simple past tense examples: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
What is the Simple Past Tense?
The simple past tense is
Simple Past Tense Illustration
Examples of When to use Simple Past
Simple Past is used for finished actions in the past. The focus is on the action itself, not on its present consequences. Simple Past is often used to describe a series of events or to tell stories. For example, when describing what you did during a day in the past.
For habits or repeated, regular events
The bus came at 7 am every morning.
Sometimes I went to the park during lunch break.
They often trained together before races.
Past event that happened at a given point in time
I went to bed at 12 pm last night.
She was born in 2000.
What time did your flight leave on Wednesday?
Past event with an indefinite point in time
She was my best friend.
I bought this watch a long time ago.
I bumped into my high school sweetheart the other day.
Structure of Simple Present
The Simple Past Tense has the simplest past structures. In an affirmative sentence, there is no auxiliary verb. The action verb needs to be used in past participle. The past participle of the verb is created the following way:
subject
+
Simple Past form of the verb
+
object
She studied medicine.
Regular verbs
To create the past tense form of regular verbs, simply add -ed to the end of the verb.
want → wanted → I wanted to help you.
shift → shifted → The real power shifted to the advisor.
cook → cooked → Mom cooked a delicious meal.
wait → waited → Cinderella waited for a long time for his prince.
play → played → My best friend played tennis in high school.
bake → baked → I baked a chocolate cake last weekend.
add → added → The teacher added some extra slides to the presentation.
stay → stayed → My roommate stayed up late last night.
jump → jumped → The neighbour’s goats jumped over the fence.
look → looked → You looked wonderful in that dress.
enjoy → enjoyed → They enjoyed a night out together.
push → pushed → Tom pushed the wrong button.
walk → walked → Grandpa always walked around in the garden.
Spelling changes
However, there are some exceptions in spelling regular verbs ending in -ed. The spelling rules follow the same logic as the spelling of the progressive participle.
- Verbs ending in -e only get a -d.
live → lived
vote → voted
love → loved
create → created - Double the final letter if the verb ends in consonant + vowel + consonant.
stop → stopped
plan → planned
drop → dropped
fit → fitted - Don’t double the last consonant if the stress is on the first syllable even though the verb ends in consonant + vowel + consonant.
happen → happened
offer → offered
enter → entered - Don’t double the last consonant if the verb ends in -w, -x, -y or when the last syllable is not stressed.
follow → followed
enjoy → enjoyed
fix → fixed
Some examples:
We happened to be there at the same time.
My dad fixed my bike yesterday.
Liam dropped out of school a long time ago.
I never finished high school.
Irregular verbs
There are many common words that have irregular second and third forms that don’t end in -ed. For example,
go → went → gone
do → did → done
make → made → made
get → got → got
You can find an extensive list of the most frequently used irregular verbs here. The sooner you start learning them, the sooner you’ll finish!
Note that there is no conjugation in 3rd person singular in past tense except for the verb ‘to be’:
I was You were
He / she / it was
We were
You were
They were
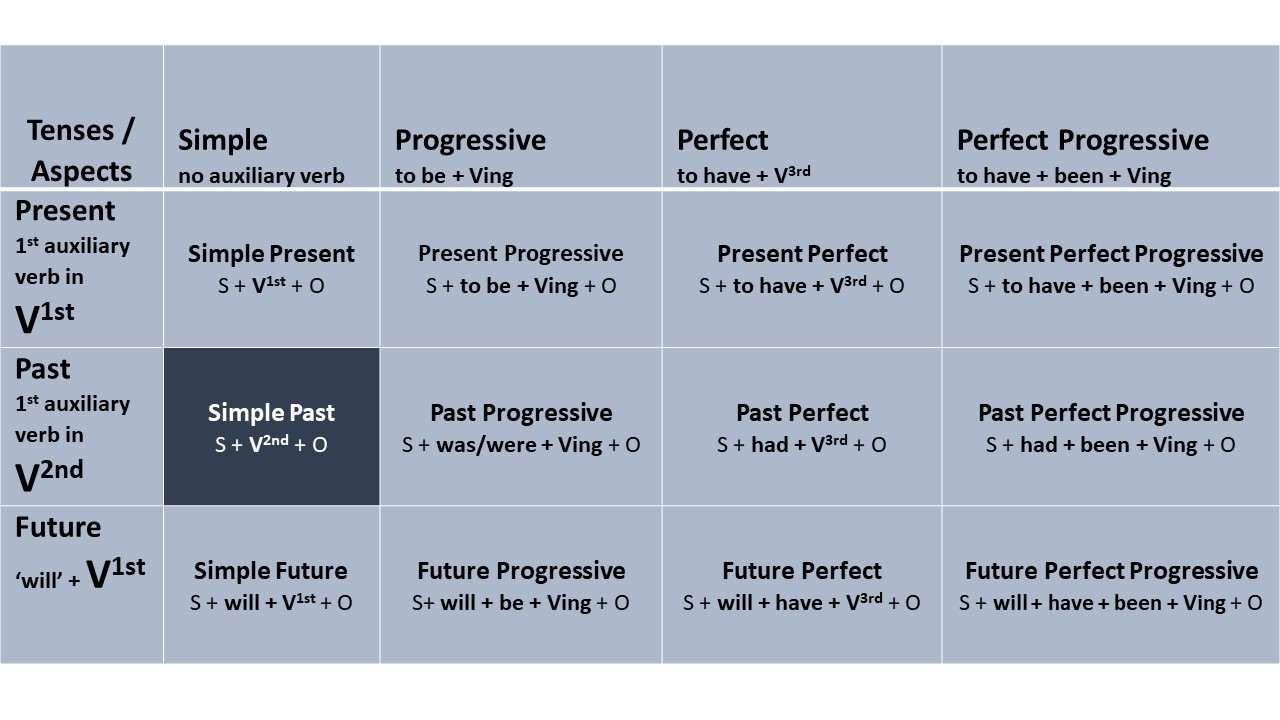
Take a look at where Simple Past is in the Verb Tenses Table:
Simple Past Negative
In the English language, negative forms of verbs are usually formed by an auxiliary verb and ‘not’. For example: She may not go out tonight. In the Simple Past Tense, the verb ‘do’ serves as an auxiliary verb to help the formation of negative and questions. The auxiliary verb, however, needs to be in second form, so the correct forms will be ‘did’ and ‘didn’t’. ‘Did’ here has no special meaning, it serves only grammatical purposes. The action verb follows the auxiliary verb which can stay in first form because the auxiliary verb already expresses the past tense. The negative of Simple Past is formed as follows:
S + did + not + bare infinitive + O
Remember to use the short version in everyday language by combing ‘did’ and ‘not’ to ‘didn’t’ and the long version ‘did not’ in a formal written context.
Examples:
I didn’t want to hang out with them last night.
She didn’t finish her paper until the deadline.
We didn’t go to the beach yesterday.
Yes/No questions in Simple Past
In the English language, questions are usually formed by switching the (first) auxiliary verb and the subject. To form questions the auxiliary verb ‘to do’ in past tense ‘did’ is used. Similarly to Simple Past Negative, the action verb stays in first form. For example:
I really liked the supper last night. → Did you like the supper last night?
They went to the nearest coffee shop. → Did they go to the nearest coffee shop?
My friend didn’t come with me to the handball game. → Did your friend come with you to the handball game?
Open-ended questions in Simple Past
To form open-ended questions, simply put the question word to the beginning of the sentence. The word order folowing the question word remains tha same as in case of yes/no questions. For example:
What did you have for supper last night?
Where did they go?
Why didn’t you friend come with you?
Typical adverbs of Simple Past
Yesterday, last night / week / year, at (2) o’clock, at (5) pm, once / twice…, … days / hours / weeks / years ago, for … hours, for a long time, a long time ago, ages ago
For example:
Yesterday I woke up at 7 am. I got out of bed and made myself a cup of coffee. I took a shower before starting to work. I worked for 3 hours and then met my friend for coffee at 11 o’clock. I invited her to come to my dinner party when she told me she didn’t have any plans for the evening. We had a great time last night.
Expressing habits in the past with ‘used to’ and ‘would’
There are two expressions used for expressing repeated actions in the past that are not tenses. In some special cases, these expressions describe the intention of the speaker more clearly than any of the past tenses. These expressions are ‘used to’ and ‘would’.
Let’s take a look at ‘used to’ first:
‘Used to’ expressed a repeated event, a habit or a state of something in the past. It describes an event or state that happened in the past but have already finished. It is frequently used for describing general past states, not specific events. Whereas Past Simple refers to a specific event with a given point in time, ‘used to’ refers to actions that regularly happened in the past.
The structure of the expression follows the same logic as the structure of Simple Past. In an affirmative sentence, ‘used to’ is followed by the bare infinitive of the action verb. In negative sentences and questions, the auxiliary verb ‘did’ helps to form the structure. As ‘did’ already expresses past tense, the -d at the end of ‘used to’ must be dropped.
Affirmative structure of ‘used to’: S + ‘used to’ + bare infinitive
Negative structure of ‘used to’: S + ‘didn’t use to’ + bare infinitive
Making questions with ‘used to’: Did + S + ‘use to’ + bare infinitive ?
For example:
I used to smoke, but I quit last week.
She used to be my best friend, but she got mad at me when I forgot about her birthday.
There used to be a lot more parks in this city.
Did you use to listen to this band in your teens?
I didn’t use to go on field trips with the class.
Expressing regular event and action in the past using ‘would’
‘Would’ is used for expressing regular actions in the past or typical event for a time period in the past. The main difference between ‘would’ and ‘used to’ is that you cannot use ‘would’ for describing states. Use ‘would’ for talking about actions and things that people can do. For example,
My grandma would be a teacher when he was younger.
My grandma used to be a teacher when he was younger.
She would complain about the kids all the time. ✓
She used to complain about the kids all the time. ✓
The structure of expressing regular past events with ‘would’ is the same as if you were using ‘would’ as a modal verb:
Affirmative: S + ‘would’ + bare infinitive
Negative: S + ‘wouldn’t / would not’ + bare infinitive
Questions: Would + S + bare infinitive ?
[NEW] Past simple tense in English: Explained with examples | simple past tense examples – NATAVIGUIDES

There are four different types of past tense in English, but the past simple tense is the one most students start with. The past simple tense will allow you to express yourself and hold conversations, so it’s essential to understand it.
This article will look in detail at how the past simple tense works, when you should use it, and some common past tense verbs that you can use in sentences. Keep reading to learn more.
What is the past simple tense?
You can describe the past in English in four different tenses. They are:
-
Past simple (also called
preterite)
-
Past continuous
-
Past perfect
-
Past perfect
continuous
The past simple tense is used to talk about things that both started and ended in the past. It is one of the most commonly used tenses in English as it indicates something that has already happened.
When to use the past simple tense
-
To talk about events that happened in the past —
-
To talk about moods or states of being in the past —
-
To talk about repeated actions in the past —
Pro tip – Past simple is only used when the action or event in the past was completed. If an action started in the past but is continuing into the future that is a different tense (present perfect).
How to construct the simple past tense
Regular verbs
Regular verbs always follow the same rules and so once you have understood how this rule works, you can apply this to all regular verbs. The rule for simple past tense is very easy to remember.
You just need to add -ed to the base form or infinitive verb, (or -d if the root form already ends in an e). The infinitive or base form of the verb is how the verb appears in the dictionary, for example, “walk.”
For example:
-
To walk → walk + ed =
walked
-
To paint → paint + ed =
painted
-
To love → love + d =
loved
Additionally, verbs in the simple past do not change depending on the subject, they always stay the same. For example:
- I
smile,
she
smiled,
he
smiled,
you
smiled,
we
smiled,
they
smiled.
If you want to put this theory into practice, try this free online exercise sheet.
Irregular verbs
Of course, there are some exceptions to the English grammar rules around simple past. Irregular verbs, like “to be” for example, don’t follow a pattern or rule like regular verbs and so just have to be memorized.
That might seem like a big task, but to learn English you only need to focus on the most important ones. Here are fifty of the most common irregular verbs to get you started:
Infinitive verb
Past simple verb
To be
was (I/he/she) were (you/we/they)
To go
went
To do
did
To have
had
To get
got
To eat
ate
To fall
fell
To feel
felt
To dream
dreamt
To speak
spoke
To give
gave
To take
took
To find
found
To draw
drew
Can
could
To drink
drank
To choose
chose
To buy
bought
To grow
grew
To hear
heard
To know
knew
To make
made
To pay
paid
To read
read (in the past tense, this word is pronounced “red”)
To let
let
To meet
met
To lose
lost
To say
said
To sell
sold
To run
ran
To shut
shut
To sleep
slept
To smell
smelt
To sing
sang
To tell
told
To understand
understood
To write
wrote
To teach
taught
To swim
swam
To win
won
To think
thought
To sit
sat
To send
sent
To see
saw
To keep
kept
To leave
left
To drive
drove
To cut
cut
To cost
cost
To fly
flew
Irregular verbs are used in sentences in the same way as regular ones. For example:
How to use the past simple tense

You can use past simple with time expressions that refer to a point of time in the past, for example, “earlier today”, “yesterday”, “last week”, “last month” or “last Tuesday”.
You can also use phrases that refer to an indefinite period of time in the past, often marked by the word “ago”. For example, “a long time ago”, “a month ago”, “several years ago”.
Or phrases that suggest frequency, for things which happened multiple times in the past: “often”, “sometimes”, “never”, “every”.
Pronunciation
A quick note on pronunciation! Not all regular past tense verbs with “ed” at the end are pronounced the same way. Most of the time, the “ed” is pronounced like a soft “d”.
-
Hop
ed
-
Plac
ed
-
Clos
ed
Sometimes, the ending of the word is pronounced like an “id” to rhyme with “lid”.
-
Paint
ed
-
Correct
ed
-
Erect
ed
Other times, the “ed” sounds more like the soft “t” sound, like at the end of “paint.”
-
Lik
ed
-
Walk
ed
-
Pick
ed
Pronunciation will become easier the more you practice speaking and listening to English. Watching TV in English with subtitles is a great way to practice listening and you can hear how native speakers pronounce words.
How to form negative statements in the past simple tense
To make negative sentences in the past tense, add the auxiliary verb “did not” (can be shortened to “didn’t”) before the present verb tense. “Did not” is the past tense of “do not.”
[Subject]+ [did not / didn’t] + [present tense verb form]
If you want to practice making negative simple past tense statements, check out this online exercise.
Exceptions
There are only a few exceptions when forming negative statements in the simple past, but they are important. The first is the verb “to be.” In the past tense, “to be” becomes “was” or “were” depending on the subject.
Subject
Verb (To be)
I
Was
You
Were
He/She
/It
Was
We
Were
They
Were
The negative of “was” is “was not” or “wasn’t” for short. The negative of “were” is “were not” or “weren’t”. For example:
The other exception is modal verbs. Modal verbs describe whether something is certain, possible, or impossible: they are: “could,” “might,” “should,” and “would.”
To make a modal verb into a negative, you write the verb + “not”. For example:
- Should not – shouldn’t
- Could not – couldn’t
- Would not – wouldn’t
- Might not – mightn’t
- Must not – mustn’t
Here are some examples of negative statements using modal verbs:
-
I
could not
remember his name
-
He
should not
worry too much
-
You
mustn’t
spend too much time watching TV
-
They
wouldn’t
eat my spicy curry
We have online tutors in more than 50 languages.
Preply is one of the leading educational platforms that provide 1-on-1 lessons with certified tutors via the exclusive video chat.
- Find my online tutor now
Turn theory into practice
This article is a starting point for understanding the past simple tense in English. Don’t worry if it doesn’t “stick” straight away. Learning English grammar rules is 5% theory and 95% practice, so the next step is to try and use what you’ve learned.
Book some lessons with a Preply English tutor — prices start from just $5 per hour, and you can put the past simple tense theory into conversations. If you get stuck or have any questions, there is a native-speaking tutor on hand to help you out, so you’ll soon be a master of the past simple tense.
Frequently asked questions
Which sentences contain a verb in the simple past tense?
Many sentences contain verbs in the simple past tense. An example of a simple past sentence is “I walked home
last night
.” The verb walk (present tense) adds “ed” to become walked (past tense).
What is simple past tense?
Simple past tense is one of four types of past tense in
English
. It describes an action, event, or state of being that both started and finished in the past. For example, “I ate this morning.”
What is the function of simple past tense?
The function of the simple past tense is to indicate an action, event, or state that began and concluded in the past, for example, “I was happy
last night
.” It allows you to describe things that have happened in the past and differentiate them from the present or future.
What are simple past and past continuous tenses?
The simple past tense describes something that started and finished in the past, for example, ‘We talked yesterday”. The
past continuous tense
is a bit more complicated and can describe multiple things, including conditions in the past. For example, “The sun was shining when we left the house”. It can also describe habitual action, for example, “He was constantly running
last year
”.
Past Simple Tense – Song
A nice song using many verbs in past simple tense.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

What were you doing? – Past Continuous
Learn how to use Past Continuous/Progressive through a short story in this video. We use this tense 1. for a continuous action in the past which was interrupted by another action \”I was reading the label, when the jar slipped out of my hands\”; 2. to describe the atmosphere \”The sun was shining\”; 3. for two actions which happened in the same time in the past \”I was sitting in the living room and she was taking a shower\”

Simple Past Tense Quiz
Simple past tense quiz for beginners and kids.
10 multiplechoice questions.
Each quiz question is given out with a timer and shows the correct answers to the questions.
You will be quizzed with appealing animations 🙂
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCYAqshTpc9OP_GYiMUbSqA

Learn Past Simple Tense English Grammar Course
QUIZ: https://shawenglish.com/quizzes/pasttenseenglishgrammarquiz/
Learn Past Simple Tense with Esther! In her new English grammar course, she teaches how to use English grammar plus practice the English grammar. Be sure to watch all of Esther’s grammar course videos. All her English lessons are free.
0:00 Start
0:20 Usage 1 | ‘be’ verb | was/were
1:24 Usage 2 | Regular Verbs
2:45 Usage 3 | Irregular Verbs
4:09 Usage 4 | Negative Form | was/were
5:14 Usage 5 | Negative Form | non ‘be’ verbs
6:18 Usage 6 | Question Form
8:08 Usage 7 | ‘Wh’ Question Form
9:45 Channel Membership
❤️✩Support Us! ✩
✭ Channel Membership: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC_OskgZBoS4dAnVUgJVexcw/join
✭ PayPal: https://paypal.me/shawenglish
✭ Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/ShawEnglish
👉✩ Connect With Us✩
✭ Website: http://www.shawenglish.com
✭ Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/shawenglish/
✭ Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/162048911162706/
✭ WhatsApp: http://shawenglish.com/whatsapplearnenglishwithrobin/
✭ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/shawenglishonline/
✭ Twitter: https://twitter.com/ShawEnglishNow
✭ Line: https://line.me/R/ti/g/5AJpLqlaln
✭ Telegram: https://t.me/ShawEnglish
✭ KakaoTalk: https://open.kakao.com/o/gcIHXP1
✭ Naver Café (네이버 카페): http://cafe.naver.com/shawenglish
🧔Learn English With Robin Shaw: http://shawenglish.com/learnenglishwithrobin/
👩🏫 Learn English with a live teacher NOW!
https://www.youtube.com/LearnEnglishLive
EnglishCourse BasicEnglish LearnEnglishGrammar

What Did You Do? Simple Past Tense
Learn how to talk about your day or about your weekend and how to ask questions using Past Tense Verbs.

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆMAKE MONEY ONLINE
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ simple past tense examples