กริยา 3 ช่อง climb: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
รวมเฉลย Exercise พร้อมคำอธิบายละเอียด!
Chapter 1 : Part of Speech
Chapter 2 : Determiner
Chapter 3 : Tense
Chapter 4 : Sentence Structure
Chapter 5 : Question
Chapter 6 : Negative Sentence
Chapter 7 : Imperative Sentence
Chapter 8 : Subject-Verb Agreement
Chapter 9 : Subjunctive Sentence
Chapter 10 : Reported Speech
Chapter 11 : Relative Clause
Chapter 12 : Participles
Chapter 13 : Active-Passive Voice
Chapter 14 : Comparison
Chapter 15 : If-Clause
———————————————————————–
Chapter 1 : Part of Speech
Noun
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
คำนามหน้าตาแบบนี้เป็นประเภทไหนกันนะ ดูำศัพท์ที่ให้มา แล้วเติมคำตอบลงในช่องว่างเลย!
Common Noun = 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9
Proper Noun = 3, 6, 7, 10
Countable Noun = 2, 5, 9
Uncountable Noun = 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10
Singular Noun = 2, 4, 8, 9
Plural Noun = 1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ช่วยวงกลมคำนามในประโยค และบอกหน้าที่ของคำนามนั้นให้หน่อยนะ!
Subject Object of Preposition
(ตัวอย่าง) Hermione is known for her intelligence.
Subject Subject Complement
1. His name is Harry.
Object of Preposition Object of Preposition
2. He lived with his uncle and aunt in England.
Subject Direct Object
3. Harry was invited to join a school.
Subject Subject Complement
4. This school is a magical school.
Direct Object Object of Preposition
5. He met Ron and Hermione on the train.
Object Complement
6. He introduced himself and said, “You can call me Harry”.
Subject Subject Complement
7. Ron and Hermione became Harry’s best friends.
Subject Indirect Object Direct Object
8. Ron gave Harry a sweater.
Subject Subject Complement Object of Preposition
9. Dolores is a professor at the school.
Subject Direct Object
10. Harry rides a broomstick very well.
Verb
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
คำกริยาที่ขีดเส้นใต้ในประโยคต่อไปนี้เป็นคำกริยาประเภทไหนกันนะ กากบาทในช่องสี่เหลี่ยมที่ถูกต้องเลย!

1. My parents have just arrived at the airport.
-
arrive (V.1) / arrived (V.2) / arrived (V.3) – เป็น Intransitive Verb (ไม่ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Regular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบปกติโดยการเติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้ arrive (V.) ใช้ Present Perfect Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เพิ่งเกิดขึ้นและจบไป หรือเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นชั่วระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และยังส่งผลมาถึงปัจจุบัน จึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + have/has + V.3
-
ทั้งนี้ arrive (V.) เป็น Intransitive Verb เพราะไม่ต้องมีกรรม (O) มารองรับ สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้ เช่น They have arrived. = พวกเขามาถึงแล้ว หากต้องการขยายเพิ่มว่ามาถึงที่ไหน สามารถเติมคำบุพบท (Prepo.) บอกสถานที่เข้าไปได้ เช่น They have arrived at the supermarket. = พวกเขามาถึงที่ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ตแล้ว
2. All students are sitting at the desk.
-
sit (V.1) / sat (V.2) / sat (V.3) – เป็น Intransitive Verb (ไม่ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Irregular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบเปลี่ยนรูปไปไม่ได้เติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้
sit (V.) ใช้ Present Continuous Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นอยู่ในปัจจุบัน จึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + is/am/are + V.ing
-
ทั้งนี้ sit (V.) เป็น Intransitive Verb เพราะไม่ต้องมีกรรม (O) มารองรับ สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้ เช่น The boy is sitting. = เด็กผู้ชายกำลังนั่งอยู่ หากต้องการขยายเพิ่มว่านั่งอยู่ที่ไหน หรือบนสิ่งของอะไร สามารถเติมคำบุพบท (Prepo.) บอกสถานที่เข้าไปได้
เช่น
The boy is sitting in the classroom. = เด็กผู้ชายกำลังนั่งอยู่ในห้องเรียน หรือ The boy is sitting on the couch. = เด็กผู้ชายกำลังนั่งอยู่บนโซฟา
3. Nicole opened the birthday gift.
-
open (V.1) / opened (V.2) / opened (V.3) – เป็น Transitive Verb (ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Regular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบปกติโดยการเติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้
open (V.) ใช้ Past Simple Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นและจบลงอย่างสมบูรณ์แล้วในอดีต จึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + V.2
-
ทั้งนี้ open (V.) เป็น Transitive Verb เพราะต้องมีกรรม (O.) มารองรับ ไม่สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้ เช่น He opens the door for me. = เขาเปิดประตูให้ฉัน => the door ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรม (O.) ของ open (V.)
และในประโยค
Nicole opened the birthday gift. = นิโคลเปิด/แกะของขวัญวันเกิด => the birthday gift ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรม (O.) ของ open (V.)
4. James always asks the teacher a question.
-
ask (V.1) / asked (V.2) / asked (V.3) – เป็น Transitive Verb (ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Regular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบปกติโดยการเติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้
ask (V.) ใช้ Present Simple Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำหรือพูดถึงโดยทั่วไปในปัจจุบัน จึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + V.1 (กริยาผันตามประธานเอกพจน์/พหูพจน์)
-
ทั้งนี้
ask (V.) เป็น Transitive Verb เพราะต้องมีกรรม (O.) มารองรับเสมอ ไม่สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้
โดยปกติแล้ว ask (V.) สามารถตามด้วยกรรมตรง (Direct Object) ที่เป็นสิ่งของ และกรรมรอง (Indirect Object) ที่เป็นคน ในประโยคเดียวกันได้เลยดังเช่นประโยคที่ให้มา
ซึ่งคำกริยานี้มักใช้โครงสร้าง
to ask someone (IO.) something (DO.)
James asks the teacher a question. = เจมส์ถามคำถามกับคุณครู => the teacher เป็นกรรมรอง (IO.) และ a question เป็นกรรมตรง (DO.)
ตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม เช่น
He asked me to join his team. = เขาขอให้ฉันเข้าร่วมกับทีมเขา => ask ในที่นี้แปลว่า ขอ, ร้องขอ ได้เช่นกัน และ me เป็นกรรมตรง (DO.) แต่ไม่ใช่กรรมรอง (IO.) นะ เพราะว่ากรรมรอง (IO.) จะมีหรือไม่มีใ
ประโยคก็ได้ แต่กรรมตรง (DO.) ต้องมีเสมอ
5. My boyfriend gave me a watch.
-
give (V.1) / gave (V.2) / given (V.3) – เป็น Transitive Verb (ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Irregular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบเปลี่ยนรูปไป ไม่ได้เติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้
give (V.) ใช้ Past Simple Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นและจบลงอย่างสมบูรณ์แล้วในอดีตจึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + V.2
-
ทั้งนี้
give (V.) เป็น Transitive Verb เพราะต้องมีกรรม (O.) มารองรับเสมอ ไม่สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้
โดยปกติแล้ว give (V.) สามารถตามด้วยกรรมตรง (Direct Object)
ที่เป็นสิ่งของ และกรรมรอง (Indirect Object) ที่เป็นคน ในประโยคเดียวกันได้เลยดังเช่นข้อที่แล้ว
ซึ่งคำกริยานี้ก็ใช้โครงสร้าง
to give someone (IO.) something (DO.)
ด้วยเช่นกัน
My boyfriend gave me a watch. = แฟนของฉันให้นาฬิกาข้อมือกับฉัน => me เป็นกรรมรอง (IO.) และ a watch เป็นกรรมตรง (DO.)
ตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม เช่น I gave an apple to a boy = ฉันให้แอปเปิลผลหนึ่งกับเด็กผู้ชายคนหนึ่ง => an apple เป็นกรรมตรง (DO.) และ a boy เป็นกรรมรอง (IO.)

1. I saw a cat climbing a tree.
เป็น Irregular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 เปลี่ยนรูปไปเลยเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = see V.2 = saw V.3 = seen
2. Our family went to Phuket together last summer.
เป็น Irregular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 เปลี่ยนรูปไปเลยเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = go V.2 = went V.3 = gone
3. We watched a movie on Netflix.
เป็น Regular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 มีรูปแบบการเติม -ed เหมือนกันเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = watch V.2 = watched V.3 = watched
4. Have you ever been to Cambridge?
เป็น Irregular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 เปลี่ยนรูปไปเลยเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = be (is/am/are) V.2 = was/were V.3 = been
5. He has stayed with his grandmother for 2 years.
เป็น Regular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 มีรูปแบบการเติม -ed เหมือนกันเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = stay V.2 = stayed V.3 = stayed

1. The dinner smells very nice.
เป็น Linking Verb เพราะตามมาด้วยคำคุณศัพท์ (Adj.) ที่บ่งบอกลักษณะของประธานข้างหน้า (The dinner) ว่าเป็นอย่างไร
2. He became the first love of my life.
เป็น Linking Verb เพราะตามมาด้วยคำนาม (N.) ที่บ่งบอกว่าประธานข้างหน้า (He) เป็นใคร โดย became เป็น Past Tense
ของ become นั่นเอง
3. I should go now.
เป็น Modal Verb เพราะ should + คำกริยาที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V. infinitive) คือ go ซึ่งเป็นไปตามกฎของการใช้ Modal Verb
4. Lisa may write a letter to her idol tomorrow.
เป็น Modal Verb เพราะ may + คำกริยาที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V. infinitive) คือ write ซึ่งเป็นไปตามกฎของการใช้ Modal Verb
5. Jenny was my best friend during high school.
เป็น Linking Verb เพราะตามมาด้วยคำนาม (N.) ที่บ่งบอกว่าประธานข้างหน้า (Jennie) เป็นใคร โดย was เป็น Past Tense
ของ V. to be นั่นเอง
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
Track 3
เติมคำกริยาที่ได้ยินในประโยค และวงกลมเลือกประเภทของคำกริยานั้นให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) What time _____is_____ it now? (Main Verb | Helping Verb)
ตอบ is เป็น Main Verb เพราะว่าในประโยคนี้มีกริยาอยู่ตัวเดียว ซึ่งหากขาด is ไปจะไม่เป็นประโยคที่สมบูรณ์และสื่อความหมายไม่ได้
1. Do you know what time it is? (Transitive Verb | Intransitive Verb)
ตอบ know เป็น Transitive Verb เพราะว่ามี wh-clause ที่ตามหลังมา คือ what time it is ซึ่งมีความหมายว่า เป็นเวลากี่โมง ทำหน้าที่
เสมือนกรรมของ V. know ความจริงแล้วนั้น know สามารถเป็นได้ทั้ง Transitive Verb และ Intransitive Verb แต่ขึ้นอยู่กับความหมาย
ของแต่ละประโยค
2. Do you have the time? (Helping Verb | Main Verb)
ตอบ Do เป็น Helping Verb เพราะว่าต้องใช้ V. to do ที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นคำกริยาช่วยมาช่วยสร้างประโยคคำถามเสมอ โดยคำกริยาช่วยนี้จะไม่มี
ความหมายในตัวเอง แต่มี have เป็นคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) และมีความหมายว่า “มี”
3. Could you tell me the time? (Helping Verb | Modal Verb)
ตอบ Could เป็น Modal Verb เพราะว่าเป็นคำกริยาช่วยชนิดหนึ่งที่ไม่สามารถอยู่เดี่ยว ๆ หรือเป็นคำกริยาหลักในประโยคอย่าง Helping Verb
อื่น ๆ (V. to be, V. to do และ V. to have) ได้ นอกจากนี้ Modal Verb + V. infinitive เสมอ ซึ่งในข้อนี้คือ Could + tell
4. Do you happen to have the time? (Main Verb | Linking Verb)
ตอบ happen เป็น Main Verb เพราะว่าใช้ Do ซึ่งเป็น Helping Verb มาช่วยในการสร้างประโยคคำถามแล้ว สิ่งที่ขาดจึงเป็นคำกริยาหลัก
(Main Verb) โดยเหตุผลที่ have ไม่ใช่ Main Verb เพราะว่าตามหลัง to ซึ่งเราเรียกคำกริยาประเภทนี้ว่า V. infinitive with to นั่นเอง
5. What time will the meeting start? (Main Verb | Modal Verb)
ตอบ will เป็น Modal Verb เพราะว่าเป็นคำกริยาช่วยชนิดหนึ่งที่ไม่สามารถอยู่เดี่ยว ๆ ได้ โดยคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ของประโยคนี้คือ start
6. When will you come back home? (Main Verb | Modal Verb)
ตอบ will เป็น Modal Verb เพราะว่าเป็นคำกริยาช่วยชนิดหนึ่งที่ไม่สามารถอยู่เดี่ยว ๆ ได้ โดยคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ของประโยคนี้คือ come
7. Have you got the time? (Regular Verb | Irregular Verb)
ตอบ got เป็น Irregular Verb เพราะเป็นช่อง 2 และ 3 ของ get (ช่อง 3 สามารถเขียนได้ทั้งในรูป got และ gotten) ซึ่งไม่ได้ผันแบบเติม -ed
แบบปกติ
8. Sure, it is two thirty. (Linking Verb | Modal Verb)
ตอบ is เป็น Linking Verb ไม่ใช่ Modal Verb เพราะสามารถอยู่เดี่ยว ๆ ได้ ไม่ต้องมีคำกริยาอื่นตามมา
9. It is almost ten. (Main Verb | Helping Verb)
ตอบ is เป็น Main Verb (และอยู่ในกลุ่ม Linking Verb ด้วย) ไม่ใช่ Helping Verb เพราะไม่มีคำกริยาอื่นตามมา
10. Sorry, I do not have the time. (Main Verb | Helping Verb)
ตอบ do เป็น Helping Verb เพราะว่าเป็นการนำ do มาช่วยในการสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธ โดยคำกริยาหลักในประโยคนี้คือ have
Adjective
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
Track 5
เขียนบรรยายลักษณะที่ได้ยินลงไปให้ถูกต้องเลย!
*ขีดเส้นใต้ = คำคุณศัพท์ (Adjective)*
1.
My father is a tall man. (พ่อของฉันเป็นคนตัวสูง)
He has short black hair and brown eyes. (พ่อมีผมสั้นสีดำและตาสีน้ำตาล)
He is a funny and warm person. (พ่อเป็นคนตลกและอบอุ่น)
2.
My mother is a slim woman. (แม่ของฉันเป็นผู้หญิงผอมเพรียว)
She has long blonde hair and blue eyes. (แม่มีผมยาวสีบลอนด์และตาสีฟ้า)
She is a beautiful and kind person. (แม่เป็นคนสวยและใจดี)
3.
My brother is a chubby boy. (น้องชายของฉันเป็นเด็กผู้ชายอวบ)
He has very short brown hair and blue eyes. (เขามีผมสั้นมากสีน้ำตาลและตาสีฟ้า)
He is an adorable boy. (เขาเป็นเด็กผู้ชายที่น่าเอ็นดู)
4.
I am a lovely teenage girl. (ฉันเป็นเด็กผู้หญิงวัยรุ่นที่น่ารัก)
I have shoulder-length brown hair and green eyes. (ฉันมีผมยาวประบ่าสีน้ำตาลและตาสีเขียว)
I am a nice and friendly person. (ฉันเป็นคนนิสัยดีและเป็นกันเอง)
5.
KruDew is an English teacher. (ครูดิวเป็นคุณครูภาษาอังกฤษ)
He has short black hair and dark brown eyes. (ครูดิวมีผมสั้นสีดำและตาสีน้ำตาลเข้ม)
He is a funny and smart person. (ครูดิวเป็นคนตลกและฉลาด)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
เรียงคำคุณศัพท์ในประโยคต่อไปนี้ตามลำดับให้ถูกต้องกันเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I really love my cute little sister. (little, cute)
cute = ความคิดเห็น little = ขนาด
1. Our family lives in a simple small house. (simple, a, small)
a = คำนำหน้านาม simple = ความคิดเห็น small = ขนาด
2. My stepbrother enjoys spicy Thai food. (spicy, Thai)
spicy = ความคิดเห็น Thai = สัญชาติ
3. I used to try on a traditional Japanese Kimono when going to Japan. (a, Japanese, traditional)
a = คำนำหน้านาม traditional = อายุ Japanese = สัญชาติ
4. My fiancé gave me a large heart-shaped diamond ring. (a, diamond, heart-shaped, large)
a = คำนำหน้านาม large = ขนาด heart-shaped = รูปร่าง diamond = วัสดุ
5. Do you like these comfortable black leather boots? (black, leather, comfortable, these)
these = คำนำหน้านาม comfortable = ความคิดเห็น black = สี leather = วัสดุ
6. My grandmother always carries a tiny wooden walking stick. (walking, a, wooden, tiny)
a = คำนำหน้านาม tiny = ขนาด wooden = วัสดุ walking = จุดประสงค์
7. We donated these lovely flat pink running shoes to the kids. (lovely, these, flat, running, pink)
these = คำนำหน้านาม lovely = ความคิดเห็น flat = รูปร่าง pink = สี running = จุดประสงค์
8. This store sells a lot of gorgeous short modern cotton dress. (short, gorgeous, a lot of, cotton, modern)
a lot of = คำนำหน้านาม gorgeous = ความคิดเห็น short = ขนาด modern = อายุ cotton = วัสดุ
9. My father always wanted this beautiful vintage yellow British car. (British, this, vintage, beautiful, yellow)
this = คำนำหน้านาม beautiful = ความคิดเห็น vintage = อายุ yellow = สี British = สัญชาติ
10. My mother just bought expensive new red British woolen sweaters. (new, red, expensive, woolen, British)
expensive = ความคิดเห็น new = อายุ red = สี British = สัญชาติ woolen = วัสดุ
Adverb of Manner
ช่วยเติมคำที่ให้มาในกรอบสี่เหลี่ยมลงไปในประโยคให้ถูกต้องทีนะ!

1. Q: Why do you think the boy is running?
A: The boy is running quickly
because he might be late for school.
(เด็กผู้ชายวิ่งอย่างรวดเร็วเพราะว่าเขาอาจจะไปโรงเรียนสาย)
2. Q: Do you know how long it has been raining?
A: It has been raining hard since yesterday morning.
It’s still raining cats and dogs today.
(ฝนตกหนักมาตั้งแต่เมื่อวานตอนเช้าแล้ว วันนี้ก็ยังตกหนักมากอยู่)
3. Q: Do you have any idea what the woman is doing?
A: The woman is shopping and jumping excitedly
because it is a mid-year sale at the department store.
(ผู้หญิงคนนั้นกำลังชอปปิงและกระโดดอย่างตื่นเต้น
เพราะเป็นช่วงลดราคากลางปีของห้างสรรพสินค้า)
4. Q: What do you think Joe is doing on his day off?
A: I think he is staying at home and
lazily lying on the couch watching TV.
(ฉันคิดว่าเขาคงอยู่ที่บ้านและเอนตัวอย่างขี้เกียจดูทีวีอยู่บนโซฟา)
5. Q: What do you think about John speaking loudly on the phone?
(คุณคิดอย่างไรที่จอห์นคุยโทรศัพท์เสียงดัง)
A: I think he annoys other passengers on the train.
(ฉันคิดว่าเขารบกวนผู้โดยสารคนอื่น ๆ บนรถไฟ)
Adverb of Place
ดูภาพประกอบและนำ Adverb of Place ที่ให้มาในกรอบสี่เหลี่ยม ไปเติมในช่องว่างของแต่ละประโยคให้ถูกต้องกันเถอะ!

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. The teacher is coming here. We have to run away!
(คุณครูกำลังมาที่นี่ เราต้องวิ่งหนี)
1. Would it be possible to meet you downstairs at 10 a.m.?
(จะเป็นไปได้ไหมถ้าฉันจะขอเจอคุณที่ชั้นล่างตอน 10 โมง)
2. There’s no school today, so I’m going outside for a walk.
(วันนี้ไม่มีเรียน ฉันเลยจะออกไปข้างนอกเพื่อเดินเล่น)
3. I’m coming nearby, so I wonder if you are available to meet me.
(ฉันมาใกล้ ๆ เลยอยากรู้ว่าเธอสะดวกมาเจอกันไหม)
4. I will be there in 5 minutes. Please come inside and wait in the living room.
(ฉันจะไปที่นั่นในอีก 5 นาที กรุณาเข้ามาข้างในและรอในห้องนั่งเล่น)
5. I will have an appointment with the international client overseas, so I’ll be out of office for a week.
(ฉันมีนัดกับลูกค้าต่างชาติที่ต่างประเทศ เลยอาจจะไม่อยู่ออฟฟิศประมาณสัปดาห์หนึ่งนะ
Adverb of Time
เลือก Adverb of Time ในวงเล็บ 2 จาก 3 คำ ไปใส่ในตำแหน่งที่ถูกต้องของประโยคให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. My grandfather told me yesterday that he went to The Beatles’ concert 60 years ago. (ago, yesterday, later)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
yesterday (เมื่อวาน) เพราะ told เป็น V.2 ซึ่งใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นแล้วในอดีต เราจึงไม่สามารถใช้ later ที่ต้องใช้กับ
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอนาคตได้
และ ago นั้นต้องมีจำนวนเวลาบอก เช่น 2 days ago
-
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
ago (…ที่แล้ว) เพราะมีจำนวนเวลา
มาให้คือ 60 years
ไม่สามารถตามด้วย yesterday หรือ later ได้
1. I haven’t seen you in ages. Would you like to come over for dinner tonight? (ago, in ages, tonight)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
in ages (เป็นเวลานาน) เพราะเป็นสำนวนที่มักจะพูดกันบ่อย ๆ ในความหมายว่า “ฉันไม่ได้เจอคุณมาตั้งนานแล้ว”
ไม่สามารถใช้ago ได้เพราะไม่มีจำนวนเวลาบอก และใช้ tonight ไม่ได้ เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่ดำเนินมาระยะหนึ่งตั้งแต่อดีต
จนถึงปัจจุบัน ไม่ใช่อนาคต -
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
tonight (คืนนี้) เพราะทั้ง ago และ in ages พูดถึงเวลาในอดีต แต่ในประโยคเป็นการเชิญชวนให้ไปทานมื้อค่ำกัน
คืนนี้หลังจากที่ไม่เจอกันนาน จึงเป็นการพูดถึงเรื่องอนาคต
2. My friend asked me to go to Liverpool last week, but I was busy at that time. (later, at that time, last week)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
last week (สัปดาห์ที่แล้ว) เพราะคำกริยา asked เป็น V.2 ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีตและจบไปแล้ว
เราไม่สามารถใช้ at that timeมาตอบในส่วนแรกได้เพราะยังไม่เคยมีการพูดถึงมาก่อนว่าเป็นตอนช่วงเวลาไหน และ
later (ในภายหลัง) นั้นไม่เข้ากับบริบทเท่าไรเมื่ออ่านครบประโยค -
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
at that time (ในเวลานั้น) เพราะอ้างอิงถึงส่วนแรกคือ last week
3. Are you leaving now? Would you like to have lunch together later? (later, already, now)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
now (เดี๋ยวนี้ / ตอนนี้) เพราะประโยคที่ให้มาเป็น Present Continuous Tense ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้น
ขณะนั้นหรือช่วงนั้น ไม่สามารถใช้ later หรือalready ได้
-
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
later (หลังจากนี้) เพราะว่าเป็นการชวนไปทานข้าวกันทีหลัง แสดงว่าไม่ได้ทานอยู่ หรือไม่ได้ทานกันไปแล้ว
จึงใช้ now และ already ไม่ได้
4. I haven’t sent you an invitation card yet, but I want you to join our party next month. (already, next month, yet)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
yet (ยัง) เพราะเป็น keyword ที่ใช้กับโครงสร้างประโยค Present Perfect Tense (has / have + V.3) แปลว่า
“ฉันยังไม่ได้ส่งบัตรเชิญให้คุณเลย…”ซึ่งแม้ว่า already จะเป็น keyword สำหรับ Tense นี้เหมือนกัน แต่ก็ไม่สามารถใช้ตอบได้
เพราะว่า already มีความหมายว่า …ไปแล้ว และไม่สามารถใช้กับประโยคปฏิเสธได้เพราะความหมายขัดแย้งกัน -
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
next month (เดือนหน้า) เพราะเป็นการเชิญชวน ซึ่งเหตุการณ์นั้นยังไม่เกิดขึ้น
5. Do you think it will rain soon? How about going to the beach tomorrow instead? (soon, lately, tomorrow)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
soon (เร็ว ๆ นี้) เพราะ Tense ที่ปรากฏในประโยคคือ Future Simple Tense (will + V. infinitive) ซึ่งใช้กับ
เหตุการณ์ที่กำลังจะเกิดในอนาคต จริง ๆ แล้วtomorrow ก็สามารถใช้กับ Tense นี้ได้เช่นกัน แต่หากนำ soon ไปตอบที่ส่วนท้าย
และนำ tomorrow มาไว้ที่ส่วนหน้าแทนแล้ว ความหมายจะไม่เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน ในขณะที่ lately (ช่วงนี้ / พักนี้) นั้นมักจะใช้กับ
Present Perfect Tense (has / have + V.3) มากกว่า เช่น What have you been doing lately? แปลว่า “ช่วงนี้คุณทำอะไร
อยู่เหรอ” -
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
tomorrow (วันพรุ่งนี้) เพราะว่าในประโยคนี้ keyword คำว่า instead (…แทน) คือ “ทำไมเราไม่ไปที่ชายหาดกันใน
วันพรุ่งนี้แทนล่ะ” หมายความว่าได้วางแผนเอาไว้แล้ว แต่เพราะฝนจะตกในเร็ว ๆ นี้ จึงจะไปวันพรุ่งนี้แทน
Adverb of Frequency
นำ Adverb of Frequency ในวงเล็บไปใส่ในตำแหน่งที่ถูกต้องของประโยคให้หน่อยนะ!
คำอธิบาย ตำแหน่งของ Adverb of Frequency มักอยู่หลังประธาน (Subject) และหน้าคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) เข่น
He barely eats vegetables. (เขาแทบจะไม่กินผักเลย) แต่หากมี V. to be หรือ Linking Verb ในประโยค
Adverb of Frequency มักจะตามหลังเสมอ เช่น She is always good to me. (หล่อนดีกับฉันเสมอ)
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. My mother gets up at 7 a.m. (always) => My mother always gets up at 7 a.m.
My mother (คุณแม่ของฉัน) = Subject, always (เป็นประจำ) = Adverb of Frequency, gets up (ตื่นนอน) = Main Verb
1. I go to the game center after school. (usually) => I usually go to the game center after school.
I (ฉัน) = Subject, usually (โดยปกติ) = Adverb of Frequency, go (ไป) = Main Verb
2. Nana is late for work. She’s very punctual. (never) => Nana is never late for work. She’s very punctual.
Nana (นานะ) = Subject, is = Linking Verb, never (ไม่เคย) = Adverb of Frequency และประโยคที่เสริมมาด้านหลัง
เป็นคำใบ้เพิ่มเติมคือ She’s very punctual. (เธอเป็นคนตรงเวลามาก ๆ)
3. Ken plays tennis because he’s been busy these days. (rarely) => Ken rarely plays tennis because he’s been
busy these days.
Ken (เคน) = Subject, rarely (แทบจะไม่) = Adverb of Frequency, play (เล่น) = Main Verb และอนุประโยคที่เสริมมาด้านหลัง
เป็นคำใบ้เพิ่มเติมคือ because he’s been busy these days. (เพราะช่วงนี้เขายุ่ง)
4. I watch dramas or series when I’m free. (often) => I often watch dramas or series when I’m free.
I (ฉัน) = Subject, often (บ่อย ๆ) = Adverb of Frequency, watch (ดู) = Main Verb
5. I listen to music when I’m bored. (sometimes) => I sometimes listen to music when I’m bored.
I (ฉัน) = Subject, sometimes (บางครั้ง) = Adverb of Frequency, listen (ฟัง) = Main Verb
Adverb of Degree
ช่วยบอกหน่อยสิว่า Adverb of Degree ที่ขีดเส้นใต้ในประโยคต่อไปนี้ขยายคำไหนในประโยคกันนะ!
ขยาย Adv. (hard) ขยาย Adv. (well)
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Do you think I work hard enough to pass the exam? – Sure, you did quite well.
(เธอคิดว่าฉันอ่านหนังสือหนักพอที่จะสอบผ่านหรือยัง) (แน่นอน เธอทำได้ค่อนข้างเยี่ยมเลย)
ขยาย Adj. (big) ขยาย Adv. (well)
1. Do you think these shoes are too big? – No, I think they fit you very well.
(เธอคิดว่ารองเท้าคู่นี้ใหญ่เกินไปไหม) (ไม่นะ ฉันคิดว่าพอดีเป๊ะมากเลย)
ขยาย Adj. (pretty) ขยาย Adj. (gorgeous)
2. That lady is really pretty. She looks like a star. – Couldn’t agree more. She is so gorgeous.
(สุภาพสตรีคนนั้นน่ารักมาก เธอดูเหมือนดาราเลย) (เห็นด้วยที่สุด เธอสวยมาก)
ขยาย Adj. (high-pitched) ขยาย Adj. (talented)
3. My singing coach said I had extremely high-pitched voice. – Wow! You are absolutely talented.
(ครูสอนร้องเพลงของฉันบอกว่าฉันมีเสียงที่สูงสุด ๆ) (ว้าว! เธอมีพรสวรรค์สุด ๆ เลย)
ขยาย Adj. (correct) ขยาย Adj. (proud)
4. I got 100 scores in Biology. The exam was entirely correct. – Perfect! I am totally proud of you.
(ฉันได้ 100 คะแนนในวิชาชีววิทยาล่ะ ข้อสอบถูกต้องทั้งหมดเลย) (เยี่ยมมาก! ฉันภูมิใจในตัวเธอสุด ๆ เลย)
ขยาย V. (finish) ขยาย Adj. (good)
5. I almost finish my writing homework. There is only one paragraph left. – Great! You are such a very good student.
(ฉันเกือบจะทำการบ้านวิชาการเขียนเสร็จแล้ว เหลือแค่อีกหนึ่งย่อหน้าเท่านั้น) (เยี่ยม! เธอช่างเป็นนักเรียนที่ดีมากเลย)
เฉลยแบบฝึกหัดรวมเรื่อง Adverb
อ่านเนื้อเรื่องที่ให้มา ขีดเส้นใต้ Adverb ที่เจอในเรื่อง แล้วนำมาเขียนแยกใส่ตารางตามประเภทให้ทีนะ!
I usually get up at 7 a.m. to go to school nearby. Today, I woke up at 8 a.m. because
it is Sunday. My mother cooked a very delicious omelet for me. She also eagerly handed me a glass
of freshly squeezed orange juice. It was really refreshing so I drank it up completely. Later, we
went outside because we needed to do some groceries. My mother carefully picked organic vegetables,
but I spoke to myself quietly that I absolutely hated them. She accidentally heard me, so she
kindly told me that she would buy some fruits for me instead.
Adverb of Manner
Adverb of Place
Adverb of Time
Adverb of Frequency
Adverb of Degree
eagerly (อย่างกระตือรือร้น)
freshly (อย่างสดใหม่)
carefully (อย่างระวัง)
quietly (อย่างเงียบ ๆ)
accidentally (โดยบังเอิญ)
kindly (อย่างใจดี)
nearby (ใกล้ ๆ)
outside (ข้างนอก)
Today (วันนี้)
Later (ทีหลัง / หลังจากนั้น)
usually (โดยปกติ)
very (มาก)
really (มาก / จริง ๆ)
completely (อย่างทั้งหมด / โดยสิ้นเชิง)
absolutely (อย่างแน่นอน / โดยสิ้นเชิง)
Pronoun
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ในประโยคมีสรรพนามที่ใช้ผิดอยู่ ช่วยแก้ไขสรรพนามนั้นให้ถูกต้องทีนะ!
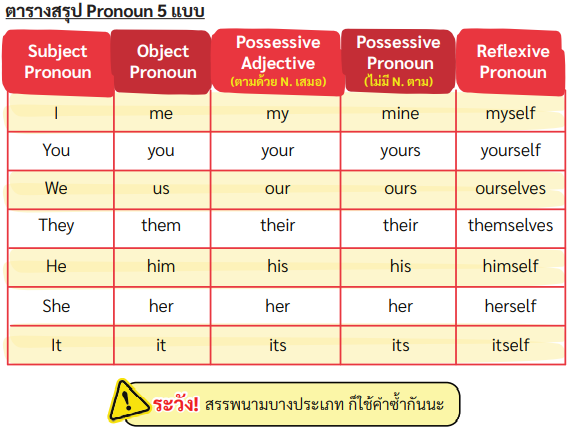
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Kathy has a dog. It fur is white. เปลี่ยนจาก it => its
คำอธิบาย
เป็น It ไม่ได้ เพราะส่วนประธาน (หน้าคำกริยา is) มีคำนาม (fur = ขนของสัตว์) มาให้แล้ว จึงต้องเปลี่ยนให้เป็น Its (Possessive Adjective)
ที่ต้องตามด้วย N. เสมอ
1. Is blue you favorite color? เปลี่ยนจาก you => your
คำอธิบาย
เป็น you ไม่ได้ เพราะประโยคที่ให้มานั้นหมายความว่า “สีฟ้าใช่สีโปรดของคุณไหม” จะเห็นว่ามีคำนาม (favorite color) ที่ให้มาแล้ว
ฉะนั้นต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น your (Possessive Adjective) ที่ต้องตามด้วย N. เสมอ
2. Those are your shoes, and these are me. เปลี่ยนจาก me => mine
คำอธิบาย
เป็น me ไม่ได้ เพราะประโยคจะหมายความว่า “โน่นคือรองเท้าของคุณ และนี่คือฉัน” แต่เรากำลังพูดถึงสิ่งของอยู่ ซึ่งก็คือรองเท้า
ฉะนั้นต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น mine ที่แปลว่า (รองเท้า)ของฉัน เราไม่เปลี่ยนเป็น my เพราะว่า my (Possessive Adjective) จะต้องตามด้วย
คำนาม (shoes) เสมอ แต่ mine (Possessive Pronoun ไม่ต้องมีคำนาม สามารถใช้เดี่ยว ๆ ได้ (เพราะผู้ฟังและผู้พูดรู้อยู่แล้วว่าสิ่งนั้น
คืออะไร)
3. Her likes my red skirt a lot. เปลี่ยนจาก Her => She
คำอธิบาย
เป็น Her ไม่ได้ เพราะ her เป็นได้สองอย่างคือ Object Pronoun (ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรมของประโยค) และ Possessive Adjective
(ทำหน้าที่แสดงความเป็นเจ้าของ ต้องตามด้วย N. เสมอ) การขึ้นต้นประโยคเป็นประธาน เราจะใช้ Subject Pronoun คือ She จึงจะถูกต้อง
4. He loves to study by him. เปลี่ยนจาก him => himself
คำอธิบาย
เป็น him ไม่ได้ เพราะ him เป็น Object Pronoun ต้องอยู่ตามหลังคำกริยา (V.) เสมอ เช่น I love him. แต่ในข้อนี้ความหมายคือ
“เขารักที่จะเรียนด้วยตนเอง” การทำบางสิ่งบางอย่างด้วยตนเอง เรามักใช้ Reflexive Pronoun เข้ามาช่วย ข้อนี้จึงต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น
himself (ด้วยตัวของเขาเอง)
5. I name is Pimmy. What about yours? เปลี่ยนจาก I => My
คำอธิบาย
เป็น I ไม่ได้ เพราะส่วนประธาน (หน้าคำกริยา is) มีคำนาม (name = ชื่อ) มาให้แล้ว และประธาน I จะใช้กับ am ใน Present Simple Tense
จึงต้องเปลี่ยน I (Subject Pronoun) ให้เป็น My ที่ต้องตามด้วย N. แทน จึงเป็น My name (ชื่อของฉัน) ซึ่งสามารถตามด้วยคำกริยา is ได้
ส่วน yours ประโยคต่อมานั้นใช้ถูกต้องแล้ว เพราะต้องการถามว่า “แล้ว (ชื่อ) ของคุณคืออะไร”
6. Would your like this trendy bag? เปลี่ยนจาก your => you
คำอธิบาย
เป็น your ไม่ได้ เพราะ your เป็น Possessive Adjective ต้องมี N. ตามหลังเสมอ ในข้อนี้ต้องเป็น you เพราะยังขาดประธานของประโยค
และเรามักใช้โครงสร้างประโยค “Would you like…?” เพื่อสอบถามความต้องการว่า “คุณอยาก / ต้องการ…ไหม”
7. Jen didn’t like the new laptop which she bought by hers. เปลี่ยนจาก hers => herself
คำอธิบาย
เป็น hers ไม่ได้ เพราะ her เป็น Possessive Pronoun ใช้กล่าวเพื่อแสดงความเป็นเจ้าของ เช่น That bag is hers. “กระเป๋าใบนั้นเป็น (กระเป๋า)
ของหล่อน” แต่ในข้อนี้ความหมายคือ “เจนไม่ชอบแลปท็อปเครื่องใหม่ที่หล่อนซื้อด้วยตัวเอง” เป็นการเน้นการทำบางสิ่งบางอย่างด้วยตนเอง
เราจึงมักใช้ Reflexive Pronoun เข้ามาช่วย ข้อนี้เลยต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น herself (ด้วยตัวของหล่อนเอง)
8. I would like to introduce mine. เปลี่ยนจาก mine => myself
คำอธิบาย
ข้อนี้จะตอบ mine ได้ถ้าหากมีบริบทที่พูดถึงบางสิ่งมาก่อนแล้ว แต่ในข้อนี้หมายถึง “ฉันอยากจะแนะนำตัวเอง” เมื่อพูดถึงสิ่งที่ทำเองหรือเกี่ยวกับ
ตัวเองเราต้องใช้ Reflexive Pronoun เข้ามาช่วย จึงเป็น introduce myself ที่หมายความว่า “แนะนำตัวเอง” ตัวอย่างเหตุการณ์ที่พบบ่อย เช่น
เวลาสมัครงานที่มักจะเจอประโยคบอกให้คุณแนะนำตัวเอง อย่าง “Please introduce yourself.” นั่นเอง
9. Last week, I went to the cinema with a friend of me. เปลี่ยนจาก mine => mine
คำอธิบาย
เป็น me ไม่ได้ เพราะ me คือ Object Pronoun แต่ในข้อนี้ต้องเป็น mine (Possessive Pronoun) เนื่องจาก of + Possessive Pronoun
(a friend of mine = เพื่อนของฉัน) โดยมีความหมายเดียวกับ Possessive Adjective + N. (My friend) นั่นเอง
10. Do their like our Christmas gift? เปลี่ยนจาก their => they
คำอธิบาย
เป็น their ไม่ได้ เพราะ their เป็น Possessive Adjective ต้องมี N. ตามหลังเสมอ ในข้อนี้ต้องเป็น they (Subject Pronoun) เพราะยังขาด
ประธานของประโยค
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
จงเติมคำสรรพนามลงในช่องว่างให้ถูกต้อง
The teacher gave us homework to talk about (0.) our favorite things.
My favorite things are (1.) my bed and my cell phone because (2.) I love to sleep and
read online novels. I can stay by (3.) myself all day in the bedroom.
My friend, Sarah, really likes collecting dolls. She bought them (4.) herself from
the internet. (5.) Her dolls are all cute and fluffy. Sometimes, I bought (6.) them as
a birthday present for her, too.
David is another friend of (7.) mine / ours. He always takes a good care of
(8.) his books. He wants to be able to speak many languages, so (9.) he likes reading
books and watching foreign movies. They have helped him improve (10.) his language skills
tremendously.
Preposition
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
Track 13
ดูรูปภาพ และเติมคำตอบที่ได้ยินลงในช่องว่างเลย จุดหมายของแต่ละข้ออยู่ที่เลขไหนกันนะ
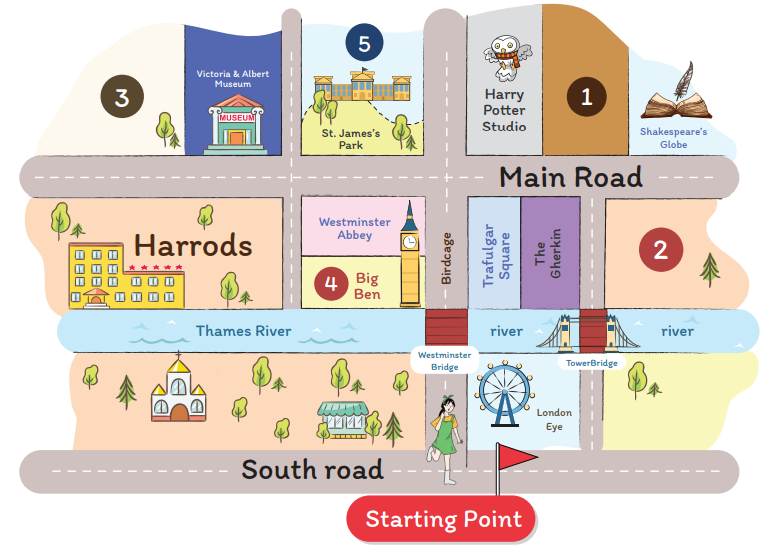
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. A : Excuse me, do you know how I can get to Big Ben from here? (ขอโทษนะคะ คุณรู้ไหมคะว่าจากที่นี่ฉันจะไปบิกเบน
ได้อย่างไร)
B : Go straight toward the river and cross the Westminster bridge.
Then, turn left. It is beside Westminster Abbey.
(ตรงไปทางแม่น้ำแล้วก็ข้ามสะพานเวสต์มินสเตอร์นะครับ จากนั้นเลี้ยวซ้าย
มันอยู่ข้าง ๆ เวสต์มินสเตอร์แอบบีย์ครับ)
The destination is number _____4_____.
1. A : Excuse me, could you tell me where the National History Museum is? (ขอโทษนะคะ ช่วยบอกฉันหน่อยได้ไหมคะว่าพิพิธภัณฑ์
ประวัติศาสตร์แห่งชาติอยู่ที่ไหน)
B : Sure. Cross the Westminster Bridge and turn left at Westminster Abbey.
Cross the intersection to Harrods. The National Museum is opposite
Harrods and next to Victoria & Albert Museum.
(แน่นอนครับ ข้ามสะพานเวสต์มินสเตอร์ไปแล้วเลี้ยวซ้ายที่เวสต์มินสเตอร์แอบบีย์นะครับ ข้ามสี่แยกไปทางแฮร์รอดส์
พิพิธภัณฑ์ประวัติศาสตร์แห่งชาติอยู่ตรงข้ามกับแฮร์รอดส์และอยู่ถัดจากพิพิธภัณฑ์วิคตอเรียแอนด์อัลเบิร์ตครับ)
The destination is number _____3_____.
2. A : Hello, could you help me? Do you know where the Sherlock Holmes Museum is?
(สวัสดีค่ะ คุณช่วยอะไรฉันหน่อยได้ไหมคะ คุณรู้ไหมคะว่าพิพิธภัณฑ์เชอร์ล็อก โฮล์มส์อยู่ที่ไหน)
B : Of course. Go straight along the Birdcage Walk.
Then, turn right at Trafalgar Square and cross the Main Road.
The Sherlock Holmes Museum is between the Harry Potter Studio and Shakespeare’s Globe.
(ได้สิครับ เดินตรงไปทางถนนเบิร์ดเคจวอล์ก จากนั้นเลี้ยวขวาที่ทราฟัลการ์สแควร์และข้ามถนนหลักไป
พิพิธภัณฑ์เชอร์ล็อก โฮล์มส์ตั้งอยู่ระหว่างแฮร์รี่ พอตเตอร์สตูดิโอกับโรงละครเช็คสเปียร์โกลบครับ)
The destination is number _____1_____.
3. A : Excuse me, could you tell me the way to Buckingham Palace? (ขอโทษค่ะ คุณช่วยบอกทางไปพระราชวังบักกิงแฮม
ให้ฉันได้ไหมคะ)
B : Certainly! Go straight ahead and take the second turn on the left.
The Buckingham Palace is behind St. James’s Park.
(แน่นอนครับ ตรงไปข้างหน้าแล้วก็เลี้ยวซ้ายตรงทางแยกที่สองนะครับ
พระราชวังบักกิงแฮมอยู่ข้างหลังสวนสาธารณะเซนต์เจมส์ครับ)
The destination is number _____5_____.
4. A : Hi! Excuse me. I would like to go to the Tower of London. Could you please tell me how to get there?
(สวัสดีค่ะ ขอโทษนะคะ ฉันอยากไปหอคอยแห่งลอนดอน คุณช่วยบอกฉันได้ไหมคะว่าจะไปที่นั่นได้อย่างไร)
B : Yes, of course. Take the South Road and turn left to cross the Tower Bridge.
Continue straight and you will see it on your right.
(ได้แน่นอนครับ ใช้ถนนเซาท์โรดและเลี้ยวซ้ายเพื่อข้ามสะพานทาวเวอร์บริดจ์
เดินตรงต่อไปแล้วคุณจะเห็นมันอยู่ทางขวาครับ)
The destination is number _____2_____.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
มาดูรูปภาพและเลือกคำตอบที่ถูกต้องกันเถอะ!
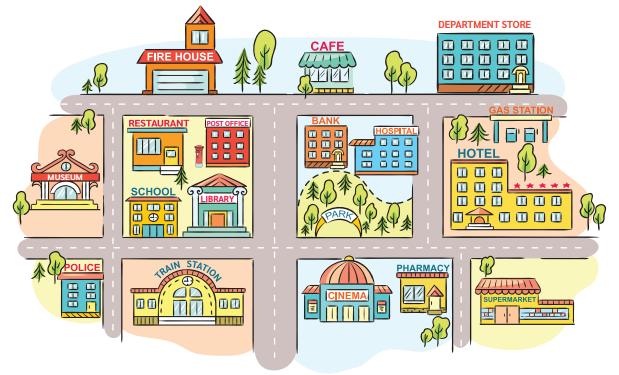
1. The school is (next to/behind) the library and (at/opposite) the train station.
It is closed (on/in) weekends.
(โรงเรียนอยู่ถัดจากห้องสมุดและตรงข้ามกับสถานีรถไฟ โรงเรียนปิดในวันหยุดสุดสัปดาห์)
2. The café is located (beside/between) the fire house and the department store.
It is usually open (from/since) Tuesday to Sunday and closed (in/on) Mondays.
(คาเฟ่ตั้งอยู่ระหว่างสถานีดับเพลิงและห้างสรรพสินค้า โดยปกติคาเฟ่นี้เปิดตั้งแต่วันอังคารถึงวันอาทิตย์และปิดในวันจันทร์)
3. The restaurant is (in front of/behind) the school and (between/next to) the post office.
This restaurant is open every day (from/at) 9 a.m. to 9 p.m.
(ร้านอาหารตั้งอยู่หลังโรงเรียนและถัดจากที่ทำการไปรษณีย์ ร้านอาหารแห่งนี้เปิดทุกวันตั้งแต่เก้าโมงเช้าจนถึงสามทุ่ม)
4. The park is (across/in front of) the hospital and the bank.
The park’s gate is closed (in/at) the evening.
(สวนสาธารณะตั้งอยู่ข้างหน้าโรงพยาบาลและธนาคาร ประตูสวนสาธารณะปิดในตอนเย็น)
5. The supermarket is (opposite/below) the hotel and there is a pharmacy (across/above) the road.
It is open (after/at) night and closed (during/over) the day.
(ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ตอยู่ตรงข้ามโรงแรมและมีร้านขายยาอยู่ตรงข้ามฝั่งถนน ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ตเปิดตอนกลางคืนและปิดระหว่างวัน)
Conjunction
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
เลือกตัวเชื่อมที่ให้มาในกรอบสี่เหลี่ยม แล้วเติมลงในช่องว่างของประโยคให้ถูกต้องเลย!

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Do you like living in the city or prefer settling down in the countryside?
(คุณชอบอาศัยอยู่ในเมือง_____ชอบใช้ชีวิตในชนบทมากกว่า) – ให้เลือกอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่งจึงตอบ or (หรือ)
1. I used to live in the outskirt, but I recently moved to the downtown area.
(ฉันเคยอาศัยอยู่แถบชานเมือง _____ฉันเพิ่งย้ายมาอยู่ที่แถวใจกลางเมืองเมื่อไม่นานมานี้) – แสดงความขัดแย้งจึงตอบ but (แต่)
2. The traffic around my house was congested yesterday, so I was late for school.
(การจราจรแถวบ้านของฉันติดขัดมากเมื่อวาน _____ฉันเลยไปโรงเรียนสาย) – แสดงความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลจึงตอบ so (ดังนั้น)
3. We have played together since we were children, for our houses are close to each other.
(พวกเราเล่นด้วยกันมาตั้งแต่เด็ก _____บ้านของพวกเราอยู่ใกล้กัน) – แสดงความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลจึงตอบ for (เพราะว่า)
4. Patrick’s apartment is only 10 minutes’ walk to the university, but/yet he is always late.
(อพาร์ตเมนต์ของแพททริกอยู่ห่างจากมหาวิทยาลัยแค่สิบนาทีโดยการเดิน _____เขามาสายตลอด) – แสดงความขัดแย้งกันจึงตอบ but (แต่)/yet (แต่กระนั้น / แต่ก็ยัง)
5. Is your room on the third floor or the fourth floor?
(ห้องของเธออยู่ที่ชั้น 3 _____ ชั้น 4 นะ) – แสดงความขัดแย้ง ไม่แน่ใจระหว่างบางสิ่งจึงตอบ or (หรือ)
6. My room is not on the third floor, nor is it on the fourth floor. It’s on the fifth floor.
(ห้องของฉันไม่ได้อยู่ที่ชั้น 3 _____ ชั้น 4 มันอยู่ที่ชั้น 5) – ประโยคเป็นเชิงปฏิเสธและสื่อว่าไม่ใช่ทั้ง 2 อย่างที่กล่าวมาจึงตอบ nor (และไม่…)
7. My place is in perfect location. It is near the beach, the cinema, and the supermarket.
(ที่อยู่ของฉันอยู่ในทำเลที่สมบูรณ์แบบ มันอยู่ใกล้ ๆ กับชายหาด โรงภาพยนตร์ _____ ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ต) – ประโยคแสดงความคล้อยตามกันจึงตอบ and (และ)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
อ่านเนื้อเรื่องด้านล่าง แล้วเลือกเติมตัวเลือกคำเชื่อมที่ถูกต้องลงในช่องว่างเลย!
I lived with my grandparents in the countryside (0) when I was young, and I attended
a local school there. (1) Although my grandparents’ house was not in the central area of the city, it only
took around 20 minutes to get to school by bus. Later, I had to move back to live with my parents in
the capital city (2) because I went to another school downtown. (3) Even though my house was
not far from the school, it still took me almost an hour to get there. (4) Since the traffic was
so bad in the city, I had to leave my house very early in the morning. I can (5) neither focus
nor pay attention to the lessons. I felt (6) not only exhausted but also drained
every time after school, (7) so I decided to move closer to the school to avoid these
problems. My parents told me to choose (8) either an apartment or a dormitory,
so I chose the nearest one which was the dormitory. I had stayed there (9) until I graduated
from high school. I felt (10) both focused and refreshed!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. a. when (เมื่อ / ตอนที่) b. as (เพราะ / เพราะว่า)
I lived with my grandparents in the countryside (0) when I was young, and I attended a local school there.
(ฉันเคยอาศัยอยู่กับปู่ย่า / ตายายในชนบท ตอนที่ฉันยังเด็ก และฉันเข้าโรงเรียนในชุมชนที่นั่น) – ใช้ when เพราะเมื่อดูในบริบทแล้ว
เป็นการพูดถึงสิ่งที่เคยเกิดขึ้นในอดีต สังเกตจาก lived ที่เป็น V.2 ใช้ใน Past Simple Tense ฉะนั้นจึงไม่ใช้ as เพราะไม่ได้แสดง
ความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลกันกับประโยคก่อนหน้า
1. a. Although (แม้ว่า) b. Therefore (ดังนั้น)
(1) Although my grandparents’ house was not in the central area of the city, it only took around 20 minutes
to get to school by bus.
(แม้ว่าบ้านของปู่ย่า / ตายายของฉันไม่ได้อยู่ในพื้นที่ใจกลางเมือง แต่ก็ใช้เวลาเพียง 20 นาทีเพื่อไปโรงเรียนโดยรถบัส) –
จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้ากับประโยคหลังแสดงความขัดแย้งกันอยู่ ไม่ได้เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน เราจึงใช้ Although จึงจะเหมาะสม
2. a. until (จนกระทั่ง) b. because (เพราะ / เพราะว่า)
Later, I had to move back to live with my parents in the capital city (2) because I went to another school downtown.
(หลังจากนั้น ฉันต้องย้ายกลับมาอยู่กับพ่อแม่ในเมืองหลวง เพราะว่าฉันเข้าโรงเรียนอีกที่หนึ่งในเมือง) – จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้า
กับประโยคหลังนั้นแสดงความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน “ต้องย้ายกลับมา เพราะไปเข้าเรียนอีกที่หนึ่ง” ถ้าใช้ until จะต้องแสดงให้เห็นว่า
เหตุการณ์หนึ่งเกิดก่อนอีกเหตุการณ์หนึ่งชัดเจน
3. a. Since (เพราะ / เพราะว่า) b. Even though (ถึงแม้ว่า)
(3) Even though my house was not far from the school, it still took me almost an hour to get there.
(ถึงแม้ว่าบ้านฉันจะไม่ได้ไกลจากโรงเรียน แต่ก็ยังใช้เวลาเป็นชั่วโมงกว่าจะไปถึงที่นั่น) – จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้าและประโยคหลัง
แสดงความขัดแย้งกัน แม้บ้านอยู่ใกล้ แต่ยังใช้เวลานานกว่าจะไปถึง จึงตอบ Even though เราไม่สามารถใช้ Since ได้ เพราะ
ทั้งสองประโยคไม่ได้เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน
4. a. As a result (ด้วยเหตุที่กล่าวมา) b. Since (เพราะ / เพราะว่า)
(4) Since the traffic was so bad in the city, I had to leave my house very early in the morning.
(เพราะว่าการจราจรในเมืองนั้นแย่มาก ฉันจึงต้องออกจากบ้านเร็วมาก ๆ ในตอนเช้า) – จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้าและประโยคหลัง
เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน เราจึงต้องใช้ Since และไม่สามารถใช้ As a result ได้เพราะว่า As a result ตามด้วยประโยค (S+V) ไม่ได้
จะต้องเป็น Noun, Noun Phrase, หรือ Prepositional Phrase เท่านั้น
5. a. neither…nor (ทั้งไม่… และ…) b. either…or (ไม่…ก็…)
I can (5) neither focus nor pay attention to the lessons.
(ฉันทั้งไม่สามารถจดจ่อและให้ความสนใจกับบทเรียนได้) – ข้อนี้สามารถดูความหมายของประโยคในข้อ 4. เพื่ออ้างอิงได้
การออกจากบ้านเช้ามาก ๆ ทำให้ไม่สามารถจดจ่อกับการเรียนได้ และประโยคที่ให้มาในข้อนี้ไม่ได้มีความหมายให้เลือก
อย่างใดอย่างหนึ่ง จึงตอบ neither…nor
6. a. neither…nor (ทั้งไม่…และ…) b. not only…but also (ไม่เพียงแค่…แต่ยัง…)
I felt (6) not only exhausted but also drained every time after school.
(ฉันรู้สึกไม่เพียงแค่เหนื่อย แต่ยังหมดพลังทุกครั้งหลังเลิกเรียน) – จะเห็นว่าประโยคนี้เป็นผลมาจากเรื่องที่เล่ามาในหลาย ๆ
ประโยคก่อนหน้า รถติด ใช้เวลาเดินทางนาน > ต้องออกจากบ้านเช้ามาก ๆ > เรียนไม่รู้เรื่อง > หมดแรง ข้อนี้เราจึงต้องตอบ
not only…but also เพราะหากเราตอบ neither…nor จะแสดงความขัดแย้งกับเนื้อเรื่องที่ผ่านมา
7. a. so (ดังนั้น) b. but (แต่)
(7) So, I decided to move closer to the school to avoid these problems.
(ดังนั้น ฉันจึงตัดสินใจย้ายไปอยู่ใกล้โรงเรียนมากขึ้นเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาเหล่านี้) – ข้อนี้ตอบ so เพราะว่าเป็น Adv. ที่ใช้แสดง
ความเป็นเหตุเป็นผล สามารถใช้ขึ้นต้นประโยคได้และความหมายสอดคล้องกับเนื้อเรื่อง เราไม่สามารถใช้ but ได้ เพราะ but
ใช้เชื่อมระหว่างประโยค 2 ประโยคที่มีความหมายขัดแย้งกัน ความหมายจึงไม่สอดคล้องกับข้อนี้
8. a. both…and (ทั้ง…และ…) b. either…or (ไม่…ก็…)
My parents told me to choose (8) either an apartment or a dormitory, so I chose the nearest one which was the dormitory.
(พ่อแม่ของฉันบอกให้ฉันเลือกไม่อพาร์ตเมนต์ก็หอพัก ดังนั้นฉันเลยเลือกที่ที่ใกล้ที่สุดนั่นก็คือหอพัก) – จะเห็นได้ว่าในประโยคมี keyword
คำว่า choose อยู่ คือให้เลือกอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่ง จึงตอบ either…or
9. a. hence (ดังนั้น) b. until (จนกระทั่ง)
I had stayed there (9) until I graduated from high school.
(ฉันพักอยู่ที่นั่นจนกระทั่งฉันเรียนจบมัธยมปลาย) – จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้าและประโยคหลังนั้นไม่ได้เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน จึงไม่สามารถ
ตอบ hence ได้ แต่ข้อนี้แสดงให้เห็นลำดับเหตุการณ์ในอดีต
10. a. both…and (ทั้ง…และ…) b. neither…nor (ทั้งไม่…และ…)
I felt (10) both focused and refreshed!
(ฉันรู้สึกทั้งมีสมาธิและสดชื่น) – เมื่ออ่านเนื้อเรื่องจะเห็นว่าเป็นการพูดถึงสาเหตุ > ปัญหาที่เผชิญ > วิธีแก้ > ผลลัพธ์ใหม่ ฉะนั้นเราจึงต้อง
ตอบสิ่งที่จะเติมเต็มเนื้อเรื่องให้สมบูรณ์จากตอนแรกที่ไม่สามารถจดจ่อได้ > มีสมาธิมากขึ้น จึงต้องตอบ both…and
———————————————————————–
Chapter 2 : Determiner
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
จับคู่ประโยคที่ให้มากับ Determiner ให้ถูกต้องกัน! (Determiner 1 ตัว สามารถตอบได้มากกว่า 1 ข้อ)
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I have _____ severe headache. a
ตอบ a เพราะ headache เป็นคำนามนับได้ และมักใช้พูดแบบไม่ชี้เฉพาะ
1. The doctor is waiting for you in the examination room. the
ตอบ the เพราะข้อนี้ต้องเลือก determiner คำเดียวที่ใช้ได้ทั้งกับ doctor และ examination room
ซึ่งเป็นคำนามนับได้เอกพจน์ทั้งคู่ นอกจากนี้ the ยังใช้ได้ทั้งกับคำนามที่ขึ้นต้นด้วยเสียงสระและ
เสียงพยัญชนะอีกด้วย
2. I felt dizzy when I was riding a/the balloon in Cappadocia. a / the
ตอบ a หรือ the ก็ได้ ที่ตอบ a ก็เพราะไม่ต้องการเจาะจงคำว่า balloon เป็นการพูดถึงแบบทั่วไป
อีกทั้ง balloon ยังเป็นคำนามนับได้ด้วย จึงสามารถใช้ a ได้ และที่ตอบ the ได้ก็เพราะ
เป็นการชี้เฉพาะหรือเจาะจงคำว่า balloon นั่นเอง
3. Do you have a fever? a
ตอบ a เพราะ fever เป็นคำนามนับได้ และมักใช้พูดแบบไม่ชี้เฉพาะ
4. I will give you some painkillers. some
ตอบ some เพราะ painkillers เป็นคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์ (มี -s) แต่ไม่ตอบ the เพราะจะเป็นการเจาะจงยี่ห้อ
หรือประเภทของยา ไม่นิยมใช้ อีกทั้งปกติหมอก็มักจะให้ยาแก้ปวด (painkiller) หลาย ๆ เม็ดอยู่แล้ว
ไม่ได้ให้เพียง 1 หรือ 2 เม็ด เลยไม่ตอบ two เช่นกัน
5. How many tablets should I take each time? each
ตอบ each เพราะ each time แปลว่าแต่ละครั้ง นอกจากนี้ each ยังตามด้วยคำนามนับได้เอกพจน์
อย่าง time ได้ด้วย
6. You should take two/some tablets before going to bed. two/some
ตอบ two (สอง) หรือ some (บ้าง / จำนวนหนึ่ง) ก็ได้ เพราะ tablet เติม -s มีจำนวนมากกว่าหนึ่ง
7. Please drink a lot of/some water. a lot of/some
ตอบ a lot of หรือ some ก็ได้ เพราะ water เป็นคำนามนับไม่ได้ และ a lot of กับ some ก็สามารถตาม
ด้วยคำนามนับไม่ได้ได้ด้วย ทั้งนี้ ไม่ตอบ little เพราะประโยคนี้แปลว่ากรุณาดื่มน้ำเยอะ ๆ และปกติแล้ว
ไม่มีใครส่งเสริมให้ดื่มน้ำน้อยนั่นเอง
8. I had an accident and my legs hurt. an
ตอบ an เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงอุบัติเหตุแบบไม่ชี้เฉพาะ และคำว่า accident ยังออกเสียงขึ้นต้นด้วยเสียงสระด้วย
9. You need to undergo an operation. an
ตอบ an เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงการผ่าตัดแบบไม่ชี้เฉพาะ และคำว่า operation ยังออกเสียงขึ้นต้นด้วยเสียงสระด้วย
10. I’ve got very little energy. little
ตอบ little เพราะ energy เป็นคำนามนับไม่ได้ และประโยคนี้ยังแปลว่า ฉันมีพลังงานน้อยมาก หรือไม่ค่อยมีแรงนั่นเอง
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
Track 16
เติมคำแนะนำจากแพทย์ที่ได้ยินลงในช่องว่างให้ถูกต้องเลย
1. I have been feeling hot and cold for a few days.
I also have a fever and runny nose.
You should get plenty of rest
and drink some hot tea
such as chamomile or ginger.
ตอบ plenty of rest เพราะ plenty of สามารถตามด้วยคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์ หรือคำนามนับไม่ได้อย่าง rest ในกรณีนี้ได้
และตอบ some hot tea เพราะ some สามารถตามได้ทั้งคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์ และคำนามนับไม่ได้อย่าง tea ในกรณีนี้ก็ได้
2. I can’t force myself to sleep,
and I’ve been losing some weight lately.
You should not stress. Take a hot bath and relax.
Drink a lot of water for several hours before bedtime.
ตอบ a ตรง hot bath เพราะ bath เป็นคำนามนับได้ อีกทั้งยังออกเสียงขึ้นต้นด้วยเสียงพยัญชนะด้วย
และตอบ a lot of water เพราะ a lot of ตามได้ทั้งคำนามนับได้ หรือนับไม่ได้อย่าง water ก็ได้
นอกจากนี้ยังตอบ several หน้า hours ได้ด้วย เนื่องจาก several (จำนวนมากกว่า 3 ขึ้นไป แต่ไม่เท่า many)
ต้องตามด้วยคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์อย่าง hours เสมอ
3. I have a sore throat. It’s so painful that
I struggle to eat or drink anything.
You have tonsillitis. Try to eat bland and soft foods.
Have some dark chocolate ice cream. It will ease the inflammation.
ตอบ some ตรง dark chocolate ice cream เพราะ ice cream เป็นได้ทั้งคำนามนับได้ และนับไม่ได้
นอกจากนี้ some ยังใช้ได้ทั้งกับคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์ หรือคำนามนับไม่ได้ก็ได้
4. I’ve had backpain for some time
because I usually sit in front of the computer all day.
That’s a sign of office syndrome.
You should try to take a rest for 5-10 minutes every hour.
Select the chair that supports your back well.
ตอบ a ตรง rest เพราะ a สามารถตามด้วยคำนามนับได้อย่าง rest ในกรณีนี้ได้
(ปกติ rest เป็นได้ทั้งคำนามนับได้ และนับไม่ได้)
และตอบ every ตรง hour เพราะ every สามารถตามด้วยคำนามนับได้เอกพจน์อย่าง hour ได้
นอกจากนี้ยังตอบ the ตรง chair เพราะเป็นการชี้เฉพาะว่าหมายถึงเก้าอี้ตัวไหน
ซึ่งในที่นี้หมายถึงเก้าอี้ตัวที่สามารถรองรับหลังได้ดีนั่นเอง
5. I’m having diarrhea and vomiting.
I feel exhausted and dehydrated.
Drink plenty of clear fluid, like fruit juices, soda, or sports drinks.
Avoid milk or milk-based products.
ตอบ plenty of clear fluid เพราะ plenty of สามารถตามด้วยคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์
หรือคำนามนับไม่ได้อย่าง fluid ที่เป็นทั้งคำนามนับได้ หรือนับไม่ได้ก็ได้
———————————————————————–
Chapter 3 : Tense
Present Simple
เลือกคำกริยาที่ให้มาไปใส่ในช่องว่าง โดยผันรูปกริยาตามประธาน (Subject) และกาล (Tense) ให้ถูกต้องด้วยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. The sun sets in the west. (set)
ตอบ sets แบบเติม -s เพราะ the sun หรือพระอาทิตย์มีดวงเดียว และใช้ Present Simple เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงความจริงทั่วไป หรือพูดถึงวิทยาศาสตร์
1. The meeting starts at 9 o’clock in the morning. (start)
ตอบ starts แบบเติม -s เพราะ the meeting เป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ อีกทั้งยังเป็นการพูดถึงตารางเวลาด้วย จึงใช้ Present Simple
2. All the ferries leave from this dock. (leave)
ตอบ leave แบบไม่เติม -s เพราะ the ferries เติม -s เป็นคำนามพหูพจน์ และใช้ Present Simple เพราะพูดถึงเรื่องตารางเวลา
3. The first flight to New York departs at 5 a.m. daily. (depart)
ตอบ departs แบบเติม -s เพราะ the first flight to New York (เที่ยวบินแรกที่ไปนิวยอร์ก) เป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ และใช้ Present Simple
เพราะพูดถึงเรื่องตารางเวลา
4. The plane takes off at 10 p.m. Please be at the gate 45 minutes before boarding time. (take off)
ตอบ takes off แบบเติม -s เพราะ the plane ไม่เติม -s จึงเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ อีกทั้งยังเป็นการพูดถึงตารางเวลาด้วย จึงใช้ Present Simple
5. I usually take a bus to school because it is convenient. (take)
ตอบ take แบบไม่เติม -s เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I ซึ่งต้องใช้กับคำกริยาที่ไม่เติม -s เสมอ อีกทั้งยังใช้ Present Simple ด้วย
เพราะมีกริยาวิเศษณ์บอกความถี่คำว่า usually ที่มักจะเจอใน Present Simple
Present Continuous
วงกลม Keyword บอกเวลาของ Present Continuous ในประโยค
และเติมคำกริยาที่ผันตามประธาน (Subject) และกาล (Tense) ลงไปให้ถูกต้องเลย
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I am shopping with friends at Times Square now. (shop)
ตอบ am shopping เพราะ Present Continuous มีโครงสร้างคือ S + is/am/are + V.ing ซึ่งประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I จึงต้องใช้คู่กับ
V. to be “am” ใน Present Continuous เสมอ นอกจากนี้ now (ตอนนี้) ยังถือเป็น Keyword บอกเวลาของกาล (Tense) นี้ด้วย เนื่องจาก
Present Continuous จะใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นอยู่ในขณะนี้
1. Mom is baking a cake at the moment. (bake)
ตอบ is baking เพราะ Present Continuous มีโครงสร้างคือ S + is/am/are + V.ing และประธานของประโยคอย่าง mom ต้องใช้คู่กับ
V. to be “is” ใน Present Continuous เสมอ นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า at the moment (ตอนนี้) ก็เพราะว่าคำนี้ถือเป็น Keyword
บอกเวลาของกาล (Tense) นี้นั่นเอง
2. They are staying in New York this summer. (stay)
ตอบ are staying เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + is/am/are + V.ing ของ Present Continuous และประธานของประโยคอย่าง they
ซึ่งเป็นคำสรรพนามพหูพจน์ก็ต้องใช้คู่กับ V. to be “are” ที่เป็นคำกริยาพหูพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า this summer (ฤดูร้อนนี้)
ก็เพราะว่าคำนี้เป็น Keyword บอกเวลาคำหนึ่งของกาล (Tense) นี้ เพราะนอกจากกาล (Tense) นี้จะใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นอยู่ในขณะนี้
แล้ว ยังสามารถใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่บอกเวลาคร่าว ๆ ว่าเกิดขึ้นในช่วงนี้ได้ด้วย
3. Sam is currently studying at ABC University as an exchange student. (study)
ตอบ is studying เพราะ Present Continuous มีโครงสร้างคือ S + is/am/are + V.ing และประธานของประโยคอย่างชื่อคน หรือ Sam
ก็ต้องใช้คู่กับ V. to be “is” ใน Present Continuous เสมอ นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า currently (ในปัจจุบัน) ก็เพราะว่าคำนี้ถือเป็น Keyword
บอกเวลาของ Present Continuous นั่นเอง
4. We are having a party tonight at NY club. (have)
ตอบ are having เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + is/am/are + V.ing ของ Present Continuous และประธานของประโยคหรือ we
ก็ต้องใช้คู่กับ V. to be “are” ที่เป็นคำกริยาพหูพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า tonight (คืนนี้) เพราะถือเป็น Keyword
บอกเวลาของ Present Continuous นั่นเอง
5. Kate is busy right now. She is talking to her friend. (talk)
ตอบ is talking เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + is/am/are + V.ing ของ Present Continuous และประธานของประโยคคือชื่อคน หรือ Kate
ซึ่งเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ จึงต้องใช้คู่กับ V. to be “is” ที่เป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า right now (ตอนนี้) เพราะถือเป็น
Keyword บอกเวลาของ Present Continuous นั่นเอง
Present Perfect
เรียงประโยคต่อไปนี้ให้อยู่ในโครงสร้าง Present Perfect และอย่าลืมผันคำกริยาให้ถูกต้องตามกาล (Tense) ด้วยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. have / I / study / English / 5 years / for / . => I have studied English for 5 years.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have studied English เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I
จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาที่ไม่มี -s อย่างคำว่า have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า study ก็คือ studied นอกจากนี้ Present Perfect ยังมักตามด้วย
for + ช่วงเวลาด้วย จึงต้องเขียน for 5 years ไว้ท้ายประโยคนั่นเอง
1. I / have / have / already / dinner / . => I have had dinner already. / I have already had dinner.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have had dinner เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I จึงต้องใช้คู่กับ
คำกริยาที่ไม่มี -s อย่างคำว่า have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า have ก็คือ had นั่นเอง (สามารถวาง have had ติดกันได้) แต่ทั้งนี้สามารถเขียน
ประโยคนี้ได้ 2 แบบเพราะจะวางคำว่า already ที่เป็นคำกริยาวิเศษณ์ไว้ท้ายประโยคเป็น I have had dinner already. หรือวางไว้ระหว่าง
คำกริยาสองตัว (V. ตบหน้า ตบหลัง ตรงกลางคือ Adv.) เป็น I have already had dinner. ก็ได้
2. live / New York / in / since / have / 2010 / I / . => I have lived in New York since 2010.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have lived in New York เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I
จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาที่ไม่มี -s อย่างคำว่า have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า live ก็คือ lived ซึ่งมักตามด้วยที่อยู่ เพื่อบอกว่าอาศัยอยู่ที่ไหน
ดังนั้นจึงต้องเติม in New York ตามหลังด้วย นอกจากนี้ Present Perfect ยังมักตามด้วย since + ปี จึงต้องเขียน since 2010 ไว้
ท้ายประโยคนั่นเอง
3. never / be / I / yet / have / to / place / your / . => I have never been to your place yet.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have never been to your place เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I
จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาที่ไม่มี -s อย่างคำว่า have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า be ก็คือ been นั่นเอง ซึ่งจะตามด้วยสถานที่ เพื่อบอกว่าเคยหรือ
ไม่เคยไปที่ใดมาก่อน จึงต้องเติม to your place ตามหลังด้วย ส่วนคำว่า never ที่แปลว่า ไม่เคย มักจะวางไว้ระหว่างคำกริยาสองตัวเพื่อ
ทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ ได้เป็น have never been to your place นอกจากนี้ หากจะใช้คำว่า yet ก็มักจะวางไว้ท้ายประโยค ดังนั้นจึงได้
เป็นประโยค I have never been to your place yet. นั่นเอง
4. since / talk / ever / We / have / other / to / each / never / . => We have never talked to each other ever since.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have never talked to each other เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า
We จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาพหูพจน์อย่าง have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า talk ก็คือ talked ซึ่งจะตามด้วยบุคคล หรือ each other (ซึ่งกันและ
กัน) ก็ได้ เพื่อบอกว่าคุยกับใคร ดังนั้นจึงต้องเติม to each other ตามหลัง ส่วนคำว่า never ที่แปลว่า ไม่เคย มักจะวางไว้ระหว่างคำกริยาสองตัว
เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ จึงได้เป็น have never talked to each other นอกจากนี้หากจะเติมคำว่า ever since ก็มักจะวางไว้ท้ายประโยค
จึงได้เป็น We have never talked to each other ever since. นั่นเอง
5. so / My / far / life / great / be / has / . => My life has been great so far.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ has been great เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า My life ที่เป็นเอกพจน์
จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาเอกพจน์อย่าง has เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า be ก็คือ been ซึ่งสามารถตามด้วยคำคุณศัพท์ได้ จึงต้องเขียน great
ที่เป็นคำคุณศัพท์ไว้ตามหลัง นอกจากนี้หากจะเติมคำว่า so far ก็มักจะวางไว้ท้ายประโยค จึงได้เป็น My life has been great so far. นั่นเอง
Present Perfect Continuous
เติมคำกริยาที่ให้มาลงในช่องว่าง โดยให้อยู่ในโครงสร้าง Present Perfect Continuous ที่ถูกต้องด้วยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. She has been playing volleyball since she was nine. (play)
ตอบ has been playing เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้างของ Present Perfect Continuous คือ S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยใช้ has
เพราะประธานของประโยคคือ she ซึ่งเป็นคำที่ต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์นั่นเอง
1. Diana has been reading this book for weeks. (read)
ตอบ has been reading เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ has เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคน
เพียง 1 คน หรือในข้อนี้ก็คือ Diana นั่นเอง ดังนั้นจึงต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์อย่าง has เสมอ
2. We have been traveling together in the States for months. (travel)
ตอบ have been traveling เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ have เพราะประธานของประโยคคือ
we ที่ต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาพหูพจน์เสมอ
3. She has been doing her homework for 2 hours. (do)
ตอบ has been doing เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ has เพราะประธานของประโยคคือ she
ที่ต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
4. I have been practicing ballet since 9 a.m. (practice)
ตอบ have been practicing เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ have เพราะประธานของประโยคคือ
I ที่ต้องใช้กับคำกริยาไม่เติม -s เสมอ
5. Mr. Bruce has been teaching English for 15 years. (teach)
ตอบ has been teaching เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ has เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคน
เพียง 1 คน หรือในข้อนี้ก็คือ Mr. Bruce ดังนั้นจึงต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์อย่าง has เสมอ
Present Tense Exercise
วงกลมตัวเลือกคำกริยาที่ใช้ Tense ได้ถูกต้องและเหมาะสมกันเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I __________ regularly in the morning
a. exercise b. am exercising c. have exercised d. have been exercising
ตอบ a. เพราะเป็น Present Simple เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า regularly (เป็นประจำ / เป็นปกติ)
1. I __________ this dish before, so I’m going to order this.
a. do not try b. am not trying c. have not tried d. have not been trying
ตอบ c. เพราะเป็น Present Perfect เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า before เพื่อบอกว่าเคย หรือไม่เคยทำสิ่งใดมาก่อน ทั้งนี้จะไม่ตอบ d.
หรือ Present Perfect Continuous เพราะการที่บอกว่าเคย หรือไม่เคยทำสิ่งใด จะอยู่ในรูปประโยคแบบ Present Perfect
2. John __________ his homework already. He is ready to go out and meet his friends.
a. finishes b. is finishing c. has finished d. has been finishing
ตอบ c. เพราะเป็น Present Perfect เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า already ที่มักใช้ในกาล (Tense) นี้เพื่อบอกว่าเกิดเหตุการณ์บางอย่าง
ที่เพิ่งจบได้ไม่นาน
3. The Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York __________ from 10 a.m. to 5 p.m. every day except Tuesday and Wednesday.
a. opens b. is opening c. has opened d. has been opening
ตอบ a. เพราะเป็น Present Simple เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า every day (ทุกวัน) รวมทั้งมีการพูดถึงเรื่องตารางเวลาด้วย
4. Sarah __________ during the day for 3 hours. Should we let her sleep or wake her up?
a. sleeps b. is sleeping c. has slept d. has been sleeping
ตอบ d. เพราะเป็น Present Perfect Continuous เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า for 3 hours (เป็นเวลา 3 ชั่วโมง) รวมทั้งประโยคที่ตามมา
ยังแปลว่า “พวกเราควรจะปล่อยให้หล่อนนอนต่อไปหรือปลุกหล่อนดี” ด้วย แสดงว่าตอนนี้หล่อนก็น่าจะยังนอนหลับอยู่แน่ ๆ และหลับมาตลอด
เลย ดังนั้นถ้าพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้น แล้วดำเนินมาถึงปัจจุบัน พร้อมทั้งแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ (นอนหลับมาตลอด 3 ชั่วโมง)
เช่นนี้ด้วย จึงต้องใช้ Present Perfect Continuous นั่นเอง
5. It’s Sunday, so they must be at the cinema. They always __________ the movies on Sunday night.
a. watch b. are watching c. have watched d. have been watching
ตอบ a. เพราะเป็น Present Simple เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า always (เป็นประจำ / สม่ำเสมอ)
6. She __________ on the new project in New York right now.
a. works b. is working c. has worked d. has been working
ตอบ b. เพราะเป็น Present Continuous เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า right now (ตอนนี้ / ในขณะนี้)
7. The marketing manager __________ here since 1995, and he will retire soon.
a. works b. is working c. has worked d. has been working
ตอบ d. เพราะเป็น Present Perfect Continuous เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า since + ปี ทั้งนี้จะตอบ c. ที่เป็น Present Perfect ก็ได้ เพียงแต่
ถ้าตอบข้อ d. ที่เป็น Present Perfect Continuous จะถูกต้องที่สุด เนื่องจากประโยคที่สอง he will retire soon. (เขาจะเกษียณเร็ว ๆ นี้) บ่งบอก
ว่าช่วงนี้เขาก็ยังทำงานอยู่ ยังไม่ได้เกษียณ จึงสามารถแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ว่าทำงานมาตลอดตั้งแต่ปี 1995 ด้วยการใช้
Present Perfect Continuous ได้นั่นเอง
8. We __________ to New York to visit our friends next week.
a. fly b. are flying c. have flown d. have been flying
ตอบ b. เพราะเป็น Present Continuous เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า next week (อาทิตย์หน้า)
9. My friend can’t speak Thai. He __________ English and Spanish only.
a. speaks b. is speaking c. has spoken d. has been speaking
ตอบ a. เพราะเป็น Present Simple เนื่องจากเป็นการพูดถึงความจริงทั่วไปว่าเขาพูดได้เพียงภาษาอังกฤษและภาษาสเปนเท่านั้น
10. They __________ a performance school in New York this summer.
a. attend b. are attending c. have attended d. have been attending
ตอบ b. เพราะมี Keyword คำว่า this summer (ฤดูร้อนนี้) เพื่อบอกว่าช่วงนี้หรือช่วงฤดูร้อนนี้กำลังทำอะไรอยู่ ซึ่งสามารถใช้ใน
Present Continuous ได้นั่นเอง
Past Simple
วงกลมคำกริยาช่อง 2 (V.2) ทั้งหมด 10 คำ ในตารางที่ใช้กับประโยค Past Simple Tense เลย!
showed
known
left
eat
listen
travel
went
send
was/were
gone
turn
got
saw
buy
drunk
called
driven
been
make
heard
worn
done
sung
knew
paid
Past Continuous
เติมคำกริยาที่ผันตาม Tense ได้ถูกต้องลงในช่องว่างเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Ken was studying (study) in San Francisco during summer last year.
ตอบ was studying เพราะตรงกับโครงสร้างของ Past Continuous คือ S + was/were + V.ing และมีจุดสังเกตคือ ข้อนี้มีการบอกช่วงเวลาที่เกิด
เหตุการณ์ด้วย (during summer) ดังนั้นต้องใช้ Past Continuous ไม่ใช่ Past Simple ธรรมดา โดยที่ใช้ was แทน were เนื่องจาก Ken เป็น
ประธานเอกพจน์
1. My sister was watching (watch) the news on TV at home
when she heard (hear) the car crash.
ตอบ was watching และ heard ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses เพื่อพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดกำลังเกิดขึ้นในอดีต (Past Continuous)
โดยมีอีกเหตุการณ์เข้ามาแทรก (Past Simple) มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ when จะตามด้วย Past Simple นอกจากนี้ยังใช้ was ตรง was watching
เพราะประธานเป็นเอกพจน์ด้วย
2. Yesterday my mother was cooking (cook)
when she hit (hit) her head on the kitchen cabinet.
ตอบ was cooking และ hit ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses เช่นเดียวกับข้อ 1. เพื่อพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดกำลังเกิดขึ้นในอดีต
(Past Continuous) โดยมีอีกเหตุการณ์เข้ามาแทรก (Past Simple) มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ when จะตามด้วย Past Simple นอกจากนี้ยังใช้
was cooking เพราะประธาน (my mother) เป็นเอกพจน์ และใช้ hit เพราะไม่ว่าจะเป็นคำกริยาช่องไหน ก็จะยังผันเป็น hit เหมือนเดิมเสมอ
ไม่ต้องเปลี่ยนรูป
3. I was walking (walk) along the Lombard street
while a drunk driver was running (run) a red light.
ตอบ was walking และ was running ตามลำดับ เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นพร้อมกันในอดีต มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ while
จะตามด้วย Past Continuous ดังนั้นประโยคที่สองต้องใช้ Past Continuous ด้วย นอกจากนี้ยังผันคำกริยาเป็น was เพราะประธานทั้งสองตัว
(I และ a drunk driver) ต้องใช้คู่กับ was เสมอ
4. Susan was playing (play) badminton last week in PE class.
ตอบ was playing เพราะตรงกับโครงสร้างของ Past Continuous คือ S + was/were + V.ing และมีจุดสังเกตคือ ข้อนี้มีการบอกช่วงเวลาที่เกิด
เหตุการณ์นอกจากคำว่า last week ด้วย นั่นก็คือคำว่า in PE class ดังนั้นต้องใช้ Past Continuous ไม่ใช่ Past Simple ปกติ โดยที่ใช้ was
เนื่องจาก Susan เป็นประธานเอกพจน์
5. I was calling (call) you from the emergency room last night,
but you were not answering (not answer) your phone.
ตอบ was calling และ were not answering ตามลำดับ เพราะตรงกับโครงสร้างของ Past Continuous คือ S + was/were + V.ing หรือ
สังเกตง่าย ๆ ก็คือ เมื่อใดก็ตามที่ใช้ FANBOYS (ในข้อนี้คือ B หรือ but) เชื่อมประโยค มักต้องใช้กาล (Tense) เดียวกันกับประโยคทั้งสองด้วย
นอกจากนี้ยังผันคำกริยาเป็น was เพราะประธานตัวแรก (I) ต้องใช้คู่กับ was เสมอ ส่วนประธานตัวหลัง (you) ต้องใช้คู่กับ were นั่นเอง
Past Perfect
เติมคำกริยาที่ให้มาและผันตาม Tense ให้ถูกต้อง!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. All the flights had been canceled (cancel) due to the storm
before I got (get) to the airport.
ตอบ had been canceled และ got ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง
และจบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ
before จะตามด้วย Past Simple นั่นเอง
1. The museum ____________________ (close) by the time
we ____________________ (get off) the bus.
ตอบ had been closed และ got off ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง
และจบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ
by the time จะตามด้วย Past Simple ดังนั้นประโยคที่สองจึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น got off นั่นเอง
2. Before we ____________________ (arrive) at the bus stop,
the cable car ____________________ (leave) already.
ตอบ arrived และ had left ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และจบลงแล้ว
ในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ before จะตามด้วย
Past Simple ดังนั้นประโยคแรก จึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น arrived ส่วนประโยคที่สองต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น had left ตามโครงสร้างของ
Past Perfect นั่นเอง
3. I ____________________ (never see) real seals
until I ____________________ (come) to Pier 39.
ตอบ had never seen และ came ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และ
จบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ until
จะตามด้วย Past Simple ดังนั้นประโยคแรก จึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น had never seen ตามโครงสร้าง S + had + V.3 ของ Past Perfect
ส่วนประโยคที่สองต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น came ตามโครงสร้าง S + V.2 ของ Past Simple
4. The plane just ____________________ (take off)
after the final call ____________________ (announce).
ตอบ took off และ had been announced ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมา
ระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และจบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple
มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ after จะตามด้วย Past Perfect ดังนั้นประโยคที่สองจึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น had been announced ตามโครงสร้าง
S + had + V.3 แต่ทั้งนี้ที่ต้องเติม been เข้ามาแทรกก็เพราะ the final call (การประกาศเรียกผู้โดยสารครั้งสุดท้าย) จะประกาศ หรือทำกริยา
announce เองไม่ได้ ต้องถูกประกาศ จึงต้องอยู่ในรูป Passive Voice หรือ has/have/had + been + V.3 ด้วย
5. My friends ____________________ (miss) the train
before they ____________________ (call) me for help.
ตอบ had missed และ called ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง
และจบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ
คือ before จะตามด้วย Past Simple ดังนั้นประโยคที่สองจึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น called ตามโครงสร้าง S + V.2 ส่วนประโยคแรกก็ต้อง
ผันคำกริยาเป็น had missed ตามโครงสร้าง S + had + V.3 นั่นเอง
Past Perfect Continuous
ผันกริยาที่ให้มาในวงเล็บให้อยู่ในรูปประโยค Past Perfect Continuous อย่างถูกต้องกันเถอะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I had been walking (walk) around San Francisco City Hall for 2 hours.
ตอบ had been walking เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous คือ S + had + been + V.ing ซึ่งเป็น
การแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
1. She ____________________(travel) in San Francisco for a week
when a burglar broke into her house.
ตอบ had been traveling เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous ทั้งนี้เมื่อนำไปใช้ในชีวิตประจำวัน ประโยคนี้สามารถใช้
Past Perfect แทนได้ เป็น had traveled เพียงแต่หากใช้ Past Perfect Continuous ก็จะเป็นการแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ด้วยนั่นเอง
2. The lost-and-found counter ____________________ (announce)
for the child’s mother for 15 minutes before she showed up.
ตอบ had been announcing เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous คือ S + had + been + V.ing ซึ่งเป็น
การแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ หรือสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ ประโยคหลัง (before she showed up) เป็น Past Simple ที่ใช้คู่กับ
Past Perfect Continuous ได้ ดังนั้นตอบ had been announcing ได้เลย
3. They ____________________ (take) care of their property together
before they were married.
ตอบ had been taking เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous ซึ่งเป็นการแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
4. Bob ____________________ (work) in this shop for several months
before the shoplifting incident happened.
ตอบ had been working เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous คือ S + had + been + V.ing ซึ่งเป็น
การแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
5. He ____________________ (wait) for his luggage for 3 days before it finally arrived.
ตอบ had been waiting เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous ซึ่งเป็นการแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
หรือสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ ประโยคหลัง (before it finally arrived) เป็น Past Simple ที่ใช้คู่กับ Past Perfect Continuous ได้
ดังนั้นตอบ had been waiting ได้เลย
Past Tense Exercise
ผันกริยาที่ให้มาในวงเล็บให้ถูกต้องตาม Tense และเติมคำตอบลงในช่องวางให้สมบูรณ์เลย!
Jessie (0) was (be) fifteen years old in 2015. She (1) had lived (live) with her family in
New York before they (2) moved (move) to San Francisco together. She (3) went (go)
to school near her house. She (4) had studied (study) at that school until she was eighteen years old.
One day she (5) was walking (walk) along the Lombard street when she (6) met (meet)
her friend, Han. Han (7) told (tell) her that the police (8) caught (catch) a pickpocket
among tourists last week. He also (9) warned (warn) her to look out for her belongings.
This kind of theft (10) had happened (happen) for many years even before she (11) came (come)
here. While Jessie (12) was talking (talk) to Han, she (13) saw (see) a woman looking
panicked. When they (14) went (go) to talk to her, she (15) had already lost (already lose)
her purse.
(0) was เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีต มีจุดสังเกตคือ in 2015 ซึ่งเป็นปีที่ผ่านมาแล้ว
(1) had lived เพราะประโยคนี้ (ตั้งแต่ข้อ 1-2) เป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses ใน 2 เหตุการณ์ เพื่อเล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลัง
ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และจบลงแล้ว โดยเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้
Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ คำว่า before ซึ่งต้องตามด้วย Past Simple แสดงว่าในส่วนของข้อ (1) ต้องเป็น
Past Perfect ที่มีโครงสร้าง S + had + V.3
(2) moved เพราะข้างหน้าคือคำว่า before ดังนั้นข้อนี้จึงต้องตอบ Past Simple ที่มีโครงสร้างเป็น S + V.2 นั่นเอง
(3) went เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตทั่ว ๆ ไป ข้อนี้ไม่มี keyword หรือจุดสังเกตใด ๆ ที่บอกว่าเป็นกาล (Tense) ไหนเลย
ดังนั้น ถ้าประโยคก่อนหน้าเล่าถึงเรื่องในอดีตมาตลอด และประโยคนี้ก็ยังจะเล่าถึงเรื่องในอดีตอยู่ จึงต้องใช้ Past Simple
ปกติ ที่มีโครงสร้างเป็น S + V.2 ได้เลย
(4) had studied เพราะเป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses ใน 2 เหตุการณ์ เพื่อเล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และ
จบลงแล้ว โดยเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ
คำว่า until ซึ่งต้องตามด้วย Past Simple (she was eighteen years old.) แสดงว่าในส่วนที่ไม่ได้อยู่หลัง until ต้องเป็น
Past Perfect
(5) was walking เพราะมี keyword บอกเวลาอย่าง one day เพื่อบอกว่ากำลังเกิดเหตุการณ์บางอย่างในช่วงเวลาใดเวลาหนึ่งอยู่
ดังนั้นจึงต้องใช้ Past Continuous
(6) met เพราะมี keyword คำว่า when ที่มักตามด้วย Past Simple อีกทั้งประโยคนี้ (ข้อ 5-6) ยังเป็นการใช้ Tense คู่ เพื่อเล่าเรื่อง
ที่เกิดก่อนและหลังด้วย ดังนั้นถ้าประโยคแรกใช้ Past Continuous (was walking) ไปแล้ว ประโยคในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้ Past Simple
นั่นเอง
(7) told เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีต มีจุดสังเกตคือ last week ซึ่งแปลว่า สัปดาห์ที่ผ่านมา
(8) caught เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีต มีจุดสังเกตคือ last week เช่นเดียวกับข้อ (7) เพราะทั้งข้อ (6) และ (7) คือประโยคเดียวกัน
หรือมีวิธีสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ ถ้าประโยคใด ๆ ไม่มี keyword บอกกาล (Tense) ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง เช่น for ที่มักใช้กับ Past Perfect แล้ว
ให้ถือว่าประโยคเดียวกันต้องใช้กาล (Tense) เดียวกัน ดังนั้นจึงต้องผัน catch เป็น caught (V.2) ให้เหมือน told ในข้อ (7) นั่นเอง
(9) warned เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีต และไม่มี keyword บอกกาล (Tense) ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง จึงใช้ Past Simple ได้เลย
(10) had happened เพราะมี keyword คำว่า for many years ที่มักใช้กับ Past Perfect อีกทั้งประโยคนี้ (ข้อ 10-11) ยังเป็นการใช้
Tense คู่ เพื่อเล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลังด้วย ดังนั้นประโยคในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้ Past Perfect นั่นเอง
(11) came เพราะมี keyword คำว่า before ที่จะตามด้วย Past Simple อีกทั้งประโยคนี้ (ข้อ 10-11) ยังเป็นการใช้ Tense คู่ เพื่อ
เล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลังด้วย ดังนั้นถ้าประโยคแรกใช้ Past Perfect (ตรง had happened) ไปแล้ว ในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้
Past Simple หรือ came นั่นเอง
(12) was talking เพราะเป็นการใช้กาล 2 กาล หรือ 2 Tenses เพื่อบอกว่ากำลังเกิดเหตุการณ์หนึ่งอยู่ แล้วมีอีกเหตุการณ์หนึ่งเข้ามา
ขัดจังหวะ โดยเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นจะใช้ Past Continuous ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เข้ามาขัดจังหวะจะใช้ Past Simple นอกจากนี้
ยังมี keyword คำว่า while ที่จะตามด้วย Past Continuous ด้วย ดังนั้นในส่วนนี้จึงต้องตอบ was talking นั่นเอง
(13) saw เพราะเป็นการพูดถึง 2 เหตุการณ์ คือมีทั้งเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้น และเหตุการณ์ที่เข้ามาแทรก หรือเข้ามาขัดจังหวะ ดังนั้น
ถ้าข้อ (12) ใช้ Past Continuous ไปแล้ว ในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้ Past Simple หรือผันคำกริยา see เป็น saw นั่นเอง
(14) went เพราะประโยคนี้ (ตั้งแต่ข้อ 14-15) เป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses ใน 2 เหตุการณ์ เพื่อเล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง
และจบลงแล้ว โดยเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ คำว่า
when ซึ่งต้องตามด้วย Past Simple แสดงว่าในส่วนของข้อ (14) ต้องเป็น Past Simple ที่มีโครงสร้าง S + V.2
(15) had already lost เพราะข้อ (14) และ (15) เป็นการใช้ 2 Tense คู่กัน ดังนั้นถ้าใช้ Past Simple ในข้อ (14) ไปแล้ว ในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้
Past Perfect ที่มีโครงสร้างเป็น S + had + V.3 นั่นเอง
Future Simple
ดูรูปภาพที่ให้มา และเติมคำทำนายจากแม่หมอให้ถูกต้องที!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Your mother will buy you a car as a birthday present. She won’t give you money.
เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างประโยคบอกเล่าของ Future Simple คือ S + will + V.1 และประโยคปฏิเสธคือ S + will not / won’t + V.1 ตามลำดับ
1. Your boyfriend __________ you this year.
ตอบ will propose เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง Future Simple ทั้งนี้ที่ใช้กาล (Tense) นี้ได้ก็เพราะโจทย์คือเหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดในอนาคต
หรือสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือมีคำบอกเวลา เช่น this year ที่ใช้กับ Future Simple ได้
2. You __________ abroad next year.
ตอบ will not study / won’t study เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธของ Future Simple คือ S + will not / won’t + V.1 ทั้งนี้ที่ใช้กาล (Tense) นี้ได้ก็เพราะมีคำบอกเวลาอย่าง next year ที่แปลว่าปีหน้าอยู่ด้วยนั่นเอง
3. You __________ a lottery this time. Don’t buy it.
ตอบ will not win / won’t win เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธของ Future Simple คือ S + will not / won’t + V.1
4. You __________ a lot of interesting people.
ตอบ will meet เพราะตรงกับโครงสร้าง S + will + V.1 ของ Future Simple นั่นเอง
5. You __________ any problems with work.
ตอบ will not have / won’t have เพราะโครงสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธของ Future Simple คือ S + will not / won’t + V.1
Future Continuous
ช่วย Ethan เติมประโยคให้ถูกต้องครบถ้วนทีนะว่าเขาวางแผนจะทำอะไรบ้างในสัปดาห์หน้า
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Ethan will be going (go) on a school trip.
ตอบ will be going เพราะเมื่อพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในช่วงเวลาใดเวลาหนึ่งในอนาคต จะใช้โครงสร้างของ Future Continuous
หรือ S + will + be + V.ing
1. Ethan ____________________ (do) his assignments.
ตอบ will be doing เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + be + V.ing
2. Ethan ____________________ (jog) in the park.
ตอบ will be jogging เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + be + V.ing แต่ทั้งนี้ตอนผันคำว่า jog ให้เป็น jogging นั้นต้องเติมตัว g
เข้ามาเพิ่มอีกตัวด้วย เนื่องจาก jog เป็นคำกริยาพยางค์เดียว มีสระและตัวสะกดตัวเดียว
3. Ethan ____________________ (plan) about the holiday trip with his family.
ตอบ will be planning เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + be + V.ing ทั้งนี้ต้องผันคำว่า plan ให้เป็น planning โดยการเติมตัว n
เพิ่มอีก 1 ตัวด้วย เนื่องจาก plan เป็นคำกริยาพยางค์เดียว มีสระ และตัวสะกดตัวเดียว
4. Ethan ____________________ (walk) his dog.
ตอบ will be walking เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Future Continuous โดยที่ to walk a dog แปลว่า พาหมาไปเดินเล่น
5. Ethan ____________________ (play) basketball at the gym.
ตอบ will be playing เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Future Continuous โดยที่ต้องผันคำกริยา play เป็น playing เพราะ
คำที่ลงท้ายด้วย y สามารถเติม -ing ได้เลย
Future Perfect
เติมคำกริยาที่ผันอย่างถูกต้องลงในประโยคด้านล่างนี้เลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. By the end of this year, I will have saved (save) $1,000.
ตอบ will have saved เพราะมี keyword ที่มักใช้กับ Future Perfect ซึ่งมักเป็น by + ช่วงเวลา หรือก็คือ by the end of this year
ในข้อนี้นั่นเอง ทั้งนี้ Future Perfect ยังมีโครงสร้างเป็น S + will + have + V.3 ด้วย จึงสามารถผันคำกริยา save เป็น will have saved
ได้เลย
1. Daniel ____________________ (graduate) from college by 15th May.
ตอบ will have graduated เพราะมี keyword ของ Future Perfect คือ by + ช่วงเวลา หรือก็คือ by 15th May ในข้อนี้ โดยที่สามารถ
ใช้กาล (Tense) นี้ได้เนื่องจากโจทย์ข้อนี้เข้าเงื่อนไขการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่คาดว่าจะจบในอนาคของ Future Perfect
2. By the time I ____________________ (be) sixty years old, I ____________________ (have) lots of grandchildren.
ตอบ am และ will have had ตามลำดับ เพราะข้อนี้เป็นการคาดการณ์เหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคต โดยเหตุการณ์
ที่จะเกิดขึ้น และจบก่อนจะใช้ Future Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่คาดว่าจะเกิดตามมาจะใช้ Present Simple ทั้งนี้ keyword ต่าง ๆ เช่น
by + ช่วงเวลา หรือ when ที่แปลว่า เมื่อ/ตอนที่ จะตามด้วย Present Simple เสมอหากใช้ในกรณีที่พูดถึง 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้น
ในอนาคตเช่นนี้ ดังนั้นประโยคแรกที่มีคำว่า by the time จึงต้องผันคำกริยา be เป็น am ให้ตรงกับประธาน I ในรูป Present Simple
และผันคำกริยาของประโยคหลังเป็น will have had ให้ตรงกับ Future Perfect นั่นเอง
3. Nana ____________________ (write) more than 10 books by next year.
ตอบ will have written เพราะมี keyword ของ Future Perfect คือ by + ช่วงเวลา หรือก็คือ by next year ในข้อนี้ โดยต้องอย่าลืม
ผันคำกริยาเป็น V.3 หรือ written ด้วย
4. By 9 a.m. tomorrow, I ____________________ (sleep) more than eight hours.
ตอบ will have slept เพราะมี keyword ของ Future Perfect คือ by + ช่วงเวลา หรือก็คือ by 9 a.m. tomorrow ในข้อนี้ โดยต้อง
อย่าลืมผันคำกริยาเป็น V.3 หรือ slept ด้วย
5. When you ____________________ (arrive) in Hawaii, you ____________________ (fly) for fourteen hours.
ตอบ arrive และ will have flown ตามลำดับ เพราะข้อนี้เป็นการคาดการณ์เหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคต โดยเหตุการณ์
ที่จะเกิดขึ้น และจบก่อนจะใช้ Future Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่คาดว่าจะเกิดตามมาจะใช้ Present Simple ทั้งนี้ keyword ต่าง ๆ เช่น
by + ช่วงเวลา หรือ when ที่แปลว่า เมื่อ/ตอนที่ จะตามด้วย Present Simple เสมอ หากพูดถึง 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตเช่นนี้
ดังนั้นประโยคแรกที่มีคำว่า when จึงต้องผันคำกริยา arrive เป็น arrive เช่นเดิมเพื่อให้ตรงกับประธาน you ในรูป Present Simple
และผันคำกริยาของประโยคหลังเป็น will have flown ให้ตรงกับโครงสร้างของ Future Perfect นั่นเอง
Future Perfect Continuous
ลองเปลี่ยนประโยคที่ให้มา ให้อยู่ในรูป Future Perfect Continuous Tense ทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. In August, he will have worked here for 10 years.
=> In August, he will have been working here for 10 years.
ตอบ will have been working เพราะสามารถใช้ Future Perfect Continuous แทน Future Perfect ธรรมดาได้ แต่ต่างกันที่
Future Perfect Continuous จะแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ และบอกเวลาชัดเจนมากกว่า Future Perfect ทั้งนี้
Future Perfect Continuous มีโครงสร้างคือ S + will + have + been + V.ing จึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น will have been working
นั่นเอง
1. I will have read a book for 15 minutes by the time he gets back from the bank.
=> I will have been reading a book for 15 minutes by the time he gets back from the bank.
ตอบ will have been reading เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Future Perfect Continuous คือ S + will + have + been + V.ing
หรือจะสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ มีคำบอกเวลาอย่าง for + ระยะเวลา ซึ่งในข้อนี้ก็คือ for 15 minutes จึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น will have been
reading นั่นเอง โดยต้องอย่าลืมว่าที่สามารถเปลี่ยนจาก Future Perfect มาเป็น Future Perfect Continuous ได้ก็เพราะทั้งสองกาล
(Tense) มีความคล้ายคลึงกัน สามารถใช้แทนกันได้ เพียงแต่ Future Perfect Continuous จะแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
และบอกเวลาชัดเจนมากกว่าเท่านั้นเอง
2. She will have paid off half of her borrowing to me by then.
=> She will have been paying off half of her borrowing to me by then.
ตอบ will have been paying เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + have + been + V.ing โดยที่ผันตรงส่วน V.ing เป็น paying เพราะว่า
คำกริยาเดิมที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V.infinitive) ของ paid หรือ paying ก็คือ pay ซึ่งคำกริยาที่ลงท้ายด้วย y อย่าง pay นี้ สามารถเติม -ing
ให้เป็น paying ได้เลย
3. By the end of this year, Jimmy will have saved up money for his child for 10 years.
=> By the end of this year, Jimmy will have been saving (save) up money for his child for 10 years.
ตอบ will have been saving เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + have + been + V.ing โดยที่ผันตรงส่วน V.ing เป็น saving เพราะว่า
คำกริยาเดิมที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V.infinitive) ของ saved หรือ saving ก็คือ save ซึ่งคำกริยาที่ลงท้ายด้วย e อย่าง save นี้ต้องตัด e ออก
แล้วจึงเติม -ing ให้เป็น saving
4. We will have collected $1,000 for our savings by next month.
=> We will have been collecting $1,000 for our savings by next month.
ตอบ will have been collecting เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + have + been + V.ing โดยที่ผันตรงส่วน V.ing เป็น collecting
เพราะว่าคำกริยาเดิมที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V.infinitive) ของ collected หรือ collecting ก็คือ collect ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาทั่วไป จึงสามารถเติม
-ing ต่อท้ายให้เป็น collecting ได้เลย
5. My mother will have spent at least $500 by the time I find her.
=> My mother will have been spending at least $500 by the time I find her
ตอบ will have been spending เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + have + been + V.ing โดยที่ผันตรงส่วน V.ing เป็น spending
เพราะว่าคำกริยาเดิมที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V.infinitive) ของ spent หรือ spending ก็คือ spend ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาทั่วไป จึงสามารถเติม -ing
ต่อท้ายให้เป็น spending ได้เลย
Future Tense Exercise
วงกลมตัวเลือกที่ถูกต้องที่สุดกันเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Have you heard of this? Rosy __________ a new house in Hawaii.
a. will buy b. will have bought
ตอบ a. เพราะข้อนี้ไม่มี keyword ที่บอก Tense ใด Tense หนึ่งเฉพาะ ดังนั้นสามารถใช้ Future Simple หรือ S + will + V.1 ในข้อ a. ได้เลย
1. What __________ tomorrow at 5 p.m.?
a. will you be doing b. will you have been doing
ตอบ a. เพราะข้อนี้ไม่มี keyword ที่ใช้ใน Future Perfect Continuous เช่น for + ช่วงเวลา / by the time / when แต่มี keyword ที่
เป็นคำบอกเวลาที่เจาะจงและชัดเจนอย่าง tomorrow at 5 p.m. ที่จะใช้ใน Future Continuous ปกติ ดังนั้นตอบ a. ได้เลย
2. I __________ my 18th birthday next Sunday evening.
a. will be celebrating b. will have celebrated
ตอบ a. เพราะข้อนี้มี keyword ที่เป็นคำบอกเวลาที่เจาะจงและชัดเจนอย่าง next Sunday in the evening ที่สามารถใช้ใน
Future Continuous ได้
3. Next month my parents __________ for 25 years.
a. will marry b. will have been married
ตอบ b. เพราะมี keyword อย่าง for 25 years ที่สามารถใช้ใน Future Perfect ได้ ทั้งนี้แม้ว่า married จะหน้าตาเหมือน V.3 ก็จริง
แต่ถือเป็น Adj. ที่บอกสถานะเฉย ๆ ว่าแต่งงานแล้ว ดังนั้น V.3 ที่แท้จริงของข้อนี้ก็คือ been ที่ผันมาจาก be นั่นเอง
4. We are late. The movie __________ for 15 minutes by the time we arrive at the cinema.
a. will be showing b. will have been showing
ตอบ b. เพราะมี keyword อย่าง for 15 minutes ที่สามารถใช้ใน Future Perfect Continuous ได้ นอกจากนี้ข้อนี้ยังเป็นการใช้ 2 กาล (Tense)
เพื่อเล่าถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตด้วย โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้น จบลงก่อน และบอกเวลาที่เกิดอย่างชัดเจน จะใช้
Future Perfect Continuous ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดตามมาจะใช้ Present Simple ดังนั้นในเมื่อประโยคหลัง (by the time we arrive at
the cinema.) ใช้ Present Simple ไปแล้ว แสดงว่ายังขาด Future Perfect Continuous จึงตอบ b. ได้เลย
5. I usually go on a trip to Hawaii for 4-5 days. Next time I __________ there for a week.
a. will go b. will have gone
ตอบ a. เพราะมี keyword คำว่า next time ที่บอกว่าจะทำในครั้งหน้า หรือในอนาคตทั่ว ๆ ไป จึงใช้ Future Simple ได้เลย
6. Juliet came to Hawaii nearly 2 years ago. She __________ in Hawaii for exactly 2 years this September.
a. will stay b. will have been staying
ตอบ b. เพราะมี keyword อย่าง for exactly 2 years this September ซึ่งเป็นการใช้ for + ระยะเวลา และมีการบ่งบอกเวลา
อย่างชัดเจน จึงสามารถใช้ Future Perfect Continuous ที่มีโครงสร้างเป็น S + will + have + been + V.ing ในข้อ b. ได้เลย
7. I can’t go surfing on Friday morning because I __________ the loan officer at 9 a.m.
a. will see b. will be seeing
ตอบ b. เพราะข้อนี้มี keyword ที่เป็นคำบอกเวลาที่เจาะจงและชัดเจนอย่าง on Friday morning และ at 9 a.m. ที่สามารถใช้ใน
Future Continuous ได้
8. This time next week we __________ on Waikiki beach in Hawaii.
a. will be sunbathing b. will have been sunbathing
ตอบ a. ซึ่งเป็น Future Continuous เพราะข้อนี้มี keyword ที่เป็นคำบอกเวลาที่เจาะจงและชัดเจนอย่าง this time next week อยู่
9. We are going to Honolulu Museum of Art after school. __________ us?
a. Will you join b. Will you be joining
ตอบ a. ซึ่งเป็น Future Simple เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเรื่องในอนาคต และข้อนี้ก็ยังไม่มี keyword บอกเวลาที่เฉพาะเจาะจงด้วย ดังนั้น
จึงใช้ Future Simple ปกติได้เลย หรือสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ ประโยคแรก (We are going to Honolulu Museum of Art after school.)
อยู่ในรูป Future Simple ดังนั้นประโยคหลังจึงมักต้องใช้กาล (Tense) เดียวกันด้วย
10. By the time I get to Sunset Beach Park, my friends __________ for half an hour.
a. will be surfing b. will have been surfing
ตอบ b. เพราะมี keyword คือ for + ระยะเวลาที่มักใช้กับ Future Perfect Continuous อีกทั้งข้อนี้ยังเป็นเป็นการใช้ 2 กาล (Tense)
เพื่อเล่าถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตด้วย โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้น จบลงก่อน และบอกเวลาที่เกิดอย่างชัดเจน จะใช้
Future Perfect Continuous ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดตามมาจะใช้ Present Simple ดังนั้นในเมื่อประโยคแรก (By the time I get to Sunset
Beach Park,) ใช้ Present Simple ไปแล้ว แสดงว่าประโยคหลังต้องใช้ Future Perfect Continuous จึงตอบ b. ได้เลย
———————————————————————–
Chapter 4 : Sentence Structure
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
เรียงคำที่ให้มาต่อไปนี้ให้เป็นประโยคที่ถูกต้องตามโครงสร้างเลย!
คำอธิบาย วิธีการเรียงประโยคอันดับแรกคือ ต้องหาประธานของประโยคให้เจอ จากนั้นจึงหาคำกริยาของประโยค และดูว่ากริยานั้น
ต้องการกรรมหรือไม่ แล้วจึงตามด้วยส่วนขยาย เช่น สถานที่ และเวลาตามลำดับ
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. sometimes / go / we / to / the cinema / . => We go to the cinema sometimes.
โครงสร้าง S + V – We = ประธานสรรพนาม (Subject Pronoun) สามารถเป็นประธานของประโยคได้ / go = คำกริยาที่ไม่ต้องการกรรม
(Intransitive Verb) / to the cinema = วลีบุพบท (Prepositional Phrase) บอกสถานที่ / sometimes = บอกเวลา
1. to Moscow / Luka and Kisa / will move / next month / . => Luka and Kisa will move to Moscow next month.
โครงสร้าง S + V – Luka and Kisa = Subject Pronoun / will move = Intransitive Verb / to Moscow = บอกสถานที่ /
next month = บอกเวลา
2. two tickets / Kiryl / me / gave / for her ballet performance / . => Kiryl gave me two tickets for her ballet performance.
โครงสร้าง S + V + IO + DO – Kiryl = ชื่อคน คำนามชี้เฉพาะ สามารถเป็นประธานของประโยคได้ (ดูให้ดีว่าไม่ได้มี Subject Pronoun ตัวอื่น) /
gave = คำกริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) เนื่องจาก V. give มักใช้ในโครงสร้าง give someone something หรือ give something to
someone ทำให้มีกรรมสองอย่างในประโยค คือ กรรมรอง (เป็นคน) และ กรรมตรง (สิ่งของ) / me = คำสรรพนามที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรมของประโยค
(Object Pronoun) และในประโยคนี้เป็นกรรมรอง (Indirect Object) / two tickets = กรรมตรง (Direct Object) / for her ballet performance =
ส่วนขยายเพิ่มเติมของ ticket
3. in the world / is / Bolshoi Ballet / ballet companies / one of the best / . => Bolshoi Ballet is one of the best ballet companies
in the world.
โครงสร้าง S + V + SC – Bolshoi Ballet = ชื่อคณะบัลเลต์ คำนามชี้เฉพาะ สามารถเป็นประธานได้ / is = คำกริยา (Linking Verb) /
one of the best ballet companies = เป็นส่วนเติมเต็มประธาน (Subject Complement) เพื่อให้รู้ว่าประธานคือใคร หรือเป็นอะไร/อย่างไร /
in the world = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่
4. sends / she / lists of movie characters / the director / to / . => She sends lists of movie characters to the director.
โครงสร้าง S + V + IO + DO – She = Subject Pronoun / sends = คำกริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) เนื่องจาก V. send
มักใช้ในโครงสร้าง send someone something หรือ send something to someone ทำให้มีกรรมสองอย่างในประโยค คือ กรรมรอง (เป็นคน)
และ กรรมตรง (สิ่งของ) / lists of movie characters = กรรมตรง (Direct Object) / to the director = กรรมรอง (Indirect Object)
5. met / last weekend / movie stars / he / at the musical theater / . => He met movie stars at the musical theater
last weekend.
โครงสร้าง S + V + O – He = Subject Pronoun / met = คำกริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) / movie stars = กรรมของประโยค
(Object) / at the musical theater = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่ / last weekend = ส่วนขยายบอกเวลา
6. he / to star / Mary / in this movie / invited / . => He invited Mary to star in this movie.
โครงสร้าง S + V + O – He = Subject Pronoun / invited = กริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) / Marry = ชื่อคน คำนามชี้เฉพาะ
เป็นกรรมของประโยคนี้ (Object) / to star = ส่วนขยาย / in this movie = ส่วนขยาย
7. three years ago / filmed / they / this movie / . => They filmed this movie three years ago.
โครงสร้าง S + V + O – They = Subject Pronoun / filmed = กริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) / this movie = กรรมของประโยค
(Object) / three years ago = ส่วนขยายบอกเวลา
8. performed / on the stage / very well / they / . => They performed very well on the stage./They performed on the stage very well.
โครงสร้าง S + V – They = Subject Pronoun / performed = คำกริยาที่ไม่ต้องการกรรม (Intransitive Verb) / very well = กริยาวิเศษณ์
(Adverb of Manner) เป็นส่วนขยายว่าทำกริยานั้นด้วยอาการอย่างไร / on the stage = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่
9. last night / series / were watching / we / at home / . => We were watching series at home last night.
โครงสร้าง S + V + O – We = Subject Pronoun / were watching = V. watch เป็นกริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) /
series = กรรมของประโยค (Object) / at home = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่ / last night = ส่วนขยายบอกเวลา
10. have lived / since / young / we / we / in St. Petersburg / were / . => We have lived in St. Petersburg since
we were young.
โครงสร้าง S + V conjunction S + V + SC (Complex Sentence) – We = Subject Pronoun / have lived = V. live เป็นกริยาที่
ไม่ต้องการกรรม (Intransitive Verb) / in St. Petersburg = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่ / Since = คำสันธานเชื่อมประโยค (Conjunction) /
we = Subject Pronoun / were = คำกริยา (Linking Verb) / young = คำคุณศัพท์ (Adjective) เป็นส่วนเติมเต็มประธาน
(Subject Complement)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ลองหาโครงสร้างของประโยค และระบุประเภทของประโยคว่าเป็น Simple, Compound, Complex หรือ Compound-Complex กันเลย!
S V O
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Have you ever watched Russian movies? = Simple Sentence
S V O S V O
1. I watched a Russian movie once, but I didn’t understand it.
= Compound Sentence
S V O S V
2. We watched Burnt by the Sun (1994) the other day because it was recommended on the website.
= Complex Sentence
S V O S V O
3. Aleksi has been studying Russian for 2 years, and now he hopes to study cinematography.
= Compound Sentence โดยที่ to study cinematography นับเป็นกรรมของ hopes
S V SC
4. Because the Russian Federation State Institute of Cinematography (RFSIC) is the world’s oldest
S Relative Clause V SC
film school, many well-known alumni [who graduated from this school] are really talented.
= Complex Sentence โดยมี who graduated from this school เป็น Relative Clause ด้วย แต่ยังนับว่าเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ
S ดังนั้น S จึงเท่ากับ many well-known alumni who graduated from this school
S V S V DO S V SC
5. I usually go to the cinema, but my mother often goes shopping when we are free.
= Compound-Complex Sentence
S V DO IO
6. Dimitri bought a movie ticket for me this time.
= Simple Sentence
S V O S V O
7. We should ask Ivan about the movie because he has already watched it.
= Complex Sentence
S V S V O
8. Before I moved to Russia, I had never watched Soviet or Russian movies.
= Complex Sentence
S V O
9. Do you like comedy movies or horror movies?
= Simple Sentence
S V IO DO Relative Clause (Dependent Clause)
10. Our teacher assigns us homework which is about watching a Soviet documentary.
= Complex Sentence ความรู้เสริม! เพราะนอกจากจะมีตัวเชื่อมประเภท Subordinating Conjunction
อย่าง because, since, as แล้ว Complex Sentence ยังรวมถึงประโยคที่มี Relative Clause
(Dependent Clause หรือ อนุประโยคไม่อิสระ อยู่เดี่ยว ๆ ไม่ได้) ด้วย เพราะ Complex Sentence
คือ ประโยคที่มี Independent Clause 1 ประโยค และ Dependent Clause 1 ประโยคขึ้นไปนั่นเอง
———————————————————————–
Chapter 5 : Question
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ดูคำตอบที่ให้มา และเติมคำในช่องว่างเพื่อสร้างประโยคคำถามให้สมบูรณ์กันเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Excuse me, where is the toilet?
– It’s over there, sir.
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามี Keyword “over there” (ทางโน้น) ซึ่งเป็น Adverb of Place อยู่ คำที่นำมาเติม
จึงต้องเป็น where (ที่ไหน)
1. What is the signature dish here? (จานเด็ดคือ_____)
– The signature dish is Chicken Makhani. (จานเด็ดคือแกงกะหรี่ไก่ใส่เนย)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มามีการกล่าวถึง signature dish ซ้ำจากคำถาม และขยายความเพิ่มเติมว่าคืออาหารอะไร ฉะนั้นจึงใช้
What (อะไร) ในประโยคคำถาม
2. How is the food here? (อาหารเป็น_____)
– The food is exceptional! (อาหารเป็นเลิศมาก)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มามีการบรรยายลักษณะ / คุณภาพของอาหาร ฉะนั้นจึงใช้ How (อย่างไร) ในประโยคคำถาม
3. Who is the restaurant owner? (_____เป็นเจ้าของร้านอาหาร)
– She is the restaurant owner. (หล่อนเป็นเจ้าของร้านอาหาร)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่าเป็นการระบุตัวคน ฉะนั้นจึงใช้ Who (ใคร) ในประโยคคำถาม ทั้งนี้ไม่ตอบ whom เพราะประโยคคำถาม
มีคนเพียงคนเดียว นั่นก็คือ who = the restaurant owner ซึ่งทำหน้าที่เป็นประธานของประโยคด้วย ไม่ได้มีกรรมเพิ่มมาอีกคน
4. When is the lunch served? (อาหารกลางวันจะเสิร์ฟ_____)
– It is served between 11.30 a.m. to 2 p.m. (อาหารกลางวันจะเสิร์ฟตอน 11 โมงครึ่งถึงบ่าย 2 โมง)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่าเกี่ยวกับเวลา จึงใช้ When (เมื่อไร / ตอนไหน) ในประโยคคำถาม
5. Why is this restaurant so popular? (_____ร้านอาหารนี้ถึงเป็นที่นิยมมาก)
– Because it was mentioned in the magazine. (เพราะว่ามันถูกพูดถึงในนิตยสารน่ะสิ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามี Because (เพราะว่า) ขึ้นต้นประโยคเพื่อแสดงความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน ฉะนั้นจึงใช้ Why (ทำไม)
ในประโยคคำถาม
6. Where should we sit? (เราควรนั่ง_____)
– We should sit at the bar. (เราควรนั่งที่บาร์)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามีคำบุพบทที่บอกสถานที่เข้ามาเพื่อขยาย จึงใช้ Where (ที่ไหน / ตรงไหน) ในประโยคคำถาม
7. Which dish is recommended? (เมนู_____ที่เป็นที่แนะนำ)
– Aloo Gobi is recommended. (Aloo Gobi เป็นที่แนะนำ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามีชื่ออาหารที่แนะนำ ซึ่งในเมนูจะมีอาหารหลากหลายชนิด จึงใช้ Which (สิ่งไหน / อันไหน)
เพื่อให้เลือกจากทั้งหมด มาใช้ในประโยคคำถาม
8. Whose name is on the reservation? (ชื่อ_____อยู่ในการจอง)
– Raj’s name is on the reservation. (ชื่อของราจอยู่ในการจอง)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบจะเห็นว่าบอกชื่อคนเข้ามาโดยใช้รูปแสดงความเป็นเจ้าของ (‘s) ที่ต้องตามด้วยคำนาม (N.) เสมอ จึงใช้ Whose
(…ของใคร) ในประโยคคำถาม
9. Whom did he invite for dinner? (เขาเชิญ_____มาทานมื้อค่ำ)
– He invited Vivaan for dinner. (เขาเชิญวิวรรณมาทานมื้อค่ำ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามีชื่อ Vivaan (คนที่เขาเชิญมาทานข้าวด้วย) ถือเป็นกรรม (O.) ของประโยค จึงใช้ Whom (ใคร)
ส่วน Who (ใคร) นั้นจะใช้เมื่อถามถึงประธาน (Subject) หรือผู้กระทำกริยานั้น ๆ จึงใช้ไม่ได้ในประโยคนี้
10. Do you accept credit card? (คุณรับบัตรเครดิตไหม)
– Yes, we do. (รับค่ะ / ครับ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากประโยคคำถามจะเห็นว่ามีคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) คือ accept แล้ว แต่ยังขาดคำกริยาช่วย (Helping Verb หรือ
Auxiliary Verb) ในการสร้างประโยคคำถาม ฉะนั้นจึงต้องใช้ V. to do เข้ามาช่วย เมื่อประธานเป็น you จึงต้องใช้กับ do หรือเราอาจจะ
สังเกตจากคำตอบที่ให้มา คือ Yes, we do. ก็ได้เช่นกัน
11. Are you the restaurant manager? (คุณคือผู้จัดการร้านใช่ไหม)
– No, I’m not. I’m just a waitress. (ไม่ใช่ค่ะ ฉันเป็นแค่พนักงานเสิร์ฟ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากประโยคคำถามจะเห็นว่ายังไม่มีคำกริยาในประโยคเลย มีเพียงคำนาม (N.) คือ the restaurant manager เท่านั้น ฉะนั้นจึงต้อง
ใช้ V. to be เข้ามาช่วย ในการสร้างประโยคคำถาม เมื่อมีคำนาม (N.) คำคุณศัพท์ (Adj.) และ V.ing ตามหลังประธาน (Subject) ประธานเป็น
you จึงต้องใช้กับ are หรือเราอาจจะสังเกตจากคำตอบที่ให้มา คือ No, I’m not. จึงรู้ว่าต้องได้ V. to be ก็ได้เช่นกัน
12. You like Indian food, don’t you? (คุณชอบอาหารอินเดีย ใช่ไหมล่ะ)
– I do actually. (จริง ๆ แล้วก็ใช่นะ)
คำอธิบาย การใช้ Question Tag ลงท้ายประโยคนั้นต้องใช้คำกริยาช่วยในการสร้าง สามารถดูจากคำกริยา (V.) ในประโยคหลักก่อนเครื่องหมาย
comma ได้ หากเป็นกริยาทั่วไป ไม่ใช่ V. to be หรือ V. to have ให้ใช้ V. to do เข้ามาช่วยแล้วผันตามกาล (Tense) ของประโยคหลักนั้นโดย
ทำรูปประโยคให้ตรงข้ามกับประโยคหลัก หากเป็นบอกเล่า ให้เปลี่ยนเป็นรูปคำถามเชิงปฏิเสธ (เติม not) และหากเป็นรูปปฏิเสธ ให้เปลี่ยนเป็น
คำถามปกติ (ตัด not) และใช้กับประธานเดิม ข้อนี้ประโยคหลักเป็น You like…จึงใช้ don’t you?
13. This curry isn’t bad, is it? (แกงกะหรี่นี้ไม่แย่เลย ใช่ไหมล่ะ)
– No, it isn’t. (ใช่ ไม่แย่เลย)
คำอธิบาย การสร้าง Question Tag มีหลักการตามที่ได้อธิบายไปในข้อที่แล้ว แต่ข้อนี้ในประโยคหลักเป็นปฏิเสธ เราจึงต้องดูที่ส่วน
Question Tag ด้านหลังไม่ให้เป็นปฏิเสธ ดังนั้นเราจึงใช้ is it (is คือคำกริยาในประโยคหลัก และ it หมายถึง this curry)
14. May I take your order now? (ขออนุญาตรับออเดอร์นะคะ / ครับ)
– Yes, you may. (ได้เลยค่ะ / ครับ)
คำอธิบาย การใช้ Modal Verb มาช่วยสร้างคำถามจะไม่เหมือนกับ V. to do แม้จะตามด้วย V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม) เหมือนกัน เพราะว่า
Modal Verb แต่ละตัวจะมีความหมายในตัวเอง เช่น must = ต้อง, should = ควร, may = อนุญาต เป็นต้น ดังนั้นจึงต้องดูความหมายที่ต้องการ
สื่อประกอบด้วย ข้อนี้จึงใช้ May (อนุญาต) ในการสร้างประโยคคำถาม หรือเราสามารถสังเกตได้จากคำตอบที่ให้มาก็ได้เช่นกัน
15. Let’s have dinner at an Indian restaurant, shall we? (เราไปทานอาหารเย็นที่ร้านอาหารอินเดียกันเถอะ ไปไหม)
– Sure, great idea! (ได้สิ ความคิดเยี่ยมเลย)
คำอธิบาย การใช้ Question Tag กับ Let’s นั้นต้องใช้ shall เสมอ
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ช่วยเปลี่ยนประโยค Direct Question เป็น Indirect Question ให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Where is the best place to eat Tandoori Chicken?
Do you know where the best place to eat Tandoori Chicken is? (Do you know…?)
คำอธิบาย หัวใจหลักของการสร้างประโยค Indirect Question คือการสลับตำแหน่งของคำกริยาและประธานในท้ายประโยค
โดยที่ประธานจะมาก่อนคำกริยาเสมอ
1. Who is the manager?
Could you tell me who the manager is?
2. What is the recommended dish?
Can you tell me what the recommended dish is?
3. What time would you like to reserve?
May I ask what time you would like to reserve?
4. When is the reservation for lunch?
Do you have any idea when the reservation for lunch is?
5. What is your reservation name, please?
May I know what your reservation name is, please?
6. Can I order a dessert?
I wonder if I could order a dessert.
7. What should I order?
Would you mind telling me what I should order?
8. Do you accept cash or credit cards?
May I ask if you accept cash or credit cards?
9. Do you enjoy the food here?
I would like to know whether you enjoy the food here.
10. How much should we tip?
I’d like to know how much we should tip.
———————————————————————–
Chapter 6 : Negative Sentence
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ตอบคำถามต่อไปนี้ให้อยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Are you Australian? (คุณเป็นคนออสเตรเลียใช่ไหม) : ถาม Are you…?
=> No, I’m not. I’m Kiwi. (ไม่ใช่ครับ ผมเป็นคนนิวซีแลนด์) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I’m not
1. Do you live in Perth? (คุณอาศัยอยู่ในเพิร์ธหรือเปล่า) : ถาม Do you…?
=> No, I don’t. I live in Brisbane. (ไม่ใช่ครับ ผมอาศัยอยู่ที่บริสเบน) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I don’t
2. Don’t you want to go to Bondi Beach with me? (คุณไม่อยากไปหาดบอนดิกับฉันเหรอ) : ถาม Don’t you…?
=> No, I don’t. I’m tired. (ไม่ล่ะ ฉันเหนื่อย) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I don’t
สังเกตว่าเมื่อประโยคคำถามอยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธ (Don’t you…) แล้วจะตอบว่า ไม่ ต้องใช้ No เช่นเดิม จะไม่ตอบ Yes หรือ ใช่
เหมือนในภาษาไทย
3. Have you ever been to Kakadu National Park? (คุณเคยไปอุทยานแห่งชาติคาคาดูไหม) : ถาม Have you…?
=> No, I haven’t. It’s quite for from where I live. (ยังไม่เคยไปเลย มันค่อนข้างไกลจากที่ฉันอยู่น่ะ) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I haven’t
4. Aren’t you afraid to go diving at the Great Barrier Reef? (คุณไม่กลัวหรอที่ไปดำน้ำที่เกรตแบร์ริเออร์รีฟ) : ถาม Aren’t you…?
=> No, I’m not. I’m well-trained. (ไม่เลย ฉันฝึกมาอย่างดีแล้ว) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I’m not
5. Did you go to Sydney with Samuel last weekend? (คุณได้ไปซิดนีย์กับซามูเอลเมื่อสัปดาห์ที่แล้วหรือเปล่า) : ถาม Did you…?
=> No, I didn’t. He went alone. (ไม่ได้ไปนะ เขาไปคนเดียว) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I didn’t
6. Why didn’t you go to the Opera House with us yesterday? (ทำไมคุณไม่ไปโอเปร่าเฮาส์กับเราเมื่อวานนี้ล่ะ) : ถาม Didn’t you…?
=> I didn’t like a crowded place. (ฉันไม่ชอบสถานที่ที่คนเยอะ ๆ น่ะ) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I didn’t
7. Are you going to visit Matt at the hospital tomorrow? (คุณจะไปเยี่ยมแมทท์ที่โรงพยาบาลพรุ่งนี้ไหม) : ถาม Are you (going to…)?
=> No, I am not going to visit him tomorrow. I already have another plan. : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I’m not (going to…)
(ไม่นะ ฉันไม่ได้จะไปเยี่ยมเขาพรุ่งนี้ ฉันมีแผนอื่นแล้วน่ะ)
8. Should I recommend Hotel ABC to my friend? (ฉันควรแนะนำโรงแรม ABC ให้เพื่อนฉันดีไหม) : ถาม Should I
=> No, you shouldn’t. It looks old and unsafe. (ไม่ควรเลย มันดูเก่าและไม่ปลอดภัย) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ You shouldn’t
9. Will you be at the Sydney Harbour Bridge tomorrow? (พรุ่งนี้คุณจะอยู่ที่สะพานซิดนีย์ฮาร์เบอร์หรือเปล่า) : ถาม Will you…?
=> No, I won’t be there tomorrow. I will be out of town. (ไม่อะ พรุ่งนี้ฉันจะไม่อยู่ที่นั่น) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I won’t
10. Were they excited to go to Dreamworld? (พวกเขาตื่นเต้นไหมที่ได้ไปดรีมเวิลด์) : ถาม Were they…?
=> No, they weren’t too excited because they had been there many times. : ตอบปฏิเสธ ใช้ They weren’t
(พวกเขาไม่ได้ตื่นเต้นมาก เพราะพวกเขาเคยไปที่นั่นมาหลายรอบแล้ว)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
เปลี่ยนประโยคบอกเล่า และประโยคคำถามต่อไปนี้ให้อยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. What do you like about Australia?
=> What do you not like about Australia?
What don’t you like about Australia? (informal)
คำอธิบาย เติม not เข้าไปหน้าคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) คือ like เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ หรือเติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Auxiliary Verb)
คือ do เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธแบบไม่เป็นทางการ (informal)
1. I have been to Taronga Zoo.
=> I have not been to Taronga Zoo. / I have never been to Taronga Zoo.
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) คือ have เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ โดยใน Present Perfect Tense เรามักใช้ never (ไม่เคย)
แทน not ได้เพื่อสื่อความหมายว่า ไม่เคยเลยตั้งแต่อดีตจนถึงปัจจุบัน โดยมีโครงสร้างคือ ต้องวาง never ไว้ระหว่างคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) และ
คำกริยาหลัก เป็น have never been เช่นข้อนี้ เป็นต้น
2. They were at Darling Harbour last Friday, weren’t they?
=> They weren’t at Darling Harbour last Friday, were they?
คำอธิบาย หากข้อนั้นมี V. to be เป็นคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ไม่มีคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) เติม not หลัง V. to be ได้เลย ซึ่งในข้อนี้คือหลัง
were โดยหากเปลี่ยนประโยคหลักแล้ว ต้องเปลี่ยน Question Tag ข้างหลังให้เป็นรูปแบบประโยคที่ตรงข้ามกันด้วย หากประโยคหลักเป็นปฏิเสธ
ส่วน Question Tag ต้องไม่ใช่รูปปฏิเสธ
3. Is she working at the Art Gallery of New South Wales?
=> Isn’t she working at the Art Gallery of New South Wales?
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) คือ Is ได้เลยเพื่อสร้างประโยคำถามแบบปฏิเสธ
4. I will go to Queen Victoria Market.
=> I won’t go to Queen Victoria Market.
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Modal Verb) คือ will เพื่อทำให้อยู่ในรูปประโยคปฏิเสธ โดยสามารถทำให้อยู่ในรูปย่อจาก
will not > won’t ได้
5. Should I go to Port Jackson Bay tomorrow?
=> Shouldn’t I go to Port Jackson Bay tomorrow?
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Modal Verb) คือ should เพื่อทำให้อยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธ โดยสามารถทำให้อยู่ในรูปย่อจาก
should not > shouldn’t ได้
6. I may invite Darwin to the party.
=> I may not invite Darwin to the party.
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Modal Verb) คือ may เพื่อทำให้อยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธ โดยการใช้ may, might จะไม่มีรูปย่อ
7. She went to Royal Botanic Garden Sydney two days ago.
=> She didn’t go to Royal Botanic Garden Sydney two days ago.
คำอธิบาย ประโยคที่มีคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ที่ไม่ใช่ V. to be เราไม่สามารถเติม not เข้าไปหลัง V. เลยได้ ต้องใช้คำกริยาช่วย (Aux.)
do, does, did เข้ามาสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธ โดยข้อนี้มีคำกริยาหลักคือ went (เป็นรูปอดีต V.2 ของ go) จึงต้องใช้ did (V.2 ของ V. to do)
เข้ามาช่วย และเติม not ที่หลัง did นอกจากนี้เรายังสามารถทำให้อยู่ในรูปย่อจาก did not > didn’t ได้
8. Who did you meet yesterday at the club?
=> Who did you not meet yesterday at the club? / Who didn’t you meet yesterday at the club? (informal)
คำอธิบาย เติม not เข้าไปหน้าคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) คือ meet เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ หรือเติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย
(Auxiliary Verb) คือ did เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธแบบไม่เป็นทางการ (informal)
9. She likes Vegemite the most.
=> She doesn’t like Vegemite the most.
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้มีคำกริยาหลักคือ like (ในโจทย์เติม s เพราะ she เป็นประธานเอกพจน์) จึงต้องใช้ does (ที่ใช้กับประธานเอกพจน์) เข้ามาช่วย
และลบ s หลัง likes ในประโยคเดิมออกเพราะ does ได้ผันตามประธานไปแล้ว จากนั้นเติม not ที่หลัง does โดยเราสามารถทำให้อยู่ในรูปย่อ
จาก does not > doesn’t ได้
10. Kangaroos are kind to people.
=> Kangaroos are not kind to people. / Kangaroos aren’t kind to people.
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้มี V. to be เป็นคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ไม่มีคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) จึงเติม not หลัง V. to be ได้เลย ซึ่งในข้อนี้คือหลัง are
โดยสามารถทำให้เป็นรูปย่อจาก are not > aren’t ได้
———————————————————————–
Chapter 7 : Imperative Sentence
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
Track 33
เติมลำดับประโยคที่ได้ยินให้ตรงกับรูปภาพ และเขียนประโยคนั้นลงไปในช่องว่างด้วยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง)
Numer 0
Do not throw litter. (ห้ามทิ้งขยะ)
1. Numer 3
Always listen to your guid. (เชื่อฟังไกด์เสมอ)
2. Numer 5
Keep your belongings with you at all times. (พกสิ่งของมีค่าไว้กับตัวคุณตลอดเวลา)
3. Numer 4
Avoid swimming in rivers or lakes. (หลีกเลี่ยงการว่ายน้ำในแม่น้ำหรือทะเลสาบ)
4. Numer 1
Don’t walk around at night. (อย่าเดินเพ่นพ่านในเวลากลางคืน)
5. Numer 2
Do not get out of your vehicle. (ห้ามลงจากรถ)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ประโยคใดต่อไปนี้เป็น Imperative Sentence ทำเครื่องหมายถูกหน้าข้อที่ใช่เลย!
✔️
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Be quiet, please.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
1. Can you do me a favor, please?
Interrogative Sentence (ประโยคคำถาม)
✔️
2. Don’t run outside. (ประโยคคำสั่ง)
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
✔️
3. Watch out for dangerous animals.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
4. What a nice day!
Exclamatory Sentence (ประโยคอุทาน)
✔️
5. Have a lovely day!
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคอวยพร)
✔️
6. You stay in the car.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
✔️
7. Never hunt the animals in the national park.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
✔️
8. Pick up your trash before leaving the park.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
9. You did a great job!
Declarative Sentence (ประโยคบอกเล่า)
✔️
10. Let’s go out for a walk.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคชักชวน)
11. I don’t want to eat.
Negative Sentence (ประโยคปฏิเสธ)
12. He lets me eat cookies.
Declarative Sentence (ประโยคบอกเล่า)
✔️
13. Do not let him get away.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
14. She never eats bananas.
Negative Sentence (ประโยคปฏิเสธ)
✔️
15. Stop talking and eat properly.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
———————————————————————–
Chapter 8 : Subject-Verb Agreement
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
วงกลมเลือกคำกริยาที่ผันตามประธานในประโยคที่ให้มาอย่างถูกต้องเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. My phone _____ dead. Can I borrow your charger? is | are
ตอบ is เพราะประธานของประโยค หรือ my phone เป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ ดังนั้นจึงต้องใช้คำกริยาเอกพจน์ด้วย
1. I _____ not have enough money. Can you lend me some? does | do
ตอบ do เพราะประธานของประโยค คือ I ซึ่งเป็นคำที่ต้องใช้กับ V. to do แบบไม่มี -es เสมอ
2. My boyfriend and I _____ an apartment in Rome. rents | rent
ตอบ rent เพราะเมื่อประธานหลายตัวเชื่อมกันด้วย and แล้ว จะใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์เสมอ ดังนั้น rent ไม่ต้องเติม -s
3. This aircraft _____ about to take off to Florence. is | are
ตอบ is เพราะถึงแม้ว่า aircraft เป็นได้ทั้งคำนามเอกพจน์และพหูพจน์ ซึ่งจะตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์หรือพหูพจน์ก็ได้ก็จริง
แต่ข้างหน้าคำนามมีคำว่า this ที่ใช้กับคำนามเอกพจน์เสมอ ดังนั้น aircraft ในข้อนี้จึงนับเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ และคำกริยาก็
ต้องผันให้เป็นเอกพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน
4. Not only Colomba but also her brother _____ to England every few months. goes | go
ตอบ goes เพราะเมื่อประธานหลายตัวเชื่อมกันด้วย not only… but also แล้ว จะต้องผันคำกริยาตามประธานตัวหลังเสมอ
ในข้อนี้ประธานตัวหลังคือ her brother ซึ่งเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ ดังนั้นจึงต้องใช้ goes ที่เป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์นั่นเอง
5. Some people _____ for more money, but don’t want to work. begs | beg
ตอบ beg ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาพหูพจน์ เพราะประธานของประโยค หรือ some people เป็นคำนามพหูพจน์ แม้จะไม่เติม -s
หลังคำว่า people ก็ตาม
6. My linguistic textbook _____ been lost. has | have
ตอบ has ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์ เพราะประธานของประโยค หรือ my linguistic textbook ไม่เติม -s จึงนับเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์
7. The number of tourists visiting Italy _____ dropped in recent years. has | have
ตอบ has ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์เพราะ the number of (จำนวนของ) ตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
8. A number of employees _____ for vacation leave this month. asks | ask
ตอบ ask ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาพหูพจน์เพราะ a number of (จำนวนมาก) ตามด้วยคำกริยาพหูพจน์เสมอ
9. There _____ not enough money in my pocket. May I borrow you 20€? is | are
ตอบ is เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประโยคขึ้นต้นด้วย there ต้องดูประธานของประโยคที่อยู่ข้างหลังคำกริยาเสมอ ทั้งนี้ประธานในที่นี้
คือคำว่า money ซึ่งถือเป็นคำนามนับไม่ได้ จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาเอกพจน์อย่าง is นั่นเอง
10. Here _____ your shoes that I borrowed yesterday. is | are
ตอบ are เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประโยคขึ้นต้นด้วย here ต้องดูประธานของประโยคที่อยู่ข้างหลังคำกริยาเสมอ ทั้งนี้ประธานในที่นี้
คือคำว่า shoes เติม -s ซึ่งเป็นคำนามพหูพจน์ ดังนั้นจึงต้องใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์อย่าง are ด้วย
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
เติมคำกริยาลงในช่องว่าง โดยผันให้ถูกต้องตามประธานของประโยคเลย!

Lorenzo (ตัวอย่าง) is (be) now studying in his last year of university. One of Lorenzo’s
friends 1. is (be) working for a charity project. Most of the people participating in this
project 2. come (come) from Milan, and everyone 3. works (work) in fashion
industry. They 4. intend (intend) to donate some clothes from their runway shows in the final
year to people in need all over the country. As the number of homeless individuals 5. is (be)
growing due to the pandemic, they 6. need (need) support from
the society. Also, some clothes that 7. are (be) difficult to wear in real life will be sold to
interested people. Every euro earned 8. goes (go) to the charity. Two thousand and
five hundred euros 9. is (be) the goal of this project. Anyone who 10. wants (want)
to support the project can visit www.clothescharityproject.it.
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. ตอบ is เพราะ Lorenzo คือชื่อคน ซึ่งเป็นคนเดียว ดังนั้นต้องใช้ is ที่เป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์
1. ตอบ is เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประธานมีคำว่า of ให้ผันคำกริยาตามคำนามหรือความหมายที่อยู่หน้า of โดยในข้อนี้คือคำว่า one
ที่แปลว่า หนึ่ง ดังนั้นจึงนับเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ เลยต้องตอบ is ที่เป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์ด้วยนั่นเอง
2. ตอบ come เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประธานมีคำว่า of ให้ผันคำกริยาตามคำนามหรือความหมายที่อยู่หน้า of ซึ่งในข้อนี้คือคำว่า most
ที่มีความหมายว่า ส่วนใหญ่ ดังนั้นต้องผันคำกริยาเป็นพหูพจน์ ไม่ต้องเติม -s
3. ตอบ works เพราะเมื่อประธานคือ everyone จะต้องใช้คำกริยาที่เป็นเอกพจน์เสมอ
4. ตอบ intend เพราะประธานคือ they จึงต้องใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์ ไม่ต้องเติม -s
5. ตอบ is เพราะ the number of (จำนวนของ) ตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
6. ตอบ need เพราะประธานคือ they จึงต้องใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์ ไม่ต้องเติม -s
7. ตอบ are เพราะ some clothes เติม -s นับเป็นคำนามพหูพจน์ จึงต้องใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน
8. ตอบ goes เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่หน้าประธานคือคำว่า every ประธานตัวนั้นต้องอยู่ในรูปเอกพจน์เสมอ และคำกริยาก็ต้องเป็นเอกพจน์ด้วย
9. ตอบ is เพราะถึงแม้ประธาน two thousand and five hundred euros จะเติม -s แต่ประธานแบบนี้คือคำที่แสดงค่า หรือปริมาณต่าง ๆ
จึงต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
10. ตอบ wants เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประธานคือ anyone จะถือว่าประธานตัวนั้นเป็นเอกพจน์ และต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
———————————————————————–
Chapter 9 : Subjunctive Sentence
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ลองเขียนประโยคต่อไปนี้ให้อยู่ในโครงสร้าง Subjunctive อย่างถูกต้องทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I should take a vacation. => My boss urges that I (should) take a vacation.
1. We should not be late.
=> He insists (that) we (should) not be late. เป็น Present Subjunctive เพราะเป็นประโยคบอกความต้องการ หรือเสนอแนะ
บางสิ่งบางอย่าง ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive ของ V. to be จะเป็นรูปสามัญ (Base Form / V. infinitive) ไม่ผัน
ไม่เปลี่ยนรูปไม่ว่าจะเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ หรือพหูพจน์ก็ตาม เราจึงใช้ not be ไม่ใช่ are not
2. I should go to the hospital.
=> Maria insisted that I (should) go to the hospital. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive จะเป็น
V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติมไม่ว่าจะเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ หรือพหูพจน์ก็ตาม เราจึงใช้ go แม้ว่าประธานอาจจะเป็น he, she, it ก็ตาม
3. She doesn’t want to come back home.
=> She’d rather not come back home. เป็น Past Subjunctive เพราะเป็นประโยคบอกความต้องการที่ไม่เป็นความจริง หรือตรงข้ามกับ
ความจริงในปัจจุบัน นอกจากนี้เมื่อใดก็ตามที่ใช้วลี would rather / would sooner และประธานในส่วนประโยคหลักกับ Subjunctive
เป็นคนเดียวกัน หรือมีประธานเพียงคนเดียว คำกริยาในส่วน Subjunctive ต้องเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ใช่ V.2
4. It’s a good idea to travel to Peru.
=> Xavier recommended that it be a good idea to travel to Peru. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่ตามมาในส่วน
Subjunctive ของ V. to be จะเป็นรูปสามัญ (Base Form / V. infinitive) ไม่ผัน ไม่เปลี่ยนรูปไม่ว่าจะเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ หรือพหูพจน์
ก็ตาม เราจึงใช้ be ไม่ใช่ is
5. He should start exercising.
=> It’s time he started exercising. เป็น Past Subjunctive ใช้วลี It’s time… เพื่อบอกว่าน่าจะทำบางสิ่งบางอย่างได้เสียที (แต่ทำช้าไป
นิดหน่อย) โดยคำกริยาที่อยู่ในส่วน Subjunctive จะใช้ V.2 จาก start > started
6. The patient should take medicine every 6 hours.
=> The doctor requested (that) the patient (should) take medicine every 6 hours. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่
ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive จะเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม แม้ว่าจะเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ (Patient) ก็จะใช้ take เฉย ๆ
7. People should stay home during the pandemic.
=> The government advises (that) people (should) stay home during the pandemic. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่
ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive จะเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม จึงใช้ stay เฉย ๆ
8. We have to carry a backpack when we go on an adventure.
=> It is advisable that we (should) carry a backpack when we go on an adventure. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่
ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive จะเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม จึงใช้ carry เฉย ๆ
9. I should see the weather forecast before leaving the house.
=> I’d rather see the weather forecast before leaving the house. เป็น Past Subjunctive โดยที่เมื่อใดก็ตามที่ใช้วลี would rather /
would sooner และประธานในส่วนประโยคหลักกับ Subjunctive เป็นคนเดียวกัน คำกริยาในส่วน Subjunctive ต้องเป็น V. infinitive
ไม่ใช่ V.2
10. You should respect other different cultures.
=> It’s essential that you (should) respect other different cultures. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่ตามมาในส่วน
Subjunctive จะเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม จึงใช้ respect เฉย ๆ
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
วงกลมคำตอบที่ถูกต้องที่สุดเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. It’s late, kids. It’s best time you __________ to bed.
a. go b. went c. would rather d. had better
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive เมื่อเจอ It’s best time… ต้องใช้คู่กับ V.2 จึงตอบ went
1. The board of directors insist that all employees __________ from home.
a. should work b. would work c. would rather work d. worked
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Present Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า insist จึงใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม)
โดยเราสามารถมี should หรือละ should ก็ได้
2. It’s crucial that you __________ fit enough to go trekking.
a. are b. be c. have been d. had been
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Present Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า It’s crucial… จึงใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม)
เราจึงใช้ be เฉย ๆ ไม่ใช้ are
3. She wishes we __________ trekking together last time.
a. go b. would go c. went d. had gone
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Perfect Subjunctive เพราะแสดงความต้องการหรือความปรารถนาที่ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงในอดีต
สังเกตได้จากคำกริยา wishes และคำบอกเวลา last time จึงตอบ had gone
4. I’d rather you __________ Romero’s advice because he’s a local guide in Peru.
a. take b. took c. be taken d. had taken
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive เมื่อเจอ would rather ต้องใช้คู่กับ V.2 เพราะมีประธานสองตัว และเป็นคนละคนกัน
จึงตอบ took
5. I suggest that we __________ for her guidance.
a. ask b. asked c. should be asked d. had asked
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Present Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า suggest จึงใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม) จึงตอบ ask ได้เลย
ทั้งนี้สามารถละคำว่า should ก่อน ask ได้
6. I’d rather __________ some medicine before setting off on a journey.
a. prepare b. prepared c. be prepared d. preparing
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive เมื่อเจอ would rather และมีประธานคนเดียว ต้องใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive เสมอ จึงตอบ prepare
7. She takes care of me very well as if she __________ my mother.
a. be b. was c. were d. had been
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า as if ต้องใช้คู่กับ V.2 เพราะตรงข้ามกับความจริงในปัจจุบัน
(เธอไม่ใช่แม่ของฉัน) จึงตอบ were โดยจะใช้ were ที่เป็นรูปอดีตของ V. to be กับประธานทุกตัว แม้ว่าประธานตัวนั้น
จะเป็นเอกพจน์ อย่างคำว่า she ในข้อนี้ก็ตาม
8. The marketing assistant demanded she __________ more for her salary.
a. pay b. paid c. be paid d. was paid
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Present Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า demanded จึงใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม)
โดยข้อนี้จะตอบ pay ไม่ได้ เพราะประโยคอยู่ในรูป Passive Voice (เธอได้รับเงินมากขึ้น [จากบริษัท]) ซึ่งโครงสร้างของ
Passive Voice คือ V. to be + V.3 จึงตอบ be paid
9. I wish I __________ enough sleep last night.
a. have b. had c. had had d. would rather have
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Perfect Subjunctive เพราะแสดงความต้องการที่ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงในอดีต สังเกตได้จากคำกริยา
wish และคำบอกเวลา last night
10. It’s raining nonstop. If only I __________ an umbrella with me.
a. bring b. brought c. have brought d. had brought
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า If only ต้องใช้คู่กับ V.2 เพราะตรงข้ามกับความจริงในปัจจุบัน
(ถ้าฉันเอาร่มมา แต่ความจริงคือ ตอนนี้ไม่มีร่ม) จึงตอบ brought ที่เป็น V.2 ของ bring นั่นเอง
———————————————————————–
Chapter 10 : Reported Speech
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
เปลี่ยนประโยค Direct Speech ให้เป็น Indirect Speech ให้ถูกต้องเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. “My father allows me to go to Copacabana beach with friends.”
=> André said his father allowed him to go to Copacabana beach with friends. เมื่อทำเป็นประโยค Indirect Speech
ต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้อง จึงได้เป็น his father allowed him เพราะ André เป็นผู้ชาย (เปลี่ยนจาก My father allows me)
นอกจากนี้ยังต้องเปลี่ยนคำกริยาให้เป็นอดีตยิ่งขึ้นด้วย ดังนั้นถ้าประโยค Direct Speech ใช้ allows (Present Simple) ประโยค
Indirect Speech จึงต้องเป็น allowed (Past Simple)
1. “Can I go to the party tonight?”
=> Silva asked his dad if / whether he could go to the party that night. เติม if/whether เพื่อทำให้ประโยคคำถามเป็น
ประโยคบอกเล่าแบบ Indirect Speech โดยเปลี่ยน can เป็น could และสลับประธานกับคำกริยา จาก can I > I could โดย
ต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
2. “Is it okay to sleep over at your place?”
=> He asked me if it was okay to sleep over at my place. เติม if/whether เพื่อทำให้ประโยคคำถามเป็นประโยคบอกเล่า
แบบ Indirect Speech โดยเปลี่ยน is (Present Simple) เป็น was (Past Simple) และสลับประธานกับคำกริยา จาก is it > it was
โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
3. “I want to see the panoramic view at Niterói Contemporary Art.”
=> She said she wanted to see the panoramic view at Niterói Contemporary Art. เปลี่ยนจาก want (Present Simple)
> wanted (Past Simple) โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
4. “Paula didn’t let me go surfing at Pipa beach.”
=> He told me that Paula hadn’t let him go surfing at Pipa beach. เปลี่ยนจาก didn’t let (Past Simple) > hadn’t let
(Past Perfect) โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
5. “I was eating breakfast at home yesterday morning.”
=> Santos said he had been eating breakfast at home the other day in the morning. เปลี่ยนจาก was eating
(Past Continuous) > had been eating (Past Perfect Continuous) และเปลี่ยน yesterday morning > the other day
in the morning
6. “I have come here several times.”
=> She said that she had gone there several times. เปลี่ยนจาก have come (Present Perfect) > had gone
(Past Perfect) และเปลี่ยน here > there โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
7. “Would you mind if I leave early?”
=> She asked me whether / if I would mind her leaving early. หรือ whether / if I would mind if she left early.
- ตอบแบบแรก
She asked me whether / if I would mind her leaving early.
ต้องเติม if/whether เพื่อทำให้ประโยค
คำถามเป็นประโยคบอกเล่าแบบ Indirect Speech โดยไม่ต้องเปลี่ยน would และสลับประธานกับกริยาจาก would you >
I would เพราะต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย คือ
you > I และ I > her
- ตอบแบบที่สอง
She asked me whether / if I would mind if she left early. ได้เช่นเดียวกัน โดยมีวิธีเปลี่ยนเหมือนแบบแรก
แต่ต่างกันที่ถ้าต้องต้องการใช้ประธาน (she) ไม่ใช่กรรม (her) เหมือนการตอบแบบแรก จะต้องใส่คำกริยาแท้ให้ประธานตัวนั้นด้วย
ซึ่งเมื่อเปลี่ยนประโยคเป็น Reported Speech แบบ Indirect Speech แล้ว ต้องอย่าลืมเปลี่ยนกาล (Tense) ให้เป็นอดีตมากขึ้น
หรือในข้อนี้ก็คือเปลี่ยนจาก Present Simple Tense (leave) เป็น Past Simple Tense (left) นั่นเอง
8. “What are you doing tomorrow?”
=> Ana asked me what I was doing the next day. สลับประธานกับกริยา are you doing > you are doing
จากประโยคคำถามให้เป็นบอกเล่า เปลี่ยนจาก are doing (Present Continuous) > was doing (Past Continuous)
โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย คือ are you doing > I was doing และเปลี่ยน tomorrow > the next day
9. “Be careful of your belongings.”
=> The police told me to be careful of my belongings. เนื่องจากข้อนี้เป็นประโยค Imperative (คำสั่ง ขอร้อง
อวยพร ชักชวน) ให้ทำบางสิ่ง เราจึงต้องใช้ to + V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม) เหมือนเดิม และต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนาม
ให้ถูกต้องด้วย โดยเปลี่ยนจาก your belongings > my belongings เพราะสังเกตได้จากคำว่า me ตรง The police
told me…
10. “Please show me your passport.”
=> The immigration officer requested me to show him/her my passport. / me to show my passport to him/her.
เนื่องจากข้อนี้เป็นประโยค Imperative (คำสั่ง ขอร้อง อวยพร ชักชวน) ให้ทำบางสิ่ง เราจึงต้องใช้ to + V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม)
โดยจะใช้โครงสร้าง show someone something หรือ show something to someone ก็ได้
นอกจากนี้ วลี Would you mind…? ยังมักตามด้วย V.ing ดังนั้นต้องใช้ I would mind her leaving early. ไม่ใช่
I would mind her leave early.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
สิ่งที่ให้มาในโจทย์ต่อไปนี้สามารถเปลี่ยนเป็นประโยค Indirect Speech ได้อย่างไร ลองจับคู่ดูนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Present Simple Tense Past Simple Tense
1. could NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง)
2. may might
3. Present Continuous Tense Past Continuous Tense
4. Imperative Sentence to + V. infinitive
5. Present Perfect Tense Past Perfect Tense
6. will would
7. should NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง)
8. Past Simple Tense Past Perfect Tense
9. can could
10. must had to
1. could – NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง) เพราะเป็นรูปสุภาพ และเป็นรูปอดีตได้ด้วย จึงไม่มีรูปอดีตกว่านี้
2. may – might เพราะเมื่อทำเป็น Indirect Speech จะต้องเปลี่ยนเป็นรูปอดีตจาก may เป็น might แต่ถ้าหากในโจทย์ให้ might มา
จะตอบ NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง) เหมือนกับ could ในข้อแรก
3. Present Continuous Tense – Past Continuous เพราะจะต้องเปลี่ยนให้เป็น Tense ที่เป็นอดีต จึงใช้ Past Continuous Tense
4. Imperative Sentence – to + V. infinitive เพราะประโยค Imperative (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง อวยพร ชักชวน)
ต้องใช้ V. infinitive (ไม่เติม ไม่ผัน) เสมอ แม้จะทำให้เป็น Indirect Speech ก็จะไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง
5. Present Perfect Tense – Past Perfect Tense เพราะจะต้องเปลี่ยนให้เป็น Tense ที่เป็นอดีต จึงใช้ Past Perfect Tense
6. will – would เพราะเมื่อทำเป็น Indirect Speech จะต้องเปลี่ยนเป็นรูปอดีตจาก will เป็น would แต่ถ้าหากในโจทย์ให้ would มา
จะตอบ NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง) เหมือนกับ could และ might
7. should – NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนรูป) เพราะเป็นการให้คำแนะนำ จะไม่มีการเปลี่ยนรูปแม้จะอยู่ใน Indirect Speech ก็ตาม
8. Past Simple Tense – Past Perfect Tense เพราะจะต้องเปลี่ยนให้เป็น Tense ที่เป็นอดีตที่เก่ากว่า จึงใช้ Past Perfect Tense
ซึ่งในการใช้ Tense คู่กันในประโยคปกติ Past Simple Tense จะเป็นเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นทีหลังเสมอ
9. can – could เพราะเมื่อทำเป็น Indirect Speech จะต้องเปลี่ยนเป็นรูปอดีตจาก can เป็น could แต่ถ้าหากในโจทย์ให้ could มา
จะตอบ NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง) เหมือนกับในข้อแรก
10. must – had to เพราะโดยปกติแล้ว must กับ have to มีความหมายคล้ายกัน แปลว่า “ต้อง” ทำบางสิ่งบางอย่าง และปกติแล้ว
เมื่อเปลี่ยนเป็นประโยคเป็น Indirect Speech จะต้องผันคำกริยาให้เป็นอดีตมากยิ่งขึ้นด้วย ฉะนั้นรูป Indirect Speech ของ must
จึงใช้ had to ที่ผันมาจาก have to อีกที
———————————————————————–
Chapter 11 : Relative Clause
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
เติม Relative Pronoun ลงในคำใบ้ที่ให้มา แล้วระบุว่าแต่ละคนในรูปคือใครกันบ้างนะ!
Clue 1: The girl who has got fair hair is not Karina.
(เด็กผู้หญิงคนที่มีผมสีสว่างไม่ใช่คาริน่า)
Clue 2: The boy who is listening to music is not Nathan.
(เด็กผู้ชายคนที่ฟังเพลงอยู่ไม่ใช่นาธาน)
Clue 3: There’s something in Maria’s hand which/that has red color.
(มีบางสิ่งอยู่ในมือมาเรียที่มีสีแดง)
Clue 4: The girl whose name is Ariana is not standing next to Maria.
(เด็กผู้หญิงที่ชื่อของเธอคืออาริอานาไม่ได้ยืนอยู่ข้างมาเรีย)
Clue 5: Karina is looking at the place where Alexandro is standing.
(คาริน่ากำลังมองไปที่ที่อเล็กซานโดรยืนอยู่)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ช่วยรวมประโยคที่ให้มา 2 ประโยคเป็นประโยคเดียวกันโดยใช้ Relative Clause ทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I just booked a hotel in Spain. The hotel is luxurious and spacious.
=> I just booked a hotel which/that is luxurious and spacious in Spain.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวถึง the hotel ซ้ำ และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
1. Andres will visit his relative. His relative’s house is in the city center.
=> Andres will visit his relative whose house is in the city center.
ใช้ whose แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง his relative’s house และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
2. Andres is going to stay at a hotel in Bilbao. His relative lives in Bilbao.
=> Andres is going to stay at a hotel in Bilbao where his relative lives/which his relative lives in.
ใช้ where หรือ which แทนการกล่าวถึง Bilbao (เมืองบิลเบา) ซ้ำ และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม โดยที่ถ้าใช้ where
ไม่ต้องมี in ต่อท้าย แต่ถ้าใช้ which ต้องมี in ต่อท้ายด้วยเพราะ which his relative lives in มีความหมาย
เหมือนกับ where his relative lives
3. Andres is staying at the hotel. His relative recommended this hotel.
=> Andres is staying at the hotel which/that his relative recommended.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the hotel และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
4. Andres’ girlfriend will be coming later tonight. His girlfriend flight is delayed.
=> Andres’ girlfriend whose flight is delayed will be coming later tonight.
ใช้ whose แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง Andres’s girlfriend’s flight และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
5. The pretty girl with dark hair is Andres’ girlfriend. The girl is carrying a pink luggage.
=> The pretty girl with dark hair who/that is carrying a pink luggage is Andres’ girlfriend.
ใช้ who หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง The girl และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
6. This hotel has a big swimming pool. Andres likes this swimming pool the most.
=> This hotel has a big swimming pool which/that Andres likes the most.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the swimming pool และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
7. The bed was so soft. They slept in this bed.
=> The bed which/that they slept in was so soft.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the bed และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
8. We can see the panoramic view from the hotel restaurant. The hotel restaurant is on the 45th floor.
=> We can see the panoramic view from the hotel restaurant which/that is on the 45th floor.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the hotel restaurant และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
9. He hasn’t found the room key yet. He lost the key.
=> He hasn’t found the room key which/that he lost yet.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the key และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
10. The man is a hotel manager. He is talking to the man.
=> The man whom/that he is talking to is a hotel manager. ใช้ whom หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the man
ที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรมของประโยค He is talking to the man. และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม ซึ่งในภาษาพูดเราอาจใช้ who
แทน whom ได้เช่นกัน
———————————————————————–
Chapter 12 : Participles
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
อ่านคำใบ้ด้านล่าง และนำคำกริยาที่เปลี่ยนเป็นรูป Participle ตามที่กำหนด มาใส่ในตารางให้ถูกต้องเลย!
แนวตั้ง
1. see (past participle) = seen (Irregular Verb ผันไม่ปกติ เปลี่ยนรูป)
2. reserve (past participle) = reserved (Regular Verb ผันเติม -ed)
3. complain (present participle) = complaining (เติม -ing)
5. book (present participle) = booking (เติม -ing)
6. call (present participle) = calling (เติม -ing)
8. leave (present participle) = leaving (เติม -ing)
9. put (past participle) = put (ไม่เปลี่ยนรูป)
แนวนอน
4. steal (past participle) = stolen (Irregular Verb ผันไม่ปกติ เปลี่ยนรูป)
7. arrive (past participle) = arrived (Regular Verb ผันเติม -ed)
10. visit (present participle) = visiting (เติม -ing)
11. wait (present participle) = waiting (เติม -ing)
12. buy (past participle) = bought (Irregular Verb ผันไม่ปกติ เปลี่ยนรูป)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
อ่านโจทย์แล้วเลือกตัวเลือกที่ถูกต้องให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Hotel guests next door turned on the music very loud last night. It was very __________.
a. annoyed b. annoying
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้ตอบ annoying (น่ารำคาญ) เพราะ it หมายถึงเสียงเพลงที่ดังเมื่อคืน ไม่สามารถตอบ annoyed (รู้สึกรำคาญ) ได้
เพราะประธานต้องเป็นคนเท่านั้นถึงจะแสดงความรู้สึกได้
1. The hotel service were excellent. I was __________ with their well-trained manners.
a. pleased b. pleasing
คำอธิบาย เห็นประธานเป็นคนขึ้นต้นประโยค ต้องตามด้วย “รู้สึก…” หรือ V.3 (-ed) ข้อนี้จะได้ว่า ฉันรู้สึกพอใจกับมารยาท
ที่ได้รับการฝึกมาอย่างดีของพวกเขา
2. We’ve won the prize for free room upgrade. The hotel suite is __________.
a. amazed b. amazing
คำอธิบาย ประธานของประโยคไม่ใช่คนแต่เป็น The hotel suite (ห้องสวีทของโรงแรม) จึงต้องตามด้วย V.ing จะใช้
“รู้สึก…” ไม่ได้ ข้อนี้จะได้ว่า ห้องสวีทของโรงแรมนั้นยอดเยี่ยม
3. Be careful! There is __________ window glass on the floor.
a. broken b. breaking
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้พูดถึง window glass (กระจกหน้าต่าง) จึงตอบ broken (ที่ถูกทำให้แตก) กระจกไม่ได้แตกเอง
4. The man __________ at the reception is a hotel manager.
a. stood b. standing
คำอธิบาย ประธานคือ The man (ผู้ชายคนนั้น) ใช้ standing เพราะประธานทำกริยานั้นเองคือ ผู้ชายที่ยืนอยู่ที่แผนกต้อนรับ
5. There is no __________ glass in the room at all.
a. drunk b. drinking
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้สังเกตที่ glass (แก้วน้ำ) ซึ่งคำที่มาขยายข้างหน้าคำนาม เราเรียกว่าคำคุณศัพท์ (Adj.) โดยการใช้คำกริยา
มาทำเป็น Adj. เพื่อบอกจุดประสงค์บางอย่าง เราจะใช้ V.ing เช่น drinking glass (แก้วสำหรับดื่มน้ำ) walking stick
(ไม้เท้าสำหรับค้ำเดิน) running shoes (รองเท้าสำหรับวิ่ง) เป็นต้น
6. I reserved a non-__________ room, but I can still smell lingering cigarette odor in the living room.
a. smoked b. smoking
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้สังเกตที่ room (ห้อง) ซึ่งคำที่มาขยายคำนามข้างหน้าจะต้องเป็น V.ing ฉะนั้นจึงต้องเป็น non-smoking room
(ห้องที่ปลอดบุหรี่) ถ้าใช้ non-smoked room จะแปลว่า ห้องที่ไม่ถูกรมควัน
7. The guest is complaining to the front office about her __________ items after the maid cleaned up her room.
a. lost b. losing
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้ไม่ได้พูดถึงคนแต่พูดถึง items (สิ่งของ) ซึ่ง “ถูกทำหายไป” (lost) ไม่ได้หายไปเอง
8. My friend was __________ because she received a gift voucher from the hotel for her birthday.
a. surprised b. surprising
คำอธิบาย ประธานของประโยคคือ My friend (เพื่อนของฉัน) ซึ่งเป็นคน เราจึงใช้ surprised (รู้สึกประหลาดใจ) ไม่ใช่
surprising (น่าประหลาดใจ)
9. The room pictures __________ on the website looked much better than the actual room.
a. posted b. posting
คำอธิบาย ประธานคือ The room pictures (รูปถ่ายของห้องพัก) ซึ่ง “ถูกโพสต์” (posted) ลงเว็บไซต์ ไม่ได้โพสต์ด้วยตัวเอง
10. Our time __________ in Berlin was truly memorable.
a. spent b. spending
คำอธิบาย ประธานคือ Our time (เวลาของพวกเรา) ซึ่ง “ถูกใช้” (spent) ในเบอร์ลิน ประธานนี้ไม่สามารถทำกริยาใช้เวลาเองได้
———————————————————————–
Chapter 13 : Active-Passive Voice
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ดูประโยคที่ให้มา และวงกลมเลือกให้ถูกต้องว่าประโยคนั้นเป็น Active Voice หรือ Passive Voice!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Harajuku is a famous place for cosplayers.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะในประโยคไม่มีกรรม และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
1. Osaka is known as the nation’s kitchen for its delicious food.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Osaka และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ is + known
2. We love to stay in a ryokan.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะประธานในประโยคคือ We ทำกริยา (love) เอง และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
3. Shinkanzen is normally used to travel between prefectures.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Shinkanzen และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ is + used
4. Geisha dance has become one of the traditional arts in Japan.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะในประโยคไม่มีกรรม และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
5. Kyoto used to be Japan’s capital for 1000 years.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะในประโยคไม่มีกรรม และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
6. Hiroshima and Nagasaki were attacked by atomic bombs during WWII.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Hiroshima and Nagasaki และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ were + attacked
7. Yakushima was chosen to be World Natural Heritage site by UNESCO.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Yakushima และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ was + chosen
8. Nikko has been a center of Shinto and Buddhist worship for many centuries.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะในประโยคไม่มีกรรม และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
9. Cherry blossom forecast will be released around late January or early February.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Cherry blossom forecast และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ be + released
10. Japanese language is considered to be a difficult language to learn.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Japanese language และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ is + considered
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
โจทย์ที่ให้มาจะมีทั้งประโยค Active Voice และ Passive Voice ช่วยเขียนใหม่ให้เป็นอีก Voice หนึ่งที่ไม่เหมือนกับโจทย์ทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. She has written a new book for 2 hours. (Active)
=> A new book has been written by her for 2 hours. (Passive)
1. I eat sushi every day. (Active)
=> Sushi is eaten by me every day. (Passive)
2. A gashapon vending machine is being repaired by him. (Passive)
=> He is repearing a gashapon vending machine. (Active)
3. The teacher teaches Japanese language at school. (Active)
=> Japanese language is taught by the teacher at school. (Passive)
4. Mount Fuji has been visited by many people. (Passive)
=> Many people have visited Mount Fuji. (Active)
5. The tour guide will take us to Tokyo Imperial Palace. (Active)
=> We will be taken to Tokyo Imperial Palace by the tour guide. (Passive)
6. Snow can be seen during winter in Hokkaido. (Passive)
=> People can see snow during winter in Hokkaido. (Active)
(เมื่อไม่เจอผู้กระทำ หรือ by + ผู้กระทำในประโยค เรามักจะใส่ผู้กระทำนั้นให้เป็น People)
7. I bought this souvenir from Shibuya. (Active)
=> This souvenir was bought by me from Shibuya. (Passive)
8. People can find many kinds of fish in Tsukiji Fish Market. (Active)
=> Many kinds of fish can be found in Tsukiji Fish Market. (Passive)
(เวลาเจอ People เป็นประธานในประโยค เรามักจะละผู้กระทำ เมื่อนำไปเขียนในรูปประโยค
Passive ซึ่งแตกต่างจากข้อ 4. ที่เป็น Many people ตรงที่ข้อ 4. นั้นจะละไม่ได้เพราะ
มีความเจาะจงว่า “คนจำนวนมาก”)
9. Visitors are feeding the deer at Nara Park. (Active)
=> The deer are being fed by visitors at Nara Park. (Passive)
10. We rent kimonos in Kyoto. (Active)
=> Kimonos are rented by us in Tokyo. (Passive)
———————————————————————–
Chapter 14 : Comparison
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ลองเขียนเปรียบเทียบขั้นกว่าของ 2 สิ่งที่ให้มาดูนะ!
ประโยคคำถามทุกข้อสามารถเอาไปประยุกต์ใช้ถามเวลาไปเที่ยวหรือซื้อของได้เลยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Q: Which one is more popular? Salted egg chips or plain potato chips? (อะไรเป็นที่นิยมมากกว่ากัน
มันฝรั่งทอดรสไข่เค็มหรือมันฝรั่งทอดรสชาติปกติ)
A: Salted egg chips are more popular than plain potato chips. (popular) (มันฝรั่งทอดรสไข่เค็มเป็นที่นิยมกว่า
มันฝรั่งทอดรสชาติปกติ)
1. Q: What’s the difference between these two things? (อะไรที่แตกต่างกันระหว่างสองสิ่งนี้)
A: Kopi O (black coffee with sugar) is more bitter than (bitter) Kopi C (coffee with sugar & evaporated milk).
(โกปี๊ โอ (กาแฟดำใส่น้ำตาล) รสขมกว่า โกปี๊ ซี (กาแฟใส่น้ำตาล และนมข้นจืด)) สังเกตว่า Kopi O นั้นขมกว่าเพราะ
มีแค่น้ำตาล แต่ Kopi C มีทั้งน้ำตาลและนมข้นจืด
2. Q: What do you recommend? (คุณแนะนำอะไรเหรอ)
A: I recommend Chilli crab. It is spicier than (spicy) Bak Kut Teh. (ฉันแนะนำปูผัดพริก มันเผ็ดกว่าบักกุ๊ดเต๋)
สังเกตว่า Chilli crab เผ็ดกว่าเพราะมีคำว่า Chilli (พริก)
3. Q: What souvenirs should I buy for my friends? (ฉันควรซื้ออะไรเป็นของฝากให้เพื่อนของฉันดี)
A: Tourists like miniature Merlion souvenirs better than (good) anything else. (นักท่องเที่ยวชอบของฝาก
เป็นเมอร์ไลออนจิ๋วมากกว่าสิ่งอื่น ๆ)
4. Q: How does it taste? (รสชาติเป็นอย่างไรเหรอ)
A: It’s great! Bakkwa (BBQ meat) is more delicious than (delicious) I thought. (เยี่ยมเลย! บักกวา (หมูแผ่น)
นั้นอร่อยกว่าที่ฉันคิดไว้อีก)
5. Q: Where is the best place to shop? (ที่ไหนดีที่สุดที่จะซื้อของเหรอ)
A: It depends on your budget. Shopping at ION Orchards is definitely more expensive than (expensive)
shopping at China town. (ขึ้นอยู่กับงบเธอน่ะ ชอปปิงที่ไอออน ออชาร์ดส์แพงกว่าชอปปิงที่ไชน่าทาวน์แน่นอนอยู่แล้ว)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ดูรูปภาพ และเติมประโยคให้สมบูรณ์โดยใช้การเปรียบเทียบที่ได้เรียนมาแล้วเลย!

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Sister Merlion is the most shopaholic person in their family. (shopaholic) *ขั้นสุด เปรียบเทียบตั้งแต่ 3 สิ่งขึ้นไป
1. Baby Merlion is younger than Sister Merlion and Granny Merlion. (young) *ขั้นกว่า
2. Granny Merlion is the oldest in the family. (old) *ขั้นสุด เปรียบเทียบตั้งแต่ 3 สิ่งขึ้นไป
3. Sister Merlion’s eyesight is better than Granny’s. (good) *ขั้นกว่า
4. Baby Merlion is not as strong as Sister Merlion. (not strong) *ขั้นเท่า
5. Granny Merlion is the kindest person in the world. (kind) *ขั้นสุด เปรียบเทียบตั้งแต่ 3 สิ่งขึ้นไป
6. Baby Merlion and Sister Merlion run faster than Granny Merlion. (fast) *ขั้นกว่า
7. Sister Merlion is the tallest of them all. (tall) *ขั้นสุด เปรียบเทียบตั้งแต่ 3 สิ่งขึ้นไป
8. Granny Merlion is taller than Baby Merlion but shorter than Sister Merlion. (tall / short) *ขั้นกว่า
9. Baby Merlion and Sister Merlion visit their Granny Merlion less/more often than last month. (often) *ขั้นกว่า
10. The warmer Granny Merlion is, the more sensitive Baby Merlion becomes. (warm / sensitive) *ขั้นกว่า
———————————————————————–
Chapter 15 : If-Clause
If-Clause Type 0
เขียนประโยคที่กำหนดมาให้อยู่ในรูป If-Clause Type 0 อย่างถูกต้อง และระบุให้หน่อยนะว่าส่วนไหนคือ
If-Clause กับ Main Clause!
If-Clause Main Clause
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. If you drink (drink) a lot of alcohol, you get (get) drunk.
If-Clause Main Clause
1. If you heat (heat) water, it boils (boil).
Main Clause If-Clause
2. I usually have (have) a cup of coffee when I get up (get up) early.
Main Clause If-Clause
3. I feel (feel) tired if I don’t get (not get) enough sleep.
If-Clause Main Clause
4. If you eat (eat) a lot of junk food, you get (get) fat.
If-Clause Main Clause
5. When you mix (mix) blue and yellow together, you get (get) green.
If-Clause Type 1
นำประโยคอิสระทั้งสองที่ให้มา เขียนเป็นประโยคเงื่อนไขให้เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกันเถอะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. James doesn’t come. / Eva is very sad. => If James doesn’t come, Eva will be very sad.
(ถ้าเจมส์ไม่มา เอวาคงจะเศร้ามาก)
1. I get a good job. / My mother is proud of me. => If I get a good job, my mother will be proud of me.
(ถ้าฉันได้งานดี ๆ แม่คงจะภูมิใจในตัวฉัน)
2. You feel sad. / I cheer you up. => If you feel sad, I will cheer you up.
(ถ้าเธอรู้สึกเศร้า ฉันจะคอยให้กำลังใจเอง)
3. I am there for you. / You need my support. => I will be there for you if you need my support.
(ฉันจะอยู่ตรงนั้นเพื่อเธอ ถ้าเธอต้องการกำลังใจ)
4. I might fail the test. / I do not study hard. => I might fail the test if I do not study hard.
(ฉันอาจจะสอบตกถ้าฉันไม่ตั้งใจเรียนให้หนัก)
5. I can help you. / You need some advice. => I can help you if you need some advice.
(ฉันสามารถช่วยเธอได้นะ ถ้าเธอต้องการคำแนะนำ)
ทุกประโยคสามารถสลับตำแหน่ง If-Clause และ Main Clause ได้ เช่น 1. My mother will be proud of me if I get a good job.
If-Clause Type 2
อ่านเนื้อเรื่อง และเติมรูปแบบประโยค If-Clause Type 2 ให้สมบูรณ์เลย!
I have a friend named Claire. (ตัวอย่าง) She wishes she could speak (can speak) Korean because she
loves Korean idols. (1) She wishes she could meet (can meet) her favorite idols every day. (2) She
would buy (buy) all of their albums if she had (have) enough money. (3) If she
were (be) rich, she would hire (hire) them to be at her birthday party. (4) It would be
(be) easier if they lived (live) in the same country. However, it is not as easy as she wishes.
(5) If I were (be) Claire, I would move (move) to live in Korea first.
ฉันมีเพื่อนคนหนึ่งชื่อแคลร์ หล่อนหวังว่าหล่อนจะพูดภาษาเกาหลีได้เพราะหล่อนรักไอดอลเกาหลี หล่อนหวังว่าหล่อน
จะได้เจอไอดอลที่หล่อนชอบทุก ๆ วัน หล่อนจะซื้ออัลบั้มของพวกเขาถ้าหล่อนมีเงินมากพอ ถ้าหล่อนรวย หล่อนจะจ้างให้พวกเขา
มางานวันเกิด มันคงจะง่ายกว่านี้ถ้าพวกเขาอาศัยอยู่ในประเทศเดียวกัน อย่างไรก็ตาม มันไม่ง่ายอย่าที่หล่อนหวัง ถ้าฉันเป็นแคลร์
ฉันจะย้ายไปเกาหลีก่อนอันดับแรกเลย
If-Clause Type 3
เปลี่ยนประโยคที่ให้มาให้อยู่ในรูป If-Clause Type 3 ที่มีความหมายสอดคล้องกันทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. He didn’t have tattoos, so I left him. => If he had had tattoos, I wouldn’t have left him.
(เขาไม่มีรอยสัก/ไม่ได้สัก ฉันจึงทิ้งเขา) (ถ้าเขามีรอยสัก/สัก ฉันคงไม่ทิ้งเขา)
1. My boyfriend asked me out because I had curly hair. (แฟนฉันขอฉันออกเดตเพราะฉันมีผมหยักศก)
=> My boyfriend wouldn’t have asked me out if I hadn’t had curly hair.
(แฟนฉันคงไม่ขอฉันออกเดต ถ้าฉันไม่ได้มีผมหยักศก)
2. I didn’t watch Korean series because I didn’t know it before. (ฉันไม่ได้ดูซีรีส์เกาหลีเพราะฉันไม่เคยรู้จักมาก่อน)
=> I would have watched Korean series if I had known it before.
(ฉันคงจะดูซีรีส์เกาหลีไปแล้ว ถ้าฉันรู้จักมันมาก่อน)
3. I didn’t date him because we were just friends. (ฉันไม่ได้เดตกับเขาเพราะเราเป็นแค่เพื่อนกัน)
=> I would have dated him if we hadn’t been just friends.
(ฉันคงจะเดตกับเขาไปแล้ว ถ้าเราไม่ได้เป็นแค่เพื่อนกัน)
4. Kim didn’t know that it was Han’s birthday, so she didn’t give him a present. (คิมไม่รู้ว่ามันเป็นวันเกิดของฮัน
ดังนั้นเธอจึงไม่ได้ให้ของขวัญกับเขา)
=> If Kim had known that it was Han’s birthday, she would have given him a present.
(ถ้าคิมรู้ว่ามันเป็นวันเกิดของฮัน เธอคงจะให้ของขวัญกับเขาแล้ว)
5. I didn’t exercise harder, so I didn’t have six packs. (ฉันไม่ได้ออกกำลังกายหนักกว่านี้ ฉันเลยไม่มีซิกซ์แพค)
=> If I had exercised harder, I would have had six packs.
(ถ้าฉันออกกำลังกายหนักกว่านี้ ฉันคงมีซิกซ์แพคไปแล้ว)
ทุกประโยคสามารถสลับตำแหน่ง If-Clause และ Main Clause ได้ เช่น 1. If I hadn’t had curly hair, my boyfriend wouldn’t have asked me out.
If-Clause Exercise
เติมประโยคเงื่อนไขให้ถูกต้องตามรูปแบบที่เรียนมาเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I wouldn’t have met him if I hadn’t been (be) to Korea 2 years ago.
(ฉันคงไม่ได้เจอเขา ถ้าฉันไม่ได้ไปเกาหลีเมื่อ 2 ปีที่แล้ว)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 3 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ผ่านไปแล้ว ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงตอนนั้น ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้ว
ฉันได้ไปเกาหลีแล้วก็ได้เจอเขา
1. If the water temperature is below zero, water turns (turn) into ice. (ถ้าอุณหภูมิของน้ำต่ำกว่าศูนย์ น้ำจะกลายเป็นน้ำแข็ง)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 0 พูดถึงความเป็นจริงทางวิทยาศาสตร์ หรือเหตุการณ์ที่เป็นจริงเสมอ
2. I would eat (eat) Kimchi Jjigae if I were able to eat spicy food. (ฉันคงจะกินซุปกิมจิไปแล้วถ้าฉันกินเผ็ดได้)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 2 พูดถึงสิ่งที่ตรงกันข้ามกับเหตุการณ์หรือความจริงในปัจจุบัน ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วตอนนี้ฉันก็กินเผ็ดไม่ได้
ฉันเลยไม่กินซุปกิมจิ
3. We will go to Korea next month when we finish (finish) our exam. (พวกเราจะไปเกาหลีกันเดือนหน้าตอนที่เราสอบเสร็จ)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 1 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่มีโอกาสหรือแนวโน้มที่จะเป็นไปได้ในอนาคต คือพวกเราจะไปเกาหลีกันเดือนหน้า
เมื่อเราสอบเสร็จ
4. If we had had (have) more time, we would have visited Busan as well. (ถ้าพวกเรามีเวลามากกว่านี้ พวกเราคงจะได้ไปเที่ยวปูซานด้วย)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 3 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ผ่านไปแล้ว ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงตอนนั้น ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วเรามีเวลาจำกัด เราเลย
ไม่ได้ไปเที่ยวปูซานด้วย)
5. If I won (win) a lottery for a million baht, I would go to every concert of my idol. (ถ้าฉันถูกลอตเตอรี่หนึ่งล้านบาท ฉันจะไป
ทุกคอนเสิร์ตของไอดอลที่ชอบเลย)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 2 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่แทบจะเป็นไปไม่ได้ หรือเป็นสิ่งที่ตรงกันข้ามกับเหตุการณ์หรือความจริงในปัจจุบัน
ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วตอนนี้ฉันไม่ได้ถูกหวยเป็นล้านบาท เลยไม่ได้ไปทุกคอนเสิร์ตของไอดอลที่ชอบ
6. Snow falls when it is (be) winter in Korea. (หิมะตกเมื่อเป็นหน้าหนาวที่เกาหลี)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 0 พูดถึงความเป็นจริงทางวิทยาศาสตร์ หรือเหตุการณ์ที่เป็นจริงเสมอ
7. Jay will go (go) on a date with me this Saturday unless he is sick. (เจย์จะออกเดตกับฉันวันเสาร์นี้ ถ้าหากเขาไม่ป่วย)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 1 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่มีโอกาสหรือแนวโน้มที่จะเป็นไปได้ในอนาคต คือเจย์จะไปเดตกับฉันวันเสาร์นี้แน่ ๆ
ถ้าหากเขาไม่ป่วย
8. If the weather had been good the other day, we would have gone (go) skiing. (ถ้าเมื่อวันก่อนอากาศดี เราคงได้ไปเล่นสกีกัน)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 3 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ผ่านไปแล้ว ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงตอนนั้น ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้ววันก่อนนั้นอากาศไม่ดี
เราเลยไม่ได้ไปเล่นสกี
9. If I debuted (debut) as an idol, I would move to Korea. (ถ้าหากฉันเดบิวต์เป็นไอดอล ฉันจะย้ายไปเกาหลี)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 2 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่แทบจะเป็นไปไม่ได้ หรือเป็นสิ่งที่ตรงกันข้ามกับเหตุการณ์หรือความจริงในปัจจุบัน
ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วฉันไม่ได้เดบิวต์เป็นไอดอล เลยไม่ได้ย้ายไปประเทศเกาหลี
10. I wouldn’t have been his fan if I had not met (not meet) him at the concert last year. (ฉันคงไม่ได้เป็นแฟนคลับเขา
ถ้าหากฉันไม่ได้เจอเขาที่คอนเสิร์ตปีที่แล้ว)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 3 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ผ่านไปแล้ว ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงตอนนั้น ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วฉันเป็นแฟนคลับเขา
เพราะฉันได้เจอเขาที่คอนเสิร์ตเมื่อปีที่แล้ว
✿ แต่ถ้าอยากติวคอร์ส KruDew ติว TOEIC มีให้ครบทุกอย่าง! ✿

ติว TOEIC กับครูดิว ดียังไง?
- คอร์สติว TOEIC ของครูดิวนั้น เรียน Online
- แบ่งบทเรียนชัดเจน เรียนง่ายไม่งง คลิ๊กเลือกบทเรียนที่ต้องการได้ทันที
- สามารถหยุด, เล่นซ้ำบทเรียนที่ต้องการได้แบบไม่อั้น! (ตลอดระยะเวลาคอร์ส)
- อัพเดทข้อสอบ New TOEIC ใหม่ล่าสุด! ครบชุด!
- มีไฟล์ E-Book (PDF) ประกอบการเรียนให้ดาวน์โหลด (และมีหนังสือเรียนเป็นเล่มส่งให้ถึงบ้าน)
- เรียนเวลาไหนก็ได้ อยู่ที่ไหนก็เรียนได้ แค่มี Internet
- หากมีข้อสงสัยเกี่ยวกับบทเรียน สามารถส่งคำถามหาทีมงานได้
- การันตีคะแนน 750+ (หากสอบแล้วไม่ถึง สามารถแจ้งทวนคอร์สได้ฟรี!)
ถ้ายังไม่แน่ใจ? ทดลองติวฟรีก่อนได้ที่ >>> คอร์ส KruDew TOEIC
TOEIC® and TOEFL® are registered trademarks of Educational Testing Service (ETS). This product is not endorsed or approved by ETS.
[NEW] Grammar Go! แจกเฉลย Exercise พร้อมคำอธิบายละเอียด! | กริยา 3 ช่อง climb – NATAVIGUIDES
รวมเฉลย Exercise พร้อมคำอธิบายละเอียด!
Chapter 1 : Part of Speech
Chapter 2 : Determiner
Chapter 3 : Tense
Chapter 4 : Sentence Structure
Chapter 5 : Question
Chapter 6 : Negative Sentence
Chapter 7 : Imperative Sentence
Chapter 8 : Subject-Verb Agreement
Chapter 9 : Subjunctive Sentence
Chapter 10 : Reported Speech
Chapter 11 : Relative Clause
Chapter 12 : Participles
Chapter 13 : Active-Passive Voice
Chapter 14 : Comparison
Chapter 15 : If-Clause
———————————————————————–
Chapter 1 : Part of Speech
Noun
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
คำนามหน้าตาแบบนี้เป็นประเภทไหนกันนะ ดูำศัพท์ที่ให้มา แล้วเติมคำตอบลงในช่องว่างเลย!
Common Noun = 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9
Proper Noun = 3, 6, 7, 10
Countable Noun = 2, 5, 9
Uncountable Noun = 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10
Singular Noun = 2, 4, 8, 9
Plural Noun = 1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ช่วยวงกลมคำนามในประโยค และบอกหน้าที่ของคำนามนั้นให้หน่อยนะ!
Subject Object of Preposition
(ตัวอย่าง) Hermione is known for her intelligence.
Subject Subject Complement
1. His name is Harry.
Object of Preposition Object of Preposition
2. He lived with his uncle and aunt in England.
Subject Direct Object
3. Harry was invited to join a school.
Subject Subject Complement
4. This school is a magical school.
Direct Object Object of Preposition
5. He met Ron and Hermione on the train.
Object Complement
6. He introduced himself and said, “You can call me Harry”.
Subject Subject Complement
7. Ron and Hermione became Harry’s best friends.
Subject Indirect Object Direct Object
8. Ron gave Harry a sweater.
Subject Subject Complement Object of Preposition
9. Dolores is a professor at the school.
Subject Direct Object
10. Harry rides a broomstick very well.
Verb
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
คำกริยาที่ขีดเส้นใต้ในประโยคต่อไปนี้เป็นคำกริยาประเภทไหนกันนะ กากบาทในช่องสี่เหลี่ยมที่ถูกต้องเลย!

1. My parents have just arrived at the airport.
-
arrive (V.1) / arrived (V.2) / arrived (V.3) – เป็น Intransitive Verb (ไม่ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Regular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบปกติโดยการเติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้ arrive (V.) ใช้ Present Perfect Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เพิ่งเกิดขึ้นและจบไป หรือเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นชั่วระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และยังส่งผลมาถึงปัจจุบัน จึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + have/has + V.3
-
ทั้งนี้ arrive (V.) เป็น Intransitive Verb เพราะไม่ต้องมีกรรม (O) มารองรับ สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้ เช่น They have arrived. = พวกเขามาถึงแล้ว หากต้องการขยายเพิ่มว่ามาถึงที่ไหน สามารถเติมคำบุพบท (Prepo.) บอกสถานที่เข้าไปได้ เช่น They have arrived at the supermarket. = พวกเขามาถึงที่ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ตแล้ว
2. All students are sitting at the desk.
-
sit (V.1) / sat (V.2) / sat (V.3) – เป็น Intransitive Verb (ไม่ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Irregular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบเปลี่ยนรูปไปไม่ได้เติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้
sit (V.) ใช้ Present Continuous Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นอยู่ในปัจจุบัน จึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + is/am/are + V.ing
-
ทั้งนี้ sit (V.) เป็น Intransitive Verb เพราะไม่ต้องมีกรรม (O) มารองรับ สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้ เช่น The boy is sitting. = เด็กผู้ชายกำลังนั่งอยู่ หากต้องการขยายเพิ่มว่านั่งอยู่ที่ไหน หรือบนสิ่งของอะไร สามารถเติมคำบุพบท (Prepo.) บอกสถานที่เข้าไปได้
เช่น
The boy is sitting in the classroom. = เด็กผู้ชายกำลังนั่งอยู่ในห้องเรียน หรือ The boy is sitting on the couch. = เด็กผู้ชายกำลังนั่งอยู่บนโซฟา
3. Nicole opened the birthday gift.
-
open (V.1) / opened (V.2) / opened (V.3) – เป็น Transitive Verb (ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Regular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบปกติโดยการเติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้
open (V.) ใช้ Past Simple Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นและจบลงอย่างสมบูรณ์แล้วในอดีต จึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + V.2
-
ทั้งนี้ open (V.) เป็น Transitive Verb เพราะต้องมีกรรม (O.) มารองรับ ไม่สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้ เช่น He opens the door for me. = เขาเปิดประตูให้ฉัน => the door ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรม (O.) ของ open (V.)
และในประโยค
Nicole opened the birthday gift. = นิโคลเปิด/แกะของขวัญวันเกิด => the birthday gift ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรม (O.) ของ open (V.)
4. James always asks the teacher a question.
-
ask (V.1) / asked (V.2) / asked (V.3) – เป็น Transitive Verb (ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Regular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบปกติโดยการเติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้
ask (V.) ใช้ Present Simple Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำหรือพูดถึงโดยทั่วไปในปัจจุบัน จึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + V.1 (กริยาผันตามประธานเอกพจน์/พหูพจน์)
-
ทั้งนี้
ask (V.) เป็น Transitive Verb เพราะต้องมีกรรม (O.) มารองรับเสมอ ไม่สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้
โดยปกติแล้ว ask (V.) สามารถตามด้วยกรรมตรง (Direct Object) ที่เป็นสิ่งของ และกรรมรอง (Indirect Object) ที่เป็นคน ในประโยคเดียวกันได้เลยดังเช่นประโยคที่ให้มา
ซึ่งคำกริยานี้มักใช้โครงสร้าง
to ask someone (IO.) something (DO.)
James asks the teacher a question. = เจมส์ถามคำถามกับคุณครู => the teacher เป็นกรรมรอง (IO.) และ a question เป็นกรรมตรง (DO.)
ตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม เช่น
He asked me to join his team. = เขาขอให้ฉันเข้าร่วมกับทีมเขา => ask ในที่นี้แปลว่า ขอ, ร้องขอ ได้เช่นกัน และ me เป็นกรรมตรง (DO.) แต่ไม่ใช่กรรมรอง (IO.) นะ เพราะว่ากรรมรอง (IO.) จะมีหรือไม่มีใ
ประโยคก็ได้ แต่กรรมตรง (DO.) ต้องมีเสมอ
5. My boyfriend gave me a watch.
-
give (V.1) / gave (V.2) / given (V.3) – เป็น Transitive Verb (ต้องมีกรรมมารองรับ) และ Irregular Verb (ผันกริยาช่อง 2 และ 3 แบบเปลี่ยนรูปไป ไม่ได้เติม -ed)
ในข้อนี้
give (V.) ใช้ Past Simple Tense ที่บอกถึงสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นและจบลงอย่างสมบูรณ์แล้วในอดีตจึงใช้โครงสร้าง S + V.2
-
ทั้งนี้
give (V.) เป็น Transitive Verb เพราะต้องมีกรรม (O.) มารองรับเสมอ ไม่สามารถอยู่ตัวเดียวได้
โดยปกติแล้ว give (V.) สามารถตามด้วยกรรมตรง (Direct Object)
ที่เป็นสิ่งของ และกรรมรอง (Indirect Object) ที่เป็นคน ในประโยคเดียวกันได้เลยดังเช่นข้อที่แล้ว
ซึ่งคำกริยานี้ก็ใช้โครงสร้าง
to give someone (IO.) something (DO.)
ด้วยเช่นกัน
My boyfriend gave me a watch. = แฟนของฉันให้นาฬิกาข้อมือกับฉัน => me เป็นกรรมรอง (IO.) และ a watch เป็นกรรมตรง (DO.)
ตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม เช่น I gave an apple to a boy = ฉันให้แอปเปิลผลหนึ่งกับเด็กผู้ชายคนหนึ่ง => an apple เป็นกรรมตรง (DO.) และ a boy เป็นกรรมรอง (IO.)

1. I saw a cat climbing a tree.
เป็น Irregular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 เปลี่ยนรูปไปเลยเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = see V.2 = saw V.3 = seen
2. Our family went to Phuket together last summer.
เป็น Irregular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 เปลี่ยนรูปไปเลยเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = go V.2 = went V.3 = gone
3. We watched a movie on Netflix.
เป็น Regular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 มีรูปแบบการเติม -ed เหมือนกันเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = watch V.2 = watched V.3 = watched
4. Have you ever been to Cambridge?
เป็น Irregular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 เปลี่ยนรูปไปเลยเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = be (is/am/are) V.2 = was/were V.3 = been
5. He has stayed with his grandmother for 2 years.
เป็น Regular Verb เพราะกริยาช่องที่ 2 และ 3 มีรูปแบบการเติม -ed เหมือนกันเมื่อผันตามกาล (Tense)
V.1 = stay V.2 = stayed V.3 = stayed

1. The dinner smells very nice.
เป็น Linking Verb เพราะตามมาด้วยคำคุณศัพท์ (Adj.) ที่บ่งบอกลักษณะของประธานข้างหน้า (The dinner) ว่าเป็นอย่างไร
2. He became the first love of my life.
เป็น Linking Verb เพราะตามมาด้วยคำนาม (N.) ที่บ่งบอกว่าประธานข้างหน้า (He) เป็นใคร โดย became เป็น Past Tense
ของ become นั่นเอง
3. I should go now.
เป็น Modal Verb เพราะ should + คำกริยาที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V. infinitive) คือ go ซึ่งเป็นไปตามกฎของการใช้ Modal Verb
4. Lisa may write a letter to her idol tomorrow.
เป็น Modal Verb เพราะ may + คำกริยาที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V. infinitive) คือ write ซึ่งเป็นไปตามกฎของการใช้ Modal Verb
5. Jenny was my best friend during high school.
เป็น Linking Verb เพราะตามมาด้วยคำนาม (N.) ที่บ่งบอกว่าประธานข้างหน้า (Jennie) เป็นใคร โดย was เป็น Past Tense
ของ V. to be นั่นเอง
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
Track 3
เติมคำกริยาที่ได้ยินในประโยค และวงกลมเลือกประเภทของคำกริยานั้นให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) What time _____is_____ it now? (Main Verb | Helping Verb)
ตอบ is เป็น Main Verb เพราะว่าในประโยคนี้มีกริยาอยู่ตัวเดียว ซึ่งหากขาด is ไปจะไม่เป็นประโยคที่สมบูรณ์และสื่อความหมายไม่ได้
1. Do you know what time it is? (Transitive Verb | Intransitive Verb)
ตอบ know เป็น Transitive Verb เพราะว่ามี wh-clause ที่ตามหลังมา คือ what time it is ซึ่งมีความหมายว่า เป็นเวลากี่โมง ทำหน้าที่
เสมือนกรรมของ V. know ความจริงแล้วนั้น know สามารถเป็นได้ทั้ง Transitive Verb และ Intransitive Verb แต่ขึ้นอยู่กับความหมาย
ของแต่ละประโยค
2. Do you have the time? (Helping Verb | Main Verb)
ตอบ Do เป็น Helping Verb เพราะว่าต้องใช้ V. to do ที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นคำกริยาช่วยมาช่วยสร้างประโยคคำถามเสมอ โดยคำกริยาช่วยนี้จะไม่มี
ความหมายในตัวเอง แต่มี have เป็นคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) และมีความหมายว่า “มี”
3. Could you tell me the time? (Helping Verb | Modal Verb)
ตอบ Could เป็น Modal Verb เพราะว่าเป็นคำกริยาช่วยชนิดหนึ่งที่ไม่สามารถอยู่เดี่ยว ๆ หรือเป็นคำกริยาหลักในประโยคอย่าง Helping Verb
อื่น ๆ (V. to be, V. to do และ V. to have) ได้ นอกจากนี้ Modal Verb + V. infinitive เสมอ ซึ่งในข้อนี้คือ Could + tell
4. Do you happen to have the time? (Main Verb | Linking Verb)
ตอบ happen เป็น Main Verb เพราะว่าใช้ Do ซึ่งเป็น Helping Verb มาช่วยในการสร้างประโยคคำถามแล้ว สิ่งที่ขาดจึงเป็นคำกริยาหลัก
(Main Verb) โดยเหตุผลที่ have ไม่ใช่ Main Verb เพราะว่าตามหลัง to ซึ่งเราเรียกคำกริยาประเภทนี้ว่า V. infinitive with to นั่นเอง
5. What time will the meeting start? (Main Verb | Modal Verb)
ตอบ will เป็น Modal Verb เพราะว่าเป็นคำกริยาช่วยชนิดหนึ่งที่ไม่สามารถอยู่เดี่ยว ๆ ได้ โดยคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ของประโยคนี้คือ start
6. When will you come back home? (Main Verb | Modal Verb)
ตอบ will เป็น Modal Verb เพราะว่าเป็นคำกริยาช่วยชนิดหนึ่งที่ไม่สามารถอยู่เดี่ยว ๆ ได้ โดยคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ของประโยคนี้คือ come
7. Have you got the time? (Regular Verb | Irregular Verb)
ตอบ got เป็น Irregular Verb เพราะเป็นช่อง 2 และ 3 ของ get (ช่อง 3 สามารถเขียนได้ทั้งในรูป got และ gotten) ซึ่งไม่ได้ผันแบบเติม -ed
แบบปกติ
8. Sure, it is two thirty. (Linking Verb | Modal Verb)
ตอบ is เป็น Linking Verb ไม่ใช่ Modal Verb เพราะสามารถอยู่เดี่ยว ๆ ได้ ไม่ต้องมีคำกริยาอื่นตามมา
9. It is almost ten. (Main Verb | Helping Verb)
ตอบ is เป็น Main Verb (และอยู่ในกลุ่ม Linking Verb ด้วย) ไม่ใช่ Helping Verb เพราะไม่มีคำกริยาอื่นตามมา
10. Sorry, I do not have the time. (Main Verb | Helping Verb)
ตอบ do เป็น Helping Verb เพราะว่าเป็นการนำ do มาช่วยในการสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธ โดยคำกริยาหลักในประโยคนี้คือ have
Adjective
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
Track 5
เขียนบรรยายลักษณะที่ได้ยินลงไปให้ถูกต้องเลย!
*ขีดเส้นใต้ = คำคุณศัพท์ (Adjective)*
1.
My father is a tall man. (พ่อของฉันเป็นคนตัวสูง)
He has short black hair and brown eyes. (พ่อมีผมสั้นสีดำและตาสีน้ำตาล)
He is a funny and warm person. (พ่อเป็นคนตลกและอบอุ่น)
2.
My mother is a slim woman. (แม่ของฉันเป็นผู้หญิงผอมเพรียว)
She has long blonde hair and blue eyes. (แม่มีผมยาวสีบลอนด์และตาสีฟ้า)
She is a beautiful and kind person. (แม่เป็นคนสวยและใจดี)
3.
My brother is a chubby boy. (น้องชายของฉันเป็นเด็กผู้ชายอวบ)
He has very short brown hair and blue eyes. (เขามีผมสั้นมากสีน้ำตาลและตาสีฟ้า)
He is an adorable boy. (เขาเป็นเด็กผู้ชายที่น่าเอ็นดู)
4.
I am a lovely teenage girl. (ฉันเป็นเด็กผู้หญิงวัยรุ่นที่น่ารัก)
I have shoulder-length brown hair and green eyes. (ฉันมีผมยาวประบ่าสีน้ำตาลและตาสีเขียว)
I am a nice and friendly person. (ฉันเป็นคนนิสัยดีและเป็นกันเอง)
5.
KruDew is an English teacher. (ครูดิวเป็นคุณครูภาษาอังกฤษ)
He has short black hair and dark brown eyes. (ครูดิวมีผมสั้นสีดำและตาสีน้ำตาลเข้ม)
He is a funny and smart person. (ครูดิวเป็นคนตลกและฉลาด)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
เรียงคำคุณศัพท์ในประโยคต่อไปนี้ตามลำดับให้ถูกต้องกันเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I really love my cute little sister. (little, cute)
cute = ความคิดเห็น little = ขนาด
1. Our family lives in a simple small house. (simple, a, small)
a = คำนำหน้านาม simple = ความคิดเห็น small = ขนาด
2. My stepbrother enjoys spicy Thai food. (spicy, Thai)
spicy = ความคิดเห็น Thai = สัญชาติ
3. I used to try on a traditional Japanese Kimono when going to Japan. (a, Japanese, traditional)
a = คำนำหน้านาม traditional = อายุ Japanese = สัญชาติ
4. My fiancé gave me a large heart-shaped diamond ring. (a, diamond, heart-shaped, large)
a = คำนำหน้านาม large = ขนาด heart-shaped = รูปร่าง diamond = วัสดุ
5. Do you like these comfortable black leather boots? (black, leather, comfortable, these)
these = คำนำหน้านาม comfortable = ความคิดเห็น black = สี leather = วัสดุ
6. My grandmother always carries a tiny wooden walking stick. (walking, a, wooden, tiny)
a = คำนำหน้านาม tiny = ขนาด wooden = วัสดุ walking = จุดประสงค์
7. We donated these lovely flat pink running shoes to the kids. (lovely, these, flat, running, pink)
these = คำนำหน้านาม lovely = ความคิดเห็น flat = รูปร่าง pink = สี running = จุดประสงค์
8. This store sells a lot of gorgeous short modern cotton dress. (short, gorgeous, a lot of, cotton, modern)
a lot of = คำนำหน้านาม gorgeous = ความคิดเห็น short = ขนาด modern = อายุ cotton = วัสดุ
9. My father always wanted this beautiful vintage yellow British car. (British, this, vintage, beautiful, yellow)
this = คำนำหน้านาม beautiful = ความคิดเห็น vintage = อายุ yellow = สี British = สัญชาติ
10. My mother just bought expensive new red British woolen sweaters. (new, red, expensive, woolen, British)
expensive = ความคิดเห็น new = อายุ red = สี British = สัญชาติ woolen = วัสดุ
Adverb of Manner
ช่วยเติมคำที่ให้มาในกรอบสี่เหลี่ยมลงไปในประโยคให้ถูกต้องทีนะ!

1. Q: Why do you think the boy is running?
A: The boy is running quickly
because he might be late for school.
(เด็กผู้ชายวิ่งอย่างรวดเร็วเพราะว่าเขาอาจจะไปโรงเรียนสาย)
2. Q: Do you know how long it has been raining?
A: It has been raining hard since yesterday morning.
It’s still raining cats and dogs today.
(ฝนตกหนักมาตั้งแต่เมื่อวานตอนเช้าแล้ว วันนี้ก็ยังตกหนักมากอยู่)
3. Q: Do you have any idea what the woman is doing?
A: The woman is shopping and jumping excitedly
because it is a mid-year sale at the department store.
(ผู้หญิงคนนั้นกำลังชอปปิงและกระโดดอย่างตื่นเต้น
เพราะเป็นช่วงลดราคากลางปีของห้างสรรพสินค้า)
4. Q: What do you think Joe is doing on his day off?
A: I think he is staying at home and
lazily lying on the couch watching TV.
(ฉันคิดว่าเขาคงอยู่ที่บ้านและเอนตัวอย่างขี้เกียจดูทีวีอยู่บนโซฟา)
5. Q: What do you think about John speaking loudly on the phone?
(คุณคิดอย่างไรที่จอห์นคุยโทรศัพท์เสียงดัง)
A: I think he annoys other passengers on the train.
(ฉันคิดว่าเขารบกวนผู้โดยสารคนอื่น ๆ บนรถไฟ)
Adverb of Place
ดูภาพประกอบและนำ Adverb of Place ที่ให้มาในกรอบสี่เหลี่ยม ไปเติมในช่องว่างของแต่ละประโยคให้ถูกต้องกันเถอะ!

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. The teacher is coming here. We have to run away!
(คุณครูกำลังมาที่นี่ เราต้องวิ่งหนี)
1. Would it be possible to meet you downstairs at 10 a.m.?
(จะเป็นไปได้ไหมถ้าฉันจะขอเจอคุณที่ชั้นล่างตอน 10 โมง)
2. There’s no school today, so I’m going outside for a walk.
(วันนี้ไม่มีเรียน ฉันเลยจะออกไปข้างนอกเพื่อเดินเล่น)
3. I’m coming nearby, so I wonder if you are available to meet me.
(ฉันมาใกล้ ๆ เลยอยากรู้ว่าเธอสะดวกมาเจอกันไหม)
4. I will be there in 5 minutes. Please come inside and wait in the living room.
(ฉันจะไปที่นั่นในอีก 5 นาที กรุณาเข้ามาข้างในและรอในห้องนั่งเล่น)
5. I will have an appointment with the international client overseas, so I’ll be out of office for a week.
(ฉันมีนัดกับลูกค้าต่างชาติที่ต่างประเทศ เลยอาจจะไม่อยู่ออฟฟิศประมาณสัปดาห์หนึ่งนะ
Adverb of Time
เลือก Adverb of Time ในวงเล็บ 2 จาก 3 คำ ไปใส่ในตำแหน่งที่ถูกต้องของประโยคให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. My grandfather told me yesterday that he went to The Beatles’ concert 60 years ago. (ago, yesterday, later)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
yesterday (เมื่อวาน) เพราะ told เป็น V.2 ซึ่งใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นแล้วในอดีต เราจึงไม่สามารถใช้ later ที่ต้องใช้กับ
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอนาคตได้
และ ago นั้นต้องมีจำนวนเวลาบอก เช่น 2 days ago
-
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
ago (…ที่แล้ว) เพราะมีจำนวนเวลา
มาให้คือ 60 years
ไม่สามารถตามด้วย yesterday หรือ later ได้
1. I haven’t seen you in ages. Would you like to come over for dinner tonight? (ago, in ages, tonight)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
in ages (เป็นเวลานาน) เพราะเป็นสำนวนที่มักจะพูดกันบ่อย ๆ ในความหมายว่า “ฉันไม่ได้เจอคุณมาตั้งนานแล้ว”
ไม่สามารถใช้ago ได้เพราะไม่มีจำนวนเวลาบอก และใช้ tonight ไม่ได้ เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่ดำเนินมาระยะหนึ่งตั้งแต่อดีต
จนถึงปัจจุบัน ไม่ใช่อนาคต -
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
tonight (คืนนี้) เพราะทั้ง ago และ in ages พูดถึงเวลาในอดีต แต่ในประโยคเป็นการเชิญชวนให้ไปทานมื้อค่ำกัน
คืนนี้หลังจากที่ไม่เจอกันนาน จึงเป็นการพูดถึงเรื่องอนาคต
2. My friend asked me to go to Liverpool last week, but I was busy at that time. (later, at that time, last week)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
last week (สัปดาห์ที่แล้ว) เพราะคำกริยา asked เป็น V.2 ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีตและจบไปแล้ว
เราไม่สามารถใช้ at that timeมาตอบในส่วนแรกได้เพราะยังไม่เคยมีการพูดถึงมาก่อนว่าเป็นตอนช่วงเวลาไหน และ
later (ในภายหลัง) นั้นไม่เข้ากับบริบทเท่าไรเมื่ออ่านครบประโยค -
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
at that time (ในเวลานั้น) เพราะอ้างอิงถึงส่วนแรกคือ last week
3. Are you leaving now? Would you like to have lunch together later? (later, already, now)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
now (เดี๋ยวนี้ / ตอนนี้) เพราะประโยคที่ให้มาเป็น Present Continuous Tense ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้น
ขณะนั้นหรือช่วงนั้น ไม่สามารถใช้ later หรือalready ได้
-
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
later (หลังจากนี้) เพราะว่าเป็นการชวนไปทานข้าวกันทีหลัง แสดงว่าไม่ได้ทานอยู่ หรือไม่ได้ทานกันไปแล้ว
จึงใช้ now และ already ไม่ได้
4. I haven’t sent you an invitation card yet, but I want you to join our party next month. (already, next month, yet)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
yet (ยัง) เพราะเป็น keyword ที่ใช้กับโครงสร้างประโยค Present Perfect Tense (has / have + V.3) แปลว่า
“ฉันยังไม่ได้ส่งบัตรเชิญให้คุณเลย…”ซึ่งแม้ว่า already จะเป็น keyword สำหรับ Tense นี้เหมือนกัน แต่ก็ไม่สามารถใช้ตอบได้
เพราะว่า already มีความหมายว่า …ไปแล้ว และไม่สามารถใช้กับประโยคปฏิเสธได้เพราะความหมายขัดแย้งกัน -
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
next month (เดือนหน้า) เพราะเป็นการเชิญชวน ซึ่งเหตุการณ์นั้นยังไม่เกิดขึ้น
5. Do you think it will rain soon? How about going to the beach tomorrow instead? (soon, lately, tomorrow)
คำอธิบาย
-
ส่วนแรกตอบ
soon (เร็ว ๆ นี้) เพราะ Tense ที่ปรากฏในประโยคคือ Future Simple Tense (will + V. infinitive) ซึ่งใช้กับ
เหตุการณ์ที่กำลังจะเกิดในอนาคต จริง ๆ แล้วtomorrow ก็สามารถใช้กับ Tense นี้ได้เช่นกัน แต่หากนำ soon ไปตอบที่ส่วนท้าย
และนำ tomorrow มาไว้ที่ส่วนหน้าแทนแล้ว ความหมายจะไม่เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน ในขณะที่ lately (ช่วงนี้ / พักนี้) นั้นมักจะใช้กับ
Present Perfect Tense (has / have + V.3) มากกว่า เช่น What have you been doing lately? แปลว่า “ช่วงนี้คุณทำอะไร
อยู่เหรอ” -
ส่วนท้ายตอบ
tomorrow (วันพรุ่งนี้) เพราะว่าในประโยคนี้ keyword คำว่า instead (…แทน) คือ “ทำไมเราไม่ไปที่ชายหาดกันใน
วันพรุ่งนี้แทนล่ะ” หมายความว่าได้วางแผนเอาไว้แล้ว แต่เพราะฝนจะตกในเร็ว ๆ นี้ จึงจะไปวันพรุ่งนี้แทน
Adverb of Frequency
นำ Adverb of Frequency ในวงเล็บไปใส่ในตำแหน่งที่ถูกต้องของประโยคให้หน่อยนะ!
คำอธิบาย ตำแหน่งของ Adverb of Frequency มักอยู่หลังประธาน (Subject) และหน้าคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) เข่น
He barely eats vegetables. (เขาแทบจะไม่กินผักเลย) แต่หากมี V. to be หรือ Linking Verb ในประโยค
Adverb of Frequency มักจะตามหลังเสมอ เช่น She is always good to me. (หล่อนดีกับฉันเสมอ)
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. My mother gets up at 7 a.m. (always) => My mother always gets up at 7 a.m.
My mother (คุณแม่ของฉัน) = Subject, always (เป็นประจำ) = Adverb of Frequency, gets up (ตื่นนอน) = Main Verb
1. I go to the game center after school. (usually) => I usually go to the game center after school.
I (ฉัน) = Subject, usually (โดยปกติ) = Adverb of Frequency, go (ไป) = Main Verb
2. Nana is late for work. She’s very punctual. (never) => Nana is never late for work. She’s very punctual.
Nana (นานะ) = Subject, is = Linking Verb, never (ไม่เคย) = Adverb of Frequency และประโยคที่เสริมมาด้านหลัง
เป็นคำใบ้เพิ่มเติมคือ She’s very punctual. (เธอเป็นคนตรงเวลามาก ๆ)
3. Ken plays tennis because he’s been busy these days. (rarely) => Ken rarely plays tennis because he’s been
busy these days.
Ken (เคน) = Subject, rarely (แทบจะไม่) = Adverb of Frequency, play (เล่น) = Main Verb และอนุประโยคที่เสริมมาด้านหลัง
เป็นคำใบ้เพิ่มเติมคือ because he’s been busy these days. (เพราะช่วงนี้เขายุ่ง)
4. I watch dramas or series when I’m free. (often) => I often watch dramas or series when I’m free.
I (ฉัน) = Subject, often (บ่อย ๆ) = Adverb of Frequency, watch (ดู) = Main Verb
5. I listen to music when I’m bored. (sometimes) => I sometimes listen to music when I’m bored.
I (ฉัน) = Subject, sometimes (บางครั้ง) = Adverb of Frequency, listen (ฟัง) = Main Verb
Adverb of Degree
ช่วยบอกหน่อยสิว่า Adverb of Degree ที่ขีดเส้นใต้ในประโยคต่อไปนี้ขยายคำไหนในประโยคกันนะ!
ขยาย Adv. (hard) ขยาย Adv. (well)
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Do you think I work hard enough to pass the exam? – Sure, you did quite well.
(เธอคิดว่าฉันอ่านหนังสือหนักพอที่จะสอบผ่านหรือยัง) (แน่นอน เธอทำได้ค่อนข้างเยี่ยมเลย)
ขยาย Adj. (big) ขยาย Adv. (well)
1. Do you think these shoes are too big? – No, I think they fit you very well.
(เธอคิดว่ารองเท้าคู่นี้ใหญ่เกินไปไหม) (ไม่นะ ฉันคิดว่าพอดีเป๊ะมากเลย)
ขยาย Adj. (pretty) ขยาย Adj. (gorgeous)
2. That lady is really pretty. She looks like a star. – Couldn’t agree more. She is so gorgeous.
(สุภาพสตรีคนนั้นน่ารักมาก เธอดูเหมือนดาราเลย) (เห็นด้วยที่สุด เธอสวยมาก)
ขยาย Adj. (high-pitched) ขยาย Adj. (talented)
3. My singing coach said I had extremely high-pitched voice. – Wow! You are absolutely talented.
(ครูสอนร้องเพลงของฉันบอกว่าฉันมีเสียงที่สูงสุด ๆ) (ว้าว! เธอมีพรสวรรค์สุด ๆ เลย)
ขยาย Adj. (correct) ขยาย Adj. (proud)
4. I got 100 scores in Biology. The exam was entirely correct. – Perfect! I am totally proud of you.
(ฉันได้ 100 คะแนนในวิชาชีววิทยาล่ะ ข้อสอบถูกต้องทั้งหมดเลย) (เยี่ยมมาก! ฉันภูมิใจในตัวเธอสุด ๆ เลย)
ขยาย V. (finish) ขยาย Adj. (good)
5. I almost finish my writing homework. There is only one paragraph left. – Great! You are such a very good student.
(ฉันเกือบจะทำการบ้านวิชาการเขียนเสร็จแล้ว เหลือแค่อีกหนึ่งย่อหน้าเท่านั้น) (เยี่ยม! เธอช่างเป็นนักเรียนที่ดีมากเลย)
เฉลยแบบฝึกหัดรวมเรื่อง Adverb
อ่านเนื้อเรื่องที่ให้มา ขีดเส้นใต้ Adverb ที่เจอในเรื่อง แล้วนำมาเขียนแยกใส่ตารางตามประเภทให้ทีนะ!
I usually get up at 7 a.m. to go to school nearby. Today, I woke up at 8 a.m. because
it is Sunday. My mother cooked a very delicious omelet for me. She also eagerly handed me a glass
of freshly squeezed orange juice. It was really refreshing so I drank it up completely. Later, we
went outside because we needed to do some groceries. My mother carefully picked organic vegetables,
but I spoke to myself quietly that I absolutely hated them. She accidentally heard me, so she
kindly told me that she would buy some fruits for me instead.
Adverb of Manner
Adverb of Place
Adverb of Time
Adverb of Frequency
Adverb of Degree
eagerly (อย่างกระตือรือร้น)
freshly (อย่างสดใหม่)
carefully (อย่างระวัง)
quietly (อย่างเงียบ ๆ)
accidentally (โดยบังเอิญ)
kindly (อย่างใจดี)
nearby (ใกล้ ๆ)
outside (ข้างนอก)
Today (วันนี้)
Later (ทีหลัง / หลังจากนั้น)
usually (โดยปกติ)
very (มาก)
really (มาก / จริง ๆ)
completely (อย่างทั้งหมด / โดยสิ้นเชิง)
absolutely (อย่างแน่นอน / โดยสิ้นเชิง)
Pronoun
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ในประโยคมีสรรพนามที่ใช้ผิดอยู่ ช่วยแก้ไขสรรพนามนั้นให้ถูกต้องทีนะ!

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Kathy has a dog. It fur is white. เปลี่ยนจาก it => its
คำอธิบาย
เป็น It ไม่ได้ เพราะส่วนประธาน (หน้าคำกริยา is) มีคำนาม (fur = ขนของสัตว์) มาให้แล้ว จึงต้องเปลี่ยนให้เป็น Its (Possessive Adjective)
ที่ต้องตามด้วย N. เสมอ
1. Is blue you favorite color? เปลี่ยนจาก you => your
คำอธิบาย
เป็น you ไม่ได้ เพราะประโยคที่ให้มานั้นหมายความว่า “สีฟ้าใช่สีโปรดของคุณไหม” จะเห็นว่ามีคำนาม (favorite color) ที่ให้มาแล้ว
ฉะนั้นต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น your (Possessive Adjective) ที่ต้องตามด้วย N. เสมอ
2. Those are your shoes, and these are me. เปลี่ยนจาก me => mine
คำอธิบาย
เป็น me ไม่ได้ เพราะประโยคจะหมายความว่า “โน่นคือรองเท้าของคุณ และนี่คือฉัน” แต่เรากำลังพูดถึงสิ่งของอยู่ ซึ่งก็คือรองเท้า
ฉะนั้นต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น mine ที่แปลว่า (รองเท้า)ของฉัน เราไม่เปลี่ยนเป็น my เพราะว่า my (Possessive Adjective) จะต้องตามด้วย
คำนาม (shoes) เสมอ แต่ mine (Possessive Pronoun ไม่ต้องมีคำนาม สามารถใช้เดี่ยว ๆ ได้ (เพราะผู้ฟังและผู้พูดรู้อยู่แล้วว่าสิ่งนั้น
คืออะไร)
3. Her likes my red skirt a lot. เปลี่ยนจาก Her => She
คำอธิบาย
เป็น Her ไม่ได้ เพราะ her เป็นได้สองอย่างคือ Object Pronoun (ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรมของประโยค) และ Possessive Adjective
(ทำหน้าที่แสดงความเป็นเจ้าของ ต้องตามด้วย N. เสมอ) การขึ้นต้นประโยคเป็นประธาน เราจะใช้ Subject Pronoun คือ She จึงจะถูกต้อง
4. He loves to study by him. เปลี่ยนจาก him => himself
คำอธิบาย
เป็น him ไม่ได้ เพราะ him เป็น Object Pronoun ต้องอยู่ตามหลังคำกริยา (V.) เสมอ เช่น I love him. แต่ในข้อนี้ความหมายคือ
“เขารักที่จะเรียนด้วยตนเอง” การทำบางสิ่งบางอย่างด้วยตนเอง เรามักใช้ Reflexive Pronoun เข้ามาช่วย ข้อนี้จึงต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น
himself (ด้วยตัวของเขาเอง)
5. I name is Pimmy. What about yours? เปลี่ยนจาก I => My
คำอธิบาย
เป็น I ไม่ได้ เพราะส่วนประธาน (หน้าคำกริยา is) มีคำนาม (name = ชื่อ) มาให้แล้ว และประธาน I จะใช้กับ am ใน Present Simple Tense
จึงต้องเปลี่ยน I (Subject Pronoun) ให้เป็น My ที่ต้องตามด้วย N. แทน จึงเป็น My name (ชื่อของฉัน) ซึ่งสามารถตามด้วยคำกริยา is ได้
ส่วน yours ประโยคต่อมานั้นใช้ถูกต้องแล้ว เพราะต้องการถามว่า “แล้ว (ชื่อ) ของคุณคืออะไร”
6. Would your like this trendy bag? เปลี่ยนจาก your => you
คำอธิบาย
เป็น your ไม่ได้ เพราะ your เป็น Possessive Adjective ต้องมี N. ตามหลังเสมอ ในข้อนี้ต้องเป็น you เพราะยังขาดประธานของประโยค
และเรามักใช้โครงสร้างประโยค “Would you like…?” เพื่อสอบถามความต้องการว่า “คุณอยาก / ต้องการ…ไหม”
7. Jen didn’t like the new laptop which she bought by hers. เปลี่ยนจาก hers => herself
คำอธิบาย
เป็น hers ไม่ได้ เพราะ her เป็น Possessive Pronoun ใช้กล่าวเพื่อแสดงความเป็นเจ้าของ เช่น That bag is hers. “กระเป๋าใบนั้นเป็น (กระเป๋า)
ของหล่อน” แต่ในข้อนี้ความหมายคือ “เจนไม่ชอบแลปท็อปเครื่องใหม่ที่หล่อนซื้อด้วยตัวเอง” เป็นการเน้นการทำบางสิ่งบางอย่างด้วยตนเอง
เราจึงมักใช้ Reflexive Pronoun เข้ามาช่วย ข้อนี้เลยต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น herself (ด้วยตัวของหล่อนเอง)
8. I would like to introduce mine. เปลี่ยนจาก mine => myself
คำอธิบาย
ข้อนี้จะตอบ mine ได้ถ้าหากมีบริบทที่พูดถึงบางสิ่งมาก่อนแล้ว แต่ในข้อนี้หมายถึง “ฉันอยากจะแนะนำตัวเอง” เมื่อพูดถึงสิ่งที่ทำเองหรือเกี่ยวกับ
ตัวเองเราต้องใช้ Reflexive Pronoun เข้ามาช่วย จึงเป็น introduce myself ที่หมายความว่า “แนะนำตัวเอง” ตัวอย่างเหตุการณ์ที่พบบ่อย เช่น
เวลาสมัครงานที่มักจะเจอประโยคบอกให้คุณแนะนำตัวเอง อย่าง “Please introduce yourself.” นั่นเอง
9. Last week, I went to the cinema with a friend of me. เปลี่ยนจาก mine => mine
คำอธิบาย
เป็น me ไม่ได้ เพราะ me คือ Object Pronoun แต่ในข้อนี้ต้องเป็น mine (Possessive Pronoun) เนื่องจาก of + Possessive Pronoun
(a friend of mine = เพื่อนของฉัน) โดยมีความหมายเดียวกับ Possessive Adjective + N. (My friend) นั่นเอง
10. Do their like our Christmas gift? เปลี่ยนจาก their => they
คำอธิบาย
เป็น their ไม่ได้ เพราะ their เป็น Possessive Adjective ต้องมี N. ตามหลังเสมอ ในข้อนี้ต้องเป็น they (Subject Pronoun) เพราะยังขาด
ประธานของประโยค
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
จงเติมคำสรรพนามลงในช่องว่างให้ถูกต้อง
The teacher gave us homework to talk about (0.) our favorite things.
My favorite things are (1.) my bed and my cell phone because (2.) I love to sleep and
read online novels. I can stay by (3.) myself all day in the bedroom.
My friend, Sarah, really likes collecting dolls. She bought them (4.) herself from
the internet. (5.) Her dolls are all cute and fluffy. Sometimes, I bought (6.) them as
a birthday present for her, too.
David is another friend of (7.) mine / ours. He always takes a good care of
(8.) his books. He wants to be able to speak many languages, so (9.) he likes reading
books and watching foreign movies. They have helped him improve (10.) his language skills
tremendously.
Preposition
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
Track 13
ดูรูปภาพ และเติมคำตอบที่ได้ยินลงในช่องว่างเลย จุดหมายของแต่ละข้ออยู่ที่เลขไหนกันนะ

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. A : Excuse me, do you know how I can get to Big Ben from here? (ขอโทษนะคะ คุณรู้ไหมคะว่าจากที่นี่ฉันจะไปบิกเบน
ได้อย่างไร)
B : Go straight toward the river and cross the Westminster bridge.
Then, turn left. It is beside Westminster Abbey.
(ตรงไปทางแม่น้ำแล้วก็ข้ามสะพานเวสต์มินสเตอร์นะครับ จากนั้นเลี้ยวซ้าย
มันอยู่ข้าง ๆ เวสต์มินสเตอร์แอบบีย์ครับ)
The destination is number _____4_____.
1. A : Excuse me, could you tell me where the National History Museum is? (ขอโทษนะคะ ช่วยบอกฉันหน่อยได้ไหมคะว่าพิพิธภัณฑ์
ประวัติศาสตร์แห่งชาติอยู่ที่ไหน)
B : Sure. Cross the Westminster Bridge and turn left at Westminster Abbey.
Cross the intersection to Harrods. The National Museum is opposite
Harrods and next to Victoria & Albert Museum.
(แน่นอนครับ ข้ามสะพานเวสต์มินสเตอร์ไปแล้วเลี้ยวซ้ายที่เวสต์มินสเตอร์แอบบีย์นะครับ ข้ามสี่แยกไปทางแฮร์รอดส์
พิพิธภัณฑ์ประวัติศาสตร์แห่งชาติอยู่ตรงข้ามกับแฮร์รอดส์และอยู่ถัดจากพิพิธภัณฑ์วิคตอเรียแอนด์อัลเบิร์ตครับ)
The destination is number _____3_____.
2. A : Hello, could you help me? Do you know where the Sherlock Holmes Museum is?
(สวัสดีค่ะ คุณช่วยอะไรฉันหน่อยได้ไหมคะ คุณรู้ไหมคะว่าพิพิธภัณฑ์เชอร์ล็อก โฮล์มส์อยู่ที่ไหน)
B : Of course. Go straight along the Birdcage Walk.
Then, turn right at Trafalgar Square and cross the Main Road.
The Sherlock Holmes Museum is between the Harry Potter Studio and Shakespeare’s Globe.
(ได้สิครับ เดินตรงไปทางถนนเบิร์ดเคจวอล์ก จากนั้นเลี้ยวขวาที่ทราฟัลการ์สแควร์และข้ามถนนหลักไป
พิพิธภัณฑ์เชอร์ล็อก โฮล์มส์ตั้งอยู่ระหว่างแฮร์รี่ พอตเตอร์สตูดิโอกับโรงละครเช็คสเปียร์โกลบครับ)
The destination is number _____1_____.
3. A : Excuse me, could you tell me the way to Buckingham Palace? (ขอโทษค่ะ คุณช่วยบอกทางไปพระราชวังบักกิงแฮม
ให้ฉันได้ไหมคะ)
B : Certainly! Go straight ahead and take the second turn on the left.
The Buckingham Palace is behind St. James’s Park.
(แน่นอนครับ ตรงไปข้างหน้าแล้วก็เลี้ยวซ้ายตรงทางแยกที่สองนะครับ
พระราชวังบักกิงแฮมอยู่ข้างหลังสวนสาธารณะเซนต์เจมส์ครับ)
The destination is number _____5_____.
4. A : Hi! Excuse me. I would like to go to the Tower of London. Could you please tell me how to get there?
(สวัสดีค่ะ ขอโทษนะคะ ฉันอยากไปหอคอยแห่งลอนดอน คุณช่วยบอกฉันได้ไหมคะว่าจะไปที่นั่นได้อย่างไร)
B : Yes, of course. Take the South Road and turn left to cross the Tower Bridge.
Continue straight and you will see it on your right.
(ได้แน่นอนครับ ใช้ถนนเซาท์โรดและเลี้ยวซ้ายเพื่อข้ามสะพานทาวเวอร์บริดจ์
เดินตรงต่อไปแล้วคุณจะเห็นมันอยู่ทางขวาครับ)
The destination is number _____2_____.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
มาดูรูปภาพและเลือกคำตอบที่ถูกต้องกันเถอะ!

1. The school is (next to/behind) the library and (at/opposite) the train station.
It is closed (on/in) weekends.
(โรงเรียนอยู่ถัดจากห้องสมุดและตรงข้ามกับสถานีรถไฟ โรงเรียนปิดในวันหยุดสุดสัปดาห์)
2. The café is located (beside/between) the fire house and the department store.
It is usually open (from/since) Tuesday to Sunday and closed (in/on) Mondays.
(คาเฟ่ตั้งอยู่ระหว่างสถานีดับเพลิงและห้างสรรพสินค้า โดยปกติคาเฟ่นี้เปิดตั้งแต่วันอังคารถึงวันอาทิตย์และปิดในวันจันทร์)
3. The restaurant is (in front of/behind) the school and (between/next to) the post office.
This restaurant is open every day (from/at) 9 a.m. to 9 p.m.
(ร้านอาหารตั้งอยู่หลังโรงเรียนและถัดจากที่ทำการไปรษณีย์ ร้านอาหารแห่งนี้เปิดทุกวันตั้งแต่เก้าโมงเช้าจนถึงสามทุ่ม)
4. The park is (across/in front of) the hospital and the bank.
The park’s gate is closed (in/at) the evening.
(สวนสาธารณะตั้งอยู่ข้างหน้าโรงพยาบาลและธนาคาร ประตูสวนสาธารณะปิดในตอนเย็น)
5. The supermarket is (opposite/below) the hotel and there is a pharmacy (across/above) the road.
It is open (after/at) night and closed (during/over) the day.
(ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ตอยู่ตรงข้ามโรงแรมและมีร้านขายยาอยู่ตรงข้ามฝั่งถนน ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ตเปิดตอนกลางคืนและปิดระหว่างวัน)
Conjunction
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
เลือกตัวเชื่อมที่ให้มาในกรอบสี่เหลี่ยม แล้วเติมลงในช่องว่างของประโยคให้ถูกต้องเลย!

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Do you like living in the city or prefer settling down in the countryside?
(คุณชอบอาศัยอยู่ในเมือง_____ชอบใช้ชีวิตในชนบทมากกว่า) – ให้เลือกอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่งจึงตอบ or (หรือ)
1. I used to live in the outskirt, but I recently moved to the downtown area.
(ฉันเคยอาศัยอยู่แถบชานเมือง _____ฉันเพิ่งย้ายมาอยู่ที่แถวใจกลางเมืองเมื่อไม่นานมานี้) – แสดงความขัดแย้งจึงตอบ but (แต่)
2. The traffic around my house was congested yesterday, so I was late for school.
(การจราจรแถวบ้านของฉันติดขัดมากเมื่อวาน _____ฉันเลยไปโรงเรียนสาย) – แสดงความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลจึงตอบ so (ดังนั้น)
3. We have played together since we were children, for our houses are close to each other.
(พวกเราเล่นด้วยกันมาตั้งแต่เด็ก _____บ้านของพวกเราอยู่ใกล้กัน) – แสดงความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลจึงตอบ for (เพราะว่า)
4. Patrick’s apartment is only 10 minutes’ walk to the university, but/yet he is always late.
(อพาร์ตเมนต์ของแพททริกอยู่ห่างจากมหาวิทยาลัยแค่สิบนาทีโดยการเดิน _____เขามาสายตลอด) – แสดงความขัดแย้งกันจึงตอบ but (แต่)/yet (แต่กระนั้น / แต่ก็ยัง)
5. Is your room on the third floor or the fourth floor?
(ห้องของเธออยู่ที่ชั้น 3 _____ ชั้น 4 นะ) – แสดงความขัดแย้ง ไม่แน่ใจระหว่างบางสิ่งจึงตอบ or (หรือ)
6. My room is not on the third floor, nor is it on the fourth floor. It’s on the fifth floor.
(ห้องของฉันไม่ได้อยู่ที่ชั้น 3 _____ ชั้น 4 มันอยู่ที่ชั้น 5) – ประโยคเป็นเชิงปฏิเสธและสื่อว่าไม่ใช่ทั้ง 2 อย่างที่กล่าวมาจึงตอบ nor (และไม่…)
7. My place is in perfect location. It is near the beach, the cinema, and the supermarket.
(ที่อยู่ของฉันอยู่ในทำเลที่สมบูรณ์แบบ มันอยู่ใกล้ ๆ กับชายหาด โรงภาพยนตร์ _____ ซูเปอร์มาร์เก็ต) – ประโยคแสดงความคล้อยตามกันจึงตอบ and (และ)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
อ่านเนื้อเรื่องด้านล่าง แล้วเลือกเติมตัวเลือกคำเชื่อมที่ถูกต้องลงในช่องว่างเลย!
I lived with my grandparents in the countryside (0) when I was young, and I attended
a local school there. (1) Although my grandparents’ house was not in the central area of the city, it only
took around 20 minutes to get to school by bus. Later, I had to move back to live with my parents in
the capital city (2) because I went to another school downtown. (3) Even though my house was
not far from the school, it still took me almost an hour to get there. (4) Since the traffic was
so bad in the city, I had to leave my house very early in the morning. I can (5) neither focus
nor pay attention to the lessons. I felt (6) not only exhausted but also drained
every time after school, (7) so I decided to move closer to the school to avoid these
problems. My parents told me to choose (8) either an apartment or a dormitory,
so I chose the nearest one which was the dormitory. I had stayed there (9) until I graduated
from high school. I felt (10) both focused and refreshed!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. a. when (เมื่อ / ตอนที่) b. as (เพราะ / เพราะว่า)
I lived with my grandparents in the countryside (0) when I was young, and I attended a local school there.
(ฉันเคยอาศัยอยู่กับปู่ย่า / ตายายในชนบท ตอนที่ฉันยังเด็ก และฉันเข้าโรงเรียนในชุมชนที่นั่น) – ใช้ when เพราะเมื่อดูในบริบทแล้ว
เป็นการพูดถึงสิ่งที่เคยเกิดขึ้นในอดีต สังเกตจาก lived ที่เป็น V.2 ใช้ใน Past Simple Tense ฉะนั้นจึงไม่ใช้ as เพราะไม่ได้แสดง
ความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลกันกับประโยคก่อนหน้า
1. a. Although (แม้ว่า) b. Therefore (ดังนั้น)
(1) Although my grandparents’ house was not in the central area of the city, it only took around 20 minutes
to get to school by bus.
(แม้ว่าบ้านของปู่ย่า / ตายายของฉันไม่ได้อยู่ในพื้นที่ใจกลางเมือง แต่ก็ใช้เวลาเพียง 20 นาทีเพื่อไปโรงเรียนโดยรถบัส) –
จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้ากับประโยคหลังแสดงความขัดแย้งกันอยู่ ไม่ได้เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน เราจึงใช้ Although จึงจะเหมาะสม
2. a. until (จนกระทั่ง) b. because (เพราะ / เพราะว่า)
Later, I had to move back to live with my parents in the capital city (2) because I went to another school downtown.
(หลังจากนั้น ฉันต้องย้ายกลับมาอยู่กับพ่อแม่ในเมืองหลวง เพราะว่าฉันเข้าโรงเรียนอีกที่หนึ่งในเมือง) – จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้า
กับประโยคหลังนั้นแสดงความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน “ต้องย้ายกลับมา เพราะไปเข้าเรียนอีกที่หนึ่ง” ถ้าใช้ until จะต้องแสดงให้เห็นว่า
เหตุการณ์หนึ่งเกิดก่อนอีกเหตุการณ์หนึ่งชัดเจน
3. a. Since (เพราะ / เพราะว่า) b. Even though (ถึงแม้ว่า)
(3) Even though my house was not far from the school, it still took me almost an hour to get there.
(ถึงแม้ว่าบ้านฉันจะไม่ได้ไกลจากโรงเรียน แต่ก็ยังใช้เวลาเป็นชั่วโมงกว่าจะไปถึงที่นั่น) – จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้าและประโยคหลัง
แสดงความขัดแย้งกัน แม้บ้านอยู่ใกล้ แต่ยังใช้เวลานานกว่าจะไปถึง จึงตอบ Even though เราไม่สามารถใช้ Since ได้ เพราะ
ทั้งสองประโยคไม่ได้เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน
4. a. As a result (ด้วยเหตุที่กล่าวมา) b. Since (เพราะ / เพราะว่า)
(4) Since the traffic was so bad in the city, I had to leave my house very early in the morning.
(เพราะว่าการจราจรในเมืองนั้นแย่มาก ฉันจึงต้องออกจากบ้านเร็วมาก ๆ ในตอนเช้า) – จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้าและประโยคหลัง
เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน เราจึงต้องใช้ Since และไม่สามารถใช้ As a result ได้เพราะว่า As a result ตามด้วยประโยค (S+V) ไม่ได้
จะต้องเป็น Noun, Noun Phrase, หรือ Prepositional Phrase เท่านั้น
5. a. neither…nor (ทั้งไม่… และ…) b. either…or (ไม่…ก็…)
I can (5) neither focus nor pay attention to the lessons.
(ฉันทั้งไม่สามารถจดจ่อและให้ความสนใจกับบทเรียนได้) – ข้อนี้สามารถดูความหมายของประโยคในข้อ 4. เพื่ออ้างอิงได้
การออกจากบ้านเช้ามาก ๆ ทำให้ไม่สามารถจดจ่อกับการเรียนได้ และประโยคที่ให้มาในข้อนี้ไม่ได้มีความหมายให้เลือก
อย่างใดอย่างหนึ่ง จึงตอบ neither…nor
6. a. neither…nor (ทั้งไม่…และ…) b. not only…but also (ไม่เพียงแค่…แต่ยัง…)
I felt (6) not only exhausted but also drained every time after school.
(ฉันรู้สึกไม่เพียงแค่เหนื่อย แต่ยังหมดพลังทุกครั้งหลังเลิกเรียน) – จะเห็นว่าประโยคนี้เป็นผลมาจากเรื่องที่เล่ามาในหลาย ๆ
ประโยคก่อนหน้า รถติด ใช้เวลาเดินทางนาน > ต้องออกจากบ้านเช้ามาก ๆ > เรียนไม่รู้เรื่อง > หมดแรง ข้อนี้เราจึงต้องตอบ
not only…but also เพราะหากเราตอบ neither…nor จะแสดงความขัดแย้งกับเนื้อเรื่องที่ผ่านมา
7. a. so (ดังนั้น) b. but (แต่)
(7) So, I decided to move closer to the school to avoid these problems.
(ดังนั้น ฉันจึงตัดสินใจย้ายไปอยู่ใกล้โรงเรียนมากขึ้นเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาเหล่านี้) – ข้อนี้ตอบ so เพราะว่าเป็น Adv. ที่ใช้แสดง
ความเป็นเหตุเป็นผล สามารถใช้ขึ้นต้นประโยคได้และความหมายสอดคล้องกับเนื้อเรื่อง เราไม่สามารถใช้ but ได้ เพราะ but
ใช้เชื่อมระหว่างประโยค 2 ประโยคที่มีความหมายขัดแย้งกัน ความหมายจึงไม่สอดคล้องกับข้อนี้
8. a. both…and (ทั้ง…และ…) b. either…or (ไม่…ก็…)
My parents told me to choose (8) either an apartment or a dormitory, so I chose the nearest one which was the dormitory.
(พ่อแม่ของฉันบอกให้ฉันเลือกไม่อพาร์ตเมนต์ก็หอพัก ดังนั้นฉันเลยเลือกที่ที่ใกล้ที่สุดนั่นก็คือหอพัก) – จะเห็นได้ว่าในประโยคมี keyword
คำว่า choose อยู่ คือให้เลือกอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่ง จึงตอบ either…or
9. a. hence (ดังนั้น) b. until (จนกระทั่ง)
I had stayed there (9) until I graduated from high school.
(ฉันพักอยู่ที่นั่นจนกระทั่งฉันเรียนจบมัธยมปลาย) – จะเห็นได้ว่าประโยคหน้าและประโยคหลังนั้นไม่ได้เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน จึงไม่สามารถ
ตอบ hence ได้ แต่ข้อนี้แสดงให้เห็นลำดับเหตุการณ์ในอดีต
10. a. both…and (ทั้ง…และ…) b. neither…nor (ทั้งไม่…และ…)
I felt (10) both focused and refreshed!
(ฉันรู้สึกทั้งมีสมาธิและสดชื่น) – เมื่ออ่านเนื้อเรื่องจะเห็นว่าเป็นการพูดถึงสาเหตุ > ปัญหาที่เผชิญ > วิธีแก้ > ผลลัพธ์ใหม่ ฉะนั้นเราจึงต้อง
ตอบสิ่งที่จะเติมเต็มเนื้อเรื่องให้สมบูรณ์จากตอนแรกที่ไม่สามารถจดจ่อได้ > มีสมาธิมากขึ้น จึงต้องตอบ both…and
———————————————————————–
Chapter 2 : Determiner
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
จับคู่ประโยคที่ให้มากับ Determiner ให้ถูกต้องกัน! (Determiner 1 ตัว สามารถตอบได้มากกว่า 1 ข้อ)
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I have _____ severe headache. a
ตอบ a เพราะ headache เป็นคำนามนับได้ และมักใช้พูดแบบไม่ชี้เฉพาะ
1. The doctor is waiting for you in the examination room. the
ตอบ the เพราะข้อนี้ต้องเลือก determiner คำเดียวที่ใช้ได้ทั้งกับ doctor และ examination room
ซึ่งเป็นคำนามนับได้เอกพจน์ทั้งคู่ นอกจากนี้ the ยังใช้ได้ทั้งกับคำนามที่ขึ้นต้นด้วยเสียงสระและ
เสียงพยัญชนะอีกด้วย
2. I felt dizzy when I was riding a/the balloon in Cappadocia. a / the
ตอบ a หรือ the ก็ได้ ที่ตอบ a ก็เพราะไม่ต้องการเจาะจงคำว่า balloon เป็นการพูดถึงแบบทั่วไป
อีกทั้ง balloon ยังเป็นคำนามนับได้ด้วย จึงสามารถใช้ a ได้ และที่ตอบ the ได้ก็เพราะ
เป็นการชี้เฉพาะหรือเจาะจงคำว่า balloon นั่นเอง
3. Do you have a fever? a
ตอบ a เพราะ fever เป็นคำนามนับได้ และมักใช้พูดแบบไม่ชี้เฉพาะ
4. I will give you some painkillers. some
ตอบ some เพราะ painkillers เป็นคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์ (มี -s) แต่ไม่ตอบ the เพราะจะเป็นการเจาะจงยี่ห้อ
หรือประเภทของยา ไม่นิยมใช้ อีกทั้งปกติหมอก็มักจะให้ยาแก้ปวด (painkiller) หลาย ๆ เม็ดอยู่แล้ว
ไม่ได้ให้เพียง 1 หรือ 2 เม็ด เลยไม่ตอบ two เช่นกัน
5. How many tablets should I take each time? each
ตอบ each เพราะ each time แปลว่าแต่ละครั้ง นอกจากนี้ each ยังตามด้วยคำนามนับได้เอกพจน์
อย่าง time ได้ด้วย
6. You should take two/some tablets before going to bed. two/some
ตอบ two (สอง) หรือ some (บ้าง / จำนวนหนึ่ง) ก็ได้ เพราะ tablet เติม -s มีจำนวนมากกว่าหนึ่ง
7. Please drink a lot of/some water. a lot of/some
ตอบ a lot of หรือ some ก็ได้ เพราะ water เป็นคำนามนับไม่ได้ และ a lot of กับ some ก็สามารถตาม
ด้วยคำนามนับไม่ได้ได้ด้วย ทั้งนี้ ไม่ตอบ little เพราะประโยคนี้แปลว่ากรุณาดื่มน้ำเยอะ ๆ และปกติแล้ว
ไม่มีใครส่งเสริมให้ดื่มน้ำน้อยนั่นเอง
8. I had an accident and my legs hurt. an
ตอบ an เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงอุบัติเหตุแบบไม่ชี้เฉพาะ และคำว่า accident ยังออกเสียงขึ้นต้นด้วยเสียงสระด้วย
9. You need to undergo an operation. an
ตอบ an เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงการผ่าตัดแบบไม่ชี้เฉพาะ และคำว่า operation ยังออกเสียงขึ้นต้นด้วยเสียงสระด้วย
10. I’ve got very little energy. little
ตอบ little เพราะ energy เป็นคำนามนับไม่ได้ และประโยคนี้ยังแปลว่า ฉันมีพลังงานน้อยมาก หรือไม่ค่อยมีแรงนั่นเอง
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
Track 16
เติมคำแนะนำจากแพทย์ที่ได้ยินลงในช่องว่างให้ถูกต้องเลย
1. I have been feeling hot and cold for a few days.
I also have a fever and runny nose.
You should get plenty of rest
and drink some hot tea
such as chamomile or ginger.
ตอบ plenty of rest เพราะ plenty of สามารถตามด้วยคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์ หรือคำนามนับไม่ได้อย่าง rest ในกรณีนี้ได้
และตอบ some hot tea เพราะ some สามารถตามได้ทั้งคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์ และคำนามนับไม่ได้อย่าง tea ในกรณีนี้ก็ได้
2. I can’t force myself to sleep,
and I’ve been losing some weight lately.
You should not stress. Take a hot bath and relax.
Drink a lot of water for several hours before bedtime.
ตอบ a ตรง hot bath เพราะ bath เป็นคำนามนับได้ อีกทั้งยังออกเสียงขึ้นต้นด้วยเสียงพยัญชนะด้วย
และตอบ a lot of water เพราะ a lot of ตามได้ทั้งคำนามนับได้ หรือนับไม่ได้อย่าง water ก็ได้
นอกจากนี้ยังตอบ several หน้า hours ได้ด้วย เนื่องจาก several (จำนวนมากกว่า 3 ขึ้นไป แต่ไม่เท่า many)
ต้องตามด้วยคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์อย่าง hours เสมอ
3. I have a sore throat. It’s so painful that
I struggle to eat or drink anything.
You have tonsillitis. Try to eat bland and soft foods.
Have some dark chocolate ice cream. It will ease the inflammation.
ตอบ some ตรง dark chocolate ice cream เพราะ ice cream เป็นได้ทั้งคำนามนับได้ และนับไม่ได้
นอกจากนี้ some ยังใช้ได้ทั้งกับคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์ หรือคำนามนับไม่ได้ก็ได้
4. I’ve had backpain for some time
because I usually sit in front of the computer all day.
That’s a sign of office syndrome.
You should try to take a rest for 5-10 minutes every hour.
Select the chair that supports your back well.
ตอบ a ตรง rest เพราะ a สามารถตามด้วยคำนามนับได้อย่าง rest ในกรณีนี้ได้
(ปกติ rest เป็นได้ทั้งคำนามนับได้ และนับไม่ได้)
และตอบ every ตรง hour เพราะ every สามารถตามด้วยคำนามนับได้เอกพจน์อย่าง hour ได้
นอกจากนี้ยังตอบ the ตรง chair เพราะเป็นการชี้เฉพาะว่าหมายถึงเก้าอี้ตัวไหน
ซึ่งในที่นี้หมายถึงเก้าอี้ตัวที่สามารถรองรับหลังได้ดีนั่นเอง
5. I’m having diarrhea and vomiting.
I feel exhausted and dehydrated.
Drink plenty of clear fluid, like fruit juices, soda, or sports drinks.
Avoid milk or milk-based products.
ตอบ plenty of clear fluid เพราะ plenty of สามารถตามด้วยคำนามนับได้พหูพจน์
หรือคำนามนับไม่ได้อย่าง fluid ที่เป็นทั้งคำนามนับได้ หรือนับไม่ได้ก็ได้
———————————————————————–
Chapter 3 : Tense
Present Simple
เลือกคำกริยาที่ให้มาไปใส่ในช่องว่าง โดยผันรูปกริยาตามประธาน (Subject) และกาล (Tense) ให้ถูกต้องด้วยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. The sun sets in the west. (set)
ตอบ sets แบบเติม -s เพราะ the sun หรือพระอาทิตย์มีดวงเดียว และใช้ Present Simple เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงความจริงทั่วไป หรือพูดถึงวิทยาศาสตร์
1. The meeting starts at 9 o’clock in the morning. (start)
ตอบ starts แบบเติม -s เพราะ the meeting เป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ อีกทั้งยังเป็นการพูดถึงตารางเวลาด้วย จึงใช้ Present Simple
2. All the ferries leave from this dock. (leave)
ตอบ leave แบบไม่เติม -s เพราะ the ferries เติม -s เป็นคำนามพหูพจน์ และใช้ Present Simple เพราะพูดถึงเรื่องตารางเวลา
3. The first flight to New York departs at 5 a.m. daily. (depart)
ตอบ departs แบบเติม -s เพราะ the first flight to New York (เที่ยวบินแรกที่ไปนิวยอร์ก) เป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ และใช้ Present Simple
เพราะพูดถึงเรื่องตารางเวลา
4. The plane takes off at 10 p.m. Please be at the gate 45 minutes before boarding time. (take off)
ตอบ takes off แบบเติม -s เพราะ the plane ไม่เติม -s จึงเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ อีกทั้งยังเป็นการพูดถึงตารางเวลาด้วย จึงใช้ Present Simple
5. I usually take a bus to school because it is convenient. (take)
ตอบ take แบบไม่เติม -s เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I ซึ่งต้องใช้กับคำกริยาที่ไม่เติม -s เสมอ อีกทั้งยังใช้ Present Simple ด้วย
เพราะมีกริยาวิเศษณ์บอกความถี่คำว่า usually ที่มักจะเจอใน Present Simple
Present Continuous
วงกลม Keyword บอกเวลาของ Present Continuous ในประโยค
และเติมคำกริยาที่ผันตามประธาน (Subject) และกาล (Tense) ลงไปให้ถูกต้องเลย
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I am shopping with friends at Times Square now. (shop)
ตอบ am shopping เพราะ Present Continuous มีโครงสร้างคือ S + is/am/are + V.ing ซึ่งประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I จึงต้องใช้คู่กับ
V. to be “am” ใน Present Continuous เสมอ นอกจากนี้ now (ตอนนี้) ยังถือเป็น Keyword บอกเวลาของกาล (Tense) นี้ด้วย เนื่องจาก
Present Continuous จะใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นอยู่ในขณะนี้
1. Mom is baking a cake at the moment. (bake)
ตอบ is baking เพราะ Present Continuous มีโครงสร้างคือ S + is/am/are + V.ing และประธานของประโยคอย่าง mom ต้องใช้คู่กับ
V. to be “is” ใน Present Continuous เสมอ นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า at the moment (ตอนนี้) ก็เพราะว่าคำนี้ถือเป็น Keyword
บอกเวลาของกาล (Tense) นี้นั่นเอง
2. They are staying in New York this summer. (stay)
ตอบ are staying เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + is/am/are + V.ing ของ Present Continuous และประธานของประโยคอย่าง they
ซึ่งเป็นคำสรรพนามพหูพจน์ก็ต้องใช้คู่กับ V. to be “are” ที่เป็นคำกริยาพหูพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า this summer (ฤดูร้อนนี้)
ก็เพราะว่าคำนี้เป็น Keyword บอกเวลาคำหนึ่งของกาล (Tense) นี้ เพราะนอกจากกาล (Tense) นี้จะใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นอยู่ในขณะนี้
แล้ว ยังสามารถใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่บอกเวลาคร่าว ๆ ว่าเกิดขึ้นในช่วงนี้ได้ด้วย
3. Sam is currently studying at ABC University as an exchange student. (study)
ตอบ is studying เพราะ Present Continuous มีโครงสร้างคือ S + is/am/are + V.ing และประธานของประโยคอย่างชื่อคน หรือ Sam
ก็ต้องใช้คู่กับ V. to be “is” ใน Present Continuous เสมอ นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า currently (ในปัจจุบัน) ก็เพราะว่าคำนี้ถือเป็น Keyword
บอกเวลาของ Present Continuous นั่นเอง
4. We are having a party tonight at NY club. (have)
ตอบ are having เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + is/am/are + V.ing ของ Present Continuous และประธานของประโยคหรือ we
ก็ต้องใช้คู่กับ V. to be “are” ที่เป็นคำกริยาพหูพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า tonight (คืนนี้) เพราะถือเป็น Keyword
บอกเวลาของ Present Continuous นั่นเอง
5. Kate is busy right now. She is talking to her friend. (talk)
ตอบ is talking เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + is/am/are + V.ing ของ Present Continuous และประธานของประโยคคือชื่อคน หรือ Kate
ซึ่งเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ จึงต้องใช้คู่กับ V. to be “is” ที่เป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน นอกจากนี้ที่วงกลมคำว่า right now (ตอนนี้) เพราะถือเป็น
Keyword บอกเวลาของ Present Continuous นั่นเอง
Present Perfect
เรียงประโยคต่อไปนี้ให้อยู่ในโครงสร้าง Present Perfect และอย่าลืมผันคำกริยาให้ถูกต้องตามกาล (Tense) ด้วยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. have / I / study / English / 5 years / for / . => I have studied English for 5 years.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have studied English เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I
จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาที่ไม่มี -s อย่างคำว่า have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า study ก็คือ studied นอกจากนี้ Present Perfect ยังมักตามด้วย
for + ช่วงเวลาด้วย จึงต้องเขียน for 5 years ไว้ท้ายประโยคนั่นเอง
1. I / have / have / already / dinner / . => I have had dinner already. / I have already had dinner.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have had dinner เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I จึงต้องใช้คู่กับ
คำกริยาที่ไม่มี -s อย่างคำว่า have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า have ก็คือ had นั่นเอง (สามารถวาง have had ติดกันได้) แต่ทั้งนี้สามารถเขียน
ประโยคนี้ได้ 2 แบบเพราะจะวางคำว่า already ที่เป็นคำกริยาวิเศษณ์ไว้ท้ายประโยคเป็น I have had dinner already. หรือวางไว้ระหว่าง
คำกริยาสองตัว (V. ตบหน้า ตบหลัง ตรงกลางคือ Adv.) เป็น I have already had dinner. ก็ได้
2. live / New York / in / since / have / 2010 / I / . => I have lived in New York since 2010.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have lived in New York เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I
จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาที่ไม่มี -s อย่างคำว่า have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า live ก็คือ lived ซึ่งมักตามด้วยที่อยู่ เพื่อบอกว่าอาศัยอยู่ที่ไหน
ดังนั้นจึงต้องเติม in New York ตามหลังด้วย นอกจากนี้ Present Perfect ยังมักตามด้วย since + ปี จึงต้องเขียน since 2010 ไว้
ท้ายประโยคนั่นเอง
3. never / be / I / yet / have / to / place / your / . => I have never been to your place yet.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have never been to your place เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า I
จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาที่ไม่มี -s อย่างคำว่า have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า be ก็คือ been นั่นเอง ซึ่งจะตามด้วยสถานที่ เพื่อบอกว่าเคยหรือ
ไม่เคยไปที่ใดมาก่อน จึงต้องเติม to your place ตามหลังด้วย ส่วนคำว่า never ที่แปลว่า ไม่เคย มักจะวางไว้ระหว่างคำกริยาสองตัวเพื่อ
ทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ ได้เป็น have never been to your place นอกจากนี้ หากจะใช้คำว่า yet ก็มักจะวางไว้ท้ายประโยค ดังนั้นจึงได้
เป็นประโยค I have never been to your place yet. นั่นเอง
4. since / talk / ever / We / have / other / to / each / never / . => We have never talked to each other ever since.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ have never talked to each other เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า
We จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาพหูพจน์อย่าง have เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า talk ก็คือ talked ซึ่งจะตามด้วยบุคคล หรือ each other (ซึ่งกันและ
กัน) ก็ได้ เพื่อบอกว่าคุยกับใคร ดังนั้นจึงต้องเติม to each other ตามหลัง ส่วนคำว่า never ที่แปลว่า ไม่เคย มักจะวางไว้ระหว่างคำกริยาสองตัว
เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ จึงได้เป็น have never talked to each other นอกจากนี้หากจะเติมคำว่า ever since ก็มักจะวางไว้ท้ายประโยค
จึงได้เป็น We have never talked to each other ever since. นั่นเอง
5. so / My / far / life / great / be / has / . => My life has been great so far.
Present Perfect มีโครงสร้างคือ S + has/have + V.3 ซึ่งข้อนี้ใช้ has been great เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคำว่า My life ที่เป็นเอกพจน์
จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาเอกพจน์อย่าง has เสมอ และ V.3 ของคำว่า be ก็คือ been ซึ่งสามารถตามด้วยคำคุณศัพท์ได้ จึงต้องเขียน great
ที่เป็นคำคุณศัพท์ไว้ตามหลัง นอกจากนี้หากจะเติมคำว่า so far ก็มักจะวางไว้ท้ายประโยค จึงได้เป็น My life has been great so far. นั่นเอง
Present Perfect Continuous
เติมคำกริยาที่ให้มาลงในช่องว่าง โดยให้อยู่ในโครงสร้าง Present Perfect Continuous ที่ถูกต้องด้วยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. She has been playing volleyball since she was nine. (play)
ตอบ has been playing เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้างของ Present Perfect Continuous คือ S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยใช้ has
เพราะประธานของประโยคคือ she ซึ่งเป็นคำที่ต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์นั่นเอง
1. Diana has been reading this book for weeks. (read)
ตอบ has been reading เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ has เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคน
เพียง 1 คน หรือในข้อนี้ก็คือ Diana นั่นเอง ดังนั้นจึงต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์อย่าง has เสมอ
2. We have been traveling together in the States for months. (travel)
ตอบ have been traveling เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ have เพราะประธานของประโยคคือ
we ที่ต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาพหูพจน์เสมอ
3. She has been doing her homework for 2 hours. (do)
ตอบ has been doing เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ has เพราะประธานของประโยคคือ she
ที่ต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
4. I have been practicing ballet since 9 a.m. (practice)
ตอบ have been practicing เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ have เพราะประธานของประโยคคือ
I ที่ต้องใช้กับคำกริยาไม่เติม -s เสมอ
5. Mr. Bruce has been teaching English for 15 years. (teach)
ตอบ has been teaching เพราะถูกต้องตามโครงสร้าง S + has/have + been + V.ing โดยที่ใช้ has เพราะประธานของประโยคคือคน
เพียง 1 คน หรือในข้อนี้ก็คือ Mr. Bruce ดังนั้นจึงต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์อย่าง has เสมอ
Present Tense Exercise
วงกลมตัวเลือกคำกริยาที่ใช้ Tense ได้ถูกต้องและเหมาะสมกันเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I __________ regularly in the morning
a. exercise b. am exercising c. have exercised d. have been exercising
ตอบ a. เพราะเป็น Present Simple เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า regularly (เป็นประจำ / เป็นปกติ)
1. I __________ this dish before, so I’m going to order this.
a. do not try b. am not trying c. have not tried d. have not been trying
ตอบ c. เพราะเป็น Present Perfect เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า before เพื่อบอกว่าเคย หรือไม่เคยทำสิ่งใดมาก่อน ทั้งนี้จะไม่ตอบ d.
หรือ Present Perfect Continuous เพราะการที่บอกว่าเคย หรือไม่เคยทำสิ่งใด จะอยู่ในรูปประโยคแบบ Present Perfect
2. John __________ his homework already. He is ready to go out and meet his friends.
a. finishes b. is finishing c. has finished d. has been finishing
ตอบ c. เพราะเป็น Present Perfect เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า already ที่มักใช้ในกาล (Tense) นี้เพื่อบอกว่าเกิดเหตุการณ์บางอย่าง
ที่เพิ่งจบได้ไม่นาน
3. The Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York __________ from 10 a.m. to 5 p.m. every day except Tuesday and Wednesday.
a. opens b. is opening c. has opened d. has been opening
ตอบ a. เพราะเป็น Present Simple เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า every day (ทุกวัน) รวมทั้งมีการพูดถึงเรื่องตารางเวลาด้วย
4. Sarah __________ during the day for 3 hours. Should we let her sleep or wake her up?
a. sleeps b. is sleeping c. has slept d. has been sleeping
ตอบ d. เพราะเป็น Present Perfect Continuous เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า for 3 hours (เป็นเวลา 3 ชั่วโมง) รวมทั้งประโยคที่ตามมา
ยังแปลว่า “พวกเราควรจะปล่อยให้หล่อนนอนต่อไปหรือปลุกหล่อนดี” ด้วย แสดงว่าตอนนี้หล่อนก็น่าจะยังนอนหลับอยู่แน่ ๆ และหลับมาตลอด
เลย ดังนั้นถ้าพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้น แล้วดำเนินมาถึงปัจจุบัน พร้อมทั้งแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ (นอนหลับมาตลอด 3 ชั่วโมง)
เช่นนี้ด้วย จึงต้องใช้ Present Perfect Continuous นั่นเอง
5. It’s Sunday, so they must be at the cinema. They always __________ the movies on Sunday night.
a. watch b. are watching c. have watched d. have been watching
ตอบ a. เพราะเป็น Present Simple เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า always (เป็นประจำ / สม่ำเสมอ)
6. She __________ on the new project in New York right now.
a. works b. is working c. has worked d. has been working
ตอบ b. เพราะเป็น Present Continuous เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า right now (ตอนนี้ / ในขณะนี้)
7. The marketing manager __________ here since 1995, and he will retire soon.
a. works b. is working c. has worked d. has been working
ตอบ d. เพราะเป็น Present Perfect Continuous เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า since + ปี ทั้งนี้จะตอบ c. ที่เป็น Present Perfect ก็ได้ เพียงแต่
ถ้าตอบข้อ d. ที่เป็น Present Perfect Continuous จะถูกต้องที่สุด เนื่องจากประโยคที่สอง he will retire soon. (เขาจะเกษียณเร็ว ๆ นี้) บ่งบอก
ว่าช่วงนี้เขาก็ยังทำงานอยู่ ยังไม่ได้เกษียณ จึงสามารถแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ว่าทำงานมาตลอดตั้งแต่ปี 1995 ด้วยการใช้
Present Perfect Continuous ได้นั่นเอง
8. We __________ to New York to visit our friends next week.
a. fly b. are flying c. have flown d. have been flying
ตอบ b. เพราะเป็น Present Continuous เนื่องจากมี Keyword คำว่า next week (อาทิตย์หน้า)
9. My friend can’t speak Thai. He __________ English and Spanish only.
a. speaks b. is speaking c. has spoken d. has been speaking
ตอบ a. เพราะเป็น Present Simple เนื่องจากเป็นการพูดถึงความจริงทั่วไปว่าเขาพูดได้เพียงภาษาอังกฤษและภาษาสเปนเท่านั้น
10. They __________ a performance school in New York this summer.
a. attend b. are attending c. have attended d. have been attending
ตอบ b. เพราะมี Keyword คำว่า this summer (ฤดูร้อนนี้) เพื่อบอกว่าช่วงนี้หรือช่วงฤดูร้อนนี้กำลังทำอะไรอยู่ ซึ่งสามารถใช้ใน
Present Continuous ได้นั่นเอง
Past Simple
วงกลมคำกริยาช่อง 2 (V.2) ทั้งหมด 10 คำ ในตารางที่ใช้กับประโยค Past Simple Tense เลย!
showed
known
left
eat
listen
travel
went
send
was/were
gone
turn
got
saw
buy
drunk
called
driven
been
make
heard
worn
done
sung
knew
paid
Past Continuous
เติมคำกริยาที่ผันตาม Tense ได้ถูกต้องลงในช่องว่างเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Ken was studying (study) in San Francisco during summer last year.
ตอบ was studying เพราะตรงกับโครงสร้างของ Past Continuous คือ S + was/were + V.ing และมีจุดสังเกตคือ ข้อนี้มีการบอกช่วงเวลาที่เกิด
เหตุการณ์ด้วย (during summer) ดังนั้นต้องใช้ Past Continuous ไม่ใช่ Past Simple ธรรมดา โดยที่ใช้ was แทน were เนื่องจาก Ken เป็น
ประธานเอกพจน์
1. My sister was watching (watch) the news on TV at home
when she heard (hear) the car crash.
ตอบ was watching และ heard ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses เพื่อพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดกำลังเกิดขึ้นในอดีต (Past Continuous)
โดยมีอีกเหตุการณ์เข้ามาแทรก (Past Simple) มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ when จะตามด้วย Past Simple นอกจากนี้ยังใช้ was ตรง was watching
เพราะประธานเป็นเอกพจน์ด้วย
2. Yesterday my mother was cooking (cook)
when she hit (hit) her head on the kitchen cabinet.
ตอบ was cooking และ hit ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses เช่นเดียวกับข้อ 1. เพื่อพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดกำลังเกิดขึ้นในอดีต
(Past Continuous) โดยมีอีกเหตุการณ์เข้ามาแทรก (Past Simple) มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ when จะตามด้วย Past Simple นอกจากนี้ยังใช้
was cooking เพราะประธาน (my mother) เป็นเอกพจน์ และใช้ hit เพราะไม่ว่าจะเป็นคำกริยาช่องไหน ก็จะยังผันเป็น hit เหมือนเดิมเสมอ
ไม่ต้องเปลี่ยนรูป
3. I was walking (walk) along the Lombard street
while a drunk driver was running (run) a red light.
ตอบ was walking และ was running ตามลำดับ เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นพร้อมกันในอดีต มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ while
จะตามด้วย Past Continuous ดังนั้นประโยคที่สองต้องใช้ Past Continuous ด้วย นอกจากนี้ยังผันคำกริยาเป็น was เพราะประธานทั้งสองตัว
(I และ a drunk driver) ต้องใช้คู่กับ was เสมอ
4. Susan was playing (play) badminton last week in PE class.
ตอบ was playing เพราะตรงกับโครงสร้างของ Past Continuous คือ S + was/were + V.ing และมีจุดสังเกตคือ ข้อนี้มีการบอกช่วงเวลาที่เกิด
เหตุการณ์นอกจากคำว่า last week ด้วย นั่นก็คือคำว่า in PE class ดังนั้นต้องใช้ Past Continuous ไม่ใช่ Past Simple ปกติ โดยที่ใช้ was
เนื่องจาก Susan เป็นประธานเอกพจน์
5. I was calling (call) you from the emergency room last night,
but you were not answering (not answer) your phone.
ตอบ was calling และ were not answering ตามลำดับ เพราะตรงกับโครงสร้างของ Past Continuous คือ S + was/were + V.ing หรือ
สังเกตง่าย ๆ ก็คือ เมื่อใดก็ตามที่ใช้ FANBOYS (ในข้อนี้คือ B หรือ but) เชื่อมประโยค มักต้องใช้กาล (Tense) เดียวกันกับประโยคทั้งสองด้วย
นอกจากนี้ยังผันคำกริยาเป็น was เพราะประธานตัวแรก (I) ต้องใช้คู่กับ was เสมอ ส่วนประธานตัวหลัง (you) ต้องใช้คู่กับ were นั่นเอง
Past Perfect
เติมคำกริยาที่ให้มาและผันตาม Tense ให้ถูกต้อง!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. All the flights had been canceled (cancel) due to the storm
before I got (get) to the airport.
ตอบ had been canceled และ got ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง
และจบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ
before จะตามด้วย Past Simple นั่นเอง
1. The museum ____________________ (close) by the time
we ____________________ (get off) the bus.
ตอบ had been closed และ got off ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง
และจบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ
by the time จะตามด้วย Past Simple ดังนั้นประโยคที่สองจึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น got off นั่นเอง
2. Before we ____________________ (arrive) at the bus stop,
the cable car ____________________ (leave) already.
ตอบ arrived และ had left ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และจบลงแล้ว
ในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ before จะตามด้วย
Past Simple ดังนั้นประโยคแรก จึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น arrived ส่วนประโยคที่สองต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น had left ตามโครงสร้างของ
Past Perfect นั่นเอง
3. I ____________________ (never see) real seals
until I ____________________ (come) to Pier 39.
ตอบ had never seen และ came ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และ
จบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ until
จะตามด้วย Past Simple ดังนั้นประโยคแรก จึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น had never seen ตามโครงสร้าง S + had + V.3 ของ Past Perfect
ส่วนประโยคที่สองต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น came ตามโครงสร้าง S + V.2 ของ Past Simple
4. The plane just ____________________ (take off)
after the final call ____________________ (announce).
ตอบ took off และ had been announced ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมา
ระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และจบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple
มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ after จะตามด้วย Past Perfect ดังนั้นประโยคที่สองจึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น had been announced ตามโครงสร้าง
S + had + V.3 แต่ทั้งนี้ที่ต้องเติม been เข้ามาแทรกก็เพราะ the final call (การประกาศเรียกผู้โดยสารครั้งสุดท้าย) จะประกาศ หรือทำกริยา
announce เองไม่ได้ ต้องถูกประกาศ จึงต้องอยู่ในรูป Passive Voice หรือ has/have/had + been + V.3 ด้วย
5. My friends ____________________ (miss) the train
before they ____________________ (call) me for help.
ตอบ had missed และ called ตามลำดับ เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง
และจบลงแล้วในอดีต โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ
คือ before จะตามด้วย Past Simple ดังนั้นประโยคที่สองจึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น called ตามโครงสร้าง S + V.2 ส่วนประโยคแรกก็ต้อง
ผันคำกริยาเป็น had missed ตามโครงสร้าง S + had + V.3 นั่นเอง
Past Perfect Continuous
ผันกริยาที่ให้มาในวงเล็บให้อยู่ในรูปประโยค Past Perfect Continuous อย่างถูกต้องกันเถอะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I had been walking (walk) around San Francisco City Hall for 2 hours.
ตอบ had been walking เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous คือ S + had + been + V.ing ซึ่งเป็น
การแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
1. She ____________________(travel) in San Francisco for a week
when a burglar broke into her house.
ตอบ had been traveling เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous ทั้งนี้เมื่อนำไปใช้ในชีวิตประจำวัน ประโยคนี้สามารถใช้
Past Perfect แทนได้ เป็น had traveled เพียงแต่หากใช้ Past Perfect Continuous ก็จะเป็นการแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ด้วยนั่นเอง
2. The lost-and-found counter ____________________ (announce)
for the child’s mother for 15 minutes before she showed up.
ตอบ had been announcing เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous คือ S + had + been + V.ing ซึ่งเป็น
การแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ หรือสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ ประโยคหลัง (before she showed up) เป็น Past Simple ที่ใช้คู่กับ
Past Perfect Continuous ได้ ดังนั้นตอบ had been announcing ได้เลย
3. They ____________________ (take) care of their property together
before they were married.
ตอบ had been taking เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous ซึ่งเป็นการแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
4. Bob ____________________ (work) in this shop for several months
before the shoplifting incident happened.
ตอบ had been working เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous คือ S + had + been + V.ing ซึ่งเป็น
การแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
5. He ____________________ (wait) for his luggage for 3 days before it finally arrived.
ตอบ had been waiting เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Past Perfect Continuous ซึ่งเป็นการแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
หรือสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ ประโยคหลัง (before it finally arrived) เป็น Past Simple ที่ใช้คู่กับ Past Perfect Continuous ได้
ดังนั้นตอบ had been waiting ได้เลย
Past Tense Exercise
ผันกริยาที่ให้มาในวงเล็บให้ถูกต้องตาม Tense และเติมคำตอบลงในช่องวางให้สมบูรณ์เลย!
Jessie (0) was (be) fifteen years old in 2015. She (1) had lived (live) with her family in
New York before they (2) moved (move) to San Francisco together. She (3) went (go)
to school near her house. She (4) had studied (study) at that school until she was eighteen years old.
One day she (5) was walking (walk) along the Lombard street when she (6) met (meet)
her friend, Han. Han (7) told (tell) her that the police (8) caught (catch) a pickpocket
among tourists last week. He also (9) warned (warn) her to look out for her belongings.
This kind of theft (10) had happened (happen) for many years even before she (11) came (come)
here. While Jessie (12) was talking (talk) to Han, she (13) saw (see) a woman looking
panicked. When they (14) went (go) to talk to her, she (15) had already lost (already lose)
her purse.
(0) was เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีต มีจุดสังเกตคือ in 2015 ซึ่งเป็นปีที่ผ่านมาแล้ว
(1) had lived เพราะประโยคนี้ (ตั้งแต่ข้อ 1-2) เป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses ใน 2 เหตุการณ์ เพื่อเล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลัง
ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และจบลงแล้ว โดยเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้
Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ คำว่า before ซึ่งต้องตามด้วย Past Simple แสดงว่าในส่วนของข้อ (1) ต้องเป็น
Past Perfect ที่มีโครงสร้าง S + had + V.3
(2) moved เพราะข้างหน้าคือคำว่า before ดังนั้นข้อนี้จึงต้องตอบ Past Simple ที่มีโครงสร้างเป็น S + V.2 นั่นเอง
(3) went เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตทั่ว ๆ ไป ข้อนี้ไม่มี keyword หรือจุดสังเกตใด ๆ ที่บอกว่าเป็นกาล (Tense) ไหนเลย
ดังนั้น ถ้าประโยคก่อนหน้าเล่าถึงเรื่องในอดีตมาตลอด และประโยคนี้ก็ยังจะเล่าถึงเรื่องในอดีตอยู่ จึงต้องใช้ Past Simple
ปกติ ที่มีโครงสร้างเป็น S + V.2 ได้เลย
(4) had studied เพราะเป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses ใน 2 เหตุการณ์ เพื่อเล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง และ
จบลงแล้ว โดยเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ
คำว่า until ซึ่งต้องตามด้วย Past Simple (she was eighteen years old.) แสดงว่าในส่วนที่ไม่ได้อยู่หลัง until ต้องเป็น
Past Perfect
(5) was walking เพราะมี keyword บอกเวลาอย่าง one day เพื่อบอกว่ากำลังเกิดเหตุการณ์บางอย่างในช่วงเวลาใดเวลาหนึ่งอยู่
ดังนั้นจึงต้องใช้ Past Continuous
(6) met เพราะมี keyword คำว่า when ที่มักตามด้วย Past Simple อีกทั้งประโยคนี้ (ข้อ 5-6) ยังเป็นการใช้ Tense คู่ เพื่อเล่าเรื่อง
ที่เกิดก่อนและหลังด้วย ดังนั้นถ้าประโยคแรกใช้ Past Continuous (was walking) ไปแล้ว ประโยคในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้ Past Simple
นั่นเอง
(7) told เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีต มีจุดสังเกตคือ last week ซึ่งแปลว่า สัปดาห์ที่ผ่านมา
(8) caught เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีต มีจุดสังเกตคือ last week เช่นเดียวกับข้อ (7) เพราะทั้งข้อ (6) และ (7) คือประโยคเดียวกัน
หรือมีวิธีสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ ถ้าประโยคใด ๆ ไม่มี keyword บอกกาล (Tense) ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง เช่น for ที่มักใช้กับ Past Perfect แล้ว
ให้ถือว่าประโยคเดียวกันต้องใช้กาล (Tense) เดียวกัน ดังนั้นจึงต้องผัน catch เป็น caught (V.2) ให้เหมือน told ในข้อ (7) นั่นเอง
(9) warned เพราะพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีต และไม่มี keyword บอกกาล (Tense) ที่เฉพาะเจาะจง จึงใช้ Past Simple ได้เลย
(10) had happened เพราะมี keyword คำว่า for many years ที่มักใช้กับ Past Perfect อีกทั้งประโยคนี้ (ข้อ 10-11) ยังเป็นการใช้
Tense คู่ เพื่อเล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลังด้วย ดังนั้นประโยคในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้ Past Perfect นั่นเอง
(11) came เพราะมี keyword คำว่า before ที่จะตามด้วย Past Simple อีกทั้งประโยคนี้ (ข้อ 10-11) ยังเป็นการใช้ Tense คู่ เพื่อ
เล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลังด้วย ดังนั้นถ้าประโยคแรกใช้ Past Perfect (ตรง had happened) ไปแล้ว ในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้
Past Simple หรือ came นั่นเอง
(12) was talking เพราะเป็นการใช้กาล 2 กาล หรือ 2 Tenses เพื่อบอกว่ากำลังเกิดเหตุการณ์หนึ่งอยู่ แล้วมีอีกเหตุการณ์หนึ่งเข้ามา
ขัดจังหวะ โดยเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นจะใช้ Past Continuous ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เข้ามาขัดจังหวะจะใช้ Past Simple นอกจากนี้
ยังมี keyword คำว่า while ที่จะตามด้วย Past Continuous ด้วย ดังนั้นในส่วนนี้จึงต้องตอบ was talking นั่นเอง
(13) saw เพราะเป็นการพูดถึง 2 เหตุการณ์ คือมีทั้งเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้น และเหตุการณ์ที่เข้ามาแทรก หรือเข้ามาขัดจังหวะ ดังนั้น
ถ้าข้อ (12) ใช้ Past Continuous ไปแล้ว ในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้ Past Simple หรือผันคำกริยา see เป็น saw นั่นเอง
(14) went เพราะประโยคนี้ (ตั้งแต่ข้อ 14-15) เป็นการใช้ 2 Tenses ใน 2 เหตุการณ์ เพื่อเล่าเรื่องที่เกิดก่อนและหลัง ดำเนินมาระยะเวลาหนึ่ง
และจบลงแล้ว โดยเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดก่อนจะใช้ Past Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดทีหลังจะใช้ Past Simple มีจุดสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ คำว่า
when ซึ่งต้องตามด้วย Past Simple แสดงว่าในส่วนของข้อ (14) ต้องเป็น Past Simple ที่มีโครงสร้าง S + V.2
(15) had already lost เพราะข้อ (14) และ (15) เป็นการใช้ 2 Tense คู่กัน ดังนั้นถ้าใช้ Past Simple ในข้อ (14) ไปแล้ว ในส่วนนี้จึงต้องใช้
Past Perfect ที่มีโครงสร้างเป็น S + had + V.3 นั่นเอง
Future Simple
ดูรูปภาพที่ให้มา และเติมคำทำนายจากแม่หมอให้ถูกต้องที!

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Your mother will buy you a car as a birthday present. She won’t give you money.
เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างประโยคบอกเล่าของ Future Simple คือ S + will + V.1 และประโยคปฏิเสธคือ S + will not / won’t + V.1 ตามลำดับ
1. Your boyfriend __________ you this year.
ตอบ will propose เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง Future Simple ทั้งนี้ที่ใช้กาล (Tense) นี้ได้ก็เพราะโจทย์คือเหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดในอนาคต
หรือสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือมีคำบอกเวลา เช่น this year ที่ใช้กับ Future Simple ได้
2. You __________ abroad next year.
ตอบ will not study / won’t study เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธของ Future Simple คือ S + will not / won’t + V.1 ทั้งนี้ที่ใช้กาล (Tense) นี้ได้ก็เพราะมีคำบอกเวลาอย่าง next year ที่แปลว่าปีหน้าอยู่ด้วยนั่นเอง
3. You __________ a lottery this time. Don’t buy it.
ตอบ will not win / won’t win เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธของ Future Simple คือ S + will not / won’t + V.1
4. You __________ a lot of interesting people.
ตอบ will meet เพราะตรงกับโครงสร้าง S + will + V.1 ของ Future Simple นั่นเอง
5. You __________ any problems with work.
ตอบ will not have / won’t have เพราะโครงสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธของ Future Simple คือ S + will not / won’t + V.1
Future Continuous
ช่วย Ethan เติมประโยคให้ถูกต้องครบถ้วนทีนะว่าเขาวางแผนจะทำอะไรบ้างในสัปดาห์หน้า

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Ethan will be going (go) on a school trip.
ตอบ will be going เพราะเมื่อพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในช่วงเวลาใดเวลาหนึ่งในอนาคต จะใช้โครงสร้างของ Future Continuous
หรือ S + will + be + V.ing
1. Ethan ____________________ (do) his assignments.
ตอบ will be doing เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + be + V.ing
2. Ethan ____________________ (jog) in the park.
ตอบ will be jogging เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + be + V.ing แต่ทั้งนี้ตอนผันคำว่า jog ให้เป็น jogging นั้นต้องเติมตัว g
เข้ามาเพิ่มอีกตัวด้วย เนื่องจาก jog เป็นคำกริยาพยางค์เดียว มีสระและตัวสะกดตัวเดียว
3. Ethan ____________________ (plan) about the holiday trip with his family.
ตอบ will be planning เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + be + V.ing ทั้งนี้ต้องผันคำว่า plan ให้เป็น planning โดยการเติมตัว n
เพิ่มอีก 1 ตัวด้วย เนื่องจาก plan เป็นคำกริยาพยางค์เดียว มีสระ และตัวสะกดตัวเดียว
4. Ethan ____________________ (walk) his dog.
ตอบ will be walking เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Future Continuous โดยที่ to walk a dog แปลว่า พาหมาไปเดินเล่น
5. Ethan ____________________ (play) basketball at the gym.
ตอบ will be playing เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Future Continuous โดยที่ต้องผันคำกริยา play เป็น playing เพราะ
คำที่ลงท้ายด้วย y สามารถเติม -ing ได้เลย
Future Perfect
เติมคำกริยาที่ผันอย่างถูกต้องลงในประโยคด้านล่างนี้เลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. By the end of this year, I will have saved (save) $1,000.
ตอบ will have saved เพราะมี keyword ที่มักใช้กับ Future Perfect ซึ่งมักเป็น by + ช่วงเวลา หรือก็คือ by the end of this year
ในข้อนี้นั่นเอง ทั้งนี้ Future Perfect ยังมีโครงสร้างเป็น S + will + have + V.3 ด้วย จึงสามารถผันคำกริยา save เป็น will have saved
ได้เลย
1. Daniel ____________________ (graduate) from college by 15th May.
ตอบ will have graduated เพราะมี keyword ของ Future Perfect คือ by + ช่วงเวลา หรือก็คือ by 15th May ในข้อนี้ โดยที่สามารถ
ใช้กาล (Tense) นี้ได้เนื่องจากโจทย์ข้อนี้เข้าเงื่อนไขการพูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่คาดว่าจะจบในอนาคของ Future Perfect
2. By the time I ____________________ (be) sixty years old, I ____________________ (have) lots of grandchildren.
ตอบ am และ will have had ตามลำดับ เพราะข้อนี้เป็นการคาดการณ์เหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคต โดยเหตุการณ์
ที่จะเกิดขึ้น และจบก่อนจะใช้ Future Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่คาดว่าจะเกิดตามมาจะใช้ Present Simple ทั้งนี้ keyword ต่าง ๆ เช่น
by + ช่วงเวลา หรือ when ที่แปลว่า เมื่อ/ตอนที่ จะตามด้วย Present Simple เสมอหากใช้ในกรณีที่พูดถึง 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้น
ในอนาคตเช่นนี้ ดังนั้นประโยคแรกที่มีคำว่า by the time จึงต้องผันคำกริยา be เป็น am ให้ตรงกับประธาน I ในรูป Present Simple
และผันคำกริยาของประโยคหลังเป็น will have had ให้ตรงกับ Future Perfect นั่นเอง
3. Nana ____________________ (write) more than 10 books by next year.
ตอบ will have written เพราะมี keyword ของ Future Perfect คือ by + ช่วงเวลา หรือก็คือ by next year ในข้อนี้ โดยต้องอย่าลืม
ผันคำกริยาเป็น V.3 หรือ written ด้วย
4. By 9 a.m. tomorrow, I ____________________ (sleep) more than eight hours.
ตอบ will have slept เพราะมี keyword ของ Future Perfect คือ by + ช่วงเวลา หรือก็คือ by 9 a.m. tomorrow ในข้อนี้ โดยต้อง
อย่าลืมผันคำกริยาเป็น V.3 หรือ slept ด้วย
5. When you ____________________ (arrive) in Hawaii, you ____________________ (fly) for fourteen hours.
ตอบ arrive และ will have flown ตามลำดับ เพราะข้อนี้เป็นการคาดการณ์เหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคต โดยเหตุการณ์
ที่จะเกิดขึ้น และจบก่อนจะใช้ Future Perfect ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่คาดว่าจะเกิดตามมาจะใช้ Present Simple ทั้งนี้ keyword ต่าง ๆ เช่น
by + ช่วงเวลา หรือ when ที่แปลว่า เมื่อ/ตอนที่ จะตามด้วย Present Simple เสมอ หากพูดถึง 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตเช่นนี้
ดังนั้นประโยคแรกที่มีคำว่า when จึงต้องผันคำกริยา arrive เป็น arrive เช่นเดิมเพื่อให้ตรงกับประธาน you ในรูป Present Simple
และผันคำกริยาของประโยคหลังเป็น will have flown ให้ตรงกับโครงสร้างของ Future Perfect นั่นเอง
Future Perfect Continuous
ลองเปลี่ยนประโยคที่ให้มา ให้อยู่ในรูป Future Perfect Continuous Tense ทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. In August, he will have worked here for 10 years.
=> In August, he will have been working here for 10 years.
ตอบ will have been working เพราะสามารถใช้ Future Perfect Continuous แทน Future Perfect ธรรมดาได้ แต่ต่างกันที่
Future Perfect Continuous จะแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์ และบอกเวลาชัดเจนมากกว่า Future Perfect ทั้งนี้
Future Perfect Continuous มีโครงสร้างคือ S + will + have + been + V.ing จึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น will have been working
นั่นเอง
1. I will have read a book for 15 minutes by the time he gets back from the bank.
=> I will have been reading a book for 15 minutes by the time he gets back from the bank.
ตอบ will have been reading เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้างของ Future Perfect Continuous คือ S + will + have + been + V.ing
หรือจะสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ มีคำบอกเวลาอย่าง for + ระยะเวลา ซึ่งในข้อนี้ก็คือ for 15 minutes จึงต้องผันคำกริยาเป็น will have been
reading นั่นเอง โดยต้องอย่าลืมว่าที่สามารถเปลี่ยนจาก Future Perfect มาเป็น Future Perfect Continuous ได้ก็เพราะทั้งสองกาล
(Tense) มีความคล้ายคลึงกัน สามารถใช้แทนกันได้ เพียงแต่ Future Perfect Continuous จะแสดงความต่อเนื่องของเหตุการณ์
และบอกเวลาชัดเจนมากกว่าเท่านั้นเอง
2. She will have paid off half of her borrowing to me by then.
=> She will have been paying off half of her borrowing to me by then.
ตอบ will have been paying เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + have + been + V.ing โดยที่ผันตรงส่วน V.ing เป็น paying เพราะว่า
คำกริยาเดิมที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V.infinitive) ของ paid หรือ paying ก็คือ pay ซึ่งคำกริยาที่ลงท้ายด้วย y อย่าง pay นี้ สามารถเติม -ing
ให้เป็น paying ได้เลย
3. By the end of this year, Jimmy will have saved up money for his child for 10 years.
=> By the end of this year, Jimmy will have been saving (save) up money for his child for 10 years.
ตอบ will have been saving เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + have + been + V.ing โดยที่ผันตรงส่วน V.ing เป็น saving เพราะว่า
คำกริยาเดิมที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V.infinitive) ของ saved หรือ saving ก็คือ save ซึ่งคำกริยาที่ลงท้ายด้วย e อย่าง save นี้ต้องตัด e ออก
แล้วจึงเติม -ing ให้เป็น saving
4. We will have collected $1,000 for our savings by next month.
=> We will have been collecting $1,000 for our savings by next month.
ตอบ will have been collecting เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + have + been + V.ing โดยที่ผันตรงส่วน V.ing เป็น collecting
เพราะว่าคำกริยาเดิมที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V.infinitive) ของ collected หรือ collecting ก็คือ collect ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาทั่วไป จึงสามารถเติม
-ing ต่อท้ายให้เป็น collecting ได้เลย
5. My mother will have spent at least $500 by the time I find her.
=> My mother will have been spending at least $500 by the time I find her
ตอบ will have been spending เพราะตรงตามโครงสร้าง S + will + have + been + V.ing โดยที่ผันตรงส่วน V.ing เป็น spending
เพราะว่าคำกริยาเดิมที่ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม (V.infinitive) ของ spent หรือ spending ก็คือ spend ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาทั่วไป จึงสามารถเติม -ing
ต่อท้ายให้เป็น spending ได้เลย
Future Tense Exercise
วงกลมตัวเลือกที่ถูกต้องที่สุดกันเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Have you heard of this? Rosy __________ a new house in Hawaii.
a. will buy b. will have bought
ตอบ a. เพราะข้อนี้ไม่มี keyword ที่บอก Tense ใด Tense หนึ่งเฉพาะ ดังนั้นสามารถใช้ Future Simple หรือ S + will + V.1 ในข้อ a. ได้เลย
1. What __________ tomorrow at 5 p.m.?
a. will you be doing b. will you have been doing
ตอบ a. เพราะข้อนี้ไม่มี keyword ที่ใช้ใน Future Perfect Continuous เช่น for + ช่วงเวลา / by the time / when แต่มี keyword ที่
เป็นคำบอกเวลาที่เจาะจงและชัดเจนอย่าง tomorrow at 5 p.m. ที่จะใช้ใน Future Continuous ปกติ ดังนั้นตอบ a. ได้เลย
2. I __________ my 18th birthday next Sunday evening.
a. will be celebrating b. will have celebrated
ตอบ a. เพราะข้อนี้มี keyword ที่เป็นคำบอกเวลาที่เจาะจงและชัดเจนอย่าง next Sunday in the evening ที่สามารถใช้ใน
Future Continuous ได้
3. Next month my parents __________ for 25 years.
a. will marry b. will have been married
ตอบ b. เพราะมี keyword อย่าง for 25 years ที่สามารถใช้ใน Future Perfect ได้ ทั้งนี้แม้ว่า married จะหน้าตาเหมือน V.3 ก็จริง
แต่ถือเป็น Adj. ที่บอกสถานะเฉย ๆ ว่าแต่งงานแล้ว ดังนั้น V.3 ที่แท้จริงของข้อนี้ก็คือ been ที่ผันมาจาก be นั่นเอง
4. We are late. The movie __________ for 15 minutes by the time we arrive at the cinema.
a. will be showing b. will have been showing
ตอบ b. เพราะมี keyword อย่าง for 15 minutes ที่สามารถใช้ใน Future Perfect Continuous ได้ นอกจากนี้ข้อนี้ยังเป็นการใช้ 2 กาล (Tense)
เพื่อเล่าถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตด้วย โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้น จบลงก่อน และบอกเวลาที่เกิดอย่างชัดเจน จะใช้
Future Perfect Continuous ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดตามมาจะใช้ Present Simple ดังนั้นในเมื่อประโยคหลัง (by the time we arrive at
the cinema.) ใช้ Present Simple ไปแล้ว แสดงว่ายังขาด Future Perfect Continuous จึงตอบ b. ได้เลย
5. I usually go on a trip to Hawaii for 4-5 days. Next time I __________ there for a week.
a. will go b. will have gone
ตอบ a. เพราะมี keyword คำว่า next time ที่บอกว่าจะทำในครั้งหน้า หรือในอนาคตทั่ว ๆ ไป จึงใช้ Future Simple ได้เลย
6. Juliet came to Hawaii nearly 2 years ago. She __________ in Hawaii for exactly 2 years this September.
a. will stay b. will have been staying
ตอบ b. เพราะมี keyword อย่าง for exactly 2 years this September ซึ่งเป็นการใช้ for + ระยะเวลา และมีการบ่งบอกเวลา
อย่างชัดเจน จึงสามารถใช้ Future Perfect Continuous ที่มีโครงสร้างเป็น S + will + have + been + V.ing ในข้อ b. ได้เลย
7. I can’t go surfing on Friday morning because I __________ the loan officer at 9 a.m.
a. will see b. will be seeing
ตอบ b. เพราะข้อนี้มี keyword ที่เป็นคำบอกเวลาที่เจาะจงและชัดเจนอย่าง on Friday morning และ at 9 a.m. ที่สามารถใช้ใน
Future Continuous ได้
8. This time next week we __________ on Waikiki beach in Hawaii.
a. will be sunbathing b. will have been sunbathing
ตอบ a. ซึ่งเป็น Future Continuous เพราะข้อนี้มี keyword ที่เป็นคำบอกเวลาที่เจาะจงและชัดเจนอย่าง this time next week อยู่
9. We are going to Honolulu Museum of Art after school. __________ us?
a. Will you join b. Will you be joining
ตอบ a. ซึ่งเป็น Future Simple เพราะเป็นการพูดถึงเรื่องในอนาคต และข้อนี้ก็ยังไม่มี keyword บอกเวลาที่เฉพาะเจาะจงด้วย ดังนั้น
จึงใช้ Future Simple ปกติได้เลย หรือสังเกตง่าย ๆ คือ ประโยคแรก (We are going to Honolulu Museum of Art after school.)
อยู่ในรูป Future Simple ดังนั้นประโยคหลังจึงมักต้องใช้กาล (Tense) เดียวกันด้วย
10. By the time I get to Sunset Beach Park, my friends __________ for half an hour.
a. will be surfing b. will have been surfing
ตอบ b. เพราะมี keyword คือ for + ระยะเวลาที่มักใช้กับ Future Perfect Continuous อีกทั้งข้อนี้ยังเป็นเป็นการใช้ 2 กาล (Tense)
เพื่อเล่าถึงเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตด้วย โดยที่เหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดขึ้น จบลงก่อน และบอกเวลาที่เกิดอย่างชัดเจน จะใช้
Future Perfect Continuous ส่วนเหตุการณ์ที่จะเกิดตามมาจะใช้ Present Simple ดังนั้นในเมื่อประโยคแรก (By the time I get to Sunset
Beach Park,) ใช้ Present Simple ไปแล้ว แสดงว่าประโยคหลังต้องใช้ Future Perfect Continuous จึงตอบ b. ได้เลย
———————————————————————–
Chapter 4 : Sentence Structure
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
เรียงคำที่ให้มาต่อไปนี้ให้เป็นประโยคที่ถูกต้องตามโครงสร้างเลย!
คำอธิบาย วิธีการเรียงประโยคอันดับแรกคือ ต้องหาประธานของประโยคให้เจอ จากนั้นจึงหาคำกริยาของประโยค และดูว่ากริยานั้น
ต้องการกรรมหรือไม่ แล้วจึงตามด้วยส่วนขยาย เช่น สถานที่ และเวลาตามลำดับ
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. sometimes / go / we / to / the cinema / . => We go to the cinema sometimes.
โครงสร้าง S + V – We = ประธานสรรพนาม (Subject Pronoun) สามารถเป็นประธานของประโยคได้ / go = คำกริยาที่ไม่ต้องการกรรม
(Intransitive Verb) / to the cinema = วลีบุพบท (Prepositional Phrase) บอกสถานที่ / sometimes = บอกเวลา
1. to Moscow / Luka and Kisa / will move / next month / . => Luka and Kisa will move to Moscow next month.
โครงสร้าง S + V – Luka and Kisa = Subject Pronoun / will move = Intransitive Verb / to Moscow = บอกสถานที่ /
next month = บอกเวลา
2. two tickets / Kiryl / me / gave / for her ballet performance / . => Kiryl gave me two tickets for her ballet performance.
โครงสร้าง S + V + IO + DO – Kiryl = ชื่อคน คำนามชี้เฉพาะ สามารถเป็นประธานของประโยคได้ (ดูให้ดีว่าไม่ได้มี Subject Pronoun ตัวอื่น) /
gave = คำกริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) เนื่องจาก V. give มักใช้ในโครงสร้าง give someone something หรือ give something to
someone ทำให้มีกรรมสองอย่างในประโยค คือ กรรมรอง (เป็นคน) และ กรรมตรง (สิ่งของ) / me = คำสรรพนามที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรมของประโยค
(Object Pronoun) และในประโยคนี้เป็นกรรมรอง (Indirect Object) / two tickets = กรรมตรง (Direct Object) / for her ballet performance =
ส่วนขยายเพิ่มเติมของ ticket
3. in the world / is / Bolshoi Ballet / ballet companies / one of the best / . => Bolshoi Ballet is one of the best ballet companies
in the world.
โครงสร้าง S + V + SC – Bolshoi Ballet = ชื่อคณะบัลเลต์ คำนามชี้เฉพาะ สามารถเป็นประธานได้ / is = คำกริยา (Linking Verb) /
one of the best ballet companies = เป็นส่วนเติมเต็มประธาน (Subject Complement) เพื่อให้รู้ว่าประธานคือใคร หรือเป็นอะไร/อย่างไร /
in the world = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่
4. sends / she / lists of movie characters / the director / to / . => She sends lists of movie characters to the director.
โครงสร้าง S + V + IO + DO – She = Subject Pronoun / sends = คำกริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) เนื่องจาก V. send
มักใช้ในโครงสร้าง send someone something หรือ send something to someone ทำให้มีกรรมสองอย่างในประโยค คือ กรรมรอง (เป็นคน)
และ กรรมตรง (สิ่งของ) / lists of movie characters = กรรมตรง (Direct Object) / to the director = กรรมรอง (Indirect Object)
5. met / last weekend / movie stars / he / at the musical theater / . => He met movie stars at the musical theater
last weekend.
โครงสร้าง S + V + O – He = Subject Pronoun / met = คำกริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) / movie stars = กรรมของประโยค
(Object) / at the musical theater = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่ / last weekend = ส่วนขยายบอกเวลา
6. he / to star / Mary / in this movie / invited / . => He invited Mary to star in this movie.
โครงสร้าง S + V + O – He = Subject Pronoun / invited = กริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) / Marry = ชื่อคน คำนามชี้เฉพาะ
เป็นกรรมของประโยคนี้ (Object) / to star = ส่วนขยาย / in this movie = ส่วนขยาย
7. three years ago / filmed / they / this movie / . => They filmed this movie three years ago.
โครงสร้าง S + V + O – They = Subject Pronoun / filmed = กริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) / this movie = กรรมของประโยค
(Object) / three years ago = ส่วนขยายบอกเวลา
8. performed / on the stage / very well / they / . => They performed very well on the stage./They performed on the stage very well.
โครงสร้าง S + V – They = Subject Pronoun / performed = คำกริยาที่ไม่ต้องการกรรม (Intransitive Verb) / very well = กริยาวิเศษณ์
(Adverb of Manner) เป็นส่วนขยายว่าทำกริยานั้นด้วยอาการอย่างไร / on the stage = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่
9. last night / series / were watching / we / at home / . => We were watching series at home last night.
โครงสร้าง S + V + O – We = Subject Pronoun / were watching = V. watch เป็นกริยาที่ต้องการกรรม (Transitive Verb) /
series = กรรมของประโยค (Object) / at home = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่ / last night = ส่วนขยายบอกเวลา
10. have lived / since / young / we / we / in St. Petersburg / were / . => We have lived in St. Petersburg since
we were young.
โครงสร้าง S + V conjunction S + V + SC (Complex Sentence) – We = Subject Pronoun / have lived = V. live เป็นกริยาที่
ไม่ต้องการกรรม (Intransitive Verb) / in St. Petersburg = ส่วนขยายบอกสถานที่ / Since = คำสันธานเชื่อมประโยค (Conjunction) /
we = Subject Pronoun / were = คำกริยา (Linking Verb) / young = คำคุณศัพท์ (Adjective) เป็นส่วนเติมเต็มประธาน
(Subject Complement)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ลองหาโครงสร้างของประโยค และระบุประเภทของประโยคว่าเป็น Simple, Compound, Complex หรือ Compound-Complex กันเลย!
S V O
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Have you ever watched Russian movies? = Simple Sentence
S V O S V O
1. I watched a Russian movie once, but I didn’t understand it.
= Compound Sentence
S V O S V
2. We watched Burnt by the Sun (1994) the other day because it was recommended on the website.
= Complex Sentence
S V O S V O
3. Aleksi has been studying Russian for 2 years, and now he hopes to study cinematography.
= Compound Sentence โดยที่ to study cinematography นับเป็นกรรมของ hopes
S V SC
4. Because the Russian Federation State Institute of Cinematography (RFSIC) is the world’s oldest
S Relative Clause V SC
film school, many well-known alumni [who graduated from this school] are really talented.
= Complex Sentence โดยมี who graduated from this school เป็น Relative Clause ด้วย แต่ยังนับว่าเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ
S ดังนั้น S จึงเท่ากับ many well-known alumni who graduated from this school
S V S V DO S V SC
5. I usually go to the cinema, but my mother often goes shopping when we are free.
= Compound-Complex Sentence
S V DO IO
6. Dimitri bought a movie ticket for me this time.
= Simple Sentence
S V O S V O
7. We should ask Ivan about the movie because he has already watched it.
= Complex Sentence
S V S V O
8. Before I moved to Russia, I had never watched Soviet or Russian movies.
= Complex Sentence
S V O
9. Do you like comedy movies or horror movies?
= Simple Sentence
S V IO DO Relative Clause (Dependent Clause)
10. Our teacher assigns us homework which is about watching a Soviet documentary.
= Complex Sentence ความรู้เสริม! เพราะนอกจากจะมีตัวเชื่อมประเภท Subordinating Conjunction
อย่าง because, since, as แล้ว Complex Sentence ยังรวมถึงประโยคที่มี Relative Clause
(Dependent Clause หรือ อนุประโยคไม่อิสระ อยู่เดี่ยว ๆ ไม่ได้) ด้วย เพราะ Complex Sentence
คือ ประโยคที่มี Independent Clause 1 ประโยค และ Dependent Clause 1 ประโยคขึ้นไปนั่นเอง
———————————————————————–
Chapter 5 : Question
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ดูคำตอบที่ให้มา และเติมคำในช่องว่างเพื่อสร้างประโยคคำถามให้สมบูรณ์กันเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Excuse me, where is the toilet?
– It’s over there, sir.
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามี Keyword “over there” (ทางโน้น) ซึ่งเป็น Adverb of Place อยู่ คำที่นำมาเติม
จึงต้องเป็น where (ที่ไหน)
1. What is the signature dish here? (จานเด็ดคือ_____)
– The signature dish is Chicken Makhani. (จานเด็ดคือแกงกะหรี่ไก่ใส่เนย)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มามีการกล่าวถึง signature dish ซ้ำจากคำถาม และขยายความเพิ่มเติมว่าคืออาหารอะไร ฉะนั้นจึงใช้
What (อะไร) ในประโยคคำถาม
2. How is the food here? (อาหารเป็น_____)
– The food is exceptional! (อาหารเป็นเลิศมาก)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มามีการบรรยายลักษณะ / คุณภาพของอาหาร ฉะนั้นจึงใช้ How (อย่างไร) ในประโยคคำถาม
3. Who is the restaurant owner? (_____เป็นเจ้าของร้านอาหาร)
– She is the restaurant owner. (หล่อนเป็นเจ้าของร้านอาหาร)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่าเป็นการระบุตัวคน ฉะนั้นจึงใช้ Who (ใคร) ในประโยคคำถาม ทั้งนี้ไม่ตอบ whom เพราะประโยคคำถาม
มีคนเพียงคนเดียว นั่นก็คือ who = the restaurant owner ซึ่งทำหน้าที่เป็นประธานของประโยคด้วย ไม่ได้มีกรรมเพิ่มมาอีกคน
4. When is the lunch served? (อาหารกลางวันจะเสิร์ฟ_____)
– It is served between 11.30 a.m. to 2 p.m. (อาหารกลางวันจะเสิร์ฟตอน 11 โมงครึ่งถึงบ่าย 2 โมง)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่าเกี่ยวกับเวลา จึงใช้ When (เมื่อไร / ตอนไหน) ในประโยคคำถาม
5. Why is this restaurant so popular? (_____ร้านอาหารนี้ถึงเป็นที่นิยมมาก)
– Because it was mentioned in the magazine. (เพราะว่ามันถูกพูดถึงในนิตยสารน่ะสิ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามี Because (เพราะว่า) ขึ้นต้นประโยคเพื่อแสดงความเป็นเหตุเป็นผลกัน ฉะนั้นจึงใช้ Why (ทำไม)
ในประโยคคำถาม
6. Where should we sit? (เราควรนั่ง_____)
– We should sit at the bar. (เราควรนั่งที่บาร์)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามีคำบุพบทที่บอกสถานที่เข้ามาเพื่อขยาย จึงใช้ Where (ที่ไหน / ตรงไหน) ในประโยคคำถาม
7. Which dish is recommended? (เมนู_____ที่เป็นที่แนะนำ)
– Aloo Gobi is recommended. (Aloo Gobi เป็นที่แนะนำ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามีชื่ออาหารที่แนะนำ ซึ่งในเมนูจะมีอาหารหลากหลายชนิด จึงใช้ Which (สิ่งไหน / อันไหน)
เพื่อให้เลือกจากทั้งหมด มาใช้ในประโยคคำถาม
8. Whose name is on the reservation? (ชื่อ_____อยู่ในการจอง)
– Raj’s name is on the reservation. (ชื่อของราจอยู่ในการจอง)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบจะเห็นว่าบอกชื่อคนเข้ามาโดยใช้รูปแสดงความเป็นเจ้าของ (‘s) ที่ต้องตามด้วยคำนาม (N.) เสมอ จึงใช้ Whose
(…ของใคร) ในประโยคคำถาม
9. Whom did he invite for dinner? (เขาเชิญ_____มาทานมื้อค่ำ)
– He invited Vivaan for dinner. (เขาเชิญวิวรรณมาทานมื้อค่ำ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากคำตอบที่ให้มาจะเห็นว่ามีชื่อ Vivaan (คนที่เขาเชิญมาทานข้าวด้วย) ถือเป็นกรรม (O.) ของประโยค จึงใช้ Whom (ใคร)
ส่วน Who (ใคร) นั้นจะใช้เมื่อถามถึงประธาน (Subject) หรือผู้กระทำกริยานั้น ๆ จึงใช้ไม่ได้ในประโยคนี้
10. Do you accept credit card? (คุณรับบัตรเครดิตไหม)
– Yes, we do. (รับค่ะ / ครับ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากประโยคคำถามจะเห็นว่ามีคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) คือ accept แล้ว แต่ยังขาดคำกริยาช่วย (Helping Verb หรือ
Auxiliary Verb) ในการสร้างประโยคคำถาม ฉะนั้นจึงต้องใช้ V. to do เข้ามาช่วย เมื่อประธานเป็น you จึงต้องใช้กับ do หรือเราอาจจะ
สังเกตจากคำตอบที่ให้มา คือ Yes, we do. ก็ได้เช่นกัน
11. Are you the restaurant manager? (คุณคือผู้จัดการร้านใช่ไหม)
– No, I’m not. I’m just a waitress. (ไม่ใช่ค่ะ ฉันเป็นแค่พนักงานเสิร์ฟ)
คำอธิบาย ดูจากประโยคคำถามจะเห็นว่ายังไม่มีคำกริยาในประโยคเลย มีเพียงคำนาม (N.) คือ the restaurant manager เท่านั้น ฉะนั้นจึงต้อง
ใช้ V. to be เข้ามาช่วย ในการสร้างประโยคคำถาม เมื่อมีคำนาม (N.) คำคุณศัพท์ (Adj.) และ V.ing ตามหลังประธาน (Subject) ประธานเป็น
you จึงต้องใช้กับ are หรือเราอาจจะสังเกตจากคำตอบที่ให้มา คือ No, I’m not. จึงรู้ว่าต้องได้ V. to be ก็ได้เช่นกัน
12. You like Indian food, don’t you? (คุณชอบอาหารอินเดีย ใช่ไหมล่ะ)
– I do actually. (จริง ๆ แล้วก็ใช่นะ)
คำอธิบาย การใช้ Question Tag ลงท้ายประโยคนั้นต้องใช้คำกริยาช่วยในการสร้าง สามารถดูจากคำกริยา (V.) ในประโยคหลักก่อนเครื่องหมาย
comma ได้ หากเป็นกริยาทั่วไป ไม่ใช่ V. to be หรือ V. to have ให้ใช้ V. to do เข้ามาช่วยแล้วผันตามกาล (Tense) ของประโยคหลักนั้นโดย
ทำรูปประโยคให้ตรงข้ามกับประโยคหลัก หากเป็นบอกเล่า ให้เปลี่ยนเป็นรูปคำถามเชิงปฏิเสธ (เติม not) และหากเป็นรูปปฏิเสธ ให้เปลี่ยนเป็น
คำถามปกติ (ตัด not) และใช้กับประธานเดิม ข้อนี้ประโยคหลักเป็น You like…จึงใช้ don’t you?
13. This curry isn’t bad, is it? (แกงกะหรี่นี้ไม่แย่เลย ใช่ไหมล่ะ)
– No, it isn’t. (ใช่ ไม่แย่เลย)
คำอธิบาย การสร้าง Question Tag มีหลักการตามที่ได้อธิบายไปในข้อที่แล้ว แต่ข้อนี้ในประโยคหลักเป็นปฏิเสธ เราจึงต้องดูที่ส่วน
Question Tag ด้านหลังไม่ให้เป็นปฏิเสธ ดังนั้นเราจึงใช้ is it (is คือคำกริยาในประโยคหลัก และ it หมายถึง this curry)
14. May I take your order now? (ขออนุญาตรับออเดอร์นะคะ / ครับ)
– Yes, you may. (ได้เลยค่ะ / ครับ)
คำอธิบาย การใช้ Modal Verb มาช่วยสร้างคำถามจะไม่เหมือนกับ V. to do แม้จะตามด้วย V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม) เหมือนกัน เพราะว่า
Modal Verb แต่ละตัวจะมีความหมายในตัวเอง เช่น must = ต้อง, should = ควร, may = อนุญาต เป็นต้น ดังนั้นจึงต้องดูความหมายที่ต้องการ
สื่อประกอบด้วย ข้อนี้จึงใช้ May (อนุญาต) ในการสร้างประโยคคำถาม หรือเราสามารถสังเกตได้จากคำตอบที่ให้มาก็ได้เช่นกัน
15. Let’s have dinner at an Indian restaurant, shall we? (เราไปทานอาหารเย็นที่ร้านอาหารอินเดียกันเถอะ ไปไหม)
– Sure, great idea! (ได้สิ ความคิดเยี่ยมเลย)
คำอธิบาย การใช้ Question Tag กับ Let’s นั้นต้องใช้ shall เสมอ
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ช่วยเปลี่ยนประโยค Direct Question เป็น Indirect Question ให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Where is the best place to eat Tandoori Chicken?
Do you know where the best place to eat Tandoori Chicken is? (Do you know…?)
คำอธิบาย หัวใจหลักของการสร้างประโยค Indirect Question คือการสลับตำแหน่งของคำกริยาและประธานในท้ายประโยค
โดยที่ประธานจะมาก่อนคำกริยาเสมอ
1. Who is the manager?
Could you tell me who the manager is?
2. What is the recommended dish?
Can you tell me what the recommended dish is?
3. What time would you like to reserve?
May I ask what time you would like to reserve?
4. When is the reservation for lunch?
Do you have any idea when the reservation for lunch is?
5. What is your reservation name, please?
May I know what your reservation name is, please?
6. Can I order a dessert?
I wonder if I could order a dessert.
7. What should I order?
Would you mind telling me what I should order?
8. Do you accept cash or credit cards?
May I ask if you accept cash or credit cards?
9. Do you enjoy the food here?
I would like to know whether you enjoy the food here.
10. How much should we tip?
I’d like to know how much we should tip.
———————————————————————–
Chapter 6 : Negative Sentence
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ตอบคำถามต่อไปนี้ให้อยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Are you Australian? (คุณเป็นคนออสเตรเลียใช่ไหม) : ถาม Are you…?
=> No, I’m not. I’m Kiwi. (ไม่ใช่ครับ ผมเป็นคนนิวซีแลนด์) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I’m not
1. Do you live in Perth? (คุณอาศัยอยู่ในเพิร์ธหรือเปล่า) : ถาม Do you…?
=> No, I don’t. I live in Brisbane. (ไม่ใช่ครับ ผมอาศัยอยู่ที่บริสเบน) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I don’t
2. Don’t you want to go to Bondi Beach with me? (คุณไม่อยากไปหาดบอนดิกับฉันเหรอ) : ถาม Don’t you…?
=> No, I don’t. I’m tired. (ไม่ล่ะ ฉันเหนื่อย) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I don’t
สังเกตว่าเมื่อประโยคคำถามอยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธ (Don’t you…) แล้วจะตอบว่า ไม่ ต้องใช้ No เช่นเดิม จะไม่ตอบ Yes หรือ ใช่
เหมือนในภาษาไทย
3. Have you ever been to Kakadu National Park? (คุณเคยไปอุทยานแห่งชาติคาคาดูไหม) : ถาม Have you…?
=> No, I haven’t. It’s quite for from where I live. (ยังไม่เคยไปเลย มันค่อนข้างไกลจากที่ฉันอยู่น่ะ) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I haven’t
4. Aren’t you afraid to go diving at the Great Barrier Reef? (คุณไม่กลัวหรอที่ไปดำน้ำที่เกรตแบร์ริเออร์รีฟ) : ถาม Aren’t you…?
=> No, I’m not. I’m well-trained. (ไม่เลย ฉันฝึกมาอย่างดีแล้ว) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I’m not
5. Did you go to Sydney with Samuel last weekend? (คุณได้ไปซิดนีย์กับซามูเอลเมื่อสัปดาห์ที่แล้วหรือเปล่า) : ถาม Did you…?
=> No, I didn’t. He went alone. (ไม่ได้ไปนะ เขาไปคนเดียว) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I didn’t
6. Why didn’t you go to the Opera House with us yesterday? (ทำไมคุณไม่ไปโอเปร่าเฮาส์กับเราเมื่อวานนี้ล่ะ) : ถาม Didn’t you…?
=> I didn’t like a crowded place. (ฉันไม่ชอบสถานที่ที่คนเยอะ ๆ น่ะ) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I didn’t
7. Are you going to visit Matt at the hospital tomorrow? (คุณจะไปเยี่ยมแมทท์ที่โรงพยาบาลพรุ่งนี้ไหม) : ถาม Are you (going to…)?
=> No, I am not going to visit him tomorrow. I already have another plan. : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I’m not (going to…)
(ไม่นะ ฉันไม่ได้จะไปเยี่ยมเขาพรุ่งนี้ ฉันมีแผนอื่นแล้วน่ะ)
8. Should I recommend Hotel ABC to my friend? (ฉันควรแนะนำโรงแรม ABC ให้เพื่อนฉันดีไหม) : ถาม Should I
=> No, you shouldn’t. It looks old and unsafe. (ไม่ควรเลย มันดูเก่าและไม่ปลอดภัย) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ You shouldn’t
9. Will you be at the Sydney Harbour Bridge tomorrow? (พรุ่งนี้คุณจะอยู่ที่สะพานซิดนีย์ฮาร์เบอร์หรือเปล่า) : ถาม Will you…?
=> No, I won’t be there tomorrow. I will be out of town. (ไม่อะ พรุ่งนี้ฉันจะไม่อยู่ที่นั่น) : ตอบปฏิเสธใช้ I won’t
10. Were they excited to go to Dreamworld? (พวกเขาตื่นเต้นไหมที่ได้ไปดรีมเวิลด์) : ถาม Were they…?
=> No, they weren’t too excited because they had been there many times. : ตอบปฏิเสธ ใช้ They weren’t
(พวกเขาไม่ได้ตื่นเต้นมาก เพราะพวกเขาเคยไปที่นั่นมาหลายรอบแล้ว)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
เปลี่ยนประโยคบอกเล่า และประโยคคำถามต่อไปนี้ให้อยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. What do you like about Australia?
=> What do you not like about Australia?
What don’t you like about Australia? (informal)
คำอธิบาย เติม not เข้าไปหน้าคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) คือ like เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ หรือเติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Auxiliary Verb)
คือ do เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธแบบไม่เป็นทางการ (informal)
1. I have been to Taronga Zoo.
=> I have not been to Taronga Zoo. / I have never been to Taronga Zoo.
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) คือ have เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ โดยใน Present Perfect Tense เรามักใช้ never (ไม่เคย)
แทน not ได้เพื่อสื่อความหมายว่า ไม่เคยเลยตั้งแต่อดีตจนถึงปัจจุบัน โดยมีโครงสร้างคือ ต้องวาง never ไว้ระหว่างคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) และ
คำกริยาหลัก เป็น have never been เช่นข้อนี้ เป็นต้น
2. They were at Darling Harbour last Friday, weren’t they?
=> They weren’t at Darling Harbour last Friday, were they?
คำอธิบาย หากข้อนั้นมี V. to be เป็นคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ไม่มีคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) เติม not หลัง V. to be ได้เลย ซึ่งในข้อนี้คือหลัง
were โดยหากเปลี่ยนประโยคหลักแล้ว ต้องเปลี่ยน Question Tag ข้างหลังให้เป็นรูปแบบประโยคที่ตรงข้ามกันด้วย หากประโยคหลักเป็นปฏิเสธ
ส่วน Question Tag ต้องไม่ใช่รูปปฏิเสธ
3. Is she working at the Art Gallery of New South Wales?
=> Isn’t she working at the Art Gallery of New South Wales?
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) คือ Is ได้เลยเพื่อสร้างประโยคำถามแบบปฏิเสธ
4. I will go to Queen Victoria Market.
=> I won’t go to Queen Victoria Market.
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Modal Verb) คือ will เพื่อทำให้อยู่ในรูปประโยคปฏิเสธ โดยสามารถทำให้อยู่ในรูปย่อจาก
will not > won’t ได้
5. Should I go to Port Jackson Bay tomorrow?
=> Shouldn’t I go to Port Jackson Bay tomorrow?
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Modal Verb) คือ should เพื่อทำให้อยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธ โดยสามารถทำให้อยู่ในรูปย่อจาก
should not > shouldn’t ได้
6. I may invite Darwin to the party.
=> I may not invite Darwin to the party.
คำอธิบาย เติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย (Modal Verb) คือ may เพื่อทำให้อยู่ในรูปปฏิเสธ โดยการใช้ may, might จะไม่มีรูปย่อ
7. She went to Royal Botanic Garden Sydney two days ago.
=> She didn’t go to Royal Botanic Garden Sydney two days ago.
คำอธิบาย ประโยคที่มีคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ที่ไม่ใช่ V. to be เราไม่สามารถเติม not เข้าไปหลัง V. เลยได้ ต้องใช้คำกริยาช่วย (Aux.)
do, does, did เข้ามาสร้างประโยคปฏิเสธ โดยข้อนี้มีคำกริยาหลักคือ went (เป็นรูปอดีต V.2 ของ go) จึงต้องใช้ did (V.2 ของ V. to do)
เข้ามาช่วย และเติม not ที่หลัง did นอกจากนี้เรายังสามารถทำให้อยู่ในรูปย่อจาก did not > didn’t ได้
8. Who did you meet yesterday at the club?
=> Who did you not meet yesterday at the club? / Who didn’t you meet yesterday at the club? (informal)
คำอธิบาย เติม not เข้าไปหน้าคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) คือ meet เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธ หรือเติม not หลังคำกริยาช่วย
(Auxiliary Verb) คือ did เพื่อทำให้เป็นประโยคปฏิเสธแบบไม่เป็นทางการ (informal)
9. She likes Vegemite the most.
=> She doesn’t like Vegemite the most.
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้มีคำกริยาหลักคือ like (ในโจทย์เติม s เพราะ she เป็นประธานเอกพจน์) จึงต้องใช้ does (ที่ใช้กับประธานเอกพจน์) เข้ามาช่วย
และลบ s หลัง likes ในประโยคเดิมออกเพราะ does ได้ผันตามประธานไปแล้ว จากนั้นเติม not ที่หลัง does โดยเราสามารถทำให้อยู่ในรูปย่อ
จาก does not > doesn’t ได้
10. Kangaroos are kind to people.
=> Kangaroos are not kind to people. / Kangaroos aren’t kind to people.
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้มี V. to be เป็นคำกริยาหลัก (Main Verb) ไม่มีคำกริยาช่วย (Aux.) จึงเติม not หลัง V. to be ได้เลย ซึ่งในข้อนี้คือหลัง are
โดยสามารถทำให้เป็นรูปย่อจาก are not > aren’t ได้
———————————————————————–
Chapter 7 : Imperative Sentence
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
Track 33
เติมลำดับประโยคที่ได้ยินให้ตรงกับรูปภาพ และเขียนประโยคนั้นลงไปในช่องว่างด้วยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง)
Numer 0
Do not throw litter. (ห้ามทิ้งขยะ)
1. Numer 3
Always listen to your guid. (เชื่อฟังไกด์เสมอ)
2. Numer 5
Keep your belongings with you at all times. (พกสิ่งของมีค่าไว้กับตัวคุณตลอดเวลา)
3. Numer 4
Avoid swimming in rivers or lakes. (หลีกเลี่ยงการว่ายน้ำในแม่น้ำหรือทะเลสาบ)
4. Numer 1
Don’t walk around at night. (อย่าเดินเพ่นพ่านในเวลากลางคืน)
5. Numer 2
Do not get out of your vehicle. (ห้ามลงจากรถ)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ประโยคใดต่อไปนี้เป็น Imperative Sentence ทำเครื่องหมายถูกหน้าข้อที่ใช่เลย!
✔️
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Be quiet, please.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
1. Can you do me a favor, please?
Interrogative Sentence (ประโยคคำถาม)
✔️
2. Don’t run outside. (ประโยคคำสั่ง)
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
✔️
3. Watch out for dangerous animals.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
4. What a nice day!
Exclamatory Sentence (ประโยคอุทาน)
✔️
5. Have a lovely day!
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคอวยพร)
✔️
6. You stay in the car.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
✔️
7. Never hunt the animals in the national park.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
✔️
8. Pick up your trash before leaving the park.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
9. You did a great job!
Declarative Sentence (ประโยคบอกเล่า)
✔️
10. Let’s go out for a walk.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคชักชวน)
11. I don’t want to eat.
Negative Sentence (ประโยคปฏิเสธ)
12. He lets me eat cookies.
Declarative Sentence (ประโยคบอกเล่า)
✔️
13. Do not let him get away.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
14. She never eats bananas.
Negative Sentence (ประโยคปฏิเสธ)
✔️
15. Stop talking and eat properly.
Imperative Sentence (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง)
———————————————————————–
Chapter 8 : Subject-Verb Agreement
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
วงกลมเลือกคำกริยาที่ผันตามประธานในประโยคที่ให้มาอย่างถูกต้องเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. My phone _____ dead. Can I borrow your charger? is | are
ตอบ is เพราะประธานของประโยค หรือ my phone เป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ ดังนั้นจึงต้องใช้คำกริยาเอกพจน์ด้วย
1. I _____ not have enough money. Can you lend me some? does | do
ตอบ do เพราะประธานของประโยค คือ I ซึ่งเป็นคำที่ต้องใช้กับ V. to do แบบไม่มี -es เสมอ
2. My boyfriend and I _____ an apartment in Rome. rents | rent
ตอบ rent เพราะเมื่อประธานหลายตัวเชื่อมกันด้วย and แล้ว จะใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์เสมอ ดังนั้น rent ไม่ต้องเติม -s
3. This aircraft _____ about to take off to Florence. is | are
ตอบ is เพราะถึงแม้ว่า aircraft เป็นได้ทั้งคำนามเอกพจน์และพหูพจน์ ซึ่งจะตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์หรือพหูพจน์ก็ได้ก็จริง
แต่ข้างหน้าคำนามมีคำว่า this ที่ใช้กับคำนามเอกพจน์เสมอ ดังนั้น aircraft ในข้อนี้จึงนับเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ และคำกริยาก็
ต้องผันให้เป็นเอกพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน
4. Not only Colomba but also her brother _____ to England every few months. goes | go
ตอบ goes เพราะเมื่อประธานหลายตัวเชื่อมกันด้วย not only… but also แล้ว จะต้องผันคำกริยาตามประธานตัวหลังเสมอ
ในข้อนี้ประธานตัวหลังคือ her brother ซึ่งเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ ดังนั้นจึงต้องใช้ goes ที่เป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์นั่นเอง
5. Some people _____ for more money, but don’t want to work. begs | beg
ตอบ beg ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาพหูพจน์ เพราะประธานของประโยค หรือ some people เป็นคำนามพหูพจน์ แม้จะไม่เติม -s
หลังคำว่า people ก็ตาม
6. My linguistic textbook _____ been lost. has | have
ตอบ has ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์ เพราะประธานของประโยค หรือ my linguistic textbook ไม่เติม -s จึงนับเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์
7. The number of tourists visiting Italy _____ dropped in recent years. has | have
ตอบ has ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์เพราะ the number of (จำนวนของ) ตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
8. A number of employees _____ for vacation leave this month. asks | ask
ตอบ ask ซึ่งเป็นคำกริยาพหูพจน์เพราะ a number of (จำนวนมาก) ตามด้วยคำกริยาพหูพจน์เสมอ
9. There _____ not enough money in my pocket. May I borrow you 20€? is | are
ตอบ is เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประโยคขึ้นต้นด้วย there ต้องดูประธานของประโยคที่อยู่ข้างหลังคำกริยาเสมอ ทั้งนี้ประธานในที่นี้
คือคำว่า money ซึ่งถือเป็นคำนามนับไม่ได้ จึงต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาเอกพจน์อย่าง is นั่นเอง
10. Here _____ your shoes that I borrowed yesterday. is | are
ตอบ are เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประโยคขึ้นต้นด้วย here ต้องดูประธานของประโยคที่อยู่ข้างหลังคำกริยาเสมอ ทั้งนี้ประธานในที่นี้
คือคำว่า shoes เติม -s ซึ่งเป็นคำนามพหูพจน์ ดังนั้นจึงต้องใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์อย่าง are ด้วย
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
เติมคำกริยาลงในช่องว่าง โดยผันให้ถูกต้องตามประธานของประโยคเลย!

Lorenzo (ตัวอย่าง) is (be) now studying in his last year of university. One of Lorenzo’s
friends 1. is (be) working for a charity project. Most of the people participating in this
project 2. come (come) from Milan, and everyone 3. works (work) in fashion
industry. They 4. intend (intend) to donate some clothes from their runway shows in the final
year to people in need all over the country. As the number of homeless individuals 5. is (be)
growing due to the pandemic, they 6. need (need) support from
the society. Also, some clothes that 7. are (be) difficult to wear in real life will be sold to
interested people. Every euro earned 8. goes (go) to the charity. Two thousand and
five hundred euros 9. is (be) the goal of this project. Anyone who 10. wants (want)
to support the project can visit www.clothescharityproject.it.
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. ตอบ is เพราะ Lorenzo คือชื่อคน ซึ่งเป็นคนเดียว ดังนั้นต้องใช้ is ที่เป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์
1. ตอบ is เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประธานมีคำว่า of ให้ผันคำกริยาตามคำนามหรือความหมายที่อยู่หน้า of โดยในข้อนี้คือคำว่า one
ที่แปลว่า หนึ่ง ดังนั้นจึงนับเป็นคำนามเอกพจน์ เลยต้องตอบ is ที่เป็นคำกริยาเอกพจน์ด้วยนั่นเอง
2. ตอบ come เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประธานมีคำว่า of ให้ผันคำกริยาตามคำนามหรือความหมายที่อยู่หน้า of ซึ่งในข้อนี้คือคำว่า most
ที่มีความหมายว่า ส่วนใหญ่ ดังนั้นต้องผันคำกริยาเป็นพหูพจน์ ไม่ต้องเติม -s
3. ตอบ works เพราะเมื่อประธานคือ everyone จะต้องใช้คำกริยาที่เป็นเอกพจน์เสมอ
4. ตอบ intend เพราะประธานคือ they จึงต้องใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์ ไม่ต้องเติม -s
5. ตอบ is เพราะ the number of (จำนวนของ) ตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
6. ตอบ need เพราะประธานคือ they จึงต้องใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์ ไม่ต้องเติม -s
7. ตอบ are เพราะ some clothes เติม -s นับเป็นคำนามพหูพจน์ จึงต้องใช้คำกริยาพหูพจน์ด้วยเช่นกัน
8. ตอบ goes เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่หน้าประธานคือคำว่า every ประธานตัวนั้นต้องอยู่ในรูปเอกพจน์เสมอ และคำกริยาก็ต้องเป็นเอกพจน์ด้วย
9. ตอบ is เพราะถึงแม้ประธาน two thousand and five hundred euros จะเติม -s แต่ประธานแบบนี้คือคำที่แสดงค่า หรือปริมาณต่าง ๆ
จึงต้องตามด้วยคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
10. ตอบ wants เพราะเมื่อใดก็ตามที่ประธานคือ anyone จะถือว่าประธานตัวนั้นเป็นเอกพจน์ และต้องใช้คู่กับคำกริยาเอกพจน์เสมอ
———————————————————————–
Chapter 9 : Subjunctive Sentence
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ลองเขียนประโยคต่อไปนี้ให้อยู่ในโครงสร้าง Subjunctive อย่างถูกต้องทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I should take a vacation. => My boss urges that I (should) take a vacation.
1. We should not be late.
=> He insists (that) we (should) not be late. เป็น Present Subjunctive เพราะเป็นประโยคบอกความต้องการ หรือเสนอแนะ
บางสิ่งบางอย่าง ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive ของ V. to be จะเป็นรูปสามัญ (Base Form / V. infinitive) ไม่ผัน
ไม่เปลี่ยนรูปไม่ว่าจะเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ หรือพหูพจน์ก็ตาม เราจึงใช้ not be ไม่ใช่ are not
2. I should go to the hospital.
=> Maria insisted that I (should) go to the hospital. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive จะเป็น
V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติมไม่ว่าจะเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ หรือพหูพจน์ก็ตาม เราจึงใช้ go แม้ว่าประธานอาจจะเป็น he, she, it ก็ตาม
3. She doesn’t want to come back home.
=> She’d rather not come back home. เป็น Past Subjunctive เพราะเป็นประโยคบอกความต้องการที่ไม่เป็นความจริง หรือตรงข้ามกับ
ความจริงในปัจจุบัน นอกจากนี้เมื่อใดก็ตามที่ใช้วลี would rather / would sooner และประธานในส่วนประโยคหลักกับ Subjunctive
เป็นคนเดียวกัน หรือมีประธานเพียงคนเดียว คำกริยาในส่วน Subjunctive ต้องเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ใช่ V.2
4. It’s a good idea to travel to Peru.
=> Xavier recommended that it be a good idea to travel to Peru. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่ตามมาในส่วน
Subjunctive ของ V. to be จะเป็นรูปสามัญ (Base Form / V. infinitive) ไม่ผัน ไม่เปลี่ยนรูปไม่ว่าจะเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ หรือพหูพจน์
ก็ตาม เราจึงใช้ be ไม่ใช่ is
5. He should start exercising.
=> It’s time he started exercising. เป็น Past Subjunctive ใช้วลี It’s time… เพื่อบอกว่าน่าจะทำบางสิ่งบางอย่างได้เสียที (แต่ทำช้าไป
นิดหน่อย) โดยคำกริยาที่อยู่ในส่วน Subjunctive จะใช้ V.2 จาก start > started
6. The patient should take medicine every 6 hours.
=> The doctor requested (that) the patient (should) take medicine every 6 hours. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่
ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive จะเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม แม้ว่าจะเป็นประธานเอกพจน์ (Patient) ก็จะใช้ take เฉย ๆ
7. People should stay home during the pandemic.
=> The government advises (that) people (should) stay home during the pandemic. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่
ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive จะเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม จึงใช้ stay เฉย ๆ
8. We have to carry a backpack when we go on an adventure.
=> It is advisable that we (should) carry a backpack when we go on an adventure. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่
ตามมาในส่วน Subjunctive จะเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม จึงใช้ carry เฉย ๆ
9. I should see the weather forecast before leaving the house.
=> I’d rather see the weather forecast before leaving the house. เป็น Past Subjunctive โดยที่เมื่อใดก็ตามที่ใช้วลี would rather /
would sooner และประธานในส่วนประโยคหลักกับ Subjunctive เป็นคนเดียวกัน คำกริยาในส่วน Subjunctive ต้องเป็น V. infinitive
ไม่ใช่ V.2
10. You should respect other different cultures.
=> It’s essential that you (should) respect other different cultures. เป็น Present Subjunctive ฉะนั้นคำกริยาที่ตามมาในส่วน
Subjunctive จะเป็น V. infinitive ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม จึงใช้ respect เฉย ๆ
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
วงกลมคำตอบที่ถูกต้องที่สุดเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. It’s late, kids. It’s best time you __________ to bed.
a. go b. went c. would rather d. had better
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive เมื่อเจอ It’s best time… ต้องใช้คู่กับ V.2 จึงตอบ went
1. The board of directors insist that all employees __________ from home.
a. should work b. would work c. would rather work d. worked
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Present Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า insist จึงใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม)
โดยเราสามารถมี should หรือละ should ก็ได้
2. It’s crucial that you __________ fit enough to go trekking.
a. are b. be c. have been d. had been
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Present Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า It’s crucial… จึงใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม)
เราจึงใช้ be เฉย ๆ ไม่ใช้ are
3. She wishes we __________ trekking together last time.
a. go b. would go c. went d. had gone
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Perfect Subjunctive เพราะแสดงความต้องการหรือความปรารถนาที่ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงในอดีต
สังเกตได้จากคำกริยา wishes และคำบอกเวลา last time จึงตอบ had gone
4. I’d rather you __________ Romero’s advice because he’s a local guide in Peru.
a. take b. took c. be taken d. had taken
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive เมื่อเจอ would rather ต้องใช้คู่กับ V.2 เพราะมีประธานสองตัว และเป็นคนละคนกัน
จึงตอบ took
5. I suggest that we __________ for her guidance.
a. ask b. asked c. should be asked d. had asked
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Present Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า suggest จึงใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม) จึงตอบ ask ได้เลย
ทั้งนี้สามารถละคำว่า should ก่อน ask ได้
6. I’d rather __________ some medicine before setting off on a journey.
a. prepare b. prepared c. be prepared d. preparing
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive เมื่อเจอ would rather และมีประธานคนเดียว ต้องใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive เสมอ จึงตอบ prepare
7. She takes care of me very well as if she __________ my mother.
a. be b. was c. were d. had been
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า as if ต้องใช้คู่กับ V.2 เพราะตรงข้ามกับความจริงในปัจจุบัน
(เธอไม่ใช่แม่ของฉัน) จึงตอบ were โดยจะใช้ were ที่เป็นรูปอดีตของ V. to be กับประธานทุกตัว แม้ว่าประธานตัวนั้น
จะเป็นเอกพจน์ อย่างคำว่า she ในข้อนี้ก็ตาม
8. The marketing assistant demanded she __________ more for her salary.
a. pay b. paid c. be paid d. was paid
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Present Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า demanded จึงใช้คู่กับ V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม)
โดยข้อนี้จะตอบ pay ไม่ได้ เพราะประโยคอยู่ในรูป Passive Voice (เธอได้รับเงินมากขึ้น [จากบริษัท]) ซึ่งโครงสร้างของ
Passive Voice คือ V. to be + V.3 จึงตอบ be paid
9. I wish I __________ enough sleep last night.
a. have b. had c. had had d. would rather have
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Perfect Subjunctive เพราะแสดงความต้องการที่ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงในอดีต สังเกตได้จากคำกริยา
wish และคำบอกเวลา last night
10. It’s raining nonstop. If only I __________ an umbrella with me.
a. bring b. brought c. have brought d. had brought
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้เป็น Past Subjunctive สังเกตได้จากคำว่า If only ต้องใช้คู่กับ V.2 เพราะตรงข้ามกับความจริงในปัจจุบัน
(ถ้าฉันเอาร่มมา แต่ความจริงคือ ตอนนี้ไม่มีร่ม) จึงตอบ brought ที่เป็น V.2 ของ bring นั่นเอง
———————————————————————–
Chapter 10 : Reported Speech
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
เปลี่ยนประโยค Direct Speech ให้เป็น Indirect Speech ให้ถูกต้องเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. “My father allows me to go to Copacabana beach with friends.”
=> André said his father allowed him to go to Copacabana beach with friends. เมื่อทำเป็นประโยค Indirect Speech
ต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้อง จึงได้เป็น his father allowed him เพราะ André เป็นผู้ชาย (เปลี่ยนจาก My father allows me)
นอกจากนี้ยังต้องเปลี่ยนคำกริยาให้เป็นอดีตยิ่งขึ้นด้วย ดังนั้นถ้าประโยค Direct Speech ใช้ allows (Present Simple) ประโยค
Indirect Speech จึงต้องเป็น allowed (Past Simple)
1. “Can I go to the party tonight?”
=> Silva asked his dad if / whether he could go to the party that night. เติม if/whether เพื่อทำให้ประโยคคำถามเป็น
ประโยคบอกเล่าแบบ Indirect Speech โดยเปลี่ยน can เป็น could และสลับประธานกับคำกริยา จาก can I > I could โดย
ต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
2. “Is it okay to sleep over at your place?”
=> He asked me if it was okay to sleep over at my place. เติม if/whether เพื่อทำให้ประโยคคำถามเป็นประโยคบอกเล่า
แบบ Indirect Speech โดยเปลี่ยน is (Present Simple) เป็น was (Past Simple) และสลับประธานกับคำกริยา จาก is it > it was
โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
3. “I want to see the panoramic view at Niterói Contemporary Art.”
=> She said she wanted to see the panoramic view at Niterói Contemporary Art. เปลี่ยนจาก want (Present Simple)
> wanted (Past Simple) โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
4. “Paula didn’t let me go surfing at Pipa beach.”
=> He told me that Paula hadn’t let him go surfing at Pipa beach. เปลี่ยนจาก didn’t let (Past Simple) > hadn’t let
(Past Perfect) โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
5. “I was eating breakfast at home yesterday morning.”
=> Santos said he had been eating breakfast at home the other day in the morning. เปลี่ยนจาก was eating
(Past Continuous) > had been eating (Past Perfect Continuous) และเปลี่ยน yesterday morning > the other day
in the morning
6. “I have come here several times.”
=> She said that she had gone there several times. เปลี่ยนจาก have come (Present Perfect) > had gone
(Past Perfect) และเปลี่ยน here > there โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย
7. “Would you mind if I leave early?”
=> She asked me whether / if I would mind her leaving early. หรือ whether / if I would mind if she left early.
- ตอบแบบแรก
She asked me whether / if I would mind her leaving early.
ต้องเติม if/whether เพื่อทำให้ประโยค
คำถามเป็นประโยคบอกเล่าแบบ Indirect Speech โดยไม่ต้องเปลี่ยน would และสลับประธานกับกริยาจาก would you >
I would เพราะต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย คือ
you > I และ I > her
- ตอบแบบที่สอง
She asked me whether / if I would mind if she left early. ได้เช่นเดียวกัน โดยมีวิธีเปลี่ยนเหมือนแบบแรก
แต่ต่างกันที่ถ้าต้องต้องการใช้ประธาน (she) ไม่ใช่กรรม (her) เหมือนการตอบแบบแรก จะต้องใส่คำกริยาแท้ให้ประธานตัวนั้นด้วย
ซึ่งเมื่อเปลี่ยนประโยคเป็น Reported Speech แบบ Indirect Speech แล้ว ต้องอย่าลืมเปลี่ยนกาล (Tense) ให้เป็นอดีตมากขึ้น
หรือในข้อนี้ก็คือเปลี่ยนจาก Present Simple Tense (leave) เป็น Past Simple Tense (left) นั่นเอง
8. “What are you doing tomorrow?”
=> Ana asked me what I was doing the next day. สลับประธานกับกริยา are you doing > you are doing
จากประโยคคำถามให้เป็นบอกเล่า เปลี่ยนจาก are doing (Present Continuous) > was doing (Past Continuous)
โดยต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนามให้ถูกต้องด้วย คือ are you doing > I was doing และเปลี่ยน tomorrow > the next day
9. “Be careful of your belongings.”
=> The police told me to be careful of my belongings. เนื่องจากข้อนี้เป็นประโยค Imperative (คำสั่ง ขอร้อง
อวยพร ชักชวน) ให้ทำบางสิ่ง เราจึงต้องใช้ to + V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม) เหมือนเดิม และต้องเปลี่ยนคำสรรพนาม
ให้ถูกต้องด้วย โดยเปลี่ยนจาก your belongings > my belongings เพราะสังเกตได้จากคำว่า me ตรง The police
told me…
10. “Please show me your passport.”
=> The immigration officer requested me to show him/her my passport. / me to show my passport to him/her.
เนื่องจากข้อนี้เป็นประโยค Imperative (คำสั่ง ขอร้อง อวยพร ชักชวน) ให้ทำบางสิ่ง เราจึงต้องใช้ to + V. infinitive (ไม่ผัน ไม่เติม)
โดยจะใช้โครงสร้าง show someone something หรือ show something to someone ก็ได้
นอกจากนี้ วลี Would you mind…? ยังมักตามด้วย V.ing ดังนั้นต้องใช้ I would mind her leaving early. ไม่ใช่
I would mind her leave early.
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
สิ่งที่ให้มาในโจทย์ต่อไปนี้สามารถเปลี่ยนเป็นประโยค Indirect Speech ได้อย่างไร ลองจับคู่ดูนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Present Simple Tense Past Simple Tense
1. could NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง)
2. may might
3. Present Continuous Tense Past Continuous Tense
4. Imperative Sentence to + V. infinitive
5. Present Perfect Tense Past Perfect Tense
6. will would
7. should NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง)
8. Past Simple Tense Past Perfect Tense
9. can could
10. must had to
1. could – NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง) เพราะเป็นรูปสุภาพ และเป็นรูปอดีตได้ด้วย จึงไม่มีรูปอดีตกว่านี้
2. may – might เพราะเมื่อทำเป็น Indirect Speech จะต้องเปลี่ยนเป็นรูปอดีตจาก may เป็น might แต่ถ้าหากในโจทย์ให้ might มา
จะตอบ NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง) เหมือนกับ could ในข้อแรก
3. Present Continuous Tense – Past Continuous เพราะจะต้องเปลี่ยนให้เป็น Tense ที่เป็นอดีต จึงใช้ Past Continuous Tense
4. Imperative Sentence – to + V. infinitive เพราะประโยค Imperative (ประโยคคำสั่ง ขอร้อง อวยพร ชักชวน)
ต้องใช้ V. infinitive (ไม่เติม ไม่ผัน) เสมอ แม้จะทำให้เป็น Indirect Speech ก็จะไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง
5. Present Perfect Tense – Past Perfect Tense เพราะจะต้องเปลี่ยนให้เป็น Tense ที่เป็นอดีต จึงใช้ Past Perfect Tense
6. will – would เพราะเมื่อทำเป็น Indirect Speech จะต้องเปลี่ยนเป็นรูปอดีตจาก will เป็น would แต่ถ้าหากในโจทย์ให้ would มา
จะตอบ NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง) เหมือนกับ could และ might
7. should – NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนรูป) เพราะเป็นการให้คำแนะนำ จะไม่มีการเปลี่ยนรูปแม้จะอยู่ใน Indirect Speech ก็ตาม
8. Past Simple Tense – Past Perfect Tense เพราะจะต้องเปลี่ยนให้เป็น Tense ที่เป็นอดีตที่เก่ากว่า จึงใช้ Past Perfect Tense
ซึ่งในการใช้ Tense คู่กันในประโยคปกติ Past Simple Tense จะเป็นเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นทีหลังเสมอ
9. can – could เพราะเมื่อทำเป็น Indirect Speech จะต้องเปลี่ยนเป็นรูปอดีตจาก can เป็น could แต่ถ้าหากในโจทย์ให้ could มา
จะตอบ NO CHANGE (ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง) เหมือนกับในข้อแรก
10. must – had to เพราะโดยปกติแล้ว must กับ have to มีความหมายคล้ายกัน แปลว่า “ต้อง” ทำบางสิ่งบางอย่าง และปกติแล้ว
เมื่อเปลี่ยนเป็นประโยคเป็น Indirect Speech จะต้องผันคำกริยาให้เป็นอดีตมากยิ่งขึ้นด้วย ฉะนั้นรูป Indirect Speech ของ must
จึงใช้ had to ที่ผันมาจาก have to อีกที
———————————————————————–
Chapter 11 : Relative Clause
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
เติม Relative Pronoun ลงในคำใบ้ที่ให้มา แล้วระบุว่าแต่ละคนในรูปคือใครกันบ้างนะ!

Clue 1: The girl who has got fair hair is not Karina.
(เด็กผู้หญิงคนที่มีผมสีสว่างไม่ใช่คาริน่า)
Clue 2: The boy who is listening to music is not Nathan.
(เด็กผู้ชายคนที่ฟังเพลงอยู่ไม่ใช่นาธาน)
Clue 3: There’s something in Maria’s hand which/that has red color.
(มีบางสิ่งอยู่ในมือมาเรียที่มีสีแดง)
Clue 4: The girl whose name is Ariana is not standing next to Maria.
(เด็กผู้หญิงที่ชื่อของเธอคืออาริอานาไม่ได้ยืนอยู่ข้างมาเรีย)
Clue 5: Karina is looking at the place where Alexandro is standing.
(คาริน่ากำลังมองไปที่ที่อเล็กซานโดรยืนอยู่)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ช่วยรวมประโยคที่ให้มา 2 ประโยคเป็นประโยคเดียวกันโดยใช้ Relative Clause ทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I just booked a hotel in Spain. The hotel is luxurious and spacious.
=> I just booked a hotel which/that is luxurious and spacious in Spain.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวถึง the hotel ซ้ำ และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
1. Andres will visit his relative. His relative’s house is in the city center.
=> Andres will visit his relative whose house is in the city center.
ใช้ whose แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง his relative’s house และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
2. Andres is going to stay at a hotel in Bilbao. His relative lives in Bilbao.
=> Andres is going to stay at a hotel in Bilbao where his relative lives/which his relative lives in.
ใช้ where หรือ which แทนการกล่าวถึง Bilbao (เมืองบิลเบา) ซ้ำ และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม โดยที่ถ้าใช้ where
ไม่ต้องมี in ต่อท้าย แต่ถ้าใช้ which ต้องมี in ต่อท้ายด้วยเพราะ which his relative lives in มีความหมาย
เหมือนกับ where his relative lives
3. Andres is staying at the hotel. His relative recommended this hotel.
=> Andres is staying at the hotel which/that his relative recommended.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the hotel และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
4. Andres’ girlfriend will be coming later tonight. His girlfriend flight is delayed.
=> Andres’ girlfriend whose flight is delayed will be coming later tonight.
ใช้ whose แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง Andres’s girlfriend’s flight และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
5. The pretty girl with dark hair is Andres’ girlfriend. The girl is carrying a pink luggage.
=> The pretty girl with dark hair who/that is carrying a pink luggage is Andres’ girlfriend.
ใช้ who หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง The girl และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
6. This hotel has a big swimming pool. Andres likes this swimming pool the most.
=> This hotel has a big swimming pool which/that Andres likes the most.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the swimming pool และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
7. The bed was so soft. They slept in this bed.
=> The bed which/that they slept in was so soft.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the bed และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
8. We can see the panoramic view from the hotel restaurant. The hotel restaurant is on the 45th floor.
=> We can see the panoramic view from the hotel restaurant which/that is on the 45th floor.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the hotel restaurant และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
9. He hasn’t found the room key yet. He lost the key.
=> He hasn’t found the room key which/that he lost yet.
ใช้ which หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the key และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
10. The man is a hotel manager. He is talking to the man.
=> The man whom/that he is talking to is a hotel manager. ใช้ whom หรือ that แทนการกล่าวซ้ำถึง the man
ที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นกรรมของประโยค He is talking to the man. และให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม ซึ่งในภาษาพูดเราอาจใช้ who
แทน whom ได้เช่นกัน
———————————————————————–
Chapter 12 : Participles
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
อ่านคำใบ้ด้านล่าง และนำคำกริยาที่เปลี่ยนเป็นรูป Participle ตามที่กำหนด มาใส่ในตารางให้ถูกต้องเลย!

แนวตั้ง
1. see (past participle) = seen (Irregular Verb ผันไม่ปกติ เปลี่ยนรูป)
2. reserve (past participle) = reserved (Regular Verb ผันเติม -ed)
3. complain (present participle) = complaining (เติม -ing)
5. book (present participle) = booking (เติม -ing)
6. call (present participle) = calling (เติม -ing)
8. leave (present participle) = leaving (เติม -ing)
9. put (past participle) = put (ไม่เปลี่ยนรูป)
แนวนอน
4. steal (past participle) = stolen (Irregular Verb ผันไม่ปกติ เปลี่ยนรูป)
7. arrive (past participle) = arrived (Regular Verb ผันเติม -ed)
10. visit (present participle) = visiting (เติม -ing)
11. wait (present participle) = waiting (เติม -ing)
12. buy (past participle) = bought (Irregular Verb ผันไม่ปกติ เปลี่ยนรูป)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
อ่านโจทย์แล้วเลือกตัวเลือกที่ถูกต้องให้หน่อยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Hotel guests next door turned on the music very loud last night. It was very __________.
a. annoyed b. annoying
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้ตอบ annoying (น่ารำคาญ) เพราะ it หมายถึงเสียงเพลงที่ดังเมื่อคืน ไม่สามารถตอบ annoyed (รู้สึกรำคาญ) ได้
เพราะประธานต้องเป็นคนเท่านั้นถึงจะแสดงความรู้สึกได้
1. The hotel service were excellent. I was __________ with their well-trained manners.
a. pleased b. pleasing
คำอธิบาย เห็นประธานเป็นคนขึ้นต้นประโยค ต้องตามด้วย “รู้สึก…” หรือ V.3 (-ed) ข้อนี้จะได้ว่า ฉันรู้สึกพอใจกับมารยาท
ที่ได้รับการฝึกมาอย่างดีของพวกเขา
2. We’ve won the prize for free room upgrade. The hotel suite is __________.
a. amazed b. amazing
คำอธิบาย ประธานของประโยคไม่ใช่คนแต่เป็น The hotel suite (ห้องสวีทของโรงแรม) จึงต้องตามด้วย V.ing จะใช้
“รู้สึก…” ไม่ได้ ข้อนี้จะได้ว่า ห้องสวีทของโรงแรมนั้นยอดเยี่ยม
3. Be careful! There is __________ window glass on the floor.
a. broken b. breaking
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้พูดถึง window glass (กระจกหน้าต่าง) จึงตอบ broken (ที่ถูกทำให้แตก) กระจกไม่ได้แตกเอง
4. The man __________ at the reception is a hotel manager.
a. stood b. standing
คำอธิบาย ประธานคือ The man (ผู้ชายคนนั้น) ใช้ standing เพราะประธานทำกริยานั้นเองคือ ผู้ชายที่ยืนอยู่ที่แผนกต้อนรับ
5. There is no __________ glass in the room at all.
a. drunk b. drinking
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้สังเกตที่ glass (แก้วน้ำ) ซึ่งคำที่มาขยายข้างหน้าคำนาม เราเรียกว่าคำคุณศัพท์ (Adj.) โดยการใช้คำกริยา
มาทำเป็น Adj. เพื่อบอกจุดประสงค์บางอย่าง เราจะใช้ V.ing เช่น drinking glass (แก้วสำหรับดื่มน้ำ) walking stick
(ไม้เท้าสำหรับค้ำเดิน) running shoes (รองเท้าสำหรับวิ่ง) เป็นต้น
6. I reserved a non-__________ room, but I can still smell lingering cigarette odor in the living room.
a. smoked b. smoking
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้สังเกตที่ room (ห้อง) ซึ่งคำที่มาขยายคำนามข้างหน้าจะต้องเป็น V.ing ฉะนั้นจึงต้องเป็น non-smoking room
(ห้องที่ปลอดบุหรี่) ถ้าใช้ non-smoked room จะแปลว่า ห้องที่ไม่ถูกรมควัน
7. The guest is complaining to the front office about her __________ items after the maid cleaned up her room.
a. lost b. losing
คำอธิบาย ข้อนี้ไม่ได้พูดถึงคนแต่พูดถึง items (สิ่งของ) ซึ่ง “ถูกทำหายไป” (lost) ไม่ได้หายไปเอง
8. My friend was __________ because she received a gift voucher from the hotel for her birthday.
a. surprised b. surprising
คำอธิบาย ประธานของประโยคคือ My friend (เพื่อนของฉัน) ซึ่งเป็นคน เราจึงใช้ surprised (รู้สึกประหลาดใจ) ไม่ใช่
surprising (น่าประหลาดใจ)
9. The room pictures __________ on the website looked much better than the actual room.
a. posted b. posting
คำอธิบาย ประธานคือ The room pictures (รูปถ่ายของห้องพัก) ซึ่ง “ถูกโพสต์” (posted) ลงเว็บไซต์ ไม่ได้โพสต์ด้วยตัวเอง
10. Our time __________ in Berlin was truly memorable.
a. spent b. spending
คำอธิบาย ประธานคือ Our time (เวลาของพวกเรา) ซึ่ง “ถูกใช้” (spent) ในเบอร์ลิน ประธานนี้ไม่สามารถทำกริยาใช้เวลาเองได้
———————————————————————–
Chapter 13 : Active-Passive Voice
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ดูประโยคที่ให้มา และวงกลมเลือกให้ถูกต้องว่าประโยคนั้นเป็น Active Voice หรือ Passive Voice!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Harajuku is a famous place for cosplayers.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะในประโยคไม่มีกรรม และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
1. Osaka is known as the nation’s kitchen for its delicious food.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Osaka และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ is + known
2. We love to stay in a ryokan.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะประธานในประโยคคือ We ทำกริยา (love) เอง และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
3. Shinkanzen is normally used to travel between prefectures.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Shinkanzen และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ is + used
4. Geisha dance has become one of the traditional arts in Japan.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะในประโยคไม่มีกรรม และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
5. Kyoto used to be Japan’s capital for 1000 years.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะในประโยคไม่มีกรรม และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
6. Hiroshima and Nagasaki were attacked by atomic bombs during WWII.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Hiroshima and Nagasaki และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ were + attacked
7. Yakushima was chosen to be World Natural Heritage site by UNESCO.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Yakushima และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ was + chosen
8. Nikko has been a center of Shinto and Buddhist worship for many centuries.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Active Voice เพราะในประโยคไม่มีกรรม และไม่มีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3
9. Cherry blossom forecast will be released around late January or early February.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Cherry blossom forecast และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ be + released
10. Japanese language is considered to be a difficult language to learn.
Active | Passive
คำอธิบาย ประโยคนี้เป็น Passive Voice เพราะมีกรรมคือ Japanese language และมีโครงสร้าง V. to be + V.3 คือ is + considered
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
โจทย์ที่ให้มาจะมีทั้งประโยค Active Voice และ Passive Voice ช่วยเขียนใหม่ให้เป็นอีก Voice หนึ่งที่ไม่เหมือนกับโจทย์ทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. She has written a new book for 2 hours. (Active)
=> A new book has been written by her for 2 hours. (Passive)
1. I eat sushi every day. (Active)
=> Sushi is eaten by me every day. (Passive)
2. A gashapon vending machine is being repaired by him. (Passive)
=> He is repearing a gashapon vending machine. (Active)
3. The teacher teaches Japanese language at school. (Active)
=> Japanese language is taught by the teacher at school. (Passive)
4. Mount Fuji has been visited by many people. (Passive)
=> Many people have visited Mount Fuji. (Active)
5. The tour guide will take us to Tokyo Imperial Palace. (Active)
=> We will be taken to Tokyo Imperial Palace by the tour guide. (Passive)
6. Snow can be seen during winter in Hokkaido. (Passive)
=> People can see snow during winter in Hokkaido. (Active)
(เมื่อไม่เจอผู้กระทำ หรือ by + ผู้กระทำในประโยค เรามักจะใส่ผู้กระทำนั้นให้เป็น People)
7. I bought this souvenir from Shibuya. (Active)
=> This souvenir was bought by me from Shibuya. (Passive)
8. People can find many kinds of fish in Tsukiji Fish Market. (Active)
=> Many kinds of fish can be found in Tsukiji Fish Market. (Passive)
(เวลาเจอ People เป็นประธานในประโยค เรามักจะละผู้กระทำ เมื่อนำไปเขียนในรูปประโยค
Passive ซึ่งแตกต่างจากข้อ 4. ที่เป็น Many people ตรงที่ข้อ 4. นั้นจะละไม่ได้เพราะ
มีความเจาะจงว่า “คนจำนวนมาก”)
9. Visitors are feeding the deer at Nara Park. (Active)
=> The deer are being fed by visitors at Nara Park. (Passive)
10. We rent kimonos in Kyoto. (Active)
=> Kimonos are rented by us in Tokyo. (Passive)
———————————————————————–
Chapter 14 : Comparison
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 1
ลองเขียนเปรียบเทียบขั้นกว่าของ 2 สิ่งที่ให้มาดูนะ!
ประโยคคำถามทุกข้อสามารถเอาไปประยุกต์ใช้ถามเวลาไปเที่ยวหรือซื้อของได้เลยนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Q: Which one is more popular? Salted egg chips or plain potato chips? (อะไรเป็นที่นิยมมากกว่ากัน
มันฝรั่งทอดรสไข่เค็มหรือมันฝรั่งทอดรสชาติปกติ)
A: Salted egg chips are more popular than plain potato chips. (popular) (มันฝรั่งทอดรสไข่เค็มเป็นที่นิยมกว่า
มันฝรั่งทอดรสชาติปกติ)
1. Q: What’s the difference between these two things? (อะไรที่แตกต่างกันระหว่างสองสิ่งนี้)
A: Kopi O (black coffee with sugar) is more bitter than (bitter) Kopi C (coffee with sugar & evaporated milk).
(โกปี๊ โอ (กาแฟดำใส่น้ำตาล) รสขมกว่า โกปี๊ ซี (กาแฟใส่น้ำตาล และนมข้นจืด)) สังเกตว่า Kopi O นั้นขมกว่าเพราะ
มีแค่น้ำตาล แต่ Kopi C มีทั้งน้ำตาลและนมข้นจืด
2. Q: What do you recommend? (คุณแนะนำอะไรเหรอ)
A: I recommend Chilli crab. It is spicier than (spicy) Bak Kut Teh. (ฉันแนะนำปูผัดพริก มันเผ็ดกว่าบักกุ๊ดเต๋)
สังเกตว่า Chilli crab เผ็ดกว่าเพราะมีคำว่า Chilli (พริก)
3. Q: What souvenirs should I buy for my friends? (ฉันควรซื้ออะไรเป็นของฝากให้เพื่อนของฉันดี)
A: Tourists like miniature Merlion souvenirs better than (good) anything else. (นักท่องเที่ยวชอบของฝาก
เป็นเมอร์ไลออนจิ๋วมากกว่าสิ่งอื่น ๆ)
4. Q: How does it taste? (รสชาติเป็นอย่างไรเหรอ)
A: It’s great! Bakkwa (BBQ meat) is more delicious than (delicious) I thought. (เยี่ยมเลย! บักกวา (หมูแผ่น)
นั้นอร่อยกว่าที่ฉันคิดไว้อีก)
5. Q: Where is the best place to shop? (ที่ไหนดีที่สุดที่จะซื้อของเหรอ)
A: It depends on your budget. Shopping at ION Orchards is definitely more expensive than (expensive)
shopping at China town. (ขึ้นอยู่กับงบเธอน่ะ ชอปปิงที่ไอออน ออชาร์ดส์แพงกว่าชอปปิงที่ไชน่าทาวน์แน่นอนอยู่แล้ว)
แบบฝึกหัดที่ 2
ดูรูปภาพ และเติมประโยคให้สมบูรณ์โดยใช้การเปรียบเทียบที่ได้เรียนมาแล้วเลย!

(ตัวอย่าง) 0. Sister Merlion is the most shopaholic person in their family. (shopaholic) *ขั้นสุด เปรียบเทียบตั้งแต่ 3 สิ่งขึ้นไป
1. Baby Merlion is younger than Sister Merlion and Granny Merlion. (young) *ขั้นกว่า
2. Granny Merlion is the oldest in the family. (old) *ขั้นสุด เปรียบเทียบตั้งแต่ 3 สิ่งขึ้นไป
3. Sister Merlion’s eyesight is better than Granny’s. (good) *ขั้นกว่า
4. Baby Merlion is not as strong as Sister Merlion. (not strong) *ขั้นเท่า
5. Granny Merlion is the kindest person in the world. (kind) *ขั้นสุด เปรียบเทียบตั้งแต่ 3 สิ่งขึ้นไป
6. Baby Merlion and Sister Merlion run faster than Granny Merlion. (fast) *ขั้นกว่า
7. Sister Merlion is the tallest of them all. (tall) *ขั้นสุด เปรียบเทียบตั้งแต่ 3 สิ่งขึ้นไป
8. Granny Merlion is taller than Baby Merlion but shorter than Sister Merlion. (tall / short) *ขั้นกว่า
9. Baby Merlion and Sister Merlion visit their Granny Merlion less/more often than last month. (often) *ขั้นกว่า
10. The warmer Granny Merlion is, the more sensitive Baby Merlion becomes. (warm / sensitive) *ขั้นกว่า
———————————————————————–
Chapter 15 : If-Clause
If-Clause Type 0
เขียนประโยคที่กำหนดมาให้อยู่ในรูป If-Clause Type 0 อย่างถูกต้อง และระบุให้หน่อยนะว่าส่วนไหนคือ
If-Clause กับ Main Clause!
If-Clause Main Clause
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. If you drink (drink) a lot of alcohol, you get (get) drunk.
If-Clause Main Clause
1. If you heat (heat) water, it boils (boil).
Main Clause If-Clause
2. I usually have (have) a cup of coffee when I get up (get up) early.
Main Clause If-Clause
3. I feel (feel) tired if I don’t get (not get) enough sleep.
If-Clause Main Clause
4. If you eat (eat) a lot of junk food, you get (get) fat.
If-Clause Main Clause
5. When you mix (mix) blue and yellow together, you get (get) green.
If-Clause Type 1
นำประโยคอิสระทั้งสองที่ให้มา เขียนเป็นประโยคเงื่อนไขให้เป็นเหตุเป็นผลกันเถอะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. James doesn’t come. / Eva is very sad. => If James doesn’t come, Eva will be very sad.
(ถ้าเจมส์ไม่มา เอวาคงจะเศร้ามาก)
1. I get a good job. / My mother is proud of me. => If I get a good job, my mother will be proud of me.
(ถ้าฉันได้งานดี ๆ แม่คงจะภูมิใจในตัวฉัน)
2. You feel sad. / I cheer you up. => If you feel sad, I will cheer you up.
(ถ้าเธอรู้สึกเศร้า ฉันจะคอยให้กำลังใจเอง)
3. I am there for you. / You need my support. => I will be there for you if you need my support.
(ฉันจะอยู่ตรงนั้นเพื่อเธอ ถ้าเธอต้องการกำลังใจ)
4. I might fail the test. / I do not study hard. => I might fail the test if I do not study hard.
(ฉันอาจจะสอบตกถ้าฉันไม่ตั้งใจเรียนให้หนัก)
5. I can help you. / You need some advice. => I can help you if you need some advice.
(ฉันสามารถช่วยเธอได้นะ ถ้าเธอต้องการคำแนะนำ)
ทุกประโยคสามารถสลับตำแหน่ง If-Clause และ Main Clause ได้ เช่น 1. My mother will be proud of me if I get a good job.
If-Clause Type 2
อ่านเนื้อเรื่อง และเติมรูปแบบประโยค If-Clause Type 2 ให้สมบูรณ์เลย!
I have a friend named Claire. (ตัวอย่าง) She wishes she could speak (can speak) Korean because she
loves Korean idols. (1) She wishes she could meet (can meet) her favorite idols every day. (2) She
would buy (buy) all of their albums if she had (have) enough money. (3) If she
were (be) rich, she would hire (hire) them to be at her birthday party. (4) It would be
(be) easier if they lived (live) in the same country. However, it is not as easy as she wishes.
(5) If I were (be) Claire, I would move (move) to live in Korea first.
ฉันมีเพื่อนคนหนึ่งชื่อแคลร์ หล่อนหวังว่าหล่อนจะพูดภาษาเกาหลีได้เพราะหล่อนรักไอดอลเกาหลี หล่อนหวังว่าหล่อน
จะได้เจอไอดอลที่หล่อนชอบทุก ๆ วัน หล่อนจะซื้ออัลบั้มของพวกเขาถ้าหล่อนมีเงินมากพอ ถ้าหล่อนรวย หล่อนจะจ้างให้พวกเขา
มางานวันเกิด มันคงจะง่ายกว่านี้ถ้าพวกเขาอาศัยอยู่ในประเทศเดียวกัน อย่างไรก็ตาม มันไม่ง่ายอย่าที่หล่อนหวัง ถ้าฉันเป็นแคลร์
ฉันจะย้ายไปเกาหลีก่อนอันดับแรกเลย
If-Clause Type 3
เปลี่ยนประโยคที่ให้มาให้อยู่ในรูป If-Clause Type 3 ที่มีความหมายสอดคล้องกันทีนะ!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. He didn’t have tattoos, so I left him. => If he had had tattoos, I wouldn’t have left him.
(เขาไม่มีรอยสัก/ไม่ได้สัก ฉันจึงทิ้งเขา) (ถ้าเขามีรอยสัก/สัก ฉันคงไม่ทิ้งเขา)
1. My boyfriend asked me out because I had curly hair. (แฟนฉันขอฉันออกเดตเพราะฉันมีผมหยักศก)
=> My boyfriend wouldn’t have asked me out if I hadn’t had curly hair.
(แฟนฉันคงไม่ขอฉันออกเดต ถ้าฉันไม่ได้มีผมหยักศก)
2. I didn’t watch Korean series because I didn’t know it before. (ฉันไม่ได้ดูซีรีส์เกาหลีเพราะฉันไม่เคยรู้จักมาก่อน)
=> I would have watched Korean series if I had known it before.
(ฉันคงจะดูซีรีส์เกาหลีไปแล้ว ถ้าฉันรู้จักมันมาก่อน)
3. I didn’t date him because we were just friends. (ฉันไม่ได้เดตกับเขาเพราะเราเป็นแค่เพื่อนกัน)
=> I would have dated him if we hadn’t been just friends.
(ฉันคงจะเดตกับเขาไปแล้ว ถ้าเราไม่ได้เป็นแค่เพื่อนกัน)
4. Kim didn’t know that it was Han’s birthday, so she didn’t give him a present. (คิมไม่รู้ว่ามันเป็นวันเกิดของฮัน
ดังนั้นเธอจึงไม่ได้ให้ของขวัญกับเขา)
=> If Kim had known that it was Han’s birthday, she would have given him a present.
(ถ้าคิมรู้ว่ามันเป็นวันเกิดของฮัน เธอคงจะให้ของขวัญกับเขาแล้ว)
5. I didn’t exercise harder, so I didn’t have six packs. (ฉันไม่ได้ออกกำลังกายหนักกว่านี้ ฉันเลยไม่มีซิกซ์แพค)
=> If I had exercised harder, I would have had six packs.
(ถ้าฉันออกกำลังกายหนักกว่านี้ ฉันคงมีซิกซ์แพคไปแล้ว)
ทุกประโยคสามารถสลับตำแหน่ง If-Clause และ Main Clause ได้ เช่น 1. If I hadn’t had curly hair, my boyfriend wouldn’t have asked me out.
If-Clause Exercise
เติมประโยคเงื่อนไขให้ถูกต้องตามรูปแบบที่เรียนมาเลย!
(ตัวอย่าง) 0. I wouldn’t have met him if I hadn’t been (be) to Korea 2 years ago.
(ฉันคงไม่ได้เจอเขา ถ้าฉันไม่ได้ไปเกาหลีเมื่อ 2 ปีที่แล้ว)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 3 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ผ่านไปแล้ว ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงตอนนั้น ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้ว
ฉันได้ไปเกาหลีแล้วก็ได้เจอเขา
1. If the water temperature is below zero, water turns (turn) into ice. (ถ้าอุณหภูมิของน้ำต่ำกว่าศูนย์ น้ำจะกลายเป็นน้ำแข็ง)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 0 พูดถึงความเป็นจริงทางวิทยาศาสตร์ หรือเหตุการณ์ที่เป็นจริงเสมอ
2. I would eat (eat) Kimchi Jjigae if I were able to eat spicy food. (ฉันคงจะกินซุปกิมจิไปแล้วถ้าฉันกินเผ็ดได้)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 2 พูดถึงสิ่งที่ตรงกันข้ามกับเหตุการณ์หรือความจริงในปัจจุบัน ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วตอนนี้ฉันก็กินเผ็ดไม่ได้
ฉันเลยไม่กินซุปกิมจิ
3. We will go to Korea next month when we finish (finish) our exam. (พวกเราจะไปเกาหลีกันเดือนหน้าตอนที่เราสอบเสร็จ)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 1 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่มีโอกาสหรือแนวโน้มที่จะเป็นไปได้ในอนาคต คือพวกเราจะไปเกาหลีกันเดือนหน้า
เมื่อเราสอบเสร็จ
4. If we had had (have) more time, we would have visited Busan as well. (ถ้าพวกเรามีเวลามากกว่านี้ พวกเราคงจะได้ไปเที่ยวปูซานด้วย)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 3 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ผ่านไปแล้ว ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงตอนนั้น ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วเรามีเวลาจำกัด เราเลย
ไม่ได้ไปเที่ยวปูซานด้วย)
5. If I won (win) a lottery for a million baht, I would go to every concert of my idol. (ถ้าฉันถูกลอตเตอรี่หนึ่งล้านบาท ฉันจะไป
ทุกคอนเสิร์ตของไอดอลที่ชอบเลย)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 2 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่แทบจะเป็นไปไม่ได้ หรือเป็นสิ่งที่ตรงกันข้ามกับเหตุการณ์หรือความจริงในปัจจุบัน
ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วตอนนี้ฉันไม่ได้ถูกหวยเป็นล้านบาท เลยไม่ได้ไปทุกคอนเสิร์ตของไอดอลที่ชอบ
6. Snow falls when it is (be) winter in Korea. (หิมะตกเมื่อเป็นหน้าหนาวที่เกาหลี)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 0 พูดถึงความเป็นจริงทางวิทยาศาสตร์ หรือเหตุการณ์ที่เป็นจริงเสมอ
7. Jay will go (go) on a date with me this Saturday unless he is sick. (เจย์จะออกเดตกับฉันวันเสาร์นี้ ถ้าหากเขาไม่ป่วย)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 1 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่มีโอกาสหรือแนวโน้มที่จะเป็นไปได้ในอนาคต คือเจย์จะไปเดตกับฉันวันเสาร์นี้แน่ ๆ
ถ้าหากเขาไม่ป่วย
8. If the weather had been good the other day, we would have gone (go) skiing. (ถ้าเมื่อวันก่อนอากาศดี เราคงได้ไปเล่นสกีกัน)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 3 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ผ่านไปแล้ว ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงตอนนั้น ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้ววันก่อนนั้นอากาศไม่ดี
เราเลยไม่ได้ไปเล่นสกี
9. If I debuted (debut) as an idol, I would move to Korea. (ถ้าหากฉันเดบิวต์เป็นไอดอล ฉันจะย้ายไปเกาหลี)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 2 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ที่แทบจะเป็นไปไม่ได้ หรือเป็นสิ่งที่ตรงกันข้ามกับเหตุการณ์หรือความจริงในปัจจุบัน
ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วฉันไม่ได้เดบิวต์เป็นไอดอล เลยไม่ได้ย้ายไปประเทศเกาหลี
10. I wouldn’t have been his fan if I had not met (not meet) him at the concert last year. (ฉันคงไม่ได้เป็นแฟนคลับเขา
ถ้าหากฉันไม่ได้เจอเขาที่คอนเสิร์ตปีที่แล้ว)
คำอธิบาย เป็น Type 3 พูดถึงเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ผ่านไปแล้ว ตรงข้ามกับความเป็นจริงตอนนั้น ซึ่งจริง ๆ แล้วฉันเป็นแฟนคลับเขา
เพราะฉันได้เจอเขาที่คอนเสิร์ตเมื่อปีที่แล้ว
✿ แต่ถ้าอยากติวคอร์ส KruDew ติว TOEIC มีให้ครบทุกอย่าง! ✿

ติว TOEIC กับครูดิว ดียังไง?
- คอร์สติว TOEIC ของครูดิวนั้น เรียน Online
- แบ่งบทเรียนชัดเจน เรียนง่ายไม่งง คลิ๊กเลือกบทเรียนที่ต้องการได้ทันที
- สามารถหยุด, เล่นซ้ำบทเรียนที่ต้องการได้แบบไม่อั้น! (ตลอดระยะเวลาคอร์ส)
- อัพเดทข้อสอบ New TOEIC ใหม่ล่าสุด! ครบชุด!
- มีไฟล์ E-Book (PDF) ประกอบการเรียนให้ดาวน์โหลด (และมีหนังสือเรียนเป็นเล่มส่งให้ถึงบ้าน)
- เรียนเวลาไหนก็ได้ อยู่ที่ไหนก็เรียนได้ แค่มี Internet
- หากมีข้อสงสัยเกี่ยวกับบทเรียน สามารถส่งคำถามหาทีมงานได้
- การันตีคะแนน 750+ (หากสอบแล้วไม่ถึง สามารถแจ้งทวนคอร์สได้ฟรี!)
ถ้ายังไม่แน่ใจ? ทดลองติวฟรีก่อนได้ที่ >>> คอร์ส KruDew TOEIC
TOEIC® and TOEFL® are registered trademarks of Educational Testing Service (ETS). This product is not endorsed or approved by ETS.
Kids vocabulary – Health Problems – hospital play – Learn English for kids
http://www.youtube.com/user/EnglishSingsing9
Kids vocabulary Health Problems hospital play Learn English for kids English educational video
This \”Kids Vocabulary\” category has been grouped thematically.
We hope you enjoy studying with our channel videos.
Have fun and subscribe to our channel. Then, you can find some more various English educational animation videos.
★ Subscribe us on YouTube: http://goo.gl/gDa963
Title: Health Problems
What’s the matter?
I have a cold.
cold
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I have a cough.
cough
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I cut myself.
cut
I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I have a fever.
fever
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I got my arm broken.
get one’s arm broken
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I have a headache.
headache
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I have a runny nose.
runny nose
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I have a sore throat.
sore throat
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I have a stomachache.
stomachache
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
What’s the matter?
I have a toothache.
toothache
Get some rest. I hope you get better soon.
Thanks for checking out the \”English Singsing\”.
© Amanta Inc.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

Kids vocabulary – [NEW] Action Verbs – Action Words – Learn English for kids
http://www.youtube.com/user/EnglishSingsing9
Kids vocabulary [NEW] Action Verbs Action Words Learn English for kids English educational video
This \”Kids Vocabulary\” category has been grouped thematically.
We hope you enjoy studying with our channel videos.
Have fun and subscribe to our channel. Then, you can find some more various English educational animation videos.
★ Subscribe us on YouTube: http://goo.gl/gDa963
Title: Action Verbs
clap
You can clap.
You can clap like a seal.
clap clap
climb
You can climb.
You can climb like a monkey.
climb climb
dance
You can dance.
You can dance like a bear.
dance dance
fly
You can fly.
You can fly like a butterfly.
fly fly
hop
You can hop.
You can hop like a rabbit.
hop hop
jump
You can jump.
You can jump like a kangaroo.
jump jump
run
You can run.
You can run like a cheetah.
run run
stand
You can stand.
You can stand like a flamingo.
stand stand
stomp
You can stomp.
You can stomp like an elephant.
stomp stomp
swim
You can swim.
You can swim like a fish.
swim swim
waddle
You can waddle.
You can waddle like a duck.
waddle waddle
walk
You can walk.
You can walk like a cat.
walk walk
Thanks for checking out the \”English Singsing\”.
© Amanta Inc.
![Kids vocabulary - [NEW] Action Verbs - Action Words - Learn English for kids](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/d8SbAkn3uvs/maxresdefault.jpg)
กริยา 3 ช่อง พร้อมตัวอย่างการใช้ | เรียนภาษาอังกฤษออนไลน์ฟรี
กริยาช่อง 3 คืออะไร และ ตัวอย่างกริยา 3 ช่องที่ใช้บ่อยมีอะไรบ้าง
กริยาช่องที่ 1 (รูปย่อคือ V.1) จะใช้กับเหตุการณ์ใน ปัจจบัน
กริยาช่องที่ 2 (รูปย่อคือ V.2) จะใช้กับเหตุการณ์ใน อดีต
กริยาช่องที่ 3 (รูปย่อคือ V.3) จะใช้กับเหตุการณ์ใน perfect tense ทุกชนิด
เรียนภาษาอังกฤษฟรี
📌 ฝึกพูดภาษาอังกฤษ ถามตอบ ประโยคพื้นฐานใช้บ่อยในชีวิตประจำวัน
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IHuK…
📌 ฝึกอ่านแปลภาษาอังกฤษ เข้าใจง่าย เรียนภาษาอังกฤษพื้นฐาน
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=URCUv…
📌 ฝึกพูดภาษาอังกฤษ ตั้งปณิธานเรื่องที่จะทำในปีใหม่ New Year’s Resolutions
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AWo2r…
📌 เรียนภาษาอังกฤษฟรี ดูโครงสร้างภาษาอังกฤษ ฝึกพูดพร้อมตัวอย่างประโยค
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UgGf1…
📌 5 โครงสร้างประโยคพื้นฐานในภาษาอังกฤษ (English sentence structures)
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iGS5s…
📌 ประโยคอวยพรปีใหม่ ภาษาอังกฤษ พร้อมคำอ่านและแปลภาษาไทย
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BYqot…
📌วิธีใช้ Used to, Be used to และ Get used to (เคย และ เคยชิน)
👉https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=in1gK…
📌 Whenever, Whatever, Whoever, However, Whichever | ใช้ยังไง
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AnAT…
📌 How far/How much/How many/How long/ ใช้อย่างไร และแปลว่าอย่างไร ภาษาอังกฤษ
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AnAT…
📌 เรียนภาษาอังกฤษ Do, Does, Did, Done | แปลว่าอย่างไร เข้าใจง่ายพร้อมตัวอย่าง
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JrNKY…
📌 คำเชื่อมประโยคภาษาอังกฤษ พื้นฐาน FANBOYS คืออะไร
👉 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6g8MlhZhBcE
Live ติว TOEIC ฟรี ท่องกริยา 3 ช่อง ยังไงให้จำได้
ท่องมาทั้งชีวิต เรียนมาตั้งแต่เด็ก แต่จำไม่เคยได้
วันนี้ครูดิวมีเทคนิค กลอนดีๆมาให้ รับรองช่วยทุกคนอัพคะแนนได้แน่นอน
krudewtoeic krudewenglish toeic grammar

Kids vocabulary – Body – parts of the body – Learn English for kids – English educational video
http://www.youtube.com/user/EnglishSingsing9
Kids vocabulary Body parts of body Learn English for kids English educational video
This \”Kids Vocabulary\” category has been grouped thematically.
We hope you enjoy studying with our channel videos.
Have fun and subscribe to our channel. Then, you can find some more various English educational animation videos.
★ Subscribe us on YouTube: http://goo.gl/gDa963
Title: Body
This is my body. This is my body.
Huh?
Let’s listen and move your body. Are you ready?
Hmm~~ OK! I’m ready!
Touch your head.
head
head
Grab your hair.
hair
hair
Touch your ears.
ears
ears
Touch your eyes.
eyes
eyes
Touch your nose.
nose
nose
Open your mouth.
mouth
mouth
Open more~~
Click your teeth.
teeth
teeth
Stick out your tongue.
tongue
tongue
Bend your neck.
neck
neck
Shake your shoulders.
shoulders
shoulders
Touch your stomach.
stomach
stomach
OK. Great!
yeah!
Wiggle your hips.
hips
hips
Shake your arms.
arms
arms
Shake your hands.
hands
hands
Shake your legs.
legs
legs
Touch your feet.
feet
feet
Perfect! It’s all over!
Yeah!
Thanks for checking out the \”English Singsing\”.
© Amanta Inc.

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆMAKE MONEY ONLINE
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ กริยา 3 ช่อง climb