verb 2: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
Are you looking for a comprehensive list of verbs in the English language? Here you will find 1000+ common verbs list with example sentences and ESL printable worksheets (in alphabetical order, by their grammatical functions, and by activity). One of the most important parts of a sentence when using the English language-or any language for that matter, is the verb. These words are used to tell the listener or reader what action is being performed by the subject of the sentence. There are a lot of verbs to learn and they fall into further subcategories.
Table of Contents
Verbs
What Are Verbs in English?
Verbs, in theory, are pretty straightforward. But, not everybody would be able to provide a definition, even if they know how to use them within a sentence. There’s also a tendency amongst people to stick to certain verbs that they know, and pushing themselves to use new ones becomes a bit of a challenge. In the interest of giving you some variety, we’ll take a look at what exactly a verb is, we’ll use some examples for you to see how they function as part of a sentence, and we’ll provide you with some lists of verbs by different categories so you can find some that might help you mix things up a little in your writing.
A verb is a word that shows action, occurrence, or a state of being. When written with the particle ‘to’ the verb is in its infinitive form. This is where you would write it like this:
- To bake
- To clean
- To cook
- To sing
There are many more verbs of course, but the above list shows you what a verb looks like in its infinitive form, making it slightly easier for you to identify whether or not a word in a sentence is a verb. Remember, a verb should show that something is happening, because an action is taking place in some way or another. Many people when first learning about verbs simply refer to them as ‘doing words’, because they always show that something has been done, is being done, or will be done in the future (depending on the tense that you are writing in).
Verb Examples
Let’s look at the examples of the verbs above in a sentence so you can see how they might work. We’ll show them in different tenses too so you can see how they would need to be changed slightly to make sense.
Verb Examples in the Simple Tenses
- I bake everyday – here the sentence works as a simple present tense sentence. Let’s change it to past.
- I baked everyday – changing it to past simple tense means we say ‘baked’ not ‘bake’. This shows that ‘I’ used to bake everyday, but don’t any longer.
- I will bake everyday – again, changing to the future means you need the word ‘will’ between the subject ‘I’ and the verb ‘bake’. There are other tenses that aren’t simple, but we couldn’t possibly explain each one thoroughly here, but take a look at some more examples below and notice the changes that have been made for yourself. We’ll provide a brief explanation to help you slightly.
Examples of Verbs in the Continuous Tenses
Throughout each of these next three sections, the past tense version will be written on top, the middle will be present tense, and the future tense will be at the bottom. So that in this case, the top one is written in the past continuous tense, the middle in the present continuous tense, and the third in the future continuous tense. It will follow the same pattern in the following two sections, but continuous will be replaced with ‘perfect’ and ‘perfect continuous’ respectively.
The easiest way to remember continuous tense, is that it’s referring to a verb that was happening over time, is still happening now, or will be happening in the future. Take a look at the examples below and see how the sentences change to show what is happening and how the verb looks different from its infinitive form:
- I was cleaning when you arrived.
- I am cleaning right now.
- I will be cleaning when you get here.
Verb Examples in the Perfect Tenses
The best way to remember the perfect tense, is that it is referring to something that was completed, has just been completed, or will be completed in the future. Again notice how the verb looks different this time compared to its infinitive form, and how the surrounding words are different to accommodate the tense:
- I had cooked everything when you arrived.
- I have cooked everything.
- I will have cooked everything when you arrive.
Verbs Examples in the Perfect Continuous Tenses
The simplest way to remember the perfect continuous tense is that it’s the previous two combined. So, it refers to something that was happening but has recently been completed, something that is happening now but will soon stop, and something that will happen and then be completed. Take a look below:
- I had been singing for an hour when you arrived.
- I have been singing for an hour.
- I will have been singing for an hour when you arrive.
List of Verbs
Now that we’ve taken a look at verbs, and all the possible tenses that you can write them in for you to think about, we’re going to provide you with some lists of verbs to help you vary your vocabulary a little bit.
In English grammar, verbs are one of the nine parts of speech. A verb is a word or group of words that describes an action, experience or expresses a state of being.
List of Verbs (in Alphabetical Order) / Examples of Verbs in Sentences
The following list of verbs will take you through various different verbs in alphabetical order for you to consider. See if you can spot one you would usually use and try to find one with the same meaning for you to try using in a sentence instead.
Verbs List (A)
List of verbs that start with A with verb examples.
- Accept: I accept your appolozy.
- Accuse: Tom accused me of lying.
- Achieve: She achieved remarkable results
- Acknowledge: She acknowledged receiving assistance.
- Acquire: Meg acquired many new friends.
- Adapt: He adapted himself to his new life.
- Add: I added a room to my house.
- Adjust: You will soon adjust to living in a dormitory.
- Admire: I admire your confidence.
- Admit: He was embarrassed to admit making a mistake.
- Adopt: I liked your idea and adopted it.
- Adore: He adores his grandfather.
- Advise: He advised applying at once.
- Afford: I can’t afford to spend any more money this week.
- Agree: Why did you agree to meet her in the first place?
- Aim: We aim to increase the speed of delivery.
- Allow: Swimming isn’t allowed here.
- Announce: She announced her intention to retire.
- Anticipate: I didn’t anticipate having to do the cooking myself!
- Apologize: You don’t have to apologize.
- Appear: Jack appears to be tired today.
- Apply: Tom applied for a leave of absence.
- Appreciate: I appreciate having a trouble with his supervisor.
- Approach: She approached him with a smile on her face.
- Approve: I don’t think Tom would approve.
- Argue: I don’t want to argue with you.
- Arise: The problem has arisen simply because you didn’t follow my instructions.
- Arrange: Have you arranged to meet Mark this weekend?
- Arrive: We arrived home late.
- Ask: Historians frequently ask to consult the collection.
- Assume: I assume Tom didn’t show up.
- Assure: I assure you Tom will be perfectly safe.
- Astonish: I was astonished by his ignorance.
- Attach: You need to attach your photo to the application form.
- Attempt: Are you going to attempt to pass the exam?
- Attend: She attends school at night.
- Attract: Tom certainly attracted a lot of attention.
- Avoid: She decided to be a nun in order to avoid meeting him.
- Awake: Tom awoke at daybreak.
Verbs List (B)
List of verbs that start with B with verb examples.
- Bake: Tom baked some muffins.
- Bathe: I bathe every day.
- Be: He is immature.
- Bear: I wish she wouldn’t eat so fast. I can’t bear watching her.
- Beat: You can’t beat me.
- Become: John became very sick.
- Beg: I beg to differ with you.
- Begin: The leaves begin to fall when autumn comes.
- Behave: Tom always behaves himself well. However, Mary does not.
- Believe: I believe you’re right.
- Belong: This bicycle belongs to me.
- Bend: Lie flat and let your knees bend.
- Bet: I bet you know French.
- Bind: Do you bind books?
- Bite: I got bitten by mosquitoes.
- Blow: Tom blew himself up accidentally.
- Boil: Please boil an egg for me.
- Borrow: I need to borrow your car.
- Bounce: Bounce the ball and try and hit it over the net.
- Bow: Every child bowed to the teacher.
- Break: We broke up.
- Breed: Rabbits breed quickly.
- Bring: I brought some dessert.
- Broadcast: We broadcast news on the hour.
- Build: We need to build a fire.
- Burn: The spy burned the papers.
- Burst: John burst into the room.
- Buy: I’ll buy a lot of candies for you.
Verbs List (C)
List of verbs that start with C with verb examples.
- Calculate: A computer can calculate very rapidly.
- Can/Could: Can you give me a ring at about 10?
- Care: Would you care to join us for dinner?
- Carry: I don’t carry cash anymore.
- Catch: Let’s catch a bite.
- Celebrate: We’re celebrating Tom’s birthday.
- Change: I changed my mind.
- Choose: Every day is beautiful if you choose to see it.
- Chop: Tom chopped down the tree that was in our front yard.
- Claim: This diet claims to eliminate toxins from the body.
- Climb: Carlos climbed the mountain.
- Cling: The mud clung to his shoes.
- Come: I’m coming today.
- Commit: David didn’t commit those crimes.
- Communicate: I can’t communicate with Anna like I used to.
- Compare: They compared the new car with the old one.
- Compete: I competed with him for the first prize.
- Complain: John complained about the weather.
- Complete: He completed drawing his pictures.
- Concern: I’m concerned for Anna’s safety.
- Confirm: The report has yet to be confirmed.
- Consent: We hope you will consent to act in his stead.
- Consider: Investors should consider putting some money into an annuity.
- Consist: A soccer team consists of eleven players.
- Consult: You’d better consult your doctor.
- Contain: This box contains five apples.
- Continue: The finance minister will continue to mastermind Poland’s economic reform.
- Convince: I’m not totally convinced of that.
- Cook: The pizza will then take about twenty minutes to cook.
- Cost: It’ll cost about 10,000 yen.
- Count: We’re counting on you.
- Crawl: Tom crawled into bed just before midnight.
- Create: I have to create a new website.
- Creep: We crept toward the enemy.
- Criticize: Tom criticized Mary for not doing the job correctly.
- Cry: The baby is crying.
- Cut: John cut his finger.
Verbs List (D)
List of verbs that start with D with verb examples.
- Dance: I want to dance.
- Dare: He didn’t dare to speak to her.
- Deal: I have to dealt with it.
- Decide: He has decided to live in France.
- Defer: She deferred writing my thesis.
- Delay: Big companies often delay paying their bills.
- Deliver: Letters are delivered every day.
- Demand: I demand to know what’s going on.
- Deny: She denied taking the money.
- Depend: I can’t depend on you anymore.
- Describe: John can’t describe how painful it was.
- Deserve: They didn’t deserve to win.
- Desire: We all desire success.
- Destroy: John’s house was destroyed by a hurricane.
- Determine: I am determined to carry out this plan.
- Develop: Swimming develops our muscles.
- Differ: My opinion differs from yours.
- Disagree: It pains me to disagree with your opinion.
- Discover: The miner discovered a valuable pocket of gold.
- Discuss: We briefly discussed buying a second car.
- Dislike: I dislike being the centre of attention.
- Distribute: The teacher distributed the leaflets.
- Dive: John learned to dive when he was five.
- Do: I don’t know.
- Doubt: I doubt if it’ll snow.
- Drag: I had to drag him out of bed.
- Dream: I dreamt about you.
- Drill: They intended to drill for oil.
- Drink: Can I have something to drink?
- Drive: He drives a truck.
- Drop: I dropped my sandwich.
- Dry: Raisins are dried grapes.
Verbs List (E)
List of verbs that start with E with verb examples.
- Earn: He earns three times more than me.
- Eat: You can’t eat your cake and have it.
- Emphasize: I want to emphasize this point in particular.
- Enable: His wealth enables him to do anything.
- Encourage: John encouraged Mary to learn how to speak French.
- Engage: We used to be engaged.
- Enhance: Can we enhance the image?
- Enjoy: I really enjoy talking to you.
- Ensure: This medicine will ensure you a good night’s sleep.
- Entail: This review procedure entails repeating the test.
- Enter: He entered the room.
- Establish: The school was established in 1650.
- Examine: The doctor examined the patients.
- Exist: I don’t believe such things to exist.
- Expand: The workers are expanding the road.
- Expect: What time do you expect to arrive home?
- Experiment: They’re experimenting with a new car.
- Explain: I can explain everything.
- Explore: He explored the Amazon jungle.
- Extend: We extended a hearty welcome to them.
Verbs List (F)
List of verbs that start with F with verb examples.
- Fail: I fail to comprehend their attitude.
- Fall: I fell in the pool.
- Feed: We just fed the baby.
- Feel: I feel that Mr. Peter is a good teacher.
- Fight: Don’t fight with me.
- Find: I can find them.
- Finish: He finished cleaning the kitchen.
- Fit: This coat doesn’t fit me.
- Fly: Tom wishes he could fly.
- Fold: Tom and Mary folded up the flag.
- Follow: We must follow the rules of the game.
- Forbid: I forbid you to smoke.
- Forget: I’ll never forget visiting them.
- Forgive: We have already forgiven you.
- Freeze: It’s freezing cold in this country.
- Fry: She fried fish in salad oil.
Verbs List (G)
List of verbs that start with G with verb examples.
- Generate: This machine generates electricity.
- Get: We’ve got to get the economy under control or it will literally eat us up.
- Give: The waiter gives me the menu.
- Go: Let’s go eat.
- Grind: We grind our coffee by hand.
- Grow: Apples grow on trees.
Verbs List (H)
List of verbs that start with H with verbs examples.
- Hang: Don’t you hang up on me.
- Happen: You made it happen.
- Hate: I hate getting to the theatre late.
- Have: I have a car.
- Hear: I will hear me.
- Hesitate: I hesitate to spend so much money on clothes.
- Hide: I’m hiding from Tim.
- Hit: I hit the jackpot.
- Hold: Hold the knife at an angle.
- Hop: I tried to hop on my good foot while holding onto Jim…
- Hope: I hope to see you again soon.
- Hug: I really need a hug.
- Hurry: It had to hurry to find a home because I was already on to something else.
- Hurt: I hurt my elbow.
Verbs List (I-J)
List of verbs that start with I & J with verbs examples.
- Identify: She identified him as the murderer.
- Ignore: He ignored her advice.
- Illustrate: The teacher will illustrate how to do it.
- Imagine: I can imagine how you felt.
- Imply: Silence implies consent.
- Impress: We’re not impressed.
- Improve: I need to improve my French.
- Include: Tom’s lunch includes a sandwich and an apple.
- Incorporate: Her business was incorporated.
- Indicate: The arrow indicates the way to go.
- Inform: I’ll inform John about our decision.
- Insist: She insisted on going there.
- Install: The man tried to install his own antenna.
- Intend: I heard they intend to marry.
- Introduce: I’ll introduce you to Tom.
- Invest: He invested his money in stocks.
- Investigate: I came here to investigate Tom’s death.
- Involve: This procedure involves testing each sample twice.
- Iron: I iron my clothes almost every day.
- Jog: I make it a rule to jog every morning.
- Jump: Can you jump over the river?
- Justify: My results justify taking drastic action.
Verbs List (K)
List of verbs that start with K with verbs examples.
- Keep: I keep thinking about Joe, all alone in that place.
- Kick: The kids love to kick a ball against my wall.
- Kiss: Did you kiss anybody?
- Kneel: Do not run, stand, kneel or spin in the slide.
- Knit: She knit him a sweater for his birthday.
- Know: We know him.
Verbs List (L)
List of verbs that start with L with verbs examples.
- Lack: Tom seems to lack energy.
- Laugh: Tom is laughing.
- Lay: He laid on his back.
- Lead: Tom leads a quiet life.
- Lean: He leaned on his elbows.
- Leap: Ken leapt over the wall.
- Learn: Children learn to creep ere they can go.
- Leave: Leave me alone!
- Lend: Tom lent Mary his camera.
- Lie (in bed): Lie back down.
- Lift: He couldn’t lift the table and no more could I.
- Light: Better to light one candle than to curse the darkness.
- Lie (not to tell the truth): He hated lying.
- Like: She likes playing tennis.
- Listen: Why won’t you listen?
- Look: It looks cold outside.
- Lose: She lost a book.
- Love: I love going out to restaurants.
Verbs List (M,N)
List of verbs that start with M & N with verbs examples.
- Maintain: Tom maintained eye contact with Mary.
- Make: I’m making tea.
- Manage: Did you manage to catch the post?
- Matter: It doesn’t matter, Tom.
- May: Each nurse may be responsible for up to twenty patients.
- Mean: I didn’t mean to hurt your feelings.
- Measure: The surfboard measures 2 meters by 55 centimeters.
- Meet: We’ve never met.
- Melt: The snow is melted.
- Mention: He mentioned going to that college.
- Might: Donna might be able to come tomorrow, but it’s very unlikely.
- Mind: Would you mind repeating what you just said?
- Miss: He had missed being elected by a single vote.
- Mix: If you mix blue and red, you get violet.
- Mow: I mowed Tom’s lawn.
- Must: I really must get some exercise.
- Need: You need to change your eating habits.
- Neglect: Don’t neglect to lock the door when you leave.
- Negotiate: The two countries negotiated a treaty.
Verbs List (O)
List of verbs that start with O with verbs examples.
- Observe: You must observe those rules.
- Obtain: I obtained the painting at an auction.
- Occur: The accident occurred yesterday morning
- Offer: She offered to help me move my things to my new house.
- Open: Open the windows.
- Operate: I can’t figure out how to operate this machine.
- Order: What do you suggest I order?
- Organize: They want me to organize the party.
- Ought to: You ought to get your watch repaired.
- Overcome: We have to overcome many difficulties.
- Overtake: Their car overtook ours.
- Owe: Tom owes me money.
- Own: I own a German car.
Verbs List (P)
List of verbs that start with P with verbs examples.
- Paint: She painted the wall pink.
- Participate: He participated in the debate.
- Pay: Can I pay by installment payment?
- Peel: Anna peeled the apple.
- Perform: Tom performs in a jazz club three nights a week.
- Persuade: I persuaded Tom to help me.
- Pinch: He pinched and scraped for many years to save money.
- Plan: Next year I plan to travel around the world.
- Play: I can play tennis.
- Point: Tom pointed to the sky.
- Possess: The old man possesses great wealth.
- Postpone: He postponed returning to Paris.
- Pour: She poured tea for me.
- Practice: Today we’re going to practice parking.
- Prefer: Chantal prefers travelling by train.
- Prepare: The doctor prepared to prescribe a receipt.
- Pretend: She was pretending to cry. I knew she was lying.
- Prevent: The rain prevented me from coming.
- Proceed: They will proceed to build another laboratory building.
- Promise: He promised to collect her from the airport.
- Propose: We propose to deal with this subject in the following chapter.
- Protect: We’re supposed to be protecting John.
- Prove: I’ll prove it to you.
- Pull: John pulled out a pen.
- Punch: You punch like a girl.
- Pursue: The police pursued the murderer.
- Push: We had to push our way through the crowd.
- Put: I put on my shoes.
Verbs List (Q,R)
List of verbs that start with Q & R with verbs examples.
- Qualify: He is qualified as an English teacher.
- Quit: She quits worrying about the problem.
- React: Tom reacted appropriately.
- Read: I read the book.
- Realize: I didn’t realise we were late.
- Recall: I don’t recall seeing any cars parked outside.
- Receive: We received a warm welcome.
- Recollect: I recollect seeing Ryder some years ago in Bonn.
- Recommend: I would never recommend using a sunbed on a regular basis.
- Reduce: I think we should reduce the price.
- Refer: I often refer to the dictionary.
- Reflect: She reflected on what she had done.
- Refuse: She refused to answer questions about her personal finances.
- Regret: I regret leaving school so young.
- Relate: She is related to him by marriage.
- Relax: We’re supposed to relax.
- Relieve: I was relieved to hear that he was alive.
- Rely: You can certainly rely on him.
- Remain: He remained poor all his life.
- Remember: He had remembered to bring a pair of gloves, unlike me.
- Remind: It reminds me of the good old days.
- Repair: He repaired his watch by himself.
- Replace: The car replaced the bicycle.
- Represent: He represented the labor union on the committee.
- Require: This task requires dexterity.
- Resent: Many conscripts resent having to do their military service.
- Resist: She can never resist buying new shoes.
- Retain: We had to retain a lawyer.
- Retire: I have decided to retire.
- Rid: You’ve got to get rid of it
- Ride: Life is a horse, and either you ride it or it rides you.
- Ring: The phone is ringing.
- Rise: The sun is about to rise.
- Risk: He risked being caught.
- Roast: He is roasting coffee beans.
- Run: Do not run too fast after gain.
Verbs List (S)
List of verbs that start with S with verbs examples.
- Sanction: They will not sanction copying without permission.
- Satisfy: He satisfied his thirst with a large glass of beer.
- Say: No one says that.
- Scrub: Tom asked Mary to scrub the toilet.
- See: Do you see that bird?
- Seem: I always seem to be unlucky at cards.
- Sell: I can’t sell you that.
- Send: They’re sending help.
- Serve: They serve good nosh in the cafeteria.
- Set: I’m going to set the table.
- Settle: The problem is not settled yet.
- Sew: Mary is sewing baby clothes.
- Shake: They shook hands when they met at the airport.
- Shall: Shall I add your name to the list?
- Shed: She tried not to shed a tear.
- Shine: Susan shined your father’s shoes.
- Shoot: I’ll shoot both of you.
- Should: The university should provide more sports facilities.
- Show: I’ll show you later.
- Shrink: My jeans shrank after I washed them.
- Shut: I shut my eyes again.
- Sing: Tom loves to sing.
- Sink: A ship sank near here yesterday.
- Sit: Sit on the floor, stretching your legs out in front of you.
- Ski: I like skiing very much.
- Sleep: I slept too much.
- Slice: It’s best to slice into a rich cake from the middle.
- Slide: He slid the money into my pocket.
- Slip: She slipped into her clothes.
- Smell: Something smells bad. What is this?
- Snore: Tom snored loudly with his mouth open.
- Solve: He solved the difficult problem.
- Sow: Farmers sow seeds in the spring.
- Speak: He speaks English.
- Specify: Tom didn’t specify how many pencils to buy.
- Spell: I don’t know how to spell the word.
- Spend: I spent some time in Boston.
- Spill: I’m afraid I spilled coffee on the tablecloth.
- Spit: I can’t put up with the way he spits.
- Spread: He spread some strawberry jam on his toast.
- Squat: Tom squatted down next to his dog.
- Stack: They are specially packaged so that they stack easily.
- Stand: Can you stand up?
- Start: He started tipping the pea pods into a pan.
- Steal: My watch was stolen.
- Stick: He stuck to his job.
- Sting: I was stung by a bee.
- Stink: It stinks in here.
- Stir: She stirred the soup with a spoon.
- Stop: I hoped he would stop asking awkward questions.
- Stretch: Breathe in through your nose as you stretch up.
- Strike: Tom struck the wall with his fist.
- Struggle: He struggled to keep his footing on the slippery floor.
- Study: She studies hard.
- Submit: I submitted the application myself.
- Succeed: He’ll succeed for sure.
- Suffer: We suffered a pretty big loss.
- Suggest: Tracey suggested meeting for a drink after work.
- Supply: I supplied Tom with everything he needed.
- Suppose: I suppose you’re hungry.
- Surprise: She surprised him when she arrived early.
- Survive: He survived the plane crash.
- Swear: Do you swear to tell the whole truth?
- Sweep: I will sweep out my room.
- Swell: The river swelled rapidly because of the heavy rain.
- Swim: She swims well.
- Swing: The lamp was swinging back and forth.
Verbs List (T)
List of verbs that start with T with verbs examples.
- Take: I took a walk.
- Talk: Tom talked a lot.
- Taste: The soup tastes salty.
- Teach: I’ll teach you how to swim.
- Tear: I tore the picture out of the album.
- Tell: I told him to come.
- Tend: She tends to be late for school.
- Think: I think that Mr. Peter is a good teacher.
- Threaten: They threatened to ban the book.
- Throw: I threw away my shoes.
- Tiptoe: Tom quietly tiptoed out of the room.
- Tolerate: We don’t tolerate smoking in the library.
- Translate: He translated the verse into English.
- Try: We tried to confuse the enemy.
Verbs List (U,V)
List of verbs that start with U & V with verbs examples.
- Understand: I knew you’d understand.
- Vacuum: Tom vacuumed his bedroom.
- Value: We value our customers.
- Vary: The boxes vary in size from small to large.
- Volunteer: They volunteer to teach introductory courses.
Verbs List (W)
List of verbs that start with W with verbs examples.
- Wait: I can’t wait to see you.
- Wake: I have to wake Tom up.
- Walk: Don’t try to walk before you can crawl.
- Want: I want to watch TV.
- Warn: We’ve got to warn Tom.
- Wash: Tom washed his hands.
- Watch: We watched a movie.
- Wave: She waved her hand to me.
- Wear: Tom wore black pants.
- Weep: She wept over her child’s death.
- Weigh: The suitcase weighs 20 pounds.
- Whip: She whipped out her pistol.
- Will: I don’t think Emma will get the job.
- Win: I can win this time.
- Wish: I wish to insert an advertisement in your newspaper.
- Would: If I lived on an island, I would know how to swim.
- Write: Write it down on a piece of paper.
List of Verbs (by Grammatical Functions)
Sometimes verbs don’t always behave the same in a sentence, so to make things easier for you to follow along, we’ve split these verbs up into their grammatical functions so you can see how they would be used in a sentence slightly differently.
A useful list of verbs classified by their grammatical functions. In this section, you will be learning about the different verbs in grammar and this will enable you to form much more concise and comprehensive sentences.
Stative Verbs List
List of common stative verbs in English
Mental State
- Know
- Believe
- Understand
- Doubt
- Think (have an opinion)
- Suppose
- Recognise
- Forget
- Remember
- Imagine
- Mean
- Agree
- Disagree
- Deny
- Promise
- Satisfy
- Realise
- Appear
- Astonish
- Please
- Impress
- Surprise
- Concern
Possession
- Have
- Own
- Possess
- Lack
- Consist
- Involve
- Include
- Contain
Emotions
- Love
- Like
- Dislike
- Hate
- Adore
- Prefer
- Care for
- Mind
- Want
- Need
- Desire
- Wish
- Hope
- Appreciate
- Value
Measure, cost, others
- Cost
- Measure
- Weigh
- Owe
- Seem
- Fit
- Depend
- Matter
Stative Verbs Examples in English | Image
 Pin
Pin
Dynamic Verbs List
In English grammar, a “dynamic verb” means that the verb describes an action rather than a state. In contrast, a “stative verb” means that the verb describes a state rather than an action.
Dynamic verbs are sometimes known as “action verbs.”
List of Verbs Can be Both Stative and Dynamic Verbs
- Look
- Appear
- Think
- Feel
- Have
- See
- Taste
- Smell
- Be
- Weigh
- Measure
- Mind
Stative and Dynamic Verbs Examples | Image
 Pin
Pin
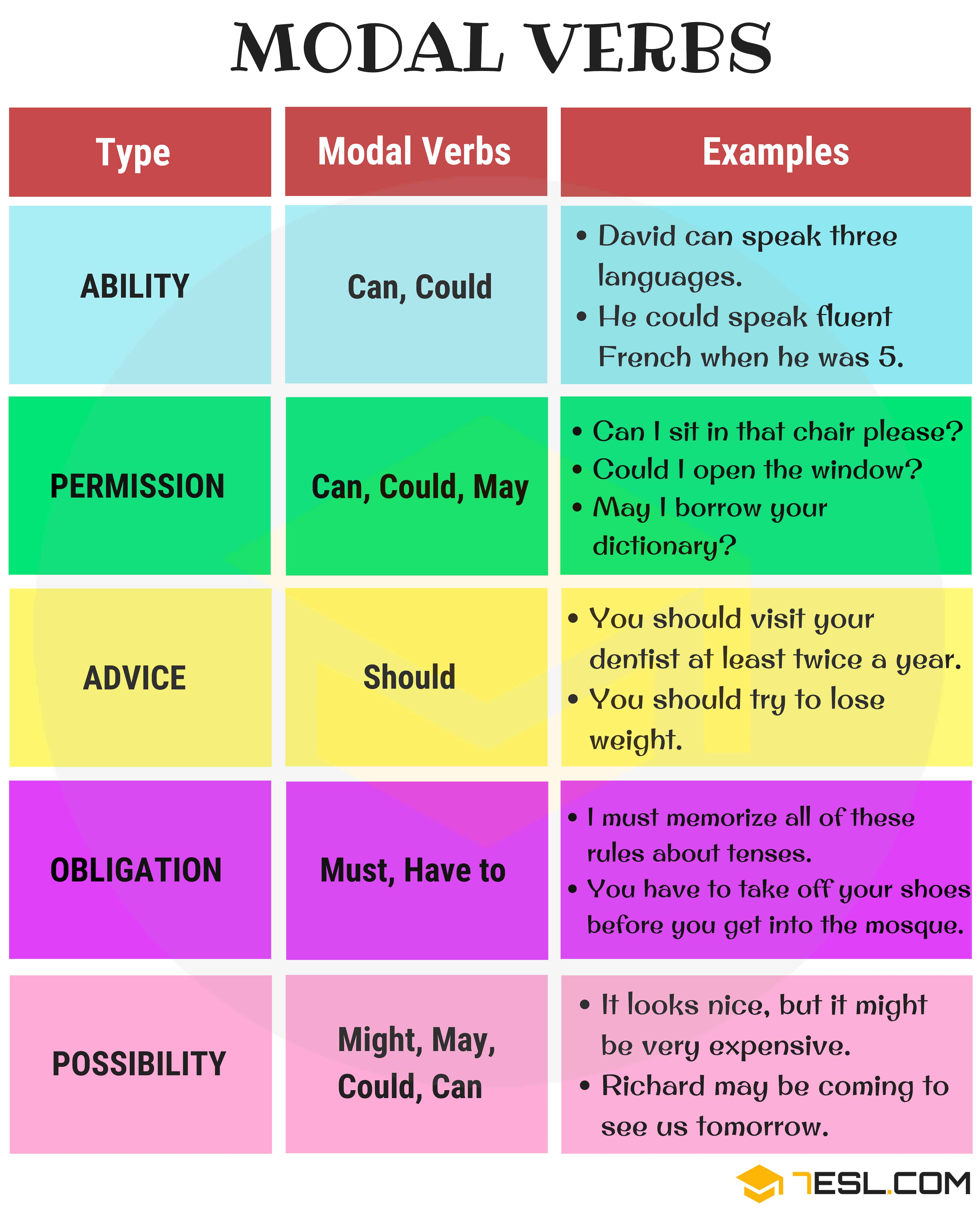
Modal Verbs List
List of modal verbs in English
- Will
- Shall
- Would
- Should
- Ought to
- Must
- Mustn’t
- May
- Might
- Can
- Could
- Have to/ Has to
- Don’t/ Doesn’t have to
Modal Verbs Examples in English | Image
 Pin
Pin
Irregular verbs List
Learn a useful list of Irregular Verbs in English
- Arise
- Awake
- Be
- Bear
- Beat
- Become
- Begin
- Bend
- Bet
- Bind
- Bite
- Bleed
- Blow
- Break
- Breed
- Bring
- Broadcast
- Build
- Burn
- Burst
- Buy
- Can
- Catch
- Choose
- Cling
- Come
- Cost
- Creep
- Cut
- Deal
- Dig
- Do
- Draw
- Dream
- Drink
- Drive
- Eat
- Fall
- Feed
- Feel
- Fight
- Find
- Fly
- Forbid
- Forget
- Forgive
- Freeze
- Get
- Give
- Go
- Grind
- Grow
- Hang
- Have
- Hear
- Hide
- Hit
- Hold
- Hurt
- Keep
- Kneel
- Know
- Lay
- Lead
- Lean
- Learn
- Leave
- Lent
- Lie (in bed)
- Lie (not to tell the truth)
- Light
- Lose
- Make
- May
- Mean
- Meet
- Mow
- Must
- Overtake
- Pay
- Put
- Read
- Ride
- Ring
- Rise
- Run
- Saw
- Say
- See
- Sell
- Send
- Set
- Sew
- Shake
- Shed
- Shine
- Shoot
- Show
- Shrink
- Shut
- Sing
- Sink
- Sit
- Sleep
- Slide
- Smell
- Sow
- Speak
- Spell
- Spend
- Spill
- Spit
- Spread
- Stand
- Steal
- Stick
- Sting
- Stink
- Strike
- Swear
- Sweep
- Swell
- Swim
- Swing
- Take
- Teach
- Tear
- Tell
- Think
- Throw
- Understand
- Wake
- Wear
- Weep
- Win
- Wind
- Write
Irregular Verbs Examples in English | Image
 Pin
Pin
Participles, Gerunds & Infinitives
The three verbals— gerunds, infinitives, and participles—are formed from verbs, but are never used alone as action words in sentences. Instead, verbals function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. These verbals are important in phrases.
Participles
A participle is a verbal that is used as an adjective and most often ends in -ing or -ed. They function as adjectives, thus participles modify nouns or pronouns.
Learn more how to form Present and Past Participles in English.
Gerunds: List of Verbs Followed by Gerunds
Gerunds are verbals that function as nouns and have an –ing ending.
Useful list of Verbs Followed by Gerunds in English
- Admit
- Advise
- Anticipate
- Acknowledge
- Appreciate
- Avoid
- Bear
- Begin
- Complete
- Consider
- Defer
- Delay
- Deny
- Discuss
- Dislike
- Enjoy
- Entail
- Finish
- Forget
- Hate
- Intend
- Involve
- Justify
- Keep
- Like
- Love
- Mention
- Mind
- Miss
- Postpone
- Practice
- Prefer
- Quit
- Recall
- Recollect
- Recommend
- Regret
- Resent
- Resist
- Risk
- Sanction
- Start
- Stop
- Suggest
- Tolerate
- Try
List of Verbs Followed by Gerunds | Image
 Pin
Pin
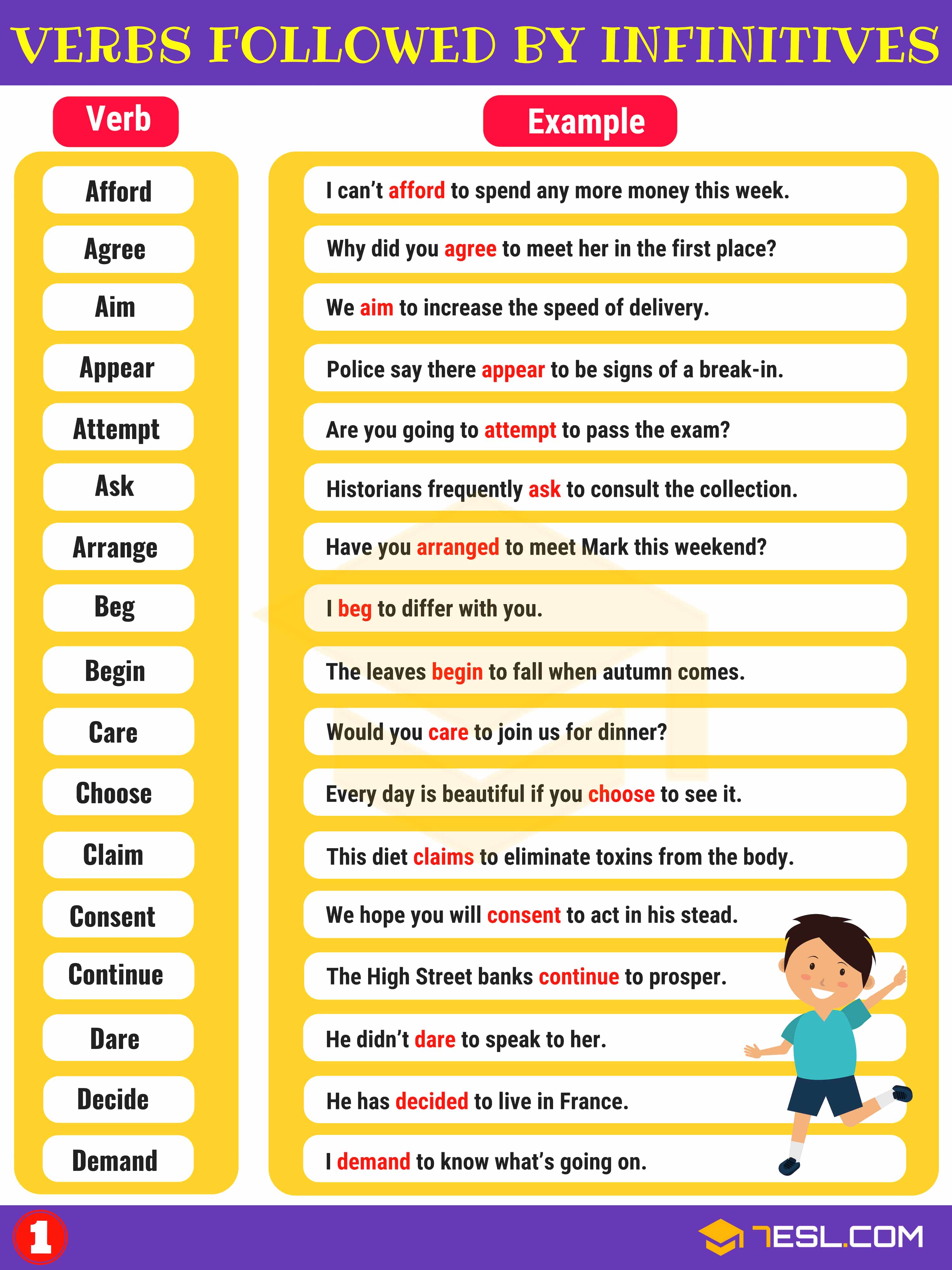
Infinitives: List of Verbs Followed by Infinitives
A to-infinitive is a verbal consisting of to + a verb, and it acts like a subject, direct object, subject complement, adjective, or adverb in a sentence. Infinitives are easy to identify because they’re written with to + a verb.
A useful list of commonly used Verbs Followed by Infinitives
- Afford
- Agree
- Aim
- Appear
- Attempt
- Ask
- Arrange
- Beg
- Begin
- Care
- Choose
- Claim
- Consent
- Continue
- Dare
- Decide
- Demand
- Deserve
- Dislike
- Expect
- Fail
- Forget
- Get
- Hesitate
- Hope
- Hurry
- Intend
- Learn
- Like
- Love
- Manage
- Mean
- Neglect
- Need
- Offer
- Plan
- Prefer
- Prepare
- Pretend
- Proceed
- Promise
- Propose
- Refuse
- Remember
- Seem
- Start
- Stop
- Struggle
- Swear
- Threaten
- Try
- Volunteer
- Wait
- Want
- Wish
List of Verbs Followed by Infinitives | Image
 Pin
Pin
Auxiliary Verbs List
List of Auxiliary Verbs in English
- Do
- Have
- Be
- Will
Causative Verbs List
List of Causative Verbs in English
- Have
- Get
- Make
- Let
Causative Verbs Examples | Image
 Pin
Pin
Verbs List (by Activity)
Finally, we’ve put together this list of verbs by activity. Whether it’s verbs associated with a restaurant, verbs associated with a sports event, or even verbs associated with body movements, we’ve categorized them all as best we can. Hopefully, you can look over them and understand different verbs that are more appropriate in some categories than in others.
List of different types of verbs with pictures in English.
Action Verbs List
List of action verbs commonly used in English.
Bathe
Eat
Sleep
Bow
Fight
Smell
Buy
Fly
Snore
Clap
Give
Stack
Climb
Hug
Stand up
Close
Jump
Talk
Cook
Kiss
Turn off
Crawl
Knit
Turn on
Cry
Laugh
Think
Cut
Listen
Throw away
Dance
Open
Wait
Dig
Paint
Wash
Dive
Play
Watch TV
Dream
Read
Win
Drink
Ride
Write
Shake
Sew
Sing
 Pin
Pin
Cooking Verb Examples with Pictures
Add
Peel
Bake
Pinch
Barbecue
Pour
Boil
Roast
Break
Roll out
Cut
Saute
Chop
Slice
Fry
Spread
Grate
Steam
Layer
Stir
Melt
Taste
Mix
Weigh
 Pin
Pin
Restaurant Verbs List with Pictures
- Give
- Drink
- Serve
- Pay
- Eat
- Cook
- Hold
- Light
- Order
- Spread
- Lift
- Write
- Slice
- Stack
- Set (the table)
 Pin
Pin
Sports Verbs List with Pictures
Bend
Pass
Bounce
Ride
Catch
Run
Dribble
Serve
Hit
Shoot
Hop
Sit
Jump
Skip
Kick
Stretch
Kneel
Throw
Lie down
Walk
 Pin
Pin
Classroom Verb Examples
Ask
Open
Calculate
Paint
Close
Play
Count
Read
Cut
Say
Draw
Show
Experiment
Sing
Explain
Spell
Give
Study
Listen
Teach
Observe
Think
 Pin
Pin
Body Movement Verbs List
Bend
Push
Dance
Lift
Run
Break
Carry
Lean
Stand
Kneel
Squat
Jog
Hold
Throw
March
Sit
Tiptoe
Wave
Drag
Walk
Talk
Jump
Hit
Open
Leap
Catch
Cartwheel
Pick up
Kick
Put down
Punch
Kiss
Stretch
Pull
Clap
Drop
Dive
Laugh
Point
Look
Trip
Slip
Crawl
Pour
Cry
 Pin
Pin
English Verbs List | Pictures
Common English Verbs List | Image 1
 Pin
Pin
English Verbs List | Image 2
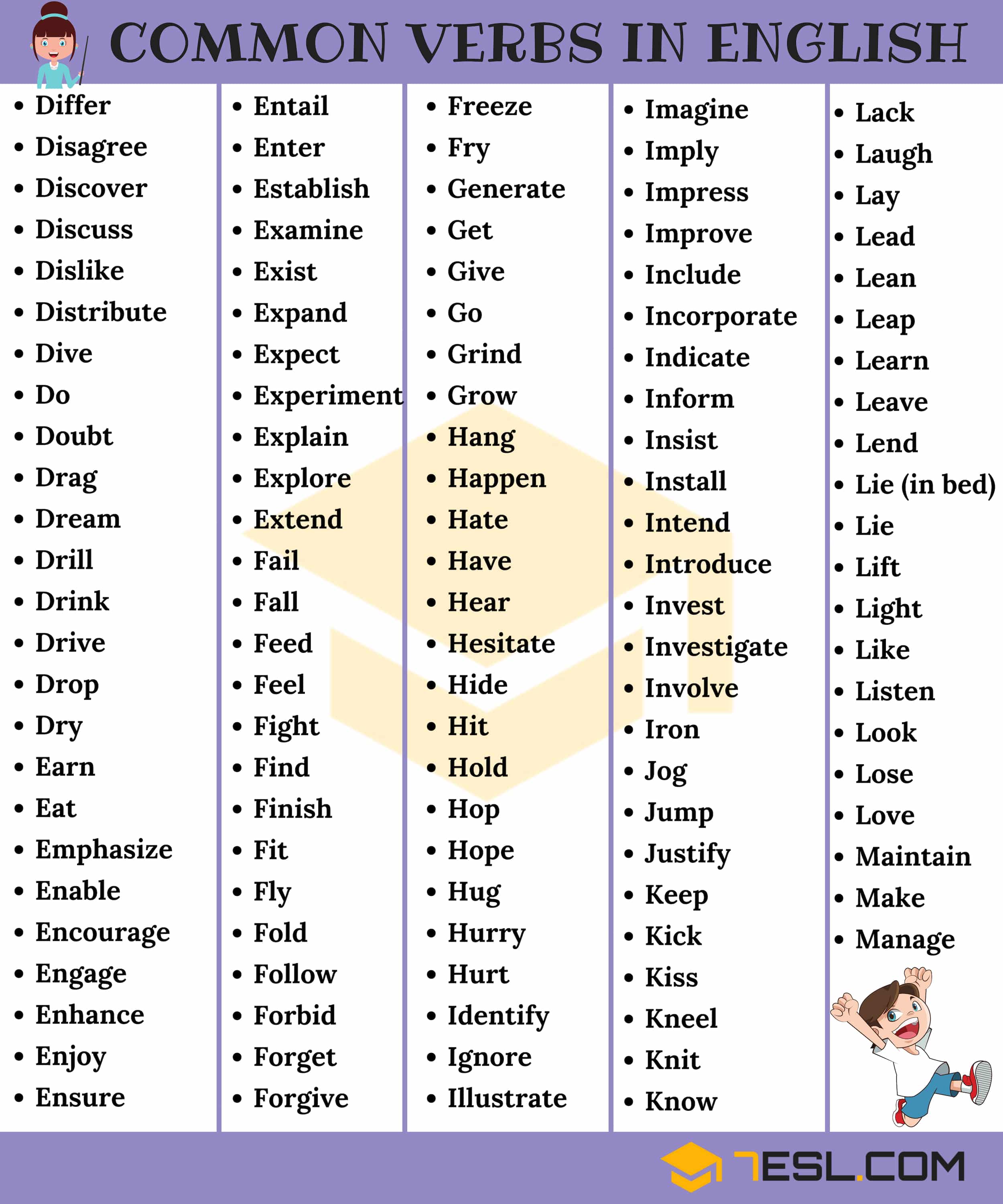 Pin
Pin
Common English Verbs List | Image 3
 Pin
Pin
English Verbs List | Image 4
 Pin
Pin
List of Verbs Videos
Verbs are relatively easy to understand, but the key to using them successfully in sentences is being aware of the tense. The best way to combat this is by reading the sentence aloud. It’s incredibly easy to pick up issues with tenses when you hear it rather than read it. Remember, you can always look back here for more information about how verbs change in tenses to give you an idea about what changes you might need to make to your sentence for it to make sense. And of course, our list of verbs will be here for you to look over for new ideas about which verbs to use in different contexts or for different grammatical functions.
Learn 450+ Most Common English Verbs List with Pronunciation.
Learn 250+ verb examples with pictures and American English pronunciation.
[Update] Types of Verbs & Examples | verb 2 – NATAVIGUIDES
What is a verb?
Verbs are the action words in a sentence that describe what the subject is doing. Along with nouns, verbs are the main part of a sentence or phrase, telling a story about what is taking place. In fact, without a verb, full thoughts can’t be properly conveyed, and even the simplest sentences, such as Maria sings, have one. Actually, a verb can be a sentence by itself, with the subject, in most case you, implied, such as, Sing! and Drive!
When learning the rules of grammar, schoolchildren are often taught that verbs are ‘doing’ words, meaning they signify the part of the sentence which explains the action taking place: He ran away, she eats chocolate cake on Sundays, the horses gallop across the fields. Ran, eats and gallop are the ‘action’ parts of those sentences, thus they are the verbs. However, it can be confusing because not all verbs are easily identifiable as action: I know your name, Jack thought about it, we considered several applications. These are non-action verbs, i.e. those that describe a state of being, emotion, possession, sense or opinion. Other non-action verbs include include love, agree, feel, am, and have.
How to Recognize a Verb
As you can see from the examples above, one clue to help you recognize a verb is its location compared to the subject. Verbs almost always come after a noun or pronoun. These nouns and pronouns are referred to as the subject. The verb thought comes after the noun Jack, so the action Jack (subject) was taking was thinking (verb).
- Mark eats his dinner quickly.
- We went to the market.
- You write neatly in your notebook.
- They thought about all the prizes in the competition.
Here are some other ways to recognize verbs in a sentence:
- If you’re not sure if a word is a verb, ask yourself, “Can I do ______?”
Can I think, wonder, walk, yawn? Yes, so these are verbs.
- You can also ask, ”What is happening?”
In the sentence Mark eats his dinner quickly, what is happening? Eating is happening, so eating is the verb.
In the sentence They thought about all the prizes what is happening? Thought (thinking) is happening, so thought is the verb.
Physical Verbs – Definition and Examples
Physical verbs are action verbs. They describe specific physical actions. If you can create a motion with your body or use a tool to complete an action, the word you use to describe it is most likely a physical verb. For example, , andEven when the action isn’t very active, if the action is done by the body or a tool, consider it a physical verb.
Physical Verb Examples
The physical verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
- Let’s run to the corner and back.
- I hear the train coming.
- Call me when you’re finished with class.
Mental Verbs – Definition and Examples
Mental verbs have meanings that are related to concepts such as discovering, understanding, thinking, or planning. In general, a mental verb refers to a cognitive state.
Mental Verb – Definition and Examples
Mental verbs have meanings that are related to concepts such as discovering, understanding, thinking, or planning. In general, a mental verb refers to a cognitive state.
Mental Verb Examples
The mental verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
- I know the answer.
- She recognized me from across the room.
- Do you believe everything people tell you?
States of Being Verbs – Definition and Examples
Also known as linking verbs, state of being verbs describe conditions or situations that exist. State of being verbs are inactive since no action is being performed. These verbs, forms of to be, such as am, is, are, are usually complemented by adjectives.
States of Being Verb Examples
The state of being verbs in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
- I am a student.
- We are circus performers.
- Please is quiet.
Types of Verbs
There are many types of verbs. In addition to the main categories of physical verbs, mental verbs, and state of being verbs, there are several other types of verbs. In fact, there are more than ten different types of verbs that are grouped together by function.
List of all Verb Types
Action Verbs
Action verbs express specific actions and are used any time you want to show action or discuss someone doing something. It’s important to remember that the action does not have to be physical.
Action verb examples:
- Run
- Dance
- Slide
- Jump
- Think
- Do
- Go
- Stand
- Smile
- Listen.
The action verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
I run faster than David.
He does it well.
She thinks about poetry all day long
Transitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are action verbs that always express doable activities that relate or affect someone or something else. These other things are generally direct objects, nouns or pronouns that are affected by the verb, though some verbs can also take an indirect object, such as show, take, and make. In a sentence with a transitive verb, someone or something receives the action of the verb.
Transitive verb examples:
-
Love
-
Respect
-
Tolerate
-
Believe
-
Maintain.
The transitive verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
Gary ate the cookies.
The transitive verb is ate, Gary is the subject, because it is Gary who is doing the eating, and the cookies are the direct object, because it is the cookies that are being eaten. Other examples:
He kicked John.
John punches him.
They sold the tickets.
Examples of verbs used with both direct and indirect objects:
They sell him the tickets.
In this sentence, the tickets are the direct object while him is the indirect object.
Mary baked her mother a pie.
In this sentence, a pie is the direct object while her mother is the indirect object.
Intransitive Verbs
Intransitive verbs are action verbs that always express doable activities. They are different from transitive verbs because there is no direct object following an intransitive verb.
Intransitive verb examples:
-
Walk
-
Laugh
-
Cough
-
Play
-
Run
The intransitive verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
We travelled to London.
The intransitive verb is travelled, the subject is we, because we are doing the travelling, but London is not a direct object because London is not receiving the action of the verb. Other examples:
I sneeze in the morning.
He arrived with moments to spare.
Kathryn sat away from the others.
John eats before leaving for school.
The last example shows that the verb eats can be both transitive and intransitive depending on whether there is a direct object or not. If the sentence read: John eats the cookies before leaving for school, eats would be transitive as there is a direct object – the cookies.
By the way, some verbs can be both transitive and intransitive. These verbs include: start, leave, change, live, stop.
Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary verbs are also known as helping verbs and are used together with a main verb to show the verb’s tense or to form a question or negative. Common examples of auxiliary verbs include have, might, will. These auxiliary verbs give some context to the main verb, for example, letting the reader know when the action took place.
Auxiliary verb examples:
-
Would
-
Should
-
Do
-
Can
-
Did
-
Could
-
May
The auxiliary verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
I will go home after football practice.
The auxiliary verb will is telling us that the action of the main verb go is going to take place in the future – after football practice has ended. If the auxiliary verb will was removed, we get the sentence:
I go home after football practice.
In this case, there is no definite time frame for the action. The sentence suggests that going home after football practice is just something the subject I generally does. Other examples:
I may dance with you later.
We did consider Bryan’s feelings.
Jenny has spoken her final words.
In addition, we can sometimes use the auxiliary very before the pronoun to make a question:
Might you dance with me later?
Did we consider Bryan’s feelings?
Has Jenny spoken her final words?
Also, auxiliary verbs are used to help form negative statements, with the use of words like not and never. These will usually split the auxiliary and main verbs:
I may never dance with you again.
We did not consider Bryan’s feelings.
Jenny has not spoken her final words.
Stative Verbs
Stative verbs can be recognized because they express a state rather than an action. They typically relate to thoughts, emotions, relationships, senses, states of being, and measurements. The best way to think about stative verbs is that they are verbs that describe things that are not actions. The stative verbs are all expressing a state: A state of doubting, a state of believing, a state of wanting. These states of being are often temporary.
The stative verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
The doctor disagrees with your analysis.
Disagree is a stative verb here, as it describes the doctor’s state of being – disagreement.
John doubts the doctor’s opinion.
I believe the doctor is right.
She wanted another opinion.
Modal Verbs
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that are used to express abilities, possibilities, permissions, and obligations.
Modal verb examples:
-
Can
-
Must
-
May
-
Should
-
Would
The modal verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
He can shoot a three-point shot easily.
The auxiliary verb can is expressing an ability, suggesting that shooting a three-point shot is a skill the subject possesses.
Please note that in the case of should and must in the examples below, the modal verbs are expressing obligations, whereas would and may are expressing possibilities.
I should go home.
You must not delay.
Sally would not recommend the sushi.
David may be late.
Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs aren’t single words; instead, they are combinations of words that are used together to take on a different meaning to that of the original verb. There are many examples of phrasal verbs, some of which have colloquial meanings, such as make up, hand in, bring up, point out, look forward to. Each time the verb takes the extra word(s) it takes on a new meaning. For example, without the expresses that something is being created, whereas with , the suggestion is that there are some lies or a fantastical element to the story and can mean either to grasp or see something difficult, or to kiss passionately.
Phrasal verb examples:
-
Run out
-
Go all out
-
Make out
-
Hand out
-
Bring out
-
Face up
-
Think through
The phrasal verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
Mary looked forward to her high school reunion.
The verb looked has taken on forward to to become a phrasal verb meaning to be excited about or eagerly await something.
He brought up the same points again and again.
Leroy handed in the wallet to the police.
I make up stories all the time.
She pointed out Donald’s mistake.
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs are those that don’t take on the regular spelling patterns of past simple and past participle verbs. Unfortunately, there are hundreds of irregular verbs in the English language. But don’t worry, while many are used often, the majority are not in common usage – or if they are, you will use them so often you will learn them quickly. Some of the most common irregular verbs include: say, make, go, take, come, know and see.
Irregular verb examples:
-
Eat
-
Think
-
Bring
-
Hold
-
Bear
-
Buy
-
Lay
-
Catch
-
Drive
-
Paid
-
Feel
-
Redo
The irregular verb examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
I take my time when I go to the shops (present tense)
I took my time when I went to the shops (past tense)
Julie makes cake for the classroom (present tense)
Julie made a cake for the classroom (past tense)
She sees a silhouette shaped like a man in the window (present tense)
She saw a silhouette shaped like a man in the window (past tense)
We come to Aunt Jane’s for Thanksgiving each year (present tense)
We came to Aunt Jane’s for Thanksgiving each year (past tense).
You should also remember that auxiliary verbs ‘do’ and ‘have’ are also irregular verbs:
I do agree.
He does it often.
We have done our homework early.
They do their homework on Fridays.
I have a suspicion about Fran
Fran has a devious look.
We have no money left.
They have had a cough twice this winter.
Hướng dẫn sử dụng linking verbs ~~~ tiếng anh 123 cơ bản.. Chúc các bạn học tốt :3
video hướng dẫn cách dùng linking verbs trong Tiếng Anh 123..
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่

[Livestream] Unit 2 – Verb | Level mất gốc, cơ bản | Luyện thi TOEIC | Anh Ngữ Ms Hoa
Chuỗi livestream: \”Từ mất gốc đến 800 TOEIC Nothing is impossible\” là series chương trình giúp các bạn nâng cao kiến thức và kĩ thuật làm bài thi TOEIC để chinh phục đỉnh cao 800 TOEIC từ con số 0.
▬▬▬▬
Unit 2: VERB
Bài học ngày hôm nay chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu cấu trúc cơ bản và cách sử dụng của ĐỌNG TỪ trong bài thi TOEIC nhé!
https://www.anhngumshoa.com/tintuc/unit14vitrichucnangdongtutrongbaithitoeic35282.html
➡️ Xem lại chuỗi Livestream: https://bit.ly/playlist800toeic
▬▬▬▬
➡️ Đừng bỏ lỡ những video bài học chất như nước cất để chinh phục 800 TOEIC nhé:
1. Lộ trình học TOEIC dành cho người mất gốc: https://youtu.be/siM6FWhlXiA
2. Phương pháp luyện NGHE max điểm: https://bit.ly/2x3Moi1
3. Kỹ năng Reading PRO trong bài thi TOEIC: https://bit.ly/34juML7
4. Series TOEIC 4 kỹ năng online MIỄN PHÍ: https://bit.ly/34iK1Uq
5. Học từ vựng theo Collocation: https://bit.ly/2xUMbOb
6. Tips hay TOEIC mỗi ngày: https://bit.ly/39T02By
7. Chữa đề New Economy TOEIC: https://bit.ly/2yB98pJ
8. Hội cao thủ 800 TOEIC: https://bit.ly/3e7jD4k
➤ Đăng ký tư vấn khóa học: bit.ly/tuvantoeic
➤ Tham gia cộng đồng tự học 990 TOEIC: http://bit.ly/21ngayluyende
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
HỆ THỐNG CƠ SỞ ANH NGỮ MS HOA:
► HÀ NỘI:
CS1: 41 Tây Sơn, Đống Đa.
CS2: 461 Hoàng Quốc Việt, Cầu Giấy.
CS3: 141 Bạch Mai, Hai Bà Trưng.
CS4: Hồ Tùng Mậu Số 20 Nguyễn Đổng Chi, Nam Từ Liêm.
CS5: Liền kề 13, KĐT Bắc Hà, Mỗ Lao, Hà Đông.
CS6: 18 Nguyễn Văn Cừ, Long Biên, Hà Nội
► HỒ CHÍ MINH:
CS7: 49 A Phan Đăng Lưu, P.3, Q. Bình Thạnh.
CS8: 569 Sư Vạn Hạnh, P.13, Q.10.
CS9: 82 Lê Văn Việt, Phường Hiệp Phú, Q.9.
CS9: 427 Cộng Hòa, Phường 15, Q.Tân Bình.
CS11: 224 Khánh Hội, Phường 6, Q4.
CS12: L30.3 Khu dân cư Cityland Park Hills, Số 18 Phan Văn Trị, P.10, Q.Gò Vấp
CS13: 213 Kinh Dương Vương, Phường 13, Quận 6
► ĐÀ NẴNG:
CS14: 233 Nguyễn Văn Linh, Q. Thanh Khê.
CS15: 254 Tôn Đức Thắng, P. Hòa Minh, Q. Liên Chiểu.
►HẢI PHÒNG:
CS16: 448 Lạch Tray, Quận Ngô Quyền
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
🍓Website: www.anhngumshoa.com/
🍓Fanpage: www.facebook.com/mshoatoeic/
🍓Group: www.facebook.com/groups/toeic4kynang
🍓Holine: 0934 489 666
TIENGANHTOEIC MSHOATOEIC HOCTOEICONLINE ANHNGUMSHOA
![[Livestream] Unit 2 - Verb | Level mất gốc, cơ bản | Luyện thi TOEIC | Anh Ngữ Ms Hoa](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/oeRB3vfK7Os/hqdefault.jpg)
Stickman Verbs 2 – In the Morning – The Kids’ Picture Show (Fun \u0026 Educational Learning Video)
Learn action verbs in this video! Learn a morning routine!
Order our books on Amazon!
Vehicles: https://www.amazon.com/dp/1524790761
Animals: https://www.amazon.com/dp/1524790745
Order our books from Barnes \u0026 Noble!
Vehicles: https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/vehicleschieridegregorio/1128509300?ean=9781524790769
Animals: https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/animalschieridegregorio/1128509299?ean=9781524790745
Find our books at your local independent bookstore!
Vehicles: https://www.indiebound.org/book/9781524790769
Animals: https://www.indiebound.org/book/9781524790745
Publisher catalog page for Vehicles \u0026 Animals:
https://www.penguinrandomhouse.com/series/2PS/thekidspictureshow
TShirts on Amazon: http://amzn.to/2kEIuA9
Buy stickers on Redbubble: http://rdbl.co/2kdLVks
Kids’ Clothes on Redbubble: http://rdbl.co/2kem9Nd
The Kids’ Picture Show playlists:
Vehicles \u0026 Animals Book Versions: https://bit.ly/2IUXHht
Fun Learning Videos: https://bit.ly/2Tn8ntU
Vehicles: https://bit.ly/2H4p3Qz
Animals: https://bit.ly/2ED6Tlg
Shapes: https://bit.ly/2C6L79c
Colors: https://bit.ly/2C7YupD
Jigsaw Puzzles: https://bit.ly/2tRGnQ5
Songs: https://bit.ly/2NLuPXL
Dinosaurs: https://bit.ly/2SOSQOu
Patterns: https://bit.ly/2HnhpAd
ABC’s and Alphabet: https://bit.ly/2NMxK2r
Numbers and Counting: https://bit.ly/2XH6FSR
Fruit \u0026 Vegetables: https://bit.ly/2ThPYia
Addition with The Number Guys: https://bit.ly/2XHPIaT
Science and Nature: https://bit.ly/2XJ9eUC
Sight Words: https://bit.ly/2EI58mC
Vocabulary Flash Cards: https://bit.ly/2J6muiS
Communication Skills: https://bit.ly/2TmpBYF
Learn to Read: Phonics \u0026 Rhyming: https://bit.ly/2ES0XpV
Picture Card Phrases PECS: https://bit.ly/2XQlKSe
Life Instructions: https://bit.ly/2EDElIh
My Fridge: https://bit.ly/2VFYEeY
Poem of the Day: https://bit.ly/2Tjv822
Collections: https://bit.ly/2ERzGUp
All Videos: https://bit.ly/2NLa2DM
Follow us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/thekidspictureshow
Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/KidsPictureShow
Looking for a kids’ channel that’s not too \”kiddie?\” Check out the Kids’ Picture Show! Learn shapes, colors, numbers, the alphabet, communications skills and more. Check out our popular 8bit vehicles and animals, along with What Shape Is It?, color balls, dinosaurs and more.
The Kids’ Picture Show is an educational channel for toddlers, preschoolers, kindergartners and elementary schoolage students to learn language and life skills. Children can explore speaking, listening and reading through poems, songs, flash cards, and lots of funny videos.
Great for all kids including reluctant learners, visual learners, ESL students and even children with developmental disabilities such as autism.

Mother’s Love – How’s the weather? (Weather) – English cartoon story
http://www.youtube.com/user/EnglishSingsing9
Mother’s Love How’s the weather? English story for Kids
English Singsing! Learn English with stories.
This video in story category is that reconstruct famous fairy tale’s contents.
Subscribe to our channel, and you can find some more fun and exciting animation.
★ Subscribe us on YouTube: http://goo.gl/gDa963
★ More Our Story: https://goo.gl/iLerPf
Title : How’s the weather
Mother : How’s the weather?
Neighbor1: It’s raining.
Mother: Oh, no.
Mother: How’s the weather?
Neighbor2: It’s sunny.
Mother: Oh, no.
Neighbor3: Look, it’s raining.
Mother: Okay, sounds good.
Neighbor3: It’s sunny now.
Mother: That’s good.
Thanks for checking out the \”English Singsing\”.
© Amanta Inc.

Ngữ pháp: THUỘC LÒNG – Cách duy nhất để nhớ cấu trúc VERB S.O TO VERB. ( 2 )
Donate ủng hộ kênh:
Võ Minh Thạo. Số TK : 102870833895. Ngân Hàng Thương Mại Cổ Phần Công Thương Việt Nam. Chi Nhánh 12 TP HCM.
Rất cám ơn tấm lòng của Quý Khán Giả. Động lực để tôi cống hiến nhiều video hay và có ích hơn cho cộng đồng!
Xem thêm danh sách video bài học theo chủ đề \r
1. Bài giảng Thì Quá Khứ Đơn: http://bit.ly/2WfYsox\r
2. Bài giảng Thì Quá Khứ Tiếp Diễn: http://bit.ly/2qCKqkZ\r
3. Bài giảng Thì Hiện Tại Tiếp Diễn: http://bit.ly/2pGjjFg\r
4. Bài giảng Thì Hiện Tại Hoàn Thành: http://bit.ly/32ERN9F\r
5. Bài giảng Thì Tương Lai Gần: http://bit.ly/32AZptI\r
6. Từ vựng tiếng Anh theo chủ đề thông dụng: http://bit.ly/32D6HNy\r
7. Trắc nghiệm nâng cao Tiếng Anh: http://bit.ly/2Pe68pE\r
8. So Sánh Tính Từ: http://bit.ly/2PEeaGS\r
9. So Sánh Trạng Từ: http://bit.ly/2PcyG2d\r
\r
Cải thiện Tiếng Anh miễn phí và nhanh chóng cùng Dạy \u0026 Học Tiếng Anh\r
✔Đăng ký kênh để nhận được thông báo bài giảng mới nhất:\r
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC1LJ6s8dg3rURCTMiDrZxlg?sub_confirmation=1\r
✔ Official Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ThayThaodayvahoctienganh/\r
✔Liên hệ kênh: [email protected]

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆLEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ verb 2