right brain or left brain แปล: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
Left Brain vs. Right Brain
By Eagle Gamma, published May 18, 2021
The brain consists of twin halves, a left hemisphere alongside a nearly symmetrical right hemisphere.
Hemispheric lateralization is the idea that both hemispheres are functionally different and that certain mental processes and
behaviors are mainly controlled by one hemisphere rather than the other.
The left hemisphere controls the right hand side of the body and receives information from the right visual field controlling speech,
language and recognition of words, letters and numbers.
The right hemisphere controls the left hand side of the body and receives information from the left visual field controlling creativity,
context and recognition of faces, places and objects.
According to the left-brain, right-brain dominance theory the left-side of the brain is considered to be adept at tasks which are considered logical, rational, calculating.
By contrast, the right side of the brain is best at artistic, creative, and spontaneous tasks (Corballis, 2014; Joseph, 1988)
Left Brain
Right Brain
Language
Creativity
Logic
Emotional Intelligence
Critical thinking
Recognizing faces
Numbers
Using imagination
Reasoning
Being intuitive
Research
Roger W. Sperry, a twentieth-century neuroscientist, made numerous contributions to the understanding of the twin halves of the brain.
Sperry (1967) conducted investigations on split-brain patients, people whose left and right brains lack the normal connections between them. These people sometimes exhibit brain side dominance, but they also display a range of distinctive behaviors from only one side or the other.
Sperry also studied animal subjects, rewiring their nervous systems to send signals to the opposite side of the body. This showed how some mental features have hard-wiring on one side of the brain, while other mental features can adapt to function correctly on either side of the brain.
Sperry’s work revealed that the left side of the brain contains critical modules for producing sentences, but that the right side of the brain retains some language capacities such as understanding social context of speech.
The psychology of left brain versus right brain dominance indicates that humans have brains with overlapping yet distinct halves.
Brain Lateralization
Brain lateralization has become a somewhat controversial topic. While evidence supports some mental capacity occurring predominantly on one side of the brain or the other, science has overturned several earlier notions relating to this topic.
Psychologists now consider functions like language, spatial processing, and certain broader tasks to have lateralization.
Language uses several brain modules, many or which are situated on the left side of the brain (Taylor, 1990).
In fact, language represents one of the main areas of interest for brain lateralization, and the function for which this neurological division was first found. Even the language neurons, however, may also be split among both halves of the brain (Riès et al., 2016), or located on the right side, which is more common in left-handed people (Beaumont, 2008).
The left side of the brain often contains language-processing regions such as Broca’s Area, which produces understandable sentences, as well as Wernicke’s area, which understands speech (Griggs, 2010).
Injuries to these areas result in speech pathologies, such as an inability to speak or listen normally (Broca, 1865; Pinel & Barnes, 2017).
Other language functions, like associating emotions with phrases, occur on the right side of the brain (Kandel et al, 2012).
As such, language can be seen as bridging together both halves of the brain, but with some specific functionality located on one side or the other (Riès et al., 2016).
Scientists have studied language, memory, and other topics through various methods, such as the “Wada test.”
This involves disabling one side of the brain chemically, then observing how the other side operates.
Logical thinking, like language, often resides primarily on the left side of the brain (Dehaene, 1999).
Again, this applies more often to right-handed people, with the reverse holding true for many left-handed people.
The right brain, by contrast, has more active involvement than the left in visual or spatial processing.
As such, this works while drawing, navigating around a room, or in other comparable situations. People who have right brain injuries may become clumsy or artistically inept (McGilchrist, 2019).
The right brain also becomes active while recognizing faces.
As with other functionalities, there is some degree of symmetry. The left brain can also do facial recognition, but it is more perfunctory than the right brain’s work. The right brain deals with other social perception, too, like body posture (Lane & Nadel, 2002).
Another feature of the right brain is to focus one’s attention. When a person thinks on one topic, this lights up regions on the right side of the brain.
Numerous other mental activities operate differently on each side of the brain.
For example, the left brain is more associated with positive emotions, while the right brain is more associated with negative emotions (Lane & Nadel, 2002). People with depression often suffer from a disproportionate ratio of right-to-left brain activity (Atchley et al., 2003; Hecht, 2010).
Comparing the left versus right sides of the brain, the left brain processes new information into an understanding of events (making it the “interpreter”), while the right brain accounts for social behaviors.
For example, the left brain may assess which actions would lead to eating food, while the right brain may nix some of these actions on the basis of social norms (one doesn’t just run through a crowd at a party to grab food).
The left brain can be seen as an analyst, breaking apart concepts into smaller, manageable chunks. By contrast, the right brain can be seen as a synthesist, developing a more cohesive view (McGilchrist, 2019).
Interestingly, the lateralization of the brain has deeper roots, in the peripheral nervous systems (Craig 2005). Nerves throughout the body feed into and out of the brain.
The left brain largely receives connections from the parasympathetic system, while the right brain largely receives connections from the sympathetic system (Conesa 1995).
Together, the two halves of the brain work with the rest of the nervous system to maintain a homeostatic balance.
The two sides of the brain are connected together by several components called “commissural nerve tracts”, largely the corpus callosum.
This segment bridges the left and right brains, sharing information. In rare cases, people are born without the corpus callosum, or have it surgically removed to reduce epileptic seizures.
These cases have revealed interesting information about the two halves of the brain.
In people without a corpus callosum, the brain can reorganize to perform functions normally occurring on one side instead on the other.
This may even result in the person developing the use of brain regions on both sides for the same task, allowing for example a person to read two texts simultaneously, one on each side of the brain.
The brain can also reorganize itself under other conditions (Gómez-Robles et al., 2013). Often this involves using either a nearby region, or a mirror opposite region, to replace lost function. This shows how the brain structure has largely symmetrical functionality on the left versus right halves.
There are, however, some slight differences.
The body is connected to the brain so that senses as well as control usually take place on the opposite side. The left brain senses and controls the right hand, the right foot, the right half of the visual field, the right ear, and so forth.
Scientists discovered this by electrically probing the brain, observing the body’s responses, which produced a map of the body’s associations in the brain.
The motor cortex produces motions for the opposite side.
In right-handed people, the left motor cortex is usually larger than the right motor cortex. Left-handed people, by contrast, often have right-brain dominance.
In addition, some people are ambidextrous (able to use both sides effectively), or have mixed dominance (using the left side for some activities, but the right side for others).
The brain evolved to have some asymmetry (Vallortigara & Rogers, 2005), which occurs at multiple levels from the basic cell arrangements differing on each side, to the right hemisphere sitting slightly forward of the left hemisphere (called Yakovlevian torque).
Numerous specific brain regions like the parietal operculum or the central sulcus have left-right asymmetry. People who have less brain asymmetry may suffer from less effective thought processes, even schizophrenia or mood disorders (Sun et al., 2015; Ribolsi et al., 2014).
Numerous other disorders also have bases in left-right brain problems (Royer et al., 2015).
In one contentious theory, called bicameralism, the left-right human brain evolved only over the last three thousand years or so from having two different identities within it.
One of these minds would speak, issuing commands, while the other mind would listen, obeying. In fact, split-brain patients often act as though they have two minds, which some neuroscientists argue may actually be the case (called “dual consciousness”).
For example, one side of the body may work to prevent the other side of the body from acting. This would put a more literal spin on the phrase “being of two minds.”
Critical Evaluation
How lateralized are brain functions? Not nearly as much as people often think. While one’s brain lateralization can affect personality, this only has a small part in the overall development of an individual.
People generally use both sides of the brain about equally. There are, however, numerous specific brain regions on either the left or right side, which can have powerful effects.
For example, a person who had part of the right prefrontal lobe removed became incapable of valuing long-term rewards over short-term considerations, while people with regions of the left brain removed exhibit different symptoms (Lane & Nadel, 2002).
The two sides of the brain have somewhat different contributions in many ways: how one thinks, how one perceives other people and the environment, how one feels (both consciously and unconsciously), how mentally healthy one is, as well as countless other facets of personality and behavior.
Left-handed people have right brain dominance for body control, which may also result in the more artistic personality for which such people are known. However, as can be seen by the fact that there are numerous right-handed artists as well as left-handed rational thinkers, brain lateralization only goes so far.
The notion of left brain versus right brain dominance has some basis in fact, but represents a false dichotomy. The complexity of the brain involves features on both sides working together, often communicating with each other through the center (Beaumont, 2008).
Many mental functions require both sides of the brain to work in unison, undermining the claim that either side outdoes the other. As a whole, the brain remains poorly understood, with scientists continuing to investigate (Halpern, 2005).
What we do know about left brain versus right brain dominance is that it seems to have certain patterns, such as language or logic often occurring in the left brain, or emotion and social cognition often occurring in the right brain.
However, these sides can be reversed in individuals, or more balanced between both sides. Also, all of these functionalities have at least some equivalent on their opposite side of the brain.
The brain has plasticity, and in cases such as injury will recruit other regions which can easily be located on the opposite side (Pulsifer, 2004).
However, each brain is unique. Some have different lateralization than others, and the location of functions can even develop during the course of one’s life.
About the Author
Eagle Gamma writes about psychology as well as other topics in science and culture. He also produces 3D animations, games, and wearable products.
How to reference this article:
How to reference this article:
Gamma, E. (2021, March 24).
Left brain vs. right brain . Simply Psychology. www.simplypsychology.org/left-brain-vs-right-brain.html
APA Style References
Atchley, R. A., Ilardi, S. S., & Enloe, A. (2003). Hemispheric asymmetry in the processing of emotional content in word meanings: The effect of current and past depression. Brain and Language, 84(1), 105–119.
Beaumont, G. J. (2008). Introduction to Neuropsychology (2nd ed.). The Guilford Press.
Broca, P. (1865). Sur le siège de la faculté du langage articulé. Bulletins de La Société d’anthropologie de Paris, 6(1), 377–393.
Conesa, J. (1995). Electrodermal Palmar Asymmetry and Nostril Dominance. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 80(1), 211–216.
Corballis, M. C. (2014). Left brain, right brain: facts and fantasies. PLoS Biol, 12(1), e1001767.
Craig, A. D. B. (2005). Forebrain emotional asymmetry: a neuroanatomical basis? Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(12), 566–571.
Dehaene, S. (1999). Sources of Mathematical Thinking: Behavioral and Brain-Imaging Evidence. Science, 284(5416), 970–974.
Drew, W. (2020). Psychology. John Wiley & Sons.
Gómez-Robles, A., Hopkins, W. D., & Sherwood, C. C. (2013). Increased morphological asymmetry, evolvability and plasticity in human brain evolution. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 280(1761), 20130575.
Griggs, R. A. (2010). Psychology: A Concise Introduction (Third ed.). Worth Publishers.
Griggs, R. A. (2010). Psychology: A Concise Introduction (Third ed.). Worth Publishers.
Halpern, M. E. (2005). Lateralization of the Vertebrate Brain: Taking the Side of Model Systems. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(45), 10351–10357.
Harenski, C. L., & Hamann, S. (2006). Neural correlates of regulating negative emotions related to moral violations. NeuroImage, 30(1), 313–324.
Hecht, D. (2010). Depression and the hyperactive right-hemisphere. Neuroscience Research, 68(2), 77–87.
Hines, T. (1987). Left Brain/Right Brain Mythology and Implications for Management and Training. The Academy of Management Review, 12(4), 600.
Joseph, R. (1988). The right cerebral hemisphere: Emotion, music, visual‐spatial skills, body‐image, dreams, and awareness. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 44(5), 630-673.
Kandel, E. R., Schwartz, J. H., Jessell, T. M., Siegelbaum, S. A., & Hudspeth, A. J. (2012). Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Edition (Principles of Neural Science (Kandel)) (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education / Medical.
Lane, R. D., & Nadel, L. (2002). Cognitive Neuroscience of Emotion (Series in Affective Science). Oxford University Press.
McGilchrist, I. (2019). The Master and His Emissary: The Divided Brain and the Making of the Western World (Second Edition, New Expanded ed.). Yale University Press.
Pinel, J. P. J., & Barnes, S. (2017). Biopsychology (10th Edition) (10th ed.). Pearson.
Pulsifer, M. B., Brandt, J., Salorio, C. F., Vining, E. P. G., Carson, B. S., & Freeman, J. M. (2004). The Cognitive Outcome of Hemispherectomy in 71 Children. Epilepsia, 45(3), 243–254.
Ribolsi, M., Daskalakis, Z. J., Siracusano, A., & Koch, G. (2014). Abnormal Asymmetry of Brain Connectivity in Schizophrenia. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 1010.
Riès, S. K., Dronkers, N. F., & Knight, R. T. (2016). Choosing words: left hemisphere, right hemisphere, or both? Perspective on the lateralization of word retrieval. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1369(1), 111–131.
Royer, C., Delcroix, N., Leroux, E., Alary, M., Razafimandimby, A., Brazo, P., Delamillieure, P., & Dollfus, S. (2015). Functional and structural brain asymmetries in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorders. Schizophrenia Research, 161(2–3), 210–214.
Sun, Y., Chen, Y., Collinson, S. L., Bezerianos, A., & Sim, K. (2015). Reduced Hemispheric Asymmetry of Brain Anatomical Networks Is Linked to Schizophrenia: A Connectome Study. Cerebral Cortex, bhv255.
Taylor, I. (1990). Psycholinguistics: Learning and Using Language (1st ed.). Pearson.
Toga, A. W., & Thompson, P. M. (2003). Mapping brain asymmetry. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 4(1), 37–48.
Vallortigara, G., & Rogers, L. (2005). Survival with an asymmetrical brain: advantages and disadvantages of cerebral lateralization. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 28(4), 575–589.
[Update] Left Brain vs Right Brain : What’s The Difference? | right brain or left brain แปล – NATAVIGUIDES
Left Brain vs Right Brain : What’s The Difference?
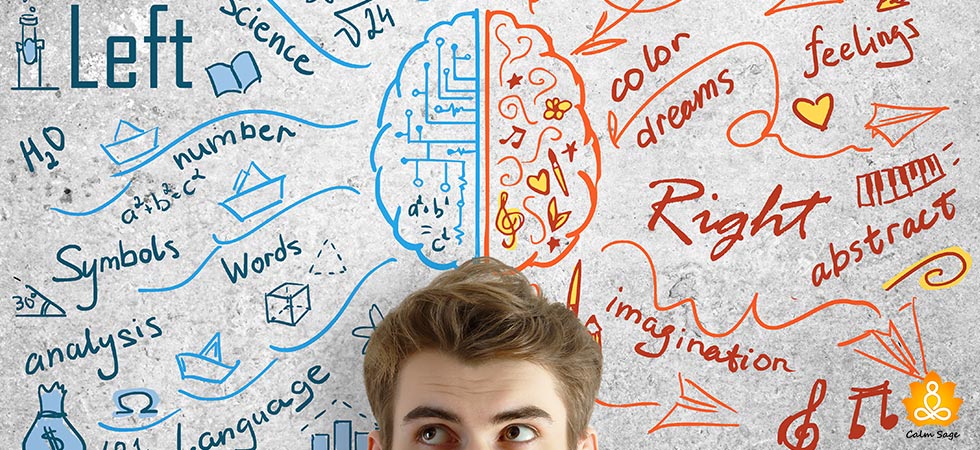

Do you often wonder why a friend is yours perform brilliantly in logical reasoning while you face difficulty doing the same!
Or While you can see the next Picasso or William Shakespeare within you and this friend of yours can barely write his own Insta bio!
Well, the answer behind this is simple…
You are a right-brain thinker and in the case of your friend the left brain dominates his thinking. Now if you are pondering what left brain vs right brain theory is all about then continue reading…
*Don’t forget to test which brain thinker you are with the two fun tests*
The Left Brain/Right Brain Theory:
We all know that our brain is divided into parts left hemisphere and right hemisphere (theory of lateralization). Ideally, each side of the brain controls different types of thinking patterns. However, we as homo sapiens allow one part to dominate over the other by choosing a particular thinking pattern.
But wait! Does that mean only one side of your brain is handling all the bodily functions?
The answer to it is a NO!
As mentioned above one side of the brain will dominate the other thus, classifying you as a left-brain thinker or the right one. However, this does not imply that only that side of the brain is functional for you. In fact, as a science writer, Carl wrote–
“No matter how lateralized the brain can get, though, the two sides still work together”
To put it in simple words, one side of the brain may dominate the other, however, they still work as a whole brain!
Quick Fact: Math skills are found to be the strongest in the ones who have both sides working equally!
So are there any specific characteristics associated with these sides of the brain?
Yes, perhaps the dual nature of your brain comes into play! Let us explore what left brain vs right brain has to offer to you
Difference Between Left Brain and Right Brain:
According to Left-Right brain Belief, Everyone has one side of the dominant brain that determines the person’s personality. Check how differently Left and right brain works?
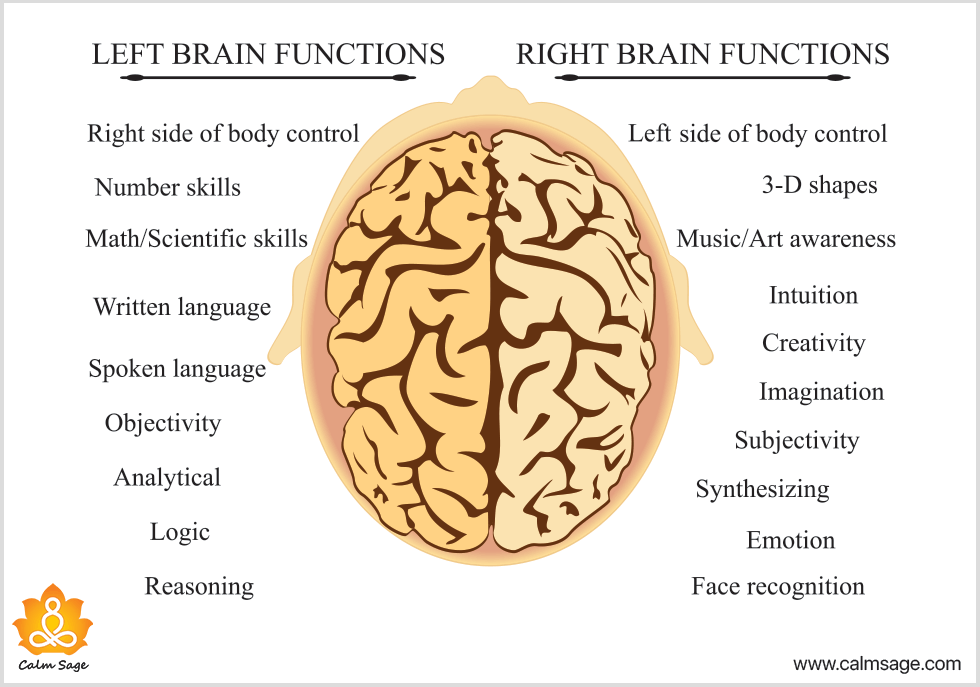
1. Qualities of Left Brain Thinkers
This brain is also referred to as the analytical side. Left side brainers are generally goal-oriented, organized, critical thinkers and demonstrate the following qualities:
- Brilliant language and comprehension
- Uses logic
- Computation Skills
- Analyses information
- Detail and fact-oriented
2. Characteristics of Right Brain Thinkers
The right-brainers are also referred to as creative thinkers. The hallmark of their thinking pattern is emotions. Along with this, there are good people and philosophy. Some of the key characteristics associated with them are:
- They excel in expressive and creative tasks
- Have free-thinking
- Try to look at the bigger picture of life
- Trust their institutions
- Imaginative thinking
Are you a Left-Brainer or a Right-Brainer: Left vs Right Brain Test
-
Below you will find a series of 7 images with three options each.
-
You have to choose the option that you see at the FIRST glance of the image.
-
Once you have all the seven answers with you swipe to find out which brain dominates you. Also, find some interesting facts about the same.
For you to find out whether you are a right-brainer or a left-brainer we have two activities for you. So, let us explore them…
1. What You See FIRST
In this fun activity you have to follow these basic steps to find out whether you are right-brained or left-brained:
Let the fun begin…
Q1. What do You See First a Duck, a Bunny, or Something else?

Q2. What Do You See First White Column, Two People or Something Else?

Q3. What Do You See First Old Woman, Young WoMan, or Something Else?

Q4. What Do You See First 3 Columns, 4 Columns, or Something Else?

Q5. What Do You See First a Face, Women Collection, or Something Else?

Q6. What Do You See First a Skull, Two Children or Something Else?

Q7. What Do You See First Apple, Two Faces, or Something Else?

Hope you are ready with your options! Time to see your results:
More A options= You are Right- Brained
Look at those creative juices flowing! Following your heart over your head not only makes you spontaneous but fills in energy within you. No doubt people love your spirit. Believing in performing rather than telling about a task, choosing physical rather than practical solutions sets you apart. P.S. Don’t stop practicing what you love doing, we see the next big artist in you.

More B options= You are LEFT-Brained
Hello Smarty-pants or shall we call you the Logical thinker! You have an eye for details. Everyone around you truly trusts you for your organization and planning. So, how about planning a surprise b’day party for someone you love 😉 Trusting the facts over your guts gives you that practical approach in life. With memory as sharp as yours even dolphins can take lessons from you (JK)!

More C options or equal A & B options = You Got Best of Both the Worlds
Kudos! You are a blessed soul, you have good from both worlds. You tend to switch between logical and creative thinking depending on what situation has to offer to you. Thus, you are out of trouble and have unique answers to the problems. Making you the Wiseman everyone turns to for solutions. Keep it up!

2. The Color or the Color
Sounds a little tricky right? It is my favorite test though!
All you have to do is look at the image given below and read the color that you see instead of the word written. Good Luck!!!

Well, if you tried to say the color more than the words then you are a right-brainer person and vice-versa. A major difference between the left brain and right brain is that the former focuses on the language more and the latter trusts the visuals represented.
Wasn’t this fun? Finally putting your left brain vs right brain confusion to an end! Don’t forget to try it with your friends and find out which side of the brain dominates their thinking pattern.
Here are Some FAQs On Left Brain vs Right Brain Theory:
1. Can a person be both left and right brained?
YES! You can be both left and right brained person. Even the test “What do you see first” gives the interpretation of you are both- left and right brained person. Depending on a situation demand either part of your brain dominates.
2. Do right and left brain see different colors?
Well, it’s a maybe situation here. There are various color perception images out there claiming that the color you see predicts which part of brain is dominates your thinking pattern. However, no one can really vouch for these ideas.
3. What jobs are good for right brain thinkers?
Some of the job profile that best fits the right brainers are:
• Managers
• Artists. …
• Graphic Designers. …
• Interior Designers.
• Psychologists and counsellors. …
• Teacher.
• visual careers like illustration, television, or marketing
4. What jobs are good for left brain thinkers?
Some of the job profile that best fits the left brainers are:
Lawyer.
Health and Safety Engineer.
• Medical Scientist. …
• Operations Research Analyst. …
• Cost Estimator
• Machine Learning Scientist
• Computer Programmer
5. Which brain dominant is best?
While the right-brain dominance ensures that you are best at expressive and creative tasks. On the other hand, the left-brain dominance is reflected in your verbal and analytical aspects of life. This makes one point clear that both brain dominance have its own perks to offer. So, irrespective of the fact which brain dominates you it is at its best. No good, better, best comparison cannot be made here.
Alarming Fact!!!
The theory of left-brain vs right-brain holds true only up to an extent! Recent research has found that this theory may be a myth!
A study in which brain scans of 1000 people were analyzed to see which part of the brain is more powerful than the other found that no sidedness in brain functioning existed. However, some brain areas were more active in particular tasks than others.
To put it in a nutshell, the concept of left-brain vs right brain is better used in the form of a figure of speech than an anatomical description.
So be a smart user of the information that is available online and use these tests and claims for fun and historical purposes only instead of letting them paint the whole picture of your personality.
Remember you are more than just the two sides of your brain!
You May Like These Also:
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting for Brain and Body
Brain Exercises To Sharpen Your Memory & Improve Focus
Top 7 Colors to Bring Positivity in Your Home
Brain Aging: Symptoms And Solutions For Brain Aging
Dopamine Fasting: Treat to Your Brain or Maladaptive Fad
Pink Sweat$ – At My Worst (Lyrics)
Subscribe and press (🔔) to join the Notification Squad and stay updated with new uploads
Pink Sweat$ At My Worst Stream/Download ‘The Prelude: https://PinkSweats.lnk.to/ThePrelude
Follow Pink Sweat$:
https://pinksweatsmusic.com
https://instagram.com/pinksweats
https://twitter.com/realpinksweats
https://facebook.com/pinksweats
https://soundcloud.com/pinksweats
Follow TheNewVibe:
https://instagram.com/_thenewvibe_
business inquiries:
[email protected]
©️If any producer or label has an issue with this song or picture, please get in contact with us and we will delete it immediately.
Lyrics:
[Verse 1]
Can I call you baby? Can you be my friend?
Can you be my lover up until the very end?
Let me show you love, oh, I don’t pretend
Stick by my side even when the world is givin’ in, yeah
[PreChorus]
Oh, oh, oh, don’t, don’t you worry
I’ll be there whenever you want me
[Chorus]
I need somebody who can love me at my worst
Know I’m not perfect, but I hope you see my worth
‘Cause it’s only you, nobody new, I put you first
And for you, girl, I swear I’d do the worst
[PostChorus]
Ooh, oohooh
Oohoohooh, oohoohoohooh
[Verse 2]
If you stay forever, let me hold your hand
I can fill those places in your heart no one else can
Let me show you love, oh, I don’t pretend, yeah
I’ll be right here, baby, you know I’ll sink or swim
[PreChorus]
Oh, oh, oh, don’t, don’t you worry
I’ll be there whenever you want me
[Chorus]
I need somebody who can love me at my worst
Know I’m not perfect, but I hope you see my worth, yeah
‘Cause it’s only you, nobody new, I put you first (You first)
And for you, girl, I swear I’d do the worst
[PostChorus]
Ooh, oohooh
Oohoohooh, oohoohoohooh
Oohoohooh, ooh, oohooh
Oohoohooh, oohoohoohooh
[Outro]
I need somebody who can love me at my worst
Know I’m not perfect but I hope you see my worth
‘Cause it’s only you, nobody new, I put you first
And for you, girl, I swear I’d do the worst
Tags
pink sweats, pink sweat$, at my worst lyrics, at my worst pink sweats, at my worst pink sweats lyrics, pink sweats at my worst, pink sweats at my worst lyrics, at my worst, pink sweats icy, pink sweats new song, pink sweat at my worst, pink sweat, the take, slow down, h.e.r., chris brown, new song, top song, chill vibes, r\u0026b chill song, rnb song, r\u0026b music, new r\u0026b song, new pop rnb song, pop rnb, chill trap rnb, chill music, new lyrics
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

Love Is Gone (Acoustic) – SLANDER ft. Dylan Matthew (Lyrics + Vietsub) ♫
Love is Gone (Acoustic) SLANDER ft. Dylan Matthew [Vietsub]
Original video: https://youtu.be/hCrtcVDgCGw
Stream/Download: http://smarturl.com/gv018
📺 Xem nhiều hơn: https://www.youtube.com/TopTikTokTV
👉 Đăng ký kênh ủng hộ bọn tớ: http://bit.ly/2BnuV2z
🎵 Follow Top Tik Tok:
https://www.facebook.com/toptiktok.music
https://www.instagram.com/__toptiktok
https://www.youtube.com/toptiktoktv
🎵 Follow SLANDER:
http://instagram.com/slanderofficial
http://facebook.com/slanderofficial
http://twitter.com/slanderofficial
http://slanderofficial.com/tour
🎵 Follow Dylan Matthew:
http://instagram.com/itsdylanmatthew/
http://facebook.com/itsdylanmatthew/
http://twitter.com/itsdylanmatthew
http://dylanmatthew.com/
📸 Background:
Artwork from (Pixiv): https://www.pixiv.net/en/artworks/75898786
Artist: MORNCOLOUR
https://twitter.com/MORNCOLOUR
https://www.instagram.com/MORNCOLOUR
Dear Artists, Producers and Labels!
Top Tik Tok is a nonprofit channel for the only purpose of promoting music and artwork and learning english together, if you as an Artist/Producer/Label feels unhappy and would like to have your music/artwork taken down, please contact us via the email ([email protected]) directly before doing anything and we will respectfully delete it immediately.
☑ We do not own the copyright for this song and artwork
☑ All rights go to their respectful owners
✉ [email protected] ✉
_____________________________________
★★★★★★VOCABULARY(từ vựng)★★★★★★
Stay(v) ▶ ở lại
Remind(v) ▶ nhắc nhở
Fall(v) ▶ rơi, ngã
Tear(n – v) ▶ nước mắt – xé rách
Turn(v) ▶ xoay, quay, quạo
Beg(v) ▶ cầu xin
Stick(v) ▶ dán dính
Leave(v) ▶ rời xa, bỏ lại
Breathe(v) ▶ thở
Weak(adj) ▶ yếu, yếu ớt
Tell(v) ▶ nói, kể
★★★★★★PHRASE(cụm từ)★★★★★★
One more time ▶ thêm một lần nữa
Fall in love ▶ sa vào lưới tình, yêu sâu đậm
Turn Sb down ▶ từ chối đề nghị
Stick around ▶ ở yên/giữ nguyên vị trí
_____________________________________
🎤 Lyrics:
Don’t go tonight
Stay here one more time
Remind me what it’s like
And let’s fall in love one more time
I need you now by my side
It tears me up when you turn me down
I’m begging please, just stick around
I’m sorry, don’t leave me, I want you here with me
I know that your love is gone
I can’t breathe, I’m so weak, I know this isn’t easy
Don’t tell me that your love is gone
That your love is gone
Don’t tell me that your love is gone
That your love is gone
I’m sorry, don’t leave me, I want you here with me
I know that your love is gone
I can’t breathe, I’m so weak, I know this isn’t easy
Don’t tell me that your love is gone
That your love is gone
That your love is gone, hmm
I can’t breathe, I’m so weak, I know this isn’t easy
Don’t tell me that your love is gone
That your love is gone
_____________________________________
loveisgone nhactiktok toptiktok

How language shapes the way we think | Lera Boroditsky
There are about 7,000 languages spoken around the world and they all have different sounds, vocabularies and structures. But do they shape the way we think? Cognitive scientist Lera Boroditsky shares examples of language from an Aboriginal community in Australia that uses cardinal directions instead of left and right to the multiple words for blue in Russian that suggest the answer is a resounding yes. \”The beauty of linguistic diversity is that it reveals to us just how ingenious and how flexible the human mind is,\” Boroditsky says. \”Human minds have invented not one cognitive universe, but 7,000.\”
Check out more TED Talks: http://www.ted.com
The TED Talks channel features the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world’s leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their lives in 18 minutes (or less). Look for talks on Technology, Entertainment and Design plus science, business, global issues, the arts and more.
Follow TED on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/TEDTalks
Like TED on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TED
Subscribe to our channel: https://www.youtube.com/TED

20210106 ม5 3 Reading Left Brain Right Brain เต็มเรื่อง

Rick Astley – Never Gonna Give You Up (Official Music Video)
The official video for “Never Gonna Give You Up” by Rick Astley
“Never Gonna Give You Up” was a global smash on its release in July 1987, topping the charts in 25 countries including Rick’s native UK and the US Billboard Hot 100. It also won the Brit Award for Best single in 1988. Stock Aitken and Waterman wrote and produced the track which was the leadoff single and lead track from Rick’s debut LP “Whenever You Need Somebody”. The album was itself a UK number one and would go on to sell over 15 million copies worldwide.
The legendary video was directed by Simon West – who later went on to make Hollywood blockbusters such as Con Air, Lara Croft – Tomb Raider and The Expendables 2. The video passed the 1bn YouTube views milestone on 28 July 2021.
Subscribe to the official Rick Astley YouTube channel: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/YTSubID
Follow Rick Astley:
Facebook: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/FBFollowID
Twitter: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/TwitterID
Instagram: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/InstagramID
Website: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/storeID
TikTok: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/TikTokID
Listen to Rick Astley:
Spotify: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/SpotifyID
Apple Music: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/AppleMusicID
Amazon Music: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/AmazonMusicID
Deezer: https://RickAstley.lnk.to/DeezerID
Lyrics:
We’re no strangers to love
You know the rules and so do I
A full commitment’s what I’m thinking of
You wouldn’t get this from any other guy
I just wanna tell you how I’m feeling
Gotta make you understand
Never gonna give you up
Never gonna let you down
Never gonna run around and desert you
Never gonna make you cry
Never gonna say goodbye
Never gonna tell a lie and hurt you
We’ve known each other for so long
Your heart’s been aching but you’re too shy to say it
Inside we both know what’s been going on
We know the game and we’re gonna play it
And if you ask me how I’m feeling
Don’t tell me you’re too blind to see
Never gonna give you up
Never gonna let you down
Never gonna run around and desert you
Never gonna make you cry
Never gonna say goodbye
Never gonna tell a lie and hurt you
RickAstley NeverGonnaGiveYouUp WheneverYouNeedSomebody OfficialMusicVideo

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆLEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ right brain or left brain แปล