แบบฝึกหัด การใช้ was were: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
TOEFL Exercise (Active-Passive Voice)
ก่อนไปเริ่มทำแบบฝึกหัด มาทบทวนความรู้กันสั้นๆ ก่อนว่า Active-Passive Voice คืออะไร?
Active Voice
- โครงสร้างประโยคปกติทั่วไปที่ Noun นั้นๆ เป็นผู้กระทำ Verb เอง เช่น John eats a slice of bread.
- โครงสร้าง Verb ของ Active Voice ก็คือโครงสร้าง V. ตามปกติ ที่ผันได้ตาม tense ทั้งหลาย
- Active Voice จะเน้นที่ “สิ่งที่คำนามหรือประธานกระทำ”
Passive Voice
- โครงสร้างประโยคแบบที่ Noun นั้น “โดนกระทำ” เช่น A slice of bread is eaten by John.
- โครงสร้าง Verb ของ Passive นั้นจะต้องมี [V. to be + V.3] เสมอ
- Passive Voice จะเน้นที่ “เกิดอะไรขึ้นกับคำนามนั้นๆ” (คือเน้นสิ่งที่เกิดขึ้นกับคำนาม โดยอาจไม่พูดถึงว่าใครหรืออะไรเป็นคนทำ)
ทบทวนกันเสร็จแล้ว ไปลองทำแบบฝึกหัด Active-Passive Voice กันเลย!
Exercise: เลือกคำที่เหมาะกับประโยค
1. Roads (blocked/were blocked) by fallen trees.
2. The River Reiner (burst/was burst) its banks after heavy rain.
3. Firefighters (received/were received) hundreds of calls for help.
4. Many people (rescued/were rescued) from the floods by fire-fighters.
5. One young girl (took/was taken) to the hospital after she broke her leg.
6. She has now (sent/been sent) home safely.
7. Wind speeds (reached/were reached) ninety miles an hour in some places.
8. Electricity lines (brought/were brought) down, leaving thousands of homes without electricity.
9. “Everything possible (is doing/is being done) to get things back to normal,” a spokesman said.
10. Millions of dollars’ worth of damage has been caused by a storm which (swept/was swept) across the north of the United States last night.
Answers
1. Roads (blocked/were blocked) by fallen trees.
block = ปิดกั้น
Roads ต้องโดนปิดกั้นด้วยต้นไม้ที่ล้มลงมา ดังนั้น ต้องโครงสร้างใช้ Passive Voice (V. to be + V.3)
2. The River White Moon (burst/was burst) its banks after heavy rain.
burst = ปะทุ, ล้นออกมา
น้ำในแม่น้ำ –ล้นออกมา— หลังฝนตกหนัก ไม่ได้ถูกใครกระทำ ดังนั้นใช้เป็น Active Voice ปกติ
*burst its banks (ใช้กับแม่น้ำ) = ล้นตลิ่ง
3. Firefighters (received/were received) hundreds of calls for help.
receive = ได้รับ
นักดับเพลิง –ได้รับ– โทรศัพท์หลายร้อยสายให้ไปช่วยเหลือ ใช้ Active Voice ปกติ
4. Many people (rescued/were rescued) from the floods by fire-fighters.
rescue = ช่วยเหลือ
สังเกตว่ามี from the floods by fire-fighters = จากน้ำท่วมโดยนักดับเพลิง แสดงว่าประธาน Many people ต้อง –ถูกช่วยเหลือ— จากน้ำท่วมโดยนักดับเพลิง ดังนั้นใช้ Passive Voice
5. One young girl (took/was taken) to the hospital after she broke her leg.
take to the hospital =พาไปโรงพยาบาล
เด็กสาวคนหนึ่ง –ถูกพาตัวไป— โรงพยาบาล หลังจากเธอขาหัก ใช้ Passive Voice เพราะประธานโดนกระทำ (โดนพาไปตัว ไม่ได้ไปเอง)
6. She has now (sent/been sent) home safely.
send home = ส่งกลับบ้าน
แสดงว่าประธานต้อง –ถูกส่งกลับบ้าน— ใช้ Passive Voice
7. Wind speeds (reached/were reached) ninety miles an hour in some places.
reach = ขึ้นไปถึง
ความเร็วลม –ขึ้นไปถึง—90 ไมล์ต่อชั่วโมงในบางพื้นที่ ข้อนี้ประธานไม่ได้โดนกระทำ ดังนั้นใช้ Active ปกติ
8. Electricity lines (brought/were brought) down, leaving thousands of homes without electricity.
bring down = ลดลง, ลากลงมา
สายไฟฟ้า –ถูกลากพังลงมา— ทำให้หลายพันครัวเรือนไฟฟ้าดับ ไม่มีไฟฟ้าใช้ ประโยคนี้เน้นว่าเกิดอะไรขึ้นกับสายไฟที่เป็นประธาน โดยที่ไม่ได้พูดถึงว่าใครเป็นคนทำ ดังนั้นใช้ Passive Voice
9. “Everything possible (is doing/is being done) to get things back to normal,” a spokesman said.
do = ทำ
ประธานคือ Everything possible ทุกสิ่งที่เป็นไปได้ กำลังถูก –ทำ/ดำเนินการ— เพื่อทำให้ทุกอย่างกลับคืนสู่สภาพปกติ
ทุกสิ่งในที่นี้ –ถูกกระทำ— ดังนั้นต้องใช้ Passive Voice
10. Millions of dollars’ worth of damage has been caused by a storm which (swept/was swept) across the north of the United States last night.
sweep = กวาด
ประธานของ V. ตัวนี้คือ a storm ที่ –กวาดทำลาย— ทั่วพื้นที่ทางเหนือของอเมริกาเอง ตัวพายุไม่ได้ถูกกวาดทำลาย ดังนั้นใช้ Active Voice
[NEW] ประโยค If-clauses ชนิดที่ 2 | แบบฝึกหัด การใช้ was were – NATAVIGUIDES
If-clause Type2
โครงสร้าง
If + Past Simple , S + would + V1
1. If + S +were + to+V1 , S+would + V1
2. Unless + Past Simple , S + would + V1
a)ผู้พูดแสดงความสงสัยว่าเหตุการณ์ที่สมมติจะไม่เกิดขึ้นเพราะฉะนั้นผลของการสมมติจะไม่เกิดขึ้นเช่นเดียวกัน
– If I had money , I would go abroad.(=I don’t have money right now.)
– What would you do if you came top in the exam?(= I have a lot of doubt.)
-John is very lazy. If he didn’t study hard , he wouldn’t pass his exam.
(=John is very lazy, he isn’t likely to study hard.)
b) เมื่อพูดถึงสิ่งที่เป็นไปไม่ได้หรือจินตนาการ (Impossible and imaginary)
– What would you do if you saw a ghost?
– If today were Sunday , I would be at home. (but today isn’t Sunday.) (= Were today Sunday
I would be at home.)
การละรูป if จะใช้กับกริยา were
– If I were you , I would go to study abroad.(=Were I you , I would go to study abroad.)
– If I were a bird , I would fly all over the world.(= Were I a bird , I would fly all over the world.)
(การละรูป if ที่ใช้กับกริยา were)
หมายเหตุ — เราใช้ were กับประธานที่เป็นทั้งเอกพจน์และพหูพจน์ เช่น if I were , if he were , if she were ,
if they were , เป็นต้น
เพราะเป็นการสมมติจากจินตนาการ แต่ถ้าใช้ was กับประธานเอกพจน์ก็ได้ เช่นกันเ ช่น If I was, ect….
นอกจาก would ที่ใช้ใน main clause แล้ว ยังมีกริยาช่วย should , might , could
ที่สามารถใช้ใน conditional Type Two นี้ได้อีก แต่ความหมายแตกต่างกันออกไป
– If she came , I should/would see her. (แสดงผลที่จะเกิดขึ้นตามสมมติ certain result)
– If she came , I might see her. (แสดงการคาดคะเน possibility)
– If it stopped snowing , he would go out. (certain result)
– If it stopped snowing , you could go out. (permission , ability)
การใช้ Conditional Sentences Type Two อื่นๆ
เราใช้ were to + V1 แทน Past Simple ใน if-clause เพื่อเน้นถึงการสมมติที่ไม่น่าจะเป็นไปได้
– If I passed the exam , he would be astonished.
– If I were to pass the exam , he would be astonished.(ในประโยคทั้งสองข้างต้นนี้ มีความหมายเหมือนกัน
แต่ประโยคที่ใช้ were to นั้น ผู้พูดมิได้หวังว่าจะสอบผ่าน)
-If he went , he would tell you first.If he were to to go , he would tell you first.(were to go
กล่าวถึงแผนการและการเสนอแนะ)
She wouldn’t cry like that if she weren’t ill.= She wouldn’t cry like that unless she were ill.
I wouldn’t eat them if I didn’t like them.= I wouldn’t like them unless I liked them.
a) เมื่อแสดงความรำคาญในกรณีที่ถูกรบกวน
– If you would stop singing , I would be able to study.
b) ใช้ในจดหมายราชการ หรือจดหมายธุรกิจ- I would be very grateful if you would pay your bill.
– We should appreciate it if you would fill in this form.
Share this:
Like this:
Like
Loading…
ฝึกแต่งประโยคภาษาอังกฤษพื้นฐาน | V.to be | is am are was were | เรียนง่ายภาษาอังกฤษ
เรียนภาษาอังกฤษ ฝึกแต่งประโยคในชีวิตประจำวัน ฟรีภาษาอังกฤษ
คลิปนี้จะมาสอนการฝึกแต่งประโยคด้วยการใช้ verb to be จะมาทำความรู้จักกับ verb to be is am are was were แต่งประโยคปัจจุบันอดีตอนาคตโครงสร้างประโยคทั่วไปประธานกริยากรรมจำที่ใช้หลัง verb to be
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่

Was, Were (Examples) ~ Grammar Class
Let’s Learn how to use \”Was\” \u0026 \”Were\” in the English Grammar.
For More Updates, Subscribe to;
For Best Nursery Rhymes:
https://www.youtube.com/user/venuskidsworld
For Hit \u0026 Latest Music:
https://www.youtube.com/user/venus
For Blockbuster Movies
https://www.youtube.com/user/VenusMovies
For Movies \u0026 Music in Regional Languages:
https://www.youtube.com/user/venusregional
For Heavenly \u0026 Peaceful Devotional Music:
https://www.youtube.com/user/venusdevotional
For More Movies \u0026 Music Videos
http://www.dailymotion.com/VenusMovies
Also You Can:
‘LIKE’ us on Facebook:
https://www.facebook.com/venusentertainment
‘FOLLOW’ us on Twitter:
https://twitter.com/venusmovies
‘CIRCLE’ us on Google+:
https://plus.google.com/+VenusMovies

Do NOT say the T in these 11 Common Words | It’s not just Californians!
In this English lesson I’ll show how Americans drop the T in many common words. It’s an important lesson on American English pronunciation—even native speakers are shocked by this! I’ll also work with you on how American English and British English differ substantially on this point. The lesson is full of examples of how to say these words like a native speaker. You will improve your English pronunciation and comprehension as you practice these words along with me.
00:00 Introduction
01:25 Identify/Identification
02:11 Twenty
03:04 Wanted
03:40 Want Another
05:52 Kitchen counter
06:16 Count
06:30 Count on
06:36 Counted
06:50 Disappointed/Disappointing
08:49 Pointed/Pointing
09:13 Printer/Printing/Printed
09:41 Rented/Renting
09:52 \”Inter\” words
10:01 Accounting/Accounted
SUBSCRIBE!: http://bit.ly/RE_sub,
Study with me in a FREE minicourse on accent reduction: http://www.RachelsEnglish.com/newsletter
New to Rachel’s English? Where to Start Playlist:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLrqHrGoMJdTRwaQFCCDp4G88yX5D3gOdP
Get Rachel’s Book: http://RachelsEnglish.com/book
Fan! http://bit.ly/RE_FB
Follow! http://www.twitter.com/Rachels_English
I’m also on Instagram 🙂 http://www.instagram.com/RachelsEnglish
Improve your American Accent / spoken English at Rachel’s English with videobased lessons and exercises. Rachel uses real life English conversation as the basis for teaching how to speak English and how to sound American improve listening comprehension skills. Study English vocabulary and English phrases such as phrasal verbs, as well as common expressions in English. Learn American idioms and American slang.
RachelsEnglish LearnEnglish

ຮ້າງກ່ອນແຕ່ງ-ເຕຊິນ ຂັນແກ້ວ /ฮ้างก่อนแต่ง -เตชิน ขัญแก้ว/Hang kon thang -Taysin khun keo
ເພງ: ຮ້າງກ່ອນແຕ່ງ
ຮ້ອງໂດຍ: ເຕຊິນ ຂັນແກ້ວ
ແຕ່ງໂດຍ: ບຸນມາ ບີເອັມ
ດົນຕຣີ: ອ.ຈ ພົບ Fuu house’s
ມິກມາສເຕີ: ອ.ຈ ບຸນມະນີ
ສັງກັດ:ບີເອັມ ຫຼວງພະບາງ
ຕິດຕໍ່ງານໂທ:02054466623;02099289990
YouTube Music : ฮ้างก่อนแต่ง
https://music.youtube.com/watch?v=wPSjpB2t3mw\u0026feature=share

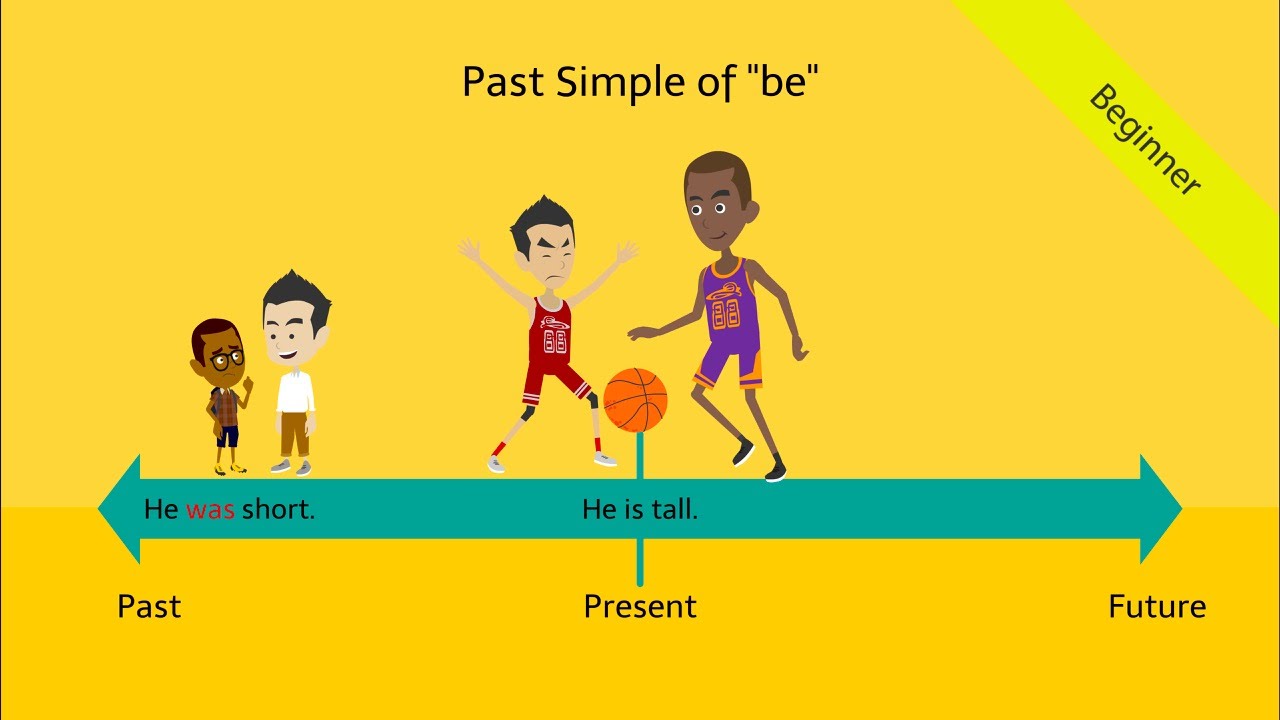
Past Simple Tense be – was / were: Fun \u0026 Interactive English Grammar ESL Video
Teach your beginner students the past simple tense be: was/were with this original \u0026 innovative video and introduce your learners to timelines.
If you love our videos, please support us at Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/oomongzu
WEBSITE: http://oomongzu.com
For more creative, engaging and interactive animated grammar teaching ESL videos, please visit our website.
For the “No Music” version of this ESL video, please click here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9TYJn8v9dr8
Title of English / ESL Video:
Past Simple Tense be: was/were
Target English Grammar:
Past simple tense be: was/were
Student Proficiency Level:
Beginner level grammar
Suggested Courses:
General English
Instructions:
– Play the video in class after delivering a warmup activity first.
– Pause the video whenever the narrator asks students a question to give students time to answer. For example, after elicitations and concept checking questions (CCQs).
Summary of English Grammar: Past Simple Tense be – was/were
Approximate chronological order:
Rules and Explanation:
Elicitation of positive example sentence: He was short.
Elicitation of negative example sentence: He wasn’t short.
Pause the video after the question to give students time to answer.
Meaning / Function (Definition):
We use the simple past to talk about the past.
Affirmative and Negative Sentences:
wasn’t = was not (contraction)
Positive and Negative Examples:
– Positive example sentence: I was a police officer.
Negative example question: I wasn’t a police officer.
– Positive example sentence: She was beautiful.
Negative example question: She wasn’t beautiful.
– Positive example sentence: It was expensive!
Negative example question: It wasn’t expensive!
– Positive example sentence: We were at home.
Negative example question: We weren’t at home.
– Positive example sentence: They were in Russia.
Negative example question: They weren’t in Thailand
Form / Structure:
Singular vs. Plural:
The simple past of “be” has two forms: was and were.
Elicit from students: Which one is singular and which one is plural? (Was is singular and were is plural.)
But sometimes English doesn’t always follow the rules. The pronoun you can be singular or plural, but we use were for both singular you and plural you.
– Positive example sentence: You were late to school.
Negative example question: You weren’t late to school.
Wh Question:
– Example question: Why were you late to school?
Yes/No Question Form:
– Example question: Were you late to school?
The short answer for a yes/no question is:
Yes, I was.
No, I wasn’t.
Further Example Wh Questions and Yes/No Questions:
When were they in Russia?
Were they in Russia?
The short answers are:
Yes, they were.
No, they weren’t.
How much was it?
Was it expensive?
(Elicit) And what are the short answers?
Yes, it was.
No, it wasn’t.
Summary:
The negatives are:
was = wasn’t
were = weren’t
was is singular.
were is plural and for you.
The short answers to yes/no questions are:
Yes, + subject + was/were.
No, + subject + wasn’t/weren’t.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่MAKE MONEY ONLINE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ แบบฝึกหัด การใช้ was were