4pm yesterday? ( Anh ấy đã rời khỏi nhà của mình trước 4 giờ chiều ngày hôm qua?)
7.3. Cách dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành
- Diễn tả hành động đã hoàn thành trước một thời điểm ở trong quá khứ.
Ex: By 4pm yesterday she had left his house. (Cô ấy rời nhà trước 4 giờ hôm qua)
- Diễn đạt một hành động xảy ra trước một hành động khác ở trong quá khứ. Hành động xảy ra trước dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành – hành động xảy ra sau dùng thì quá khứ đơn.
Ex: Before she went to bed, she had done her homework. (Trước khi cô ấy đi ngủ, cô ấy đã làm xong bài tập)
- Dùng trong câu điều kiện loại 3
Ex: If you had studied hard, you could have passed the entrance examination. (Nếu bạn học hành chăm chỉ, bạn đã đậu kỳ thi đại học)
7.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì quá khứ hoàn thành
Trong câu chứa các từ:
-
By the time, prior to that time
-
As soon as, when
-
Before, after
-
Until then
Để test trình độ và cải thiện kỹ năng tiếng Anh bài bản để đáp ứng nhu cầu công việc như viết Email, thuyết trình,…Bạn có thể tham khảo khóa học tiếng Anh giao tiếp cho người đi làm tại TOPICA Native để được trao đổi trực tiếp cùng giảng viên bản xứ.
8. Thì quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn – Past Perfect Continuous
8.1. Khái niệm
Thì quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn (Past perfect continuous tense) dùng để diễn tả một hành động, sự việc đã đang xảy ra trong quá khứ và kết thúc trước một hành động cũng xảy ra trong quá khứ.
8.2. Công thức thì quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn
-
Khẳng định: S + had been + V_ing + O
Ex: He had been watching films. (Anh ấy đã đang xem phim)
-
Phủ định: S + had + not + been + V_ing + O
Ex: He hadn’t been watching film.
-
Nghi vấn: Had + S + been + V_ing + O?
Ex: Had he been watching films? (Có phải anh ấy đã đang xem phim?)
8.3. Cách dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn – Past perfect continuous
Thì quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn (Past perfect continuous tense) dùng để nhấn mạnh khoảng thời gian của 1 hành động đã xảy ra trong quá khứ và kết thúc trước 1 hành động khác xảy ra và cũng kết thúc trong quá khứ.
Ex: Sam gained weight because he had been overeating
I had been thinking about that before you mentioned it
8.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn
Trong câu thường chứa:
-
Before, after
-
Until then
-
Since, for
Download Now: Trọn bộ Ebook ngữ pháp miễn phí

9. Thì tương lai đơn – Simple Future
9.1. Khái niệm
Thì tương lai đơn trong tiếng Anh (Simple future tense) được dùng khi không có kế hoạch hay quyết định làm gì nào trước khi chúng ta nói. Chúng ta ra quyết định tự phát tại thời điểm nói.
9.2. Công thức thì tương lai đơn
- Khẳng định: S + will/shall/ + V_inf + O
- Phủ định: S + will/shall + not + V_inf + O
- Nghi vấn: Will/shall + S + V_inf + O?
9.3. Cách dùng thì tương lai đơn
-
Diễn tả một dự đoán nhưng không có căn cứ.
Ex: I think It will rain.
-
Diễn tả một quyết định đột xuất ngay lúc nói.
Ex: I will bring coffee to you.
-
Diễn tả lời ngỏ ý, một lời hứa, đe dọa, đề nghị.
Ex: I will never speak to you again.
-
Dùng trong mệnh đề chính của câu điều kiện loại I.
Ex: If you don’t hurry, you will be late.
9.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì tương lai đơn
Trong câu thường có:
-
Tomorrow: ngày mai
-
in + thời gian
-
Next week/ month/ year: tuần tới/tháng/năm
-
10 years from now
10. Thì tương lai tiếp diễn – Future Continuous
10.1. Khái niệm
Thì tương lai tiếp diễn (Future continuous tense) dùng để diễn tả một hành động, sự việc sẽ đang diễn ra tại một thời điểm cụ thể trong tương lai.
10.2 Công thức thì tương lai tiếp diễn
-
Khẳng định: S + will/shall + be + V-ing
-
Phủ định: S + will/shall + not + be + V-ing
-
Nghi vấn: Will/shall + S + be + V-ing?
10.3. Cách dùng thì tương lai tiếp diễn
Diễn tả hành động hay sự việc đang diễn ra ở một thời điểm xác định trong tương lai hoặc hành động sẽ diễn ra và kéo dài liên tục suốt một khoảng thời gian ở tương lai.
Đôi khi nó cũng diễn tả hành động sẽ xảy ta như một phần trong kế hoạch hoặc một phần trong thời gian biểu.
Ex: She will be climbing on the mountain at this time next Saturday
The party will be starting at nine o’clock
10.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì tương lai tiếp diễn
Trong câu thường chứa các cụm từ:
-
Next year, next week
-
Next time, in the future
-
And soon
Để test trình độ và cải thiện kỹ năng nghe tiếng Anh bài bản để đáp ứng nhu cầu công việc như viết Email, thuyết trình,…Bạn có thể tham khảo khóa học tiếng Anh giao tiếp cho người đi làm tại TOPICA Native để được trao đổi trực tiếp cùng giảng viên bản xứ.
11. Thì tương lai hoàn thành – Future Perfect
11.1. Khái niệm
Thì tương lai hoàn thành (Future perfect tense) dùng để diễn tả một hành động hay sự việc hoàn thành trước một thời điểm trong tương lai.
11.2. Công thức thì tương lai hoàn thành
-
Khẳng định: S + shall/will + have + V3/ed
Ex: I will have finished my homework by 9 o’clock. (Tôi sẽ hoàn thành bài tập về nhà trước 9 giờ)
-
Phủ định: S + shall/will + NOT + have + V3/ed + O
Ex: They will have not built their house by the end of this month. (Trước cuối tháng này, họ vẫn sẽ chưa xây xong ngôi nhà)
-
Nghi vấn: Shall/Will+ S + have + V3/ed?
Ex: Will you have finished your homework by 9 o’clock? (Bạn sẽ làm xong bài trước 9 giờ chứ?)
→ Yes, I will / No, I won’t.
11.3. Cách dùng thì tương lai hoàn thành
Diễn tả 1 hành động trong tương lai sẽ kết thúc trước 1 hành động khác trong tương lai.
Ex: She will have finished her homework before 11 o’clock this evening.
When you come back, I will have typed this email.
11.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì tương lai hoàn thành
Trong câu chứa các từ:
-
By, before + thời gian tương lai
-
By the time …
-
By the end of + thời gian trong tương lai
12. Thì tương lai hoàn thành tiếp diễn – Future Perfect Continuous
12.1. Khái niệm
Thì tương lai hoàn thành tiếp diễn (Future perfect continuous tense) dùng để diễn tả một hành động, sự việc sẽ xảy ra và xảy ra liên tục trước một thời điểm nào đó trong tương lai.
12.2. Công thức thì tương lai hoàn thành tiếp diễn

-
Khẳng định: S + will/shall + have been + V_ing
Ex: We will have been living in this house for 10 years by next month.
-
Phủ định: S + will not + have been + V_ing
Ex: We will not have been living in this house for 10 years by next month.
-
Nghi vấn: Will/shall + S + have been + V-ing?
Ex: Will they have been building this house by the end of this year?
12.3. Cách dùng thì tương lai hoàn thành tiếp diễn
Diễn nhấn mạnh khoảng thời gian của 1 hành động sẽ đang xảy ra trong tương lai và sẽ kết thúc trước 1 hành động khác trong tương lai.
Ex: I will have been studying English for 10 year by the end of next month
12.4. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì tương lai hoàn thành tiếp diễn
Trong câu xuất hiện các từ:
-
For + khoảng thời gian + by/ before + mốc thời gian trong tương lai
-
For 2 years by the end of this
-
By the time
-
Month
-
By then
13. Mẹo ghi nhớ 12 thì trong tiếng Anh
Tuy đã có dấu hiệu nhận biết và công thức tổng hợp thì trong tiếng Anh nhưng để ghi nhớ tất cả các thì trong tiếng Anh thì không phải dễ dàng. Để ghi nhớ các thì tiếng anh cơ bản, bạn có thể thực hiện theo các mẹo Topica Native mách nhỏ dưới đây.
13.1. Bảng các thì trong tiếng Anh – Tóm tắt
Để tổng kết lại kiến thức, TOPICA Native xin gửi đến bạn đọc Bảng tổng hợp 12 thì trong tiếng Anh.
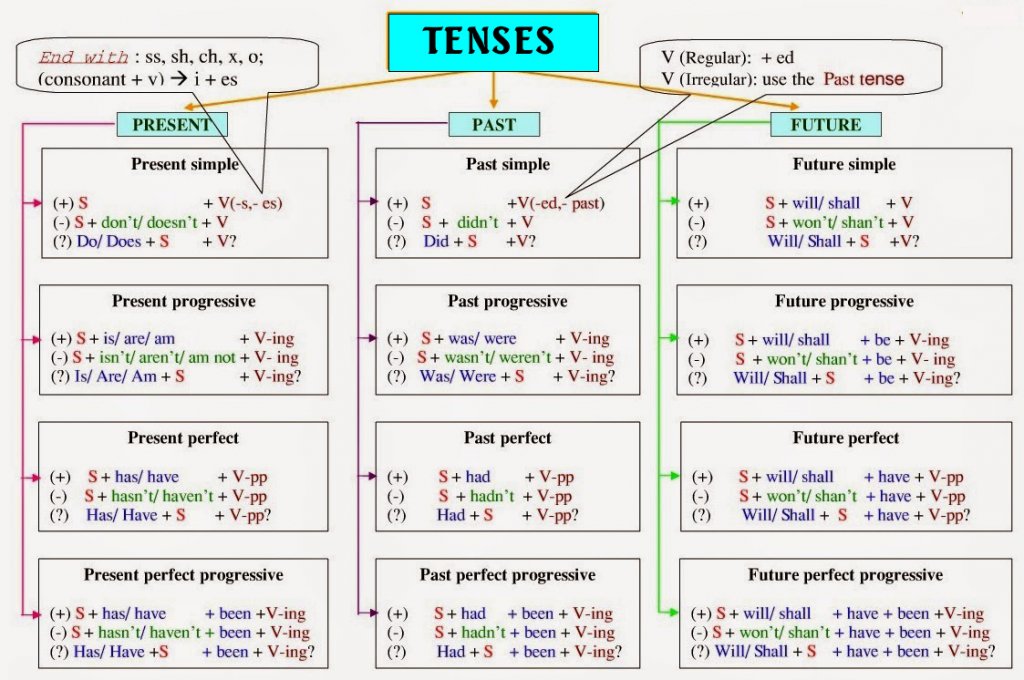
13.2. Nhớ động từ dùng trong các thì trong tiếng Anh
Mỗi thì sẽ có các cấu trúc ngữ pháp và những cách sử dụng khác nhau, để ghi nhớ được điều này, các bạn phải nắm rõ các quy tắc xây dựng của mỗi thì, có như vậy việc học 12 thì tiếng Anh cơ bản sẽ không bị nhầm lẫn nữa.
Đối với các thì hiện tại, động từ và trợ động từ được chia ở cột thứ nhất trong bảng động từ bất quy tắc.
Đối với các thì quá khứ, động từ cũng như trợ động từ sẽ được chia theo cột thứ 2 trong bảng động từ bất quy tắc.
Đối với các thì tương lai, bắt buộc phải có từ “will” trong câu và động từ có hai dạng là “to be” và “verb-ing”.
13.3.
Nhớ công thức các thì trong tiếng Anh dựa trên tên gọi
Các công thức tiếng Anh đôi khi khá khó nhớ vì có quá nhiều lý thuyết các thì trong tiếng Anh. Vậy làm cách nào để ghi nhớ các thì tiếng anh và dấu hiệu nhận biết. Hãy tham khảo mẹo sau nhé!
- Bước 1: Viết tên thì bạn cần nhớ cấu trúc
Ví dụ: Quá khứ – Hoàn thành – Tiếp diễn
- Bước 2: Nhìn tên thì vừa viết theo thứ tự từ phải qua trái – Tiếp diễn: cần có to be và V-ing. Hãy viết V-ing xuống trước tiên sau đó mới xét đến to be.
- Bước 3:
Nhìn sang bên trái có “Hoàn thành”. Ở thể hoàn thành cần có have/has/had và động từ chia ở dạng V3, do đó to be cũng ở dạng V3 (been).
Bạn có cấu trúc:… been + V-ing.
- Bước 4:
Để xác định have/has/had, bạn nhìn tiếp về phía bên trái có “Quá khứ”. Động từ quá khứ chia ở dạng V2 (quá khứ), có had thỏa mãn.
Từ đó, bạn có cấu trúc: Had + been + V-ing
Sau đó, bổ sung thêm chủ ngữ và tân ngữ, bạn sẽ nhận được cấu trúc hoàn chỉnh của thì quá khứ hoàn thành tiếp diễn.
S + had + been + V-ing + O
13.4. Thực hành và luyện tập
Với tiếng Anh nói chung và các thì nói riêng, việc quan trọng nhất vẫn là luyện tập, thực hành.
Cho dù bạn học rất kỹ lý thuyết nhưng nếu không chịu khó thực hành thì cũng rất nhanh quên.
Hãy chăm chỉ làm bài tập sau mỗi bài học về các thì, chắc chắn, kiến thức về 12 thì trong tiếng Anh sẽ không còn là vấn đề với bạn.
13.5. Vẽ khoảng thời gian sử dụng thì
Khi tổng hợp các thì trong tiếng Anh, để xác định khoảng và mốc thời gian cụ thể hơn, bạn hãy vẽ một đoạn mốc thời gian tương tự thế này. Học kỹ những kiến thức trên và thêm vào phần thì còn thiếu theo dòng thời gian đây nhé:
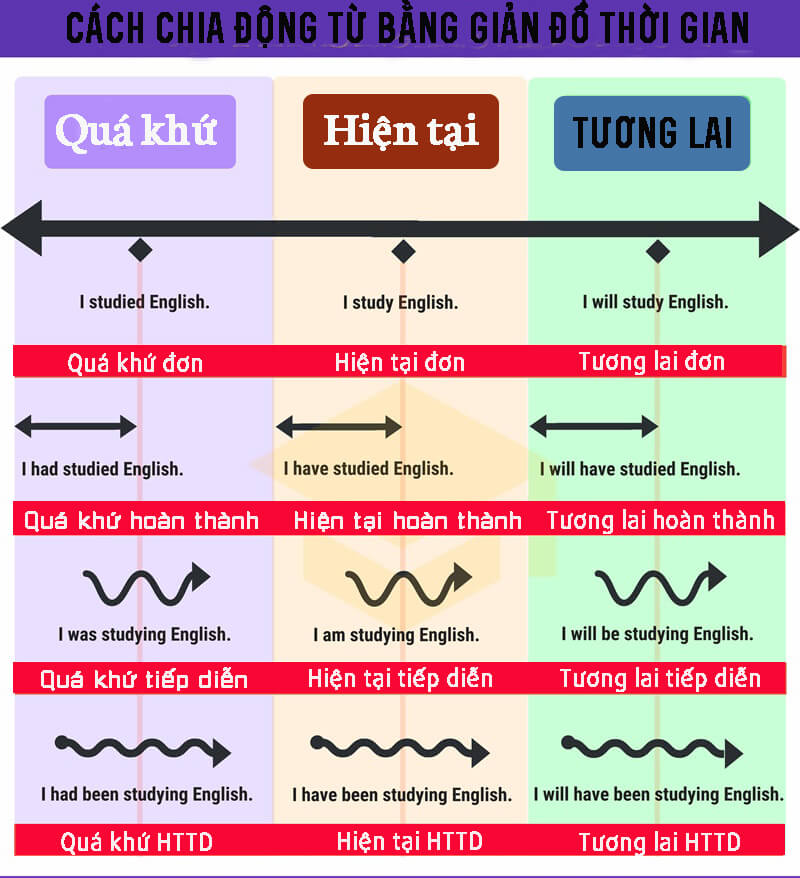
13.6. Sử dụng sơ đồ tư duy học tất cả thì trong tiếng Anh
Sơ đồ tư duy là phương pháp học tập được chứng minh rất hiệu quả để ghi nhớ. Nếu bạn có thể vận dụng phương pháp này để ghi nhớ các loại thì trong tiếng Anh thì rất tuyệt vời đúng không?
13.7. Tìm một trung tâm tiếng Anh để học thật hiệu quả
Nếu việc tự học khó khăn, hãy tìm một trung tâm thật uy tín để tiếp thu kiến thức. Giáo viên sẽ giúp bạn hiểu thật sâu vấn đề, bên cạnh đó có bạn học cùng sẽ giúp việc học không còn nhàm chán nữa.
Hiện, trong các trung tâm tiếng Anh, Topica Native là cơ sở uy tín, được nhiều người học tin tưởng và đánh giá rất cao. Với đội ngũ giáo viên giàu năng lực, giáo trình bài bản, Topica Native tự hào đã giúp hàng chục ngàn người tiếp cận và làm chủ tiếng Anh, từ đó tự tin hơn trong học tập, công việc và cuộc sống. Chắc chắn, đến với Topica Native, bạn sẽ phải bất ngờ với những gì chúng tôi mang lại. Tiếng Anh sẽ không còn là một môn học, nó sẽ trở thành niềm đam mê, yêu thích tìm tòi, khám phá và học tập với bạn.
14. Bài tập về 12 thì trong tiếng Anh có đáp án
Để thành thạo các thì cơ bản trong tiếng Anh và cấu trúc các thì trong tiếng Anh, hãy cùng luyện tập ngay bài tập cách sử dụng 12 thì dưới đây nhé!
Bài tập 1. Chia các động từ sau đây ở thì phù hợp
- I (do) … my homework at the moment.
- They (go) … out now.
- This room (smell) … terrible.
- He (go) … on a business trip tomorrow
- He (always sleep) … in class.
Đáp án
- am doing
- are going
- smells
- is going
- is always sleeping
Bài tập 2. Chia các động từ sau sao cho đúng.
- Trang (write) … that essay yesterday.
- My dad (take) … me to the zoo last weekend.
- Linh (be) … a good-looking girl at our college but now she isn’t.
- I (get) … up at six this morning and walked to school.
- We (watch) … Aquaman on the day it was released.
Đáp án
- wrote
- took
- was
- got
- watched
Bài 3. Tìm lỗi sai và sửa
- They took my pencils, ripped my books and then laugh at me.
- Susie goes out 4 hours ago and hasn’t come back, I’m worried.
- Honey, have you seen my white shirt anywhere? Our daughter need it for a school project.
- How did I met your mother? Well, we were both running late for work that day and then we was bumped into each other.
- Stop! You being hurting yourself!
- By the time I came, she is no where to be seen.
- This song is so good that I have been listening to it since 4 hours.
Đáp án
- laugh -> laughed
- goes -> went
- need -> needs
- was bumped -> bumped
- being hurting -> are hurting
- is -> was
- since -> for
Bài 4. Chia thì với các từ cho sẵn trong ngoặc
- My grandfather never (fly) … in an airplane, and he has no intention of ever doing so.
- In all the world, there (be) … only 14 mountains that (reach) … above 8,000 meters.
- When I (come) …., she (leave) …. for Nha Trang 10 minutes ago.
- Tomorrow I’m going to leave for home. When I (arrive) … at the airport, Mary (wait) … for me.
- I (visit) … my uncle’s home regularly when I (be) … a child.
- David (wash) … his hands. He just (repair) … the TV set.
- The car (be) … ready for him the time he (come) … tomorrow.
- When we (arrive) … in London tonight, it probably (rain) ….
- London (change) … a lot since we first (come) … to live here.
- On arriving at home I (find) … that she just (leave) … a few minutes before.
Đáp án
- has never flown
- are – read
- came – had left
- arrive – will be waiting
- visited – was
- is washing – has just repaired
- will have been – comes
- arrive – will probably be raining
- has changed – came
- found – had just left
Vậy là bài học về tổng hợp tất cả các thì trong tiếng Anh đã kết thúc. Nếu bạn thấy bài viết 12 thì trong tiếng Anh: công thức, cách dùng và dấu hiệu nhận biết bổ ích, hãy like share để ủng hộ đội ngũ phát triển website của TOPICA Native nhé! Topica Native luôn sẵn sàng để đồng hành cùng bạn.
[NEW] Rules for Tenses in English Grammar & How To Use Them Correctly | had + v3 – NATAVIGUIDES
Rules for Tenses in English Grammar with Examples
Rules of Tenses help one understand how to correctly use the different tenses in a sentence, without making a grammatical mistake and also by easily indicating when an event or action has occurred.
Aspirants who are willing to apply for the various Government exams 2021 must go through these tenses rules carefully, as the English language is a part of the syllabus for most of these exams.
Tenses can be divided into three parts:
Each of the three above mentioned tenses can further be divided into subparts. These subparts include:
-
Simple
-
Continuous
-
Perfect
-
Perfect Continuous
In this article, we shall discuss in detail the tenses rules for the above-mentioned types of verb tenses, followed by examples to explain them clearly.
Rules for Tenses PDF:-Download PDF Here
Present Tense
Present Tense can be defined as an expression for an activity that is currently in action or is habitually performed. It is used for a state that generally exists or is currently ongoing.
-
Simple Present
Simple Present Tense
Singular
Plural
Rule: Subject + V1 + s/es + Object
Rule: Subject + V1 + Object
Example: The girl sings a song
Here the subject is Girl (singular) and “s” has been added to the verb (sing), followed by the object (song)
Example: The girls sing a song
Here the subject is Girls (plural) and no changes have been made with V1 (first form of verb) and the object
-
Present Continuous
Present Continuous Tense
Rule: Subject + is/am/are + V1 + ing + object
Example: She is eating food
Here the subject is She, followed by “is”
The first form of verb (V1) here is “eat” and “ing” has been added to it, followed by the object “food”
-
Present Perfect
Present Perfect Tense
Singular
Plural
Rule: Subject + has + V3 + Object
Rule: Subject + have + V3 + Object
Example: He has cleaned the utensils
Here, “He” is the subject + has
“Cleaned” is the third form of verb and utensils is the object
Example: They have cleaned the utensils
Here, “They” is the subject + have
“Cleaned” is the third form of verb and utensils is the object
-
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Singular
Plural
Rule: Subject + has been + V1 + ing + Object
Rule: Subject + have been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: She has been practising since morning
Here “She” is the subject + has been, followed by “ing” added to the the first form of verb “practise” and then the object
Example: They have been practising since morning
Here “They” is the subject + have been, followed by “ing” added to the the first form of verb “practise” and then the object
Given below are a few examples that may help you differentiate between the four sub parts of present tense easily:
- Raj speaks German (Simple Present for Singular)
- They speak German (Simple Present for Plural)
- She is speaking German (Present Continuous)
- He has learnt German (Present Perfect for Singular)
- They have learnt German (Present Perfect for Plural)
- She has been learning German (Present Perfect Continuous for Singular)
- They have been learning German (Present Perfect Continuous for Plural)
Also, go through the concepts and sample questions of important English topics such as :
More such articles on the rule, lists and concepts can be found on the General English For Competitive exams.
Candidates preparing for the various government exams can refer to the detailed exam syllabus from the links given below:
The video given below explains the Tenses Rules and Concepts in the English Language. Candidates can watch the full video to gain conceptual clarity and application of tenses rules, while attempting questions in the competitive exams.

For a better understanding of the formation of words in English and to know the English words that are asked in most of the competitive exams, visit the links provided below:
Past Tense
Any event or action that took place in the past can be referred to as the past tense. Below we have discussed in detail the four sub parts of past tense in English grammar.
-
Simple Past
Simple Past Tense
Rule: Subject + V2 + Object
For example: He ran away
Here, the subject is “He” and “ran” is the second form of verb (V2) of “run” followed by the object
-
Past Continuous
Past Continuous Tense
Singular
Plural
Rule: Subject + was + V1 + ing + Object
Rule: Subject + were + V1 + ing + Object
For example: She was going shopping
Here, the subject is “She” + was
It is followed by the first form of verb (V1) “go” + “ing” and then the object “shopping”
For example: They were going shopping
Here, the subject is “They” + were
Followed by the first form of verb (V1) “go” + “ing” and then the object “shopping”
-
Past Perfect
Past Perfect Tense
Rule: Subject + had + V3 + Object
For example: Sumit had left the job
Here the subject is “Sumit” + had
Then “left”, which is the third form of verb (V3) “leave” is given followed by the object
-
Past Perfect Continuous
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Rule: Subject + had been + V1 + ing + Object
For example: They had been preparing for their performance for two months
Here the subject is “They” + had been
It is followed by “preparing”, which is the first form of verb (V1) of “prepare” and then the object
To help you understand past tense and its form even better, given below are a few examples to simply the concept:
-
I played football yesterday (Simple Past)
-
I was playing football yesterday (Past Continuous for Singular)
-
They were playing football yesterday (Past Continuous for Plural)
-
They had played football yesterday (Past Perfect)
-
They had been playing football the entire yesterday (Past Perfect Continuous)
Given below are a few articles to clarify the confusion between various common but confusing words in the English Language. It is vital aspirants gain clarity on the basic concepts to ace this section, as they are very well aware that English is an important part of the syllabus of various competitive exams.
More such concept-wise, subject-wise differences can be found on the 100 Difference between Articles page linked here.

Future Tense
The actions that are to take place in the future fall in the category of the future tense. We have discussed the subparts of the future tense in detail further below in the article, followed by the examples for the same.
-
Simple Future
Simple Future Tense
Rule: Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object
For Example: I will visit my Uncle tomorrow
Here, the subject is “I” + will
It is followed by the first form of verb (V1) “visit” and then the object
-
Future Continuous
Future Continuous Tense
Rule: Subject + will be/shall be + V1 + ing + Object
For Example: I shall be going to the market tomorrow
In this example, the subject is “I” + shall be
Following it is the first form of verb (V1) “go”+ing and then the object
-
Future Perfect
Future Perfect Tense
Rule: Subject + will have/shall have + V3 + Object
For Example: I shall have prepared the notes by tomorrow morning
In this example, the subject is “I” + shall have
It is followed by “prepared”, which is the third form of Verb (V3) “prepare” and then the object
-
Future Perfect Continuous
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Rule: Subject + will have been + V1 + ing + Object
For Example: She will have been working here since 2015
Here, the subject is “She” + will have been
It is followed by the first form of verb “work”+ing and then the object
Given below are a few examples that may help you clarify the future tense concept clearly:
-
She will go to school tomorrow (Simple Future)
-
She will be going to school tomorrow (Future Continuous)
-
She will have gone to school tomorrow (Future Perfect)
-
She will have been going to school tomorrow (Future Perfect Continuous)
Rules for Tenses PDF:-Download PDF Here
To prepare well for the English section, it is important to practise and revise Tenses regularly for conceptual clarity. Hence, go through the exercise on Tenses Questions and Answers in the given link.
Candidates can also check below the variety and scope of questions asked in the competitive exams on the other relevant topics of English language:
Check the Verbal Ability page to get more Questions and Answers articles based on different general English topics.
Candidates preparing for the upcoming government exams must carefully go through the concept of tenses rules as candidates tend to score the least in the English Language section.
For further questions or information regarding the competitive exams, study material or best books for preparation, candidates can turn to BYJU’S.
Given below are the links that may help you prepare for the upcoming Government exams 2021:
Video – Tenses Rules in English Part 2

The video on Tenses rules has more parts, candidates will find the other parts in the Tenses Questions And Answers page linked here.
Past Perfect Tense Konu Anlatımı 54#
Past Perfect Tense Konu Anlatımı videomda İngilizcedeki Mişli Geçmiş Zaman konusunu anlatıyorum.
Reklamsız, tahtaya zoomlu, sınırlı internet hatlarında bile açılabilen ve ömür boyu erişim veren Udemy Kursumu Deneyin: https://bit.ly/3Duf9BK
http://www.turengkitap.com
https://www.instagram.com/ozerkirazingilizce
https://www.facebook.com/ingilizcekonuanlatimi
Past perfect tense kullanımında bu zaman Türkçeye “Mişli Geçmiş Zaman” olarak çevrilse de, İngilizcedeki kullanım yeri bununla sınırlı değil. Past perfect tense ile kurulan pek çok cümle, Türkçeye mıştı/mişti şeklinde çevriliyor. Öte yandan, bu zamanı geçmişte olan iki olayın zaman sıralamasını anlatmakta da kullandığımız için, bazen de tıpkı dili geçmiş veya sürekli geçmiş zaman cümleleri gibi çevriliyor.
İngilizcede mişli geçmiş zaman ile cümle kurarken yardımcı fiil olarak had ve fiilin üçüncü halini kullanıyoruz. Past perfect tense’in kullanım şekli böyle. Şimdi ise bu zamanın nerelerde kullanıldığına bakalım.
Bu zamanı, mıştı/mişti şeklinde biten bağımsız cümleler kurarken kullanabiliyoruz. Tablolarda kurduğumuz cümleler buna birer örnekti. Yani past perfect tense’in bu kullanım şekli tıpkı Türkçedeki gibi; bir anımızı anlatırken ya da mıştı/mişti şeklinde cümle kurarken bu zamanı tercih edebiliriz.
Son cümlede net bir zaman verdiğimiz halde neden simple past kullanmadık diye sorabilirsiniz ancak öyle bir şart yok. Bunu present perfect tense ile karıştırmayın. Yani biz cümleye mıştı/mişti anlamını vermek istiyorsak, net bir tarih belirtsek dahi past perfect tense kullanabiliyoruz.
Geçmişte olmuş iki olayın zaman sıralamasını yaparken de bu zamanı sıkça kullanıyoruz. Mişli geçmiş zamanda bağlaç olarak önce veya sonra ifadelerinden birini kullanırsak, iki olay arasındaki zaman ilişkisi zaten net bir şekilde anlaşılır ve bu yüzden mişli geçmiş zaman kullanmamıza da gerek kalmaz. Yalnız tabi bu zamanın mıştı/mişti anlamını vermediği durumlar da var.
“İki şey geçmişte olduysa, biri de diğerinden önce olduysa önce olan için mutlaka past perfect mi kullanmak zorundayız?”
Eğer meydana gelen bu iki olay arasında kayda değer bir zaman yoksa iki tarafta da simple past kullanabiliriz.
“Before ya da after varsa iki tarafta da simple past kullanabiliriz dediniz; hep böyle midir bu?”
Hep böyle değildir. Geçmişteki bir zamanı değil de bir tecrübeyi, deneyimi ön plana çıkartmak istiyorsak mutlaka past perfect kullanmamız gerekiyor. Mesela “İtalya’ya taşınmadan önce hiç pizza yememiştim” gibi bir cümlede deneyimden bahsedildiği için, önce bağlacı geçse bile simple past tense, past perfect’in yerini tutmuyor.
Soru 3: “Mutlaka simple past past perfect şeklinde mi yapmak zorundayız? Present perfect past perfect ikilisi olmaz mı?”
Cevap: Olmaz çünkü mişli geçmiş zamanda gerçekleşen bir olayla yakın geçmiş zamanda gerçekleşen bir olay arasında ilişki kuramayız. Nihayetinde yakın geçmiş zaman şu anı da ilgilendiriyor.
Alıntı Yapılan Filmler (Alıntı Sırasıyla)
The Curious Case of Benjamin Button
Forrest Gump
Erin Brockovich
The Silence of the Lambs
The Notebook
Warlord
Goodfellas
Million Dollar Baby
Matrix
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่

Bài 30: Cấu trúc \”SHOULD HAVE V3-ed\” || Ngữ pháp cho người mất gốc
Cảm ơn bạn đã dành thời gian ghé thăm kênh mình 💜
Nếu bạn cần tư vấn về việc học tiếng Anh thì có thể liên hệ mình theo địa chỉ bên dưới nhé.
✨ Fanpage Cô Giáo Quỳnh: https://www.facebook.com/cogiaoquynh18
✨ Livestream dạy học 20h T2, T4, T6: https://vt.tiktok.com/ZSe1Ms52a/
shorts cogiaoquynh hoctienganh

Learn English Grammar: How to use the 3rd conditional
Do you wish your life were different? In today’s English grammar lesson, you’ll learn how to talk about the present if the past had been different. We often use the 3rd conditional to talk about our regrets and the life lessons we’ve learned. To use the third conditional, we use the past perfect tense with the past participle form of the verb. I’ll teach you the sentence structure so you can recognize and build these sentences yourself. I’ll also give you lots of example sentences, so you’ll be confident using the third conditional when you’re speaking or writing in English.
Make sure you understood the lesson. Take the quiz: http://www.engvid.com/learnenglishgrammarhowtousethe3rdconditional/
Watch my videos on the other conditionals in English:
FIRST CONDITIONAL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HILBmukYNZM
SECOND CONDITIONAL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aCM633yN5V4
ZERO CONDITIONAL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c7rxcDuZgN4
TRANSCRIPT
Today I am sad. I am full of regret. Uhh. Yes, that’s right, today we’re doing the third conditional. This is the conditional tense of regret, wishing that the past was different. I’m sure, girls, you’re not guilty of that. Right. We’re going to be looking at the third conditional and obviously how to use it. Hopefully it will add interest to the way in which you speak, and in which you write.
Firstly, I’d like you to think of an event that you feel bad about. Okay? So thinking back in your mind to something that you did that wasn’t very good. Okay? So it was something in the past that has started and it’s finished. Okay? Like: Yesterday I kissed a parrot and I was very sick. Okay? So it’s something… Something I regret and I feel really bad about it. And things would have been different if I hadn’t kissed this parrot. How would things have been different? Well, I wouldn’t have been sick. Okay?
So, this is how we use the third conditional: \”If I hadn’t\”, okay? \”Had not\”, this is the past perfect here, \”had\”. \”If I had not kissed a parrot I wouldn’t\”would not\”have been ill.\” Okay? The thing is we can’t change the past, but we’re looking back at the past here and going: \”Oh, if I hadn’t done that, things would have been a little bit different.\” That is the purpose of this tense. Okay?
So, what is the magic formula for this tense? Well, we use \”if\” plus past perfect. Okay? So that’s the… Basically it’s like the \”had\” plus \”ed\” is probably an easy way of thinking it. \”If I had smiled more, I might have got laid.\” I don’t know. \”If I had worked harder\”, no, that’s crap. \”If I had\”, yeah, no, no, it’s good, it’s good because we’ got the \”ed\” so past perfect. Yeah \”If I…\” Sorry. \”If\” plus past perfect plus \”could\”, or \”would\”, or \”should have\”, and then past participle. So if it’s a regular verb, obviously looking at your \”ed\”; if it’s not, then check your irregular verb forms. Okay? \”If\” past perfect, \”could\” or \”would\” plus \”have\” plus past perfect. Okay, so: \”If\”, past perfect, \”had kissed\”, \”could\” or \”would\”, well, I’ve got my \”would\” here, and then \”have\”, and then past participle, obviously, the verb \”be\” is irregular. Now, we often use the negative forms, here, so you’re kind of adding on your \”not\” after your, you know, into your past perfect structure. Okay? Ask me if you’re a bit confused. I can help. I have magic powers to help you.
So another way of putting this, another way of… You know, you’ve got your two phrases. Yeah? If we look here we have: \”If\” plus past perfect, plus \”could\” or \”would\”, plus \”have\”, plus past participle. We can change the order of this to: \”could\” or \”would\” plus \”have\”, plus past participle, plus \”if\”, plus past perfect. So, I could change this order around to: \”I wouldn’t have been ill if I hadn’t kissed the parrot.\” Okay? Obviously we’re putting in the negative there. Okay? So just a different… Slightly different way of playing it.
I’m going to give you lots of opportunity to practice this by doing the quiz later, but just a couple of examples using this first form. Don’t know if any of you have been listening to English nursery rhymes, they’re little songs we listen to when we’re kids here. But I’m referring to these here. \”If Mary had a little lamb, we would have had a farm.\” Okay? So, \”if\”, and then we have our past perfect, \”had\”, and then \”we would have had…\” Okay? If this had happened, we would have… But she didn’t have a little lamb, so there was no farm. Okay? Remember we can’t change the past. We’re just looking back and asking for it to be a little bit different.
\”If Humpty Dumpty hadn’t had a fall, I wouldn’t have spent the day picking him up.\” Okay? So this one I’m using the negative here. \”If Humpty Dumpty had\”… \”Had, had\”so, past perfect\”a fall, I wouldn’t have spent\”. Okay? There’s my past participle of \”to spend the day picking him up\”.

IF + HAD = WOULD HAVE V3 (3rd/Past Conditional) – Learn English with Papa Teach Me
Practice the grammar for Past conditionals in this lesson!
You’re welcome to share this video on your website or use it in classes and show it to your students! Happy learning!
Make sure you watch the first lesson of third conditional before watching this!!
First lesson of 3rd Conditional:
Will Tom save his job, relationship with his girlfriend and avoid losing his best friend?!?! Find out in this lesson!
3rd conditional test:
Art/Story/Visuals: Aly and Tom (Us!)
Music credits:
YouTube audio library:
\”Tuscon\”
\”Powersurge\”
\”You make me feel good\”
Incompetech.com
\”No Good Layabout\”

bqThanh và Ốc Triệu Hồi SANESS Hài Hước Đấu Với XANS VIRUS V2 Mới Nhất Xem Ai Mạnh Hơn ở Minecraft
💎 Shop Acc Free Fire Nhận 9999 Kim Cương: https://shopbqthanh.vn
❤️ ĐĂNG KÝ \u0026 RUNG CHUÔNG!
😎 CÓ THỂ BẠN CHƯA XEM:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCshA0rciz2K3O0EezIpu03A/videos
🎬 KÊNH HAY!
Thanhbq https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCdC8JBKvGhmoD3h2wMQM1tQ
ỐC TV https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCqAQ8VGrIPr1ZQNVXEECbmw
ThanhMC https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC8JJuyio11y0Z8CN4fDxjZg
🙈 Nếu bạn thích video này, hãy ĐĂNG KÝ kênh để xem thêm video mới!
✔️ Video này thân thiện với trẻ em / gia đình!
🙏THEO DÕI MÌNH!
Tiktok: https://www.tiktok.com/@bqthanh96
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/bqthanh96
Page Fb: https://www.facebook.com/bqThanhbq

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆLEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ had + v3