past perfect tense: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
Past Perfect
![]()
Carla Muniz
O Past Perfect ou Past Perfect Simple (Passado Perfeito ou Passado Perfeito Simples) é um tempo verbal usado para expressar ações passadas que aconteceram antes de outra ação que também ocorrera no passado.
Nesse tempo verbal é comum as frases serem formadas por alguns advérbios.
Os mais utilizados são:
- when (quando)
- just (acabado de; há pouco)
- already (já)
- by the time (no momento)
- ever (já; alguma vez)
- never (nunca)
- before (antes)
- after (depois)
Exemplos:
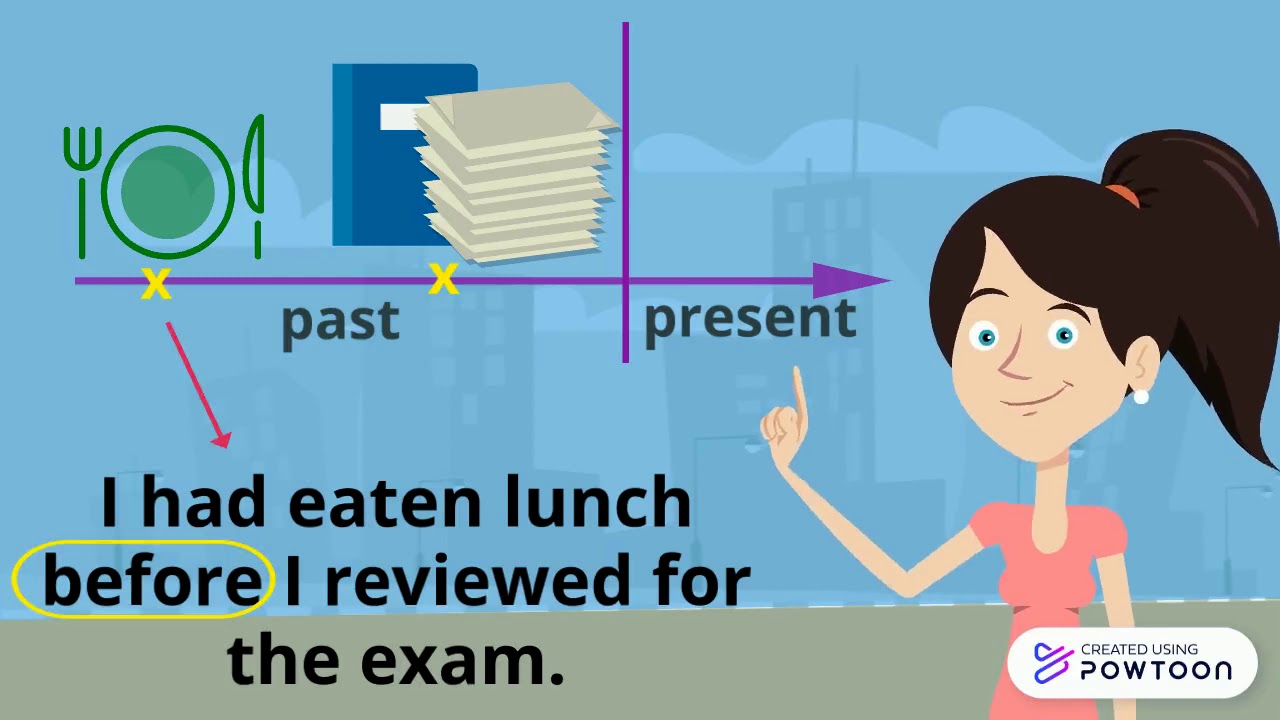
- I had already cleaned the house when my mother arrived. (Eu já tinha limpado a casa quando minha mãe chegou.)
- She had just left by the time he arrived. (Ela tinha acabado de sair quando ele chegou.)
- They did not come with us because they had visited this museum before. (Eles não vieram conosco porque tinham visitado este museu antes.)
- He asked me if I had ever been to Germany. (Ele me perguntou se eu já tinha estado na Alemanha.)
Formação do Past Perfect
O Past Perfect é formado pelo verbo auxiliar to have conjugado no Simple Past (had) + Past Participle do verbo principal.

Atenção! (Pay Attention!)
Todos os verbos regulares seguem um modelo de conjugação. No particípio passado, as flexões sempre são formadas pelo acréscimo das terminações –d, –ed ou –ied
Já os verbos irregulares, não seguem nenhum modelo ou regra de conjugação. Assim sendo, a melhor forma de conhecer suas flexões é consultar uma tabela de verbos.
Exemplos:
- Verbo to dance (regular) – particípio passado: danced
- Verbo to play (regular) – particípio passado: played
- Verbo to study (regular) – particípio passado: studied
- Verbo to go (irregular) – particípio passado: gone
- Verbo to be (irregular) – particípio passado: been
Veja também:
Verbos Irregulares em Inglês
Forma afirmativa (affirmative form)
As frases afirmativas no Past Perfect Simple são formadas da seguinte maneira:
Sujeito + verbo to have no Simple Past (had) + verbo principal no Past Participle + complemento
Exemplo:
You had changed your clothes before the end of the party. (Você tinha mudado suas roupas antes do final da festa).
Veja também:
Verbo To Have
Forma Negativa (negative form)
Nas frases negativas é necessário acrescentar o not após o verbo auxiliar:
Sujeito + verbo to have no Simple Past (had) + not + verbo principal no Past Participle + complemento
Exemplo:
You had not changed your clothes before the end of the party. (Você não tinha mudado suas roupas antes do final da festa.)
Veja também:
Passive Voice
Obs.: a forma negativa também pode ser escrita na forma contraída: had + not = hadn’t
Exemplo:
You hadn’t changed your clothes before the end of the party. (Você não tinha mudado suas roupas antes do final da festa.)
Veja também:
Simple Past
Forma Interrogativa (interrogative form)
Para fazer perguntas no Past Perfect Simple, o verbo auxiliar deve ser usado no início da frase, antes do sujeito:
Verbo to have no Simple Past + sujeito + verbo principal no Past Participle + complemento
Exemplo:
Had you changed your clothes before the end of the party? (Você tinha mudado suas roupas antes do fim da festa?)
Veja também:
Past Participle
Past Perfect Simple x Past Perfect Continuous
No Past Perfect Tense há duas formas de expressar ações passadas. Vejamos abaixo cada uma delas:
Past Perfect Simple
É usado para indicar ações no passado que ocorreram antes de outra ação no passado.
O Past Perfect Simple é formado pelo verbo auxiliar to have conjugado no Simple Past (had) + Past Participle do verbo principal.
Exemplos:
- I had finished the job when my boss arrived. (Eu tinha terminado o trabalho quando meu chefe chegou.) – AFFIRMATIVE FORM
- I had not finished the job when my boss arrived. (Eu não tinha terminado o trabalho quando meu chefe chegou.) – NEGATIVE FORM
- Had I finished the job when my boss arrived? (Eu tinha terminado o trabalho quando meu chefe chegou?) – INTERROGATIVE FORM
Veja também:
Verbos Regulares e Irregulares em Inglês
Past Perfect Continuous
É usado para indicar a continuidade de ações no passado que ocorreram antes de outra ação no passado.
O Past Perfect Continuous é formado pelo verbo to have conjugado no Simple Past (had) + verbo to be conjugado no Past Participle (been) + gerúndio do verbo principal.
Exemplos:
- I had been waiting for two hours when she arrived. (Eu tinha estado esperando por duas horas quando ela chegou.) – AFFIRMATIVE FORM
- I had not been waiting for two hours when she arrived. (Eu não tinha estado esperando por duas horas quando ela chegou.) – NEGATIVE FORM
- Had I been waiting for two hours when she arrived? (Eu tinha estado esperando por duas horas quando ela chegou?) – INTERROGATIVE FORM
Veja também:
Past Perfect Continuous
Complemente sua pesquisa sobre os verbos em inglês:
Vídeo (Video)
Assista o vídeo abaixo com um resumo do uso do Past Perfect e fique por dentro desse tempo verbal.
Exercícios (Exercises)
1. (Fundatec/2015)
Press me! The button that lies to you
The tube pulls in to a busy station along the London Underground’s Central Line. It is early evening on a Thursday. A gaggle of commuters assembles inside and outside the train, waiting for the doors to open. A moment of impatience grips one man who is nearest to them. He pushes the square, green-rimmed button which says “open”. A second later, the doors satisfyingly part. The crowds mingle, jostling on and off the train, and their journeys continue. Yet whether or not the traveller knew it, his finger had no effect on the mechanism.
Some would call this a “placebo button”– a button which, objectively speaking, provides no control over a system, but which to the user at least is psychologically fulfilling to push. It turns out that there are plentiful examples of buttons which do nothing and indeed other technologies which are purposefully designed to deceive us. But here’s the really surprising thing. Many increasingly argue that we actually benefit from the illusion that we are in control of something – even when, from the observer’s point of view, we’re not.
In 2013, BBC News Magazine discovered that pedestrian crossings all over the UK were the wellspring of placebo buttons. A crossing in central London had programmed intervals for red and green lights, for example. Pushing the button would only impact the length of these intervals between midnight and 7am. ___ several other cities during busy periods, the crossings were programmed to alternate their signals at a specific rate. The buttons did nothing, but a “wait” light would still come on when they were pressed and, yes, people still pressed them presumably believing that their actions were having an effect.
Certain psychologists would argue that the buttons were indeed having an effect – just not ___ the traffic lights themselves. Instead the effect is in the commuter’s minds. To understand this you have to go back to the early 1970s. At that time, psychologist Ellen Langer, now a professor ____ Harvard, was a Yale graduate student. During a five-card draw game of poker she dealt one set of cards in a haphazard order. “Everybody,” she says, “got crazy. The cards somehow belonged to the other person even though you couldn’t see any of them.” Langer decided to find out more about the way people regulated the playing of such games. She went to a casino where, at the slot machines, she found gamblers with elaborate ways of pulling the lever. At another time a “highly rational” fellow student tried to explain to her why tossing a pair of dice could be done in a certain way to affect the numbers which came up. “People believed that all of these behaviours were going to increase the probability of their winning,” she comments.
In 1975, she wrote a paper where she described the significance of these beliefs and coined a term for the effect that they had on people: the “illusion of control”. However, instead of framing this as an irrational delusion, Langer described the effect as a positive thing. “Feeling you have control over your world is a desirable state,” she explains. When it comes to those deceptive traffic light buttons, Langer says there could be a whole host of reasons why the placebo effect might be counted as a good thing. “Doing something is better than doing nothing, so people believe,” she says. “And when you go to press the button your attention is on the activity at hand. If I’m just standing at the corner, I may not even see the light change, or I might only catch the last part of the change, in which case I could put myself in danger.”
Also, if pedestrians wait together at the crossing and a few press the button impatiently, that creates a sense of togetherness with strangers which might otherwise be absent. All of these things may be taken as positive impacts on our mental state, and even socially reinforcing. It’s something to think about next time you cross the street.
(Source: Adapted from http://www.bbc.com/future/story/20150415-the-buttons-that-do-nothing)
In the sentence “A crossing in central London had programmed intervals for red and green lights”, the underlined verbal locution is in the ________________. If we put it in the present perfect continuous, it would be written as ______________.
Mark the alternative that correctly and respectively fill in the blanks above.
a) past perfect – had been programming
b) past perfect – has been programming
c) present perfect – have been programmed
d) present perfect – have being programmed
e) simple past – has programming
Ver Resposta
Alternativa correta: b) past perfect – has been programming
A letra b) é a alternativa correta pois “had programmed” segue a estrutura de formação do Past Perfect : had + verbo principal (neste caso to program) no Past Participle (programmed).
Para que a parte destacada da frase passe para o Present Perfect Continuous, devemos seguir a seguinte estrutura:
Present Perfect do verbo to be (has been) + verbo principal no gerúndio (programming).
2. Qual das frases abaixo não está no Past Perfect Simple:
a) Had you been waiting long before the airplane arrived?
b) You had not studied English before you moved to Brazil.
c) We had had that car for fifteen years before it broke down.
d) Before I came here, I had spoken to Jonh.
e) He had written a letter to Carlos.
Ver Resposta
Alternativa correta: a) Had you been waiting long before the airplane arrived?
A alternativa a) apresenta dois tempos verbais mas nenhum deles é o Past Perfect: 1) Past Perfect Continuous (had been waiting) e 2) Simple Past (arrived).
Veja também:
Third Conditional
3. Escreva a frase abaixo no Past Perfect Simple nas formas afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa:
I watched a good film this weekend.
Ver Resposta
AFFIRMATIVE FORM:
I had watched a good film this weekend.
Para formar frases afirmativas no Past Perfect, basta seguir a seguinte estrutura:
Sujeito + verbo to have no Simple Past (had) + verbo principal no Past Participle + complemento
NEGATIVE FORM:
I had not watched a good film this weekend.
Para formar frases negativas no Past Perfect, basta seguir a seguinte estrutura:
Sujeito + verbo to have no Simple Past (had) + not + verbo principal no Past Participle + complemento
INTERROGATIVE FORM:
Had I watched a good film this weekend?
Para formar frases interrogativas no Past Perfect, basta seguir a seguinte estrutura:
Verbo to have no Simple Past (had) + sujeito + verbo principal no Past Participle + complemento
Veja também:
Past Continuous
4. Conjugue o verbo to have na forma afirmativa do Past Perfect Simple:
Ver Resposta
I had had
You had had
He/She/It had had
We had had
You had had
They had had
Para formar frases afirmativas no Past Perfect, basta seguir a seguinte estrutura:
Sujeito + verbo to have no Simple Past (had) + verbo principal no Past Participle + complemento.
Confira um exemplo de frase com o verbo to have flexionado no Past Perfect Simple:
If I had had the opportunity, I would have studied abroad. (Se eu tivesse tido oportunidade, teria estudado no exterior.)
É importante referir que no Past Perfect, as flexões verbais são iguais para todos os pronomes pessoais.
Veja também:
Present Perfect Continuous
![]()
[Update] Past Perfect Tense (Miş’li Geçmiş Zaman): İngilizce Türkçe Detaylı Konu Anlatımı + Örnek Cümleler | past perfect tense – NATAVIGUIDES
İngilizcede zamanları öğrenmek ve doğru kullanmak, oldukça önemli. Bunun ana sebebi de bir olayı anlatmak istediğinizde fiilin çekimine dikkat edilmediğinde karşı tarafa mevzuyu doğru bir biçimde aktaramama durumudur. Bu sıkıntıyla ise en çok Past Perfect Tense kullanımlarında karşılaşıyoruz. Çünkü geçmiş zamana dair anlatımda bulunurken kullanabileceğiniz birden fazla tensiniz var ve bu tenslerden belki de en az kullanılanı.
Peki past perfect tense kullanımı nerelerde geçerli, hangi durumlarda kullanmanız uygun? İşlevleri, cümle yapısı ve örnekleri ile incelemeye ne dersiniz?

Past Perfect Tense Nedir?
Past Perfect, Türkçe’ye tam olarak çevrilemeyen bir kalıp olsa da –miş’li geçmiş zaman anlamı taşıyor.
Diyeceksiniz ki, ‘past simple var, geçmiş zamanı anlatmaya yetmiyor mu?’ İki tensin arasında belirgin farklılıklar olmakla beraber past perfect, past simple’dan önce gerçekleşen olayları anlatmak için tercih ediliyor.
Kısaca özetlemek gerekirse; iki olay olduğunu düşünelim. Bu olayların meydana gelme zamanlarını kıyaslayalım. İkisi de geçmişte oluyor, ancak biri daha önce diğeri de ondan sonra gerçekleşiyor. Önce olan için -mişli geçmiş kullanırken sonraki için sadece geçmiş zaman kullanmanız yeterli olacaktır.
Örnek:
- I had finished to cook the dinner when they arrived.
Onlar geldiğinde ben akşam yemeğini pişirmeyi bitirmiştim.
Burada önce yemeğin pişirilmesi olayının gerçekleştiğini, bu olay bittikten sonra da onların geldiğini görüyoruz. Yani pişirme olayı gelme olayından daha önce gerçekleştiği için past perfect yapısında, gelme eylemi de past simple formunda.

Past Perfect Tense’in Kullanım Yerleri
Past perfect tensi nerelerde kullanacağınızı iyi öğrenirseniz, diğer formlardan farkını rahatlıkla görebilir ve böylelikle karıştırmazsınız.
Geçmişte Olan İki Olaydan Önce Olanı Anlatırken
İki olay da olmuş, bitmiş ve tüm bunlar geçmiş bir zamanda meydana gelmişse daha önce olan olayı anlatmak için past perfect tense başvururuz. Sonraki olay ise past simple ile belirtilir.
Örnek:
- I had already finished my exam when the teacher said it was over.
Öğretmen sürenin dolduğunu söylediğinde ben çoktan sınavımı bitirmiştim. (Önce sınavı bitirmiş, sonra öğretmen sürenin bittiğini söylemiş.)
- She had watered the flowers before she went shopping.
Alışverişe gitmeden önce çiçekleri sulamıştı. (Önce çiçekleri sulamış, sonra alışverişe gitmiş.)
- They went to the cinema after they had finished work.
İşi bitirdikten sonra sinemaya gitmişlerdi. (Önce işi bitirmişler, sonra sinemaya gitmişler.)
Geçmişte Olup Biten ve Etkileri de Geçmişte Kalan Olayları Anlatırken
Gerçekleşen olay ve o olayın etkileri geçmişte kalmışsa past perfect tercih edilir.
Örnek:
- He had been a pilot for thirty five years when he got retired.
Emekli olduğunda 35 yıldır pilottu.
- She was very happy, she had bought a new dress to herself.
Çok mutluydu, kendine yeni bir elbise almıştı.
- Geçmişte Planlanmış Ama Yapılmamış Eylemleri Anlatırken
Geçmişe dair gerçekleşmemiş planlar ve isteklerden bahsederken past perfect tense kullanılır.
Örnek:
- I had wanted to go the Opera House when I was in Paris.
Pariste olduğum sırada Opera Binası’na gitmek istemiştim. (Gitmek istemiş ancak gidememiş.)
- He hadn’t studied to math exam.
Matematik sınavına çalışmamıştı. (Çalışması gerekirdi, ancak çalışmadı.)

Past Perfect Tense Cümle Yapısı
Past tenslerde present tenslerden farklı olarak verb yani fiil farklı çekimlenir. Geçmiş zaman kipini belirtmek amacıyla past perfect tensin kullanıldığı cümlelerin fiilleri takısı alır veya formu kullanılır.
Cümleye anlamı kazandırabilmek için fiiller V3 formuna çekimlenir. Ancak İngilizcedeki fiillerin hepsi aynı düzende değildir. ‘Düzenli fiiller’ dediklerimizin sonlarına ‘-ed’ eki eklenir. (worked, played, finished gibi…)
Düzensiz fiiller ise V3 formu olarak her fiilde farklılık gösterir ve ezberlenmesi gerekir.
(go- gone, do-done, tell-told, pay-paid, give-given gibi…)
Past Perfect ile Olumlu Cümle Yapısı
Past perfect için olumlu cümle kurarken özneye göre değişkenlik oluşmaz. (was/were gibi)
Cümleler aşağıdaki formüle uygun olarak kurulur;
/ Özne + Had + Yüklem (3. hâli) + Nesne
ÖZNE /YARDIMCI FİİL/ FİİL /NESNE /
I
He
She
It
We
You
They
had
washed
the car
Örnekler:
- The concert had finished before we went home back.
Biz eve geri dönmeden önce konser bitmişti. - I had just started to reading when you came in.
İçeri girdiğinde okumaya henüz başlamıştım. - They had already gone when I came in.
İçeri girdiğimde çoktan gitmişlerdi.
Past Perfect ile Olumsuz Cümle Yapısı
-Miş’li geçmiş zaman formunda olumsuz bir cümle kurmak istiyorsanız yardımcı fiilinize olumsuzluk eki eklemeniz gerekir.
Cümleler aşağıdaki formüle uygun olarak kurulur;
/ Özne + Had + Not + Yüklem (3. hâli) + Nesne
ÖZNE /YARDIMCI FİİL/ AUXILIARY VERBSFİİL /NESNE /
I
He
She
It
We
You
They
hadn’t (had not)
washed
the car
Örnekler:
- I hadn’t written anything to her yet.
Ona henüz bir şey yazmadım. - He hadn’t helped to his mother.
Annesine yardım etmemişti. - You hadn’t ever seen a movie like this.
Daha önce böyle bir film görmemiştin.
Past Perfect ile Soru Cümlesi Yapısı
Soru cümlesi kurmak için yardımcı fiilin cümlenin başına geldiğini biliyoruz. Aynı durum past perfect için de değişmiyor ve ‘had’ yardımcı fiili cümlenin başına geliyor.
Soru cümleleri aşağıdaki formüle uygun olarak kurulur;
/ Had + Özne + Yüklem (3. hâli) + Nesne?
YARDIMCI FİİL/ AUXILIARY VERBSÖZNE /FİİL /NESNE /
Had
I
He
She
It
We
You
They
washed
the car?
Örnekler:
- Had you ever visited Italy?
İtalya’yı hiç ziyaret etmiş miydin? - When had she played the volleyball?
O voleybolu ne zaman oynamıştı? - Had you eaten anything outside?
Dışarıda herhangi bir şey yemiş miydin?
Not: Soru cümlelerine cevap verirken kısa cevaplarda şu formları kullanabilirsiniz:
Yes, I/ He/ She/ It/ You/ We/ They had.
No, I/ He/ She/ It/ You/ We/ They hadn’t/ had not.
Past Perfect Tense ile Kullanılan Zaman Zarfları
Cümledeki anlam ayrımını sağlayabilmek amacıyla past perfect tenslerde sıklıkla zaman zarfları kullanılır. En sık kullanılan zaman zarfları ve Türkçe anlamları aşağıdaki gibidir.
After: -den sonra
Already: çoktan
Before: -den önce
By the time/ By/ Until: -e kadar
For/ Since: -den beri
Just: Henüz, yeni, az önce.
Yet: Henüz
When: -dığında

Cambly ile Çalışın Eksiklerinizi Tamamlayın
Her geçen gün öğrendiklerinizin üzerine bir yenisini ekleseniz de past perfect tense için çok zaman ayırmak, bol alıştırma yapmak gerekebilir. Özellikle present perfect ile ve past simple ile sık sık karıştırılan bir tense olması, bu konuyu oldukça önemli kılıyor. Örnek cümleler, boşluk doldurma alıştırmaları ve konuşma diyalogları ile konuyu pekiştirmek mümkün.
Ama neden bir uzmanla birlikte çalışarak bir üst seviyeye geçmeyesiniz ki?
İşte Cambly bunun için var. Ana dili İngilizce olan eğitmen kadrosu ile dilediğiniz yerde, evde, işte, ofiste hatta yolda online uygulama üzerinden iletişim kurabileceğiniz bu platform, size rahat rahat çalışma fırsatı sunacak. Kendi seçeceğiniz eğitmen ile dilediğiniz gün ve saat için randevu alarak özel dersinize katılabilirsiniz.
Online videolu görüşme şeklinde gerçekleşen birebir derslerde konuşma pratiği, gramer konu anlatımı ve çok daha fazlasını eğitmeniniz ile çalışabilirsiniz. Üstelik ‘blog100’ kodunu kullananlara ilk 10 dakikalık deneme dersi ücretsiz! Şimdi vakit kaybetmeden hemen pratik yap butonuna tıklayıp CAMBLY ile İngilizcenizi geliştirmenin kolaylığını yaşayın.
Learn English Tenses: PAST PERFECT
Do you ever use the PAST PERFECT TENSE (“I had worked”)? Do you know this advanced tense can help you talk about the past in a special way? In this English grammar class, I’ll teach you when to use this tense, how to use it, and what mistakes to avoid. You will learn: structure, usage, pronunciation, spelling, contractions, questions, short answers, past participles, and irregular verbs. We’ll go forward systematically and practice together, so you understand fully. This class is part of the engVid program on ALL the English verb tenses, designed to take your English to a higher level for career growth or academic success on English exams like the IELTS or TOEFL. The next class in this series compares the past simple and past perfect tenses.
Take the quiz: https://www.engvid.com/pastperfect/
In this lesson:
Past Perfect: Overview 0:00
When to use the Past Perfect tense 4:07
How to use the Past Perfect tense 8:51
Past Perfect: Common Expressions 16:44
Past Perfect: Contractions 22:35
Past Perfect: Short Answers 27:51
Past Perfect: Spelling \u0026 Pronunciation 30:56
Past Perfect: Practice 36:50
Past Perfect: Common Errors 40:43
Past Perfect: Conclusion 45:40
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่

Past Perfect
A short video explaining the \”past perfect\” tense.
Practice here: http://www.teacherdiane.com/youtube/page1
Learn English on Skype: http://www.teacherdiane.com
Follow Teacher Diane on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/teacherdianeESL

Past Perfect Tense
PastPerfectTense Educatoon
This video is about past perfect tense.
You may also follow me on Facebook at https://www.facebook.com/ayacabotaje
or on Instagram @aya.alforo for more teaching and learning updates.
Happy teaching! Happy learning!
Created using Powtoon
Học Tiếng Anh Qua Bài Hát | Perfect Vietsub 1 Hour Version | TOPICA Native
Truy cập ngay kho tài liệu Tiếng Anh giao tiếp phù hợp với mọi trình độ tại: https://topicanative.edu.vn/
Học Tiếng Anh Qua Bài Hát Perfect 1 hour version được vietsub bởi tiếng Anh giao tiếp TOPICA Native.
Cùng lắng nghe bản tình ca Perfect đầy ngọt ngào trong những giai điệu tình yêu phiên bản 1 giờ và học những từ vựng tiếng Anh thú vị thường dùng trong giao tiếp cùng chúng mình nhé.
Chuyên mục Học tiếng Anh qua bài hát giúp bạn vừa cập nhật những bài hát mới, vừa nâng cao khả năng giao tiếp tiếng Anh của bạn một cách hiệu quả.
Làm thế nào để học tiếng Anh? Học tiếng Anh trong khi ngủ. Video này có các từ và cụm từ tiếng Anh cơ bản và quan trọng nhất có thể dậy ngữ pháp một cách tự động. Chúng đặc biệt hữu ích cho người mới bắt đầu học các ngôn ngữ này. Và nó sẽ giúp bạn cải thiện kỹ năng nghe và nói của mình. Để sử dụng chỉ cần bật video trước khi ngủ.
Mục tiêu là cơ thể ở trong trạng thái thoải mái và thư giãn. Sử dụng tai nghe nếu bạn cần. Thời điểm tốt nhất là ngay trước khi bạn đi ngủ. Kế hoạch: nghe thường xuyên nhất có thể cho đến khi các từ và cụm từ nghe rất tự nhiên với bạn. Bạn sẽ hiểu các từ này rất rõ nếu bạn nghe chúng thường xuyên. Những từ và cụm từ này rất hữu ích trong cuộc sống hàng ngày.
👉 NHẤN ĐĂNG KÝ THEO DÕI (SUBSCRIBE) để Học tiếng Anh qua bài hát với phương pháp ĐỘC QUYỀN từ TOPICA Native tại http://topi.ca/ESW
===============================================================
XEM THÊM:
Full PDF+Audio tài liệu luyện nghe cho người mới bắt đầu: https://topicanative.edu.vn/tailieu/fullpdfaudioluyennghechonguoimoibatdau/
4000 từ vựng thường dùng nhất trong Tiếng Anh: https://topicanative.edu.vn/tailieu/4000tuvungthuongdungnhattrongtienganh/
Các khóa học Tiếng Anh giao tiếp online: https://topicanative.edu.vn/tongquancackhoahoctienganhgiaotiep/
Kiểm tra trình độ hoàn toàn miễn phí: https://topicanative.edu.vn/freetest/kiemtratrinhdotienganhgiaotiep/
NGHE NHẠC HỌC TIẾNG ANH Ở ĐÂY:
Những bài hát hot nhất: https://youtu.be/agf0s54xQzs
Những bài hát tiếng Anh phải nghe: https://youtu.be/tWDjZ9t4cfM
Bài hát được YÊU THÍCH NHẤT: https://youtu.be/XhLDoYWr9D0
================================================================
HocTiengAnhQuaBaiHat Perfect TopicaNative
XEM LẠI VIDEO NÀY BẰNG CÁCH GÕ TỪ KHOÁ TRÊN YOUTUBE: \”Tiếng Anh giao tiếp cơ bản\”, \”luyện nghe tiếng Anh giao tiếp\”, \”các thì tiếng Anh\”, \”từ vựng tiếng Anh theo chủ đề\”, \”học tiếng Anh\” + \”TOPICA Native\”
KẾT NỐI VỚI TOPICA NATIVE Luyện Nói Online Thỏa Thích với giáo viên Âu Úc Mỹ tại các kênh sau:
►Youtube: http://topi.ca/youtubechannel
►Website: https://topicanative.edu.vn
►Fanpage: http://topi.ca/fanpagetopica
►Học tiếng Anh qua tin nhắn Messenger: http://topi.ca/GCW
►Để lại số điện thoại/ email nếu bạn muốn nhận tư vấn của chương trình : http://topi.ca/yt2020

7- شرح زمن الماضي التام في اللغه الانجليزيه Past Perfect
درس شرح قاعدة او زمن الماضي التام Past Perfect في اللغه الانجليزيه , والحقيقه انه من اكثر الدروس التي طلبها المتابعين الكرام لدروس اللغه الانجليزيه نظرا لاعتقادهم انه زمن صعب و يواجهون الكثير من المشاكل مع فهم الماضي التام او الـ Past Perfect .
لكن احب ان ازف لك الخبر السعيد وهو ان هذا الزمن فعلياً من اسهل الازمنه في اللغه الانجليزيه وستكتشف بنفسك في الفيديو
كما يمكنك مشاهدة الدروس السابقه من هنا :
شرح زمن الماضي البسيط Past Simple
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rlbFDiuwlF0
شرح زمن المضارع البسيط Present Simple
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5TjpEcrNbCc
شرح زمن المستقبل البسيط Future Simple
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TDhm2xLyg8
شرح زمن الماضي المستمر Past Continuous
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZqQG54ydsY
شرح زمن المضارع المستمر Present Continuous
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oBzkMfEXj1s
شرح زمن المستقبل المستمر Future Continuous
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q2Vkhcvq9uw
وهذا رابط صفحتنا علي فيسبوك:
http://www.facebook.com/droosonline
وهذا الايميل الشخصي لي:
droosonilne4u@gmail.com
وهذا هو موقعنا:
http://www.droosonline.com

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่MAKE MONEY ONLINE
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ past perfect tense