simple present: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
Table of Contents
Simple Present
![]()
Carla Muniz
O Simple Present Tense, também chamado de Present Simple (presente simples), é um dos tempos verbais do inglês.
Ele é equivalente ao presente do indicativo na língua portuguesa.
Quando usar o Simple Present?
O Simple Present é um tempo verbal utilizado para indicar ações habituais que ocorrem no presente.
Além disso, ele é usado para expressar verdades universais, sentimentos, desejos, opiniões e preferências.
Por vezes, as frases no Simple Present apresentam expressões de tempo (advérbios).
As mais usuais são:
Advérbio
Tradução
now
agora
always
sempre
never
nunca
today
hoje
every day
todos os dias
daily
diariamente
often
frequentemente
sometimes
às vezes
generally
geralmente
usually
usualmente
Veja alguns exemplos de frases no Simple Present:
- He plays soccer very well. (Ele joga futebol muito bem.)
- She loves chocolate. (Ela ama chocolate.)
- They go to school in the afternoon. (Eles vão para a escola de tarde.)
- I always read the newspaper in the morning. (Eu sempre leio o jornal de manhã.)
- We generally travel to Brazil in December. (Geralmente nós viajamos para o Brasil em dezembro.)
Veja também:
Adverbs of frequency
Regras do Simple Present
A conjugação do Simple Present varia de acordo com a pessoa verbal, com a terminação do verbo e com o tipo de frase (afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa.)
Confira abaixo a explicação sobre a formação do Simple Present nas formas afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa.
Affirmative Form (forma afirmativa)
Como regra geral, pode-se dizer que para conjugar um verbo no Simple Present, basta usá-lo no infinitivo sem o to no caso dos pronomes I, you, we e they, e acrescentar -s, -es ou -ies no caso dos pronomes he, she e it.
Veja abaixo um exemplo com a conjugação do verbo to work (trabalhar; funcionar):

No entanto, há algumas regras específicas para a flexão da terceira pessoa do singular (he, she e it) que estão relacionadas com a terminação dos verbos.
Verbos terminados em -o, -z, -ss, -ch, -sh, -x
É preciso acrescentar -es no final do verbo.
Exemplos:
- to teach (ensinar) – teaches
- to watch (assistir) – watches
- to push (empurrar) – pushes
- to kiss (beijar) – kisses
- to go (ir) – goes
- to fix (consertar) – fixes
Verbos terminados em -y precedido de consoante
Retira-se o -y e acrescenta-se -ies
Exemplos:
- to fry (fritar) – fries
- to fly (voar) – flies
- to study (estudar) – studies
- to worry (preocupar-se) – worries
Verbos terminados em -y precedido de vogal
Acrescenta-se somente o -s.
Exemplos:
- to say (dizer) – says
- to play (brincar; jogar) – plays
Veja também:
Present Perfect
Posição do verbo em frases afirmativas
Veja abaixo a estrutura de formação de frases afirmativas no Simple Present:
Sujeito + verbo principal + complemento
Exemplos:
- I live in Brazil. (Eu moro no Brasil). – verbo to live (morar, viver).
- He teaches Spanish at the university. (Ele ensina espanhol na universidade.) – verbo to teach (ensinar).
- They prefer Italian food. (Eles preferem comida italiana.) – verbo to prefer (preferir).
- She watches TV every day. (Ela assiste TV todos os dias.) – verbo to watch (assistir).
- We like to go to the beach during the week. (Nós gostamos de ir à praia durante a semana.) – verbo to like (gostar).
- It pushes the door when it wants to get in. (Ele/ela empurra a porta quanto quer entrar) – verbo to push (empurrar).
- You always arrive late. (Você sempre chega atrasado.) – verbo to arrive (chegar).
- She always kisses her grandma before leaving. (Ela sempre beija a avó antes de sair.) – verbo to kiss (beijar).
- He goes to the gym on weekends. (Ele vai à academia aos fins de semana.) – verbo to go (ir).
- She fixes her car by herself. (Ela conserta o carro dela sozinha.) – verbo to fix (consertar).
Veja também:
Advérbios em Inglês
Negative Form (forma negativa)
A forma negativa do Simple Present é formada com o uso dos verbos auxiliares do e does.
Do é usado com os pronomes I, you, we e they. Já o auxiliar does é usado com he, she, it.
Veja abaixo a conjugação da forma negativa do verbo to work (trabalhar; funcionar) no Simple Present.
Observe que na forma negativa do Simple Present, o verbo sempre é usado no infinitivo sem o to, mesmo quando se trata da terceira pessoa do singular (he, she e it).
As frases na negativa podem ser escritas de forma completa (do not ou does not) ou de forma contraída (don’t ou doesn’t):
- Do + not = don’t
- Does + not = doesn’t
Posição do verbo em frases negativas
Veja abaixo a estrutura de formação de frases negativas no Simple Present:
Sujeito + verbo auxiliar + not + verbo principal + complemento
Exemplos:
- I do not live in Brazil. (Eu não moro no Brasil). – verbo to live (morar, viver).
- He does not teach Spanish at the university. (Ele não ensina espanhol na universidade.) – verbo to teach (ensinar).
- They don’t prefer Italian food. (Eles não preferem comida italiana.) – verbo to prefer (preferir).
- She doesn’t watch TV every day. (Ela não assiste TV todos os dias.) – verbo to watch (assistir).
- We do not like to go to the beach during the week. (Nós não gostamos de ir à praia durante a semana.) – verbo to like (gostar).
- It does not push the door when it wants to get in. (Ele/ela não empurra a porta quanto quer entrar.) – verbo to push (empurrar).
- You don’t arrive late. (Você não chega atrasado.) – verbo to arrive (chegar).
- She doesn’t kiss her grandma before leaving. (Ela não beija a avó antes de sair.) – verbo to kiss (beijar).
- He does not go to the gym on weekends. (Ele não vai à academia aos fins de semana.) – verbo to go (ir).
- She doesn’t fix her car by herself. (Ela não conserta o carro dela sozinha.) – verbo to fix (consertar).
Veja também:
Do e does
Interrogative Form (forma interrogativa)
Assim como acontece nas frases negativas, os auxiliares do e does são utilizados para formar frases interrogativas no Simple Present.
Do é usado com I, you, we e they, e does é usado com he, she e it.
Veja abaixo a conjugação da forma interrogativa do verbo to work (trabalhar; funcionar) no Simple Present:
Note que o verbo sempre é usado no infinitivo sem o to, mesmo quando se trata da terceira pessoa do singular (he, she e it).
Posição do verbo em frases interrogativas
Veja abaixo a estrutura de formação de frases interrogativas no Simple Present.
Verbo auxiliar + sujeito + verbo principal + complemento
Exemplos:
- Do I own you money? (Eu te devo dinheiro?). – verbo to own (dever).
- Does he teach Spanish at the university? (Ele ensina espanhol na universidade?) – verbo to teach (ensinar).
- Do they prefer Italian food? (Eles preferem comida italiana?) – verbo to prefer (preferir).
- Does she watch TV every day? (Ela assiste TV todos os dias?) – verbo to watch (assistir).
- Do we have classes on Saturdays? (Nós temos aulas aos sábados?) – verbo to have (ter).
- Does it push the door when it wants to get in? (Ele/ela empurra a porta quanto quer entrar?) – verbo to push (empurrar).
- Do you arrive late? (Você chega atrasado?) – verbo to arrive (chegar).
- Does she kiss her grandma before leaving? (Ela beija a avó antes de sair?) – verbo to kiss (beijar).
- Does he go to the gym on weekends? (Ele vai à academia aos fins de semana?) – verbo to go (ir).
- Does she fix her car by herself? (Ela conserta o carro dela sozinha?) – verbo to fix (consertar).
IMPORTANTE
O verbo to do significa fazer. No entanto, no Simple Present ele é usado como verbo auxiliar que complementa a formação das frases negativas e interrogativas.
Enquanto auxiliares, do e does não têm significado.
Os auxiliares do e does também são usados em respostas curtas.
Observe os exemplos abaixo:
Veja também:
Verbos auxiliares em inglês
Tabelas de verbos conjugados
Agora que você já aprendeu as regras do Simple Present, veja alguns exemplos de verbos conjugados.
Verbo to love (amar)
Affirmative
Negative
Interrogativa
I love
I do not/don’t love
Do I love?
You love
You do not/don’t love
Do you love?
He loves
He does not/doesn’t love
Does he love?
She loves
She does not/doesn’t love
Does she love?
It loves
It does not/doesn’t love
Does it love?
We love
We do not/don’t love
Do we love?
You love
You do not/don’t love
Do you love?
They love
They do not/don’t love
Do they love?
Veja também:
Simple Future
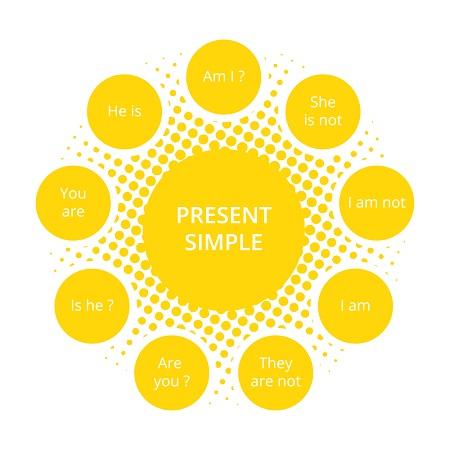
Verbo to be (ser/estar)
Affirmative
Negative
Interrogativa
I am/I’m
I am not/I’m not
Am I?
You are/You’re
You are not/aren’t
Are you?
He is/He’s
He is not/isn’t
Is he?
She is/She’s
She is not/isn’t
Is she?
It is/It’s
It is not/isn’t
Is it?
We are/We’re
We are not/aren’t
Are we?
You are/You’re
You are not/aren’t
Are you?
They are/They’re
They are not/aren’t
Are they?
OBS.: Assim como acontece com os modal verbs (verbos modais), a forma negativa e a forma interrogativa do verbo to be não são formadas com o uso dos auxiliares do e does.
Veja também:
Verbo To Be
Verbo to have (ter)
Affirmative
Negative
Interrogativa
I have
I do not/don’t have
Do I have?
You have
You do not/don’t have
Do you have?
He has
He does not/doesn’t have
Does he have?
She has
She does not/doesn’t have
Does she have?
It has
It does not/doesn’t have
Does it have?
We have
We do not/don’t have
Do we have?
You have
You do not/don’t have
Do you have?
They have
They do not/don’t have
Do they have?
Veja também:
Has e have
Simple Present x Present Continuous
Tanto o Simple Present (presente simples) quanto o Present Continuous (presente contínuo) são tempos verbais da língua inglesa que indicam tempo presente.
No entanto, é comum que ambos causem dúvidas àqueles que querem praticar e construir frases em inglês.
O Simple Present indica ações habituais ocorridas no presente e também verdades universais, sentimentos, desejos, opiniões e preferências.
Já o Present Continuous indica ações que estão ocorrendo no presente, ou seja, no momento em que se fala. Equivale ao gerúndio da língua portuguesa. Regra geral, para conjugar o Present Continuous, é preciso acrescentar -ing no fim do verbo..
Exemplos:
- They are watching a movie. (Eles estão assistindo um filme.) – verbo to watch (assistir).
- I am making a phone call. (Estou fazendo uma chamada telefônica.) – verbo to make (fazer).
Veja abaixo algumas frases no Simple Present e no Present Continuous que ilustram a diferença entre os dois tempos verbais.
Exemplos:
- He is playing baseball. (Ele está jogando basebol.) – PRESENT CONTINUOUS
- He plays baseball. (Ele joga basebol.) – SIMPLE PRESENT
- They study German. (Eles estudam alemão.) – SIMPLE PRESENT
- They are studying German. (Eles estão estudando alemão.) – PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Veja também:
Present Continuous
Que tal saber mais sobre a língua inglesa? Veja também:
Vídeo sobre Simple Present
Agora que você já viu tudo o que precisa saber sobre o Simple Present, assista o vídeo abaixo para consolidar o seu aprendizado.
Resumo do Simple Present
Confira abaixo o infográfico que o Toda Matéria preparou para você, com um resumo do uso do Simple Present tense.
Se deseja mais informações sobre como estudar inglês, vale a pena consultar os artigos abaixo:
Exercícios sobre Simple Present
Questão 1
(Unifor-CE/2001)
In the age-old battle between independence-seeking teenagers and worried parents, the older generation is packing some new weapons. Caller ID tells parents who is calling their kids. Cell-phone bills detail every local number the kid has called. New computer programs track just about everything − every Web site visited, every e-mail sent − that a teenager does online.
Parental reconnaissance is going to get worse − or good, depending on your perspective.
(Wall Street Journal, Nov. 6, 2000)
Os verbos que estão no Simple Present, no texto, são:
a) detail – track – get
b) worried – visited – sent
c) is packing – is calling – is going
d) tells – detail – track
e) worried – has called – does
Ver Resposta
Alternativa correta: d) tells – detail – track
A alternativa d) é a única onde todos os verbos estão flexionados no Simple Present.
- tells é a flexão de Simple Present do verbo to tell (dizer), na terceira pessoa de singular (he/she/it).
- detail é a flexão de Simple Present do verbo to detail (detalhar), usada com os pronomes I, you, we, they.
- track é a flexão de Simple Present do verbo to track (rastrear), usada com os pronomes I, you, we, they.
Veja quais são os tempos verbais das outras alternativas:
a) detail – track – get: detail e track estão no Simple Present, porém, no texto, o verbo get faz parte da estrutura de futuro do Simple Future, going to get.
b) worried – visited – sent: todos os verbos estão no Simple Past.
c) is packing – is calling – is going: is packing e is calling estão no Present Continuous. O is going faz parte da estrutura de futuro do Simple Future, is going to get.
e) worried – has called – does: worried está no Simple Past, has called está no Present Perfect e does é o único verbo que está no Simple Present.
Questão 2
(Ufac/2010) Choose the alternative that best completes the sentence:
Charles normally ________ water, but now he ________ Coke.
a) drinks; is drinking.
b) is drinking; drinks.
c) was drinking; drinks.
d) drink; is drinking.
e) drinks, was drinking.
Ver Resposta
Alternativa correta: a) drinks; is drinking.
Observe que foi usado na frase o advérbio normally (normalmente), que indica uma ação habitual. Assim sendo, o verbo a ser utilizado para completar a lacuna deve estar conjugado no Simple Present.
Das alternativas disponíveis, apenas as letras a), d) e e) se adequam. A letra b) inicia com uma flexão conjugada no Present Continuous (is drinking) e a letra c) tem sua primeira opção conjugada no Past Continuous (was drinking).
Na segunda parte da oração, foi utilizada a palavra now (agora), o que obriga o uso de um verbo conjugado no Present Continuous (presente contínuo) para indicar uma ação em progresso no presente.
Restam as opções a) e d). A opção correta foi a letra a) pois o sujeito da frase é Charles, que corresponde ao pronome he (ele). Para he, she e it deve-se acrescentar o -s ao fim do verbo.
Questão 3
Assinale a alternativa correta para completar com o Simple Present:
She doesn’t ________ anymore.
a) to work out
b) work out
c) working out
d) works out
e) worked out
Ver Resposta
Alternativa b: She doesn’t work out anymore.
A frase apresenta uma flexão de terceira pessoa do singular (he, she e it) da forma negativa do Simple Present, indicada pelo uso de doesn’t.
Quando o does ou o does not são utilizados, deve-se usar o verbo principal no infinitivo sem o to.
O infinitivo em questão é to work out (exercitar-se), logo, passa a work out sem o to. Assim sendo, a letra b) é a alternativa correta.
Questão 4
Preencha os espaços com a conjugação dos verbos no Simple Present:
a) Do you ______ in America? (to live)
Ver Resposta
Resposta correta: a) live
Como a frase é uma pergunta, o verbo deve ser utilizado no infinitivo sem o to. Nesse caso, como o infinitivo é to live (morar), basta usar o live.
b) Jane ______ your friend. (to love)
Ver Resposta
Resposta correta: b) loves
Jane é o sujeito da frase. Como se trata de um nome feminino, equivale ao pronome she (ela).
A flexão de Simple Present de he, she e it deve ser feita com o acréscimo de -s ao fim do verbo no infinitivo sem o to.
O infinitivo é to love (amar). Sem o to, passamos a ter apenas love. Assim sendo, basta acrescentar o -s: loves
c) Juan and Carla ______ on the beach every morning. (to run)
Ver Resposta
Resposta correta: c) run
Juan and Carla equivalem ao pronome they (eles).
Para flexionar o verbo to run (correr) na terceira pessoa do plural (they), basta usar o verbo no infinitivo sem o to. Como o infinitivo é to run, sem o to passamos a ter apenas run. Logo, Juan and Carla run.
d) She _______ English every day. (to teach)
Ver Resposta
Resposta correta: d) teaches
Quando um verbo termina em -o, -z, -ss, -ch, -sh ou -x, a flexão de Simple Present de he, she e it deve ser feita com o acréscimo de -es ao fim do verbo no infinitivo sem o to.
O infinitivo é to teach (ensinar). Sem o to, passamos a ter apenas teach. Assim sendo, basta acrescentar o -es: teaches.
e) Thomas ______ his car weekly. (to wash)
Ver Resposta
Resposta correta: washes
Quando um verbo termina em -o, -z, -ss, -ch, -sh ou -x, a flexão de Simple Present de he, she e it deve ser feita com o acréscimo de -es ao fim do verbo no infinitivo sem o to.
O infinitivo é to wash (lavar). Sem o to, passamos a ter apenas wash. Assim sendo, basta acrescentar o -es: washes.
Questão 5
Escreva a frase a seguir nas formas negativa e interrogativa:
We go to school every day.
Ver Resposta
Forma negativa:
Resposta correta: We don’t go to school every day ou We do not go to school every day.
O verbo principal da frase é to go (ir).
Para formar frases negativas no Simple Present, deve-se usar o auxiliar do ou o auxiliar does, e acrescentar o not. Também podem ser usadas as formas contraídas don’t ou doesn’t.
Does not e doesn’t são usados com os pronomes he, she e it. Com os demais pronomes (I, you, we e they) usa-se do not ou don’t.
Depois do auxiliar, é preciso usar o verbo principal no infinitivo sem o to. Como o verbo principal da frase no infinitivo é to go, sem o to passamos a ter go.
Posição do verbo em frases negativas: sujeito + verbo auxiliar + not + verbo principal + complemento
Tendo em conta que o pronome usado na frase é o we (nós), podemos optar por usar do not ou don’t:
- We don’t go to school every day.
- We do not go to school every day.
Forma interrogativa:
Resposta correta: Do we go to school every day?
O verbo principal da frase é to go (ir).
Para formar frases interrogativas no Simple Present, deve-se usar o auxiliar do ou o auxiliar does.
Does é usado com os pronomes he, she e it. Com os demais pronomes (I, you, we e they) usa-se do.
Depois do auxiliar, é preciso usar o verbo principal no infinitivo sem o to. Como o verbo principal da frase no infinitivo é to go, sem o to passamos a ter go.
Posição do verbo em frases interrogativas: verbo auxiliar + sujeito + verbo principal + complemento
Tendo em conta que o pronome usado no frase é o we (nós), a resposta correta é Do we go to school every day?
Questão 6
De acordo com a formação das frases no Simple Present, a oração em que as palavras aparecem na ordem correta é:
a) My girlfriend visits her parents on Sundays.
b) On Sundays my girlfriend her parents visits.
c) Visits her parents on Sundays my girlfriend.
d) My girlfriend parents her visits on Sundays.
e) Her parents my girlfriend visits on Sundays.
Ver Resposta
Alternativa correta: a) My girlfriend visits her parents on Sundays.
No Simple Present, a formação das frases afirmativas segue a seguinte estrutura:
Sujeito + verbo principal + complemento
- Sujeito: My girlfriend
- Verbo principal: visits
- Complemento: her parents on Sundays
Questão 7
Complete com a forma correta do verbo entre parênteses.
a) They ______ their e-mail every day. (check-checks)
b) The sun ______ in the east. (rise-rises)
c) We ______ shopping on Saturdays. (go-goes)
d) Water ______ at 100 °C. (boil-boils)
e) Daniel ______ for a big hotel in the city center. (work-works)
Ver Resposta
Para conjugar um verbo no Simple Present, basta usá-lo no infinitivo sem o to no caso dos pronomes I, you, we e they, e acrescentar -s, -es ou -ies no caso dos pronomes he, she e it. Assim, as respostas corretas são:
a) check – They check their e-mail every day. (Eles verificam seus e-mails todos os dias.)
b) rises – The sun rises in the east. (O sol nasce no leste.)
c) go – We go shopping on Saturdays. (Vamos às compras aos sábados.)
d) boils – Water boils at 100 °C. (A água ferve a 100 °C.)
e) works – Daniel works for a big hotel in the city center. (Daniel trabalha para um grande hotel no centro da cidade.)
Questão 8
Complete as lacunas com o verbo auxiliar correto: to do ou to be.
a) ______ you married?
Yes, my husband’s name is Frank.
b) ______ you have any children?
Yes, I have three sons.
c) Where ______ you work?
I’m a doctor at the local hospital.
d) What ______ their names?
Lucy and Tomas.
e) What ______ you do?
I work in a club.
Ver Resposta
Tanto o verbo to do quanto o verbo to be podem ser utilizados no inglês como verbos auxiliares.
O verbo to do, enquanto auxiliar, não possui uma tradução.
Já o verbo to be é utilizado quando o sentido da frase está relacionado com os verbos “ser” ou “estar”. Assim, as respostas das questões são:
a) are – Are you married? (Você é casado?)
b) do – Do you have any children? (Você tem filhos?)
c) do – Where do you work? (Onde você trabalha?)
d) are – What are theirs names? (Quais são os nomes deles?)
e) do – What do you do? (O que você faz?)
Questão 9
Nas frases abaixo, insira os advérbios de frequência entre parênteses no local correto.
a) Do you work late? (often)
b) I’m exhausted. (always)
c) I finish at four in the morning. (usually)
d) I work till six. (once a week)
Ver Resposta
Os advérbios de frequência são utilizados entre o sujeito e o verbo, exceto quando o verbo principal da frase é o to be. Confira as respostas corretas:
a) Do you often work late? (Você costuma trabalhar até tarde?)
b) I’m always exhausted. (Estou sempre exausta.)
c) I usually finish at four in the morning. (Eu costumo terminar às quatro da manhã.)
d) I work till six once a week. (Eu trabalho até as seis uma vez por semana.)
Questão 10
Leia as frases abaixo a respeito de regras gramaticais sobre o uso do Simple Present.
I. Ao conjugar no Simple Present um verbo terminado em y precedido de consoante, basta acrescentar o -s nas flexões das pessoas gramaticais he, she e it.
II. O Simple Present é usado para falar de hábitos e rotinas, e de verdades universais.
III. Na forma interrogativa do Simple Present, o verbo principal não é flexionado. Ele é utilizado no infinitivo sem o to.
É correto o que se afirma em:
a) I e III
b) I e II
c) II e III
d) I, II e III
e) n.d.a.
Ver Resposta
Resposta correta: c) II e III
A afirmação da frase I está incorreta, uma vez que ao conjugar no Simple Present um verbo terminado em y precedido de consoante, é necessário acrescentar -ies, e não apenas -s, nas flexões das pessoas gramaticais he, she e it.
Para mais exercícios sobre o Simple Present, veja também Simple Present exercícios
![]()
[Update] Thì hiện tại đơn (Simple present) | simple present – NATAVIGUIDES
Thì hiện tại đơn là một thì rất căn bản mà chắc chắn bạn phải biết khi nhập môn tiếng Anh. Dẫu đây là một thì khá đơn giản nhưng vẫn có những lưu ý để người học có thể sử dụng chúng thành thạo. Hiểu được điều đó, TOPICA Native đã tổng hợp những kiến thức bạn cần biết để nắm chắc thì hiện tại đơn ở bài viết dưới đây.
Download Now: Trọn bộ Ebook ngữ pháp FREE
Xem thêm:
Trong bài viết này, TOPICA Native sẽ cung cấp cho các bạn những kiến thức về khái niệm, cấu trúc, cách dùng, dấu hiệu nhận biết và những bài tập về thì hiện tại đơn để áp dụng. Nếu bạn còn cảm thấy chưa tự tin với những hiểu biết của mình về loại thì này, hãy theo dõi ngay bài viết dưới đây để trang bị cho mình những kiến thức tiếng Anh căn bản nhất.
1. Khái niệm thì hiện tại đơn (Simple present là gì)
Định nghĩa thì hiện tại đơn: Thì hiện tại đơn (Simple present tense) dùng để diễn tả một sự thật hiển nhiên hay một hành động diễn ra lặp đi lặp lại theo thói quen, phong tục, khả năng.
2. Công thức thì hiện tại đơn (Simple present tense)
Hiện tại đơn là một trong những thì cơ bản nhất trong tiếng Anh. Công thức hiện tại đơn sẽ chia làm 2 dạng dành cho động từ To be và động từ thường.
2.1. Thì hiện tại đơn với TOBE
Thể khẳng định
Cấu trúc: S + am/ is/ are + N/ Adj
Trong đó:
-
S
): Chủ ngữ
-
N/ Adj
: Danh từ/ tính từ
Lưu ý:
-
S = I + am
-
S = He/ She/ It + is
-
S = You/ We/ They + are
Ví dụ:
-
My father
is
a teacher. (Bố tôi là một giáo viên.)
-
They
are
from Japan. (Họ đến từ Nhật Bản.)
-
I
am
handsome. (Tôi đẹp trai.)
→ Ta thấy với chủ ngữ khác nhau động từ “to be” chia khác nhau.
Câu phủ định hiện tại đơn
Cấu trúc: S + am/ is/ are + not + N/ Adj
Lưu ý:
-
“Am not” không có dạng viết tắt
-
Is not = Isn’t
-
Are not = Aren’t
Ví dụ:
-
I
am not
a bad student. (Tôi không phải một học sinh hư.)
-
My litter sister
isn’t
tall. (Em gái tôi không cao.)
-
You
aren’t
from Vietnam. (Bạn không đến từ Việt Nam.)

Thể nghi vấn
Câu hỏi Yes/No question
Cấu trúc: Am/ Is/ Are + S + N/ Adj?
Trả lời:
-
Yes, S + am/ is/ are.
-
No, S + am/ is/ are + not.
Ví dụ:
- Is
she beautiful? (Cô ấy có đẹp không?)
-> Yes, she is./ No, she isn’t.
- Are
they here? (Họ có ở đây không?)
Yes, they are./ No, they aren’t.
- Am
I good enough? (Tớ có đủ tốt không?)
Yes, you are./ No, you aren’t.
Câu hỏi WH- question
Cấu trúc: WH-word + am/ is/ are + S +…?
Trả lời: S + am/ is/ are (+ not) +…
Ví dụ:
-
What
is
it? (Đây là cái gì?)
-
Where
am
I? (Tôi đang ở đâu?)
-
Who
is
that girl? (Cô gái đó là ai?)
Xoá bỏ cách học Tiếng Anh theo lối mòn, nhàm chán qua sách vở bằng phương pháp học TRỰC TUYẾN HIỆU QUẢ ngay tại đây
2.2. Thì hiện tại đơn với động từ thường
Công thức present simple với động từ thường có gì khác biệt với động từ To be? Cùng tìm hiểu nhé!
Thể khẳng định
Cấu trúc: S + V(s/ es) +…
Trong đó:
-
S
): Chủ ngữ
-
V
: Động từ
Lưu ý:
-
S = I/ You/ We/ They/ Danh từ số nhiều + ĐỘNG TỪ ở dạng NGUYÊN MẪU
-
S = He/ She/ It/ Danh từ số ít + ĐỘNG TỪ thêm “S” hoặc “ES”
Ví dụ:
-
I usually
wake
up early everyday. (Tôi thường xuyên dậy sớm mỗi ngày.)
→ Ở ví dụ này, chủ ngữ là “I” nên động từ chính “wake” ta để ở dạng nguyên mẫu không chia.
-
He never
watches
television. (Anh ấy không bao giờ xem vô tuyến.)
→ Trong câu này, chủ ngữ là “He” nên động từ chính “watch” phải thêm “es”.
(Ta sẽ tìm hiểu về quy tắc thêm “S” hoặc “ES” vào sau động từ ở phần sau)
Để luyện tập kỹ hơn, hãy làm bài tập thì hiện tại đơn nhé.
Thể phủ định
Cấu trúc: S + do/ does + not + V(nguyên mẫu) +…
Ta có:
-
Do not = don’t
-
Does not = doesn’t
Lưu ý:
-
S = I/ We/ You/ They/ Danh từ số nhiều + do + not
-
S = He/ She/ It/ Danh từ số ít + does + not
Ví dụ:
-
I
don’t go
shopping regularly. (Tôi không đi mua sắm thường xuyên.)
→ Trong câu này, chủ ngữ là “I” nên ta mượn trợ động từ “do” + not, và động từ “go” theo sau ở dạng NGUYÊN MẪU.
-
He
doesn’t work
on Sunday. (Anh ấy không làm việc vào chủ nhật.)
→ Ở ví dụ này, chủ ngữ là “He” nên ta mượn trợ động từ “does” + not, động từ “work” theo sau ở dạng NGUYÊN MẪU.
Thể nghi vấn
Câu hỏi Yes/No question
Cấu trúc: Do/ Does + S + V(nguyên mẫu) +…?
Trả lời:
-
Yes, S + do/ does.
-
No, S + do/ does + not.
Ví dụ:
- Do
you
like
eating pizza? (Bạn có thích ăn pizza không?)
Yes, I do./ No, I don’t.
→ Ở ví dụ này, chủ ngữ là “you” nên ta mượn trợ động từ “do”, động từ chính “like” ở dạng nguyên mẫu.
- Does
you mother
have
a sister? (Mẹ cậu có chị/em gái không?)
Yes, she does./ No, she doesn’t.
→ Trong câu này, chủ ngữ là “your mother” (tương ứng với ngôi “she”) nên ta mượn trợ động từ “Does” đứng trước chủ ngữ, động từ chính “have” ở dạng nguyên mẫu.
Câu hỏi WH- question
Cấu trúc: WH-word + do/ does + S + V (nguyên mẫu) +…?
Trả lời: S + V(s/ es) +…
Ví dụ:
-
What
do
you
like
doing in your free time?(Bạn thích làm gì vào thời gian rảnh?)
-
Where
does
she
work
? (Cô ấy làm việc ở đâu?)
Để test trình độ và cải thiện kỹ năng Tiếng Anh bài bản để đáp ứng nhu cầu công việc như viết Email, thuyết trình,…Bạn có thể tham khảo khóa học Tiếng Anh giao tiếp cho người đi làm tại TOPICA Native để được trao đổi trực tiếp cùng giảng viên bản xứ.
3. Cách sử dụng thì hiện tại đơn trong tiếng Anh
Cách dùng thì hiện tại đơn
Ví dụ về thì hiện tại đơn
Diễn tả một hành động, sự việc diễn ra thường xuyên, lặp đi lặp lại hay một thói quen.
-
I
watch
TV
everyday
. (Tôi xem vô tuyến mỗi ngày.)
→ Việc xem vô tuyến lặp lại hàng ngày nên ta dùng thì hiện tại đơn. Chủ ngữ là “I” nên động từ ở dạng nguyên mẫu.
-
My teacher
usually
gives
us homework. (Giáo viên thường xuyên cho chúng tôi bài về nhà.)
→ Việc giáo viên giao bài về nhà xảy ra thường xuyên nên ta dùng thì hiện tại đơn. Vì chủ ngữ là “my teacher” (tương ứng với “he” hoặc “she”) nên động từ “give” thêm “s”.
Diễn tả một sự thật hiển nhiên, một chân lý.
-
The Earth
goes
around the Sun. ( Trái đất quay quanh mặt trời.)
→ Đây là một sự thật hiển nhiên nên ta dùng thì hiện tại đơn, Chủ ngữ là “The Earth” (số ít, tương ứng với “it”) nên động từ “go” thêm “es”.
Diễn tả sự việc sẽ xảy xa theo lịch trình, thời gian biểu rõ ràng.
-
The plane
takes
off at 6 a.m today. (Máy bay sẽ cất cánh lúc 6 giờ sáng hôm nay.)
-
The train
leaves
at 10 p.m tomorrow. (Tàu sẽ rời đi vào 10 giờ tối mai.)
→ Mặc dù việc máy bay cất cánh hay tàu rời đi chưa diễn ra nhưng vì nó là một lịch trình nên ta dùng thì hiện tại đơn. Chủ ngữ là “The plane”, “The train” (số ít, tương ứng với “it”) nên động từ “take”, “leave” phải thêm “s”.
Diễn tả suy nghĩ, cảm xúc, cảm giác.
-
I
think
that your friend is a bad person. (Tớ nghĩ rằng bạn cậu là một người xấu.)
→ Động từ chính trong câu này là “think” diễn tả suy nghĩ nên ta dùng thì hiện tại đơn. Chủ ngữ là “I” nên động từ “think” ở dạng nguyên mẫu.
-
She
feels
very excited. (Cô ấy cảm thấy rất hào hứng.)
→ Động từ chính “feel” chỉ cảm giác nên ta dùng thì hiện tại đơn. Chủ ngữ là “She” nên động từ “feel” phải thêm “s”.
Để luyện tập kỹ hơn, hãy làm bài tập thì hiện tại đơn nhé.
4. Các dấu hiệu nhận biết thì hiện tại đơn trong tiếng Anh
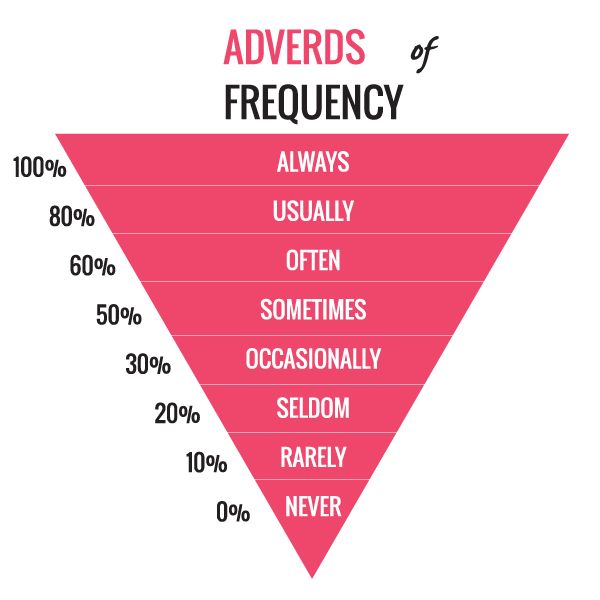
Khi trong câu có các trạng từ chỉ tần suất là dấu hiệu nhận biết hiện tại đơn
- Always (luôn luôn)
- usually (thường xuyên)
- often (thường xuyên)
- frequently (thường xuyên)
- sometimes (thỉnh thoảng)
- seldom (hiếm khi), rarely (hiếm khi)
- hardly (hiếm khi)
- never (không bao giờ)
- generally (nhìn chung)
- regularly (thường xuyên)
Ví dụ:
We sometimes go to the beach. (Thỉnh thoảng chúng tôi đi biển.)
I always drink lots of water. (Tôi thường hay uống nhiều nước.)
Ngoài ra, dấu hiệu hiện tại đơn còn có các từ:
- Every day, every week, every month, every year, every morning…(mỗi ngày, mỗi tuần, mỗi tháng, mỗi năm).
- Daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, yearly (hàng ngày, hàng tuần, hàng tháng, hàng quý, hàng năm)
Ví dụ:
They watch TV every evening. (Họ xem truyền hình mỗi tối.)
I play football weekly. (Tôi chơi đá bóng hàng tuần.)
Đặc biệt, cần chú ý đến các từ dưới đây để nhận biết dấu hiệu của thì hiện tại đơn:
- Once/ twice/ three times/ four times….. a day/ week/ month/ year,……. (một lần/ hai lần/ ba lần/ bốn lần ……..mỗi ngày/ tuần/ tháng/ năm)
Ví dụ:
He goes to the cinema three times a month. (Anh ấy đi xem phim 3 lần mỗi tháng.)
I go swimming once a week. (Tôi đi bơi mỗi tuần một lần.)
Vị trí của các trạng từ chỉ tần suất trong câu thì hiện tại đơn
Các từ nhận biết thì hiện tại đơn này thường đứng trước động từ thường, đứng sau động từ to be và trợ động từ (Always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, seldom,…).
Xem thêm: Ebook ngữ pháp cho người mới bắt đầu
5. Video hướng dẫn tất tần tật về thì hiện tại đơn
6. Quy tắc thêm “S” hoặc “ES” sau động từ
Ở dạng khẳng định của thì hiện tại đơn, với các chủ ngữ ngôi thứ 3 số ít (He/ She/ It), động từ phải thêm “S” hoặc “ES”
Nguyên tắc như sau:
1. Thêm “S” vào sau hầu hết các động từ
Ví dụ: come – comes; sit – sits; learn – learns;…
2. Thêm “ES” vào sau các động từ kết thúc bằng đuôi CH, SH, X, S, O
Ví dụ: crush – crushes; fix – fixes; kiss – kisses; box – boxes; quiz – quizzes;…
3. Nếu một động từ có đuôi “Y” mà trước nó là một nguyên âm (a, u, e, i, o) thì ta giữ nguyên “Y”, thêm “S”
Ví dụ: obey – obeys; slay – slays; annoy – annoys; display – displays;…
4. Nếu một động từ có đuôi “Y” mà trước nó là một phụ âm thì ta đổi “Y” thành “I” và thêm “ES”
Ví dụ: marry – marries; study – studies; carry – carries; worry – worries;…
5. Trường hợp đặc biệt
Ta có: have – has
Động từ “have” khi đi với chủ ngữ là ngôi thứ 3 số ít sẽ không thêm “s” mà biến đổi thành “has”.
Ví dụ:
- They have three children. (Họ có 3 người con.)
- She has two children. (Cô ấy có 2 người con.)
7. Cách phát âm phụ âm cuối s/es
Lưu ý các phát âm phụ âm cuối này phải dựa vào phiên âm quốc tế mà không phải dựa vào cách viết.
- /s/: Khi từ có tận cùng là các phụ âm /f/, /t/, /k/, /p/, /ð/
- /iz/:Khi từ có tận cùng là các âm /s/, /z/, /∫/, /t∫/, /ʒ/, /dʒ/ (thường có tận cùng là các chữ cái ce, x, z, sh, ch, s, ge)
- /z/: Khi từ có tận cùng là nguyên âm và các phụ âm còn lại
8. Cách sử dụng của thì hiện tại đơn trong bài thi IELTS
Mở đầu Speaking part 1/2/3 và Writing task 1/2
Ví dụ:
- I am a third-year student in Internal Auditing. (Tôi đang là sinh viên năm thứ ba học ngành Kiểm toán nội bộ) (Mở đầu – Speaking part 1)
- Well, my most favorite item of clothing is the yellow crop-top. (Món đồ tôi thích nhất là chiếc áo crop-top màu vàng) (Mở đầu – Speaking part 2 – “Describe your most favorite item of clothing” – Mô tả món đồ mà bạn yêu thích nhất)
- I think students should go to universities rather than vocational training courses. (Tôi nghĩ rằng sinh viên nên học đại học hơn là học nghề) (Mở đầu – Speaking part 3)
Mô tả sự thật trong Speaking part 1/2/3
Ví dụ:
- Advertisements are very relaxing and eye-catching. (Quảng cáo rất mang tính giải trí và bắt mắt) (Sự thật)
- Lady Gaga is famous all over the world. (Lady Gaga nổi tiếng trên toàn thế giới) (Sự thật)
Ngoài thì hiện tại đơn, các bạn cần học đầy đủ các thì khác để củng cố kiến thức nền tảng của mình.
9. Bài tập vận dụng thì hiện tại đơn

Để ghi nhớ hoàn toàn những kiến thức cấu trúc thì hiện tại đơn, bây giờ chúng ta hãy cùng vận dụng kiến thức để làm vài bài tập nho nhỏ về chia động từ ở thì hiện tại đơn nhé. Bài tập có cấu trúc rất cơ bản nên chắc chắn là bạn sẽ dễ dàng hoàn thành thôi.
Bài 1. Sử dụng công thức chia thì của hiện tại đơn để hoàn thành các câu sau.
-
My father always …………………………..delicious meals. (make)
-
Tom…………………………..vegetables. (not eat)
-
Rosie………………………….shopping every week. (go)
-
………………………….. Miley and David ………………………….. to work by bus every day? (go)
-
………………………….. your parents …………………………..with your decision? (agree)
-
Where……………………..that guy………………………from? (come)
-
Where ………………………….. your mother …………………………..? (work)
-
James …………………………… usually ………………………….. the trees. (not water)
-
Who …………………………..the washing in your house? (do)
-
They ………………………….. out once a week. (eat)
Đáp án
1. makes
2. doesn’t eat
3. goes
4. do…go
5. Do…agree
6. does…come
7. does…work
8. doesn’t usually water
9. does
10. eat
Bài 2. Mỗi câu sau chứa MỘT lỗi sai. Tìm và sửa chúng.
-
I often gets up early to catch the bus to go to school.
………………………………………………………………………
-
She teach students in a local high school.
………………………………………………………………………
-
They doesn’t own a house. They still have to rent one to live.
………………………………………………………………………
-
Dang Van Lam am a famous goalkeeper in the National Football Team.
………………………………………………………………………
-
What do your brother do?
………………………………………………………………………
-
Bruce and Tim doesn’t go swimming in the lake.
………………………………………………………………………
-
Hannah speak Chinese very well.
………………………………………………………………………
-
How often does she goes shopping in the supermarket?
………………………………………………………………………
-
Our dogs aren’t eat bones.
………………………………………………………………………
-
Mary’s parents is very friendly and helpful.
………………………………………………………………………
Đáp án
1. gets => get
2. teach => teaches
3. doesn’t => don’t
4. am => is
5. do your => does your
6. doesn’t => don’t
7. speak => speaks
8. goes => go
9. aren’t => don’t
10. is => are
Bài 3: Chọn dạng đúng của từ
- I catch/catches robbers. My dad is a driver.
- He always wear/wears a white coat.
- They never drink/drinks beer.
- Lucy go/goes window shopping seven times a month.
- She have/has a pen.
- Mary and Marcus cut/cuts people’s hair.
- Mark usually watch/watches TV before going to bed. Maria is a teacher.
- She teach/teaches students.
Đáp án
- catch
- wears
- drink
- goes
- has
- cut
- watches
- teaches
Bài 4: Sử dụng các động từ sau để hoàn thành câu.
believe eat flow go grow make rise tell translate
- The earth goes round the sun.
- Rice ……. in Britain.
- The sun …… in the east.
- Bees ……………….. honey.
- Vegetarians …… meat.
- An atheist ……. in God.
- An interpreter ……….. from one language into another.
- Liars are people who ………………. the truth.
- The River Amazon ……………….. into the Atlantic Ocean.
Đáp án
- goes
- doesn’t grow
- rises
- make
- don’t eat
- doesn’t believe
- translates
- don’t tell
- flows
Bài 5: Trả lời những câu hỏi sau sử dụng những trạng từ tần suất ở phần lý thuyết.
1. How often do you buy a new item of clothing?
…………………………………………………………………….
2. When do you often eat breakfast in the morning?
…………………………………………………………………….
3. What do you do?
…………………………………………………………………….
4. Do you have a pet?
…………………………………………………………………….
5. Are you afraid of spiders?
…………………………………………………………………….
Hy vọng với lý thuyết thì hiện tại đơn mà Topica Native vừa tổng hợp trên đây, bạn sẽ dễ dàng chinh phục thì tiếng Anh này. Nếu có bất kì thắc mắc gì, hãy để lại comment bên dưới để được giải đáp sớm nhất nhé. Chúc các bạn học tập tốt.
Để test trình độ và cải thiện kỹ năng Tiếng Anh bài bản để đáp ứng nhu cầu công việc như viết Email, thuyết trình,…Bạn có thể tham khảo khóa học Tiếng Anh giao tiếp cho người đi làm tại TOPICA Native để được trao đổi trực tiếp cùng giảng viên bản xứ.
Để luyện tập kỹ hơn, hãy làm bài tập thì hiện tại đơn nhé.
TOPICA Native cung cấp giải pháp học tiếng Anh trực tuyến tương tác 2 chiều với giáo viên bản ngữ hàng đầu Đông Nam Á. Tích hợp công nghệ AI hỗ trợ đào tạo, phần mềm luyện phát âm chuẩn mỹ Native Talk, giúp bạn nói tiếng Anh thành thạo chỉ sau 6 tháng từ con số 0.
present simple and present continuous
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

10-DARS | Present Simple (INGLIZ TILIDA HOZIRGI ZAMON)
Assalamu alaykum!
00:00 Kirish
01:35 Present Simple nima?
02:05 Present Simple formulasi
03:20 Inkor gap yasash (negative)
04:49 Savol gap yasash (question)
05:20 Present Simple qoidasi
06:20 Sketch misol
07:10 JUDA KUCHLI MOTIVATSIYA
General English: https://clck.ru/QMX2B
Ingliz tili 0 dan Grammatika: https://clck.ru/QMXCf
Ingliz tili 0 dan Amaliyot: https://clck.ru/QMXur
Elementary: https://clck.ru/QMhEy
English Consultant: https://clck.ru/QMhLh
Savollarga Javoblar: https://clck.ru/QMhRr
Video sizga yoqdi degan umiddamiz. Agar shunday bo’lsa, kanalimizga obuna(подписаться, subscribe) bo’ling hamda \”Like\”ni bosing.
Savol yoki takliflaringiz bo’lsa, komentariyda qoldirsangiz bo’ladi. Hammasiga javob berishga harakat qilamiz.
Online darslar:
https://www.leapenglish.uz
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/leapenglish
Online kutubxona:
https://t.me/Leaplibrary
Biz bilan bog’lanish:
https://t.me/Leapeng
Englishonline Ingliz_tili Present_Simple
KEEP MOVING AND LEAP FORWARD!

Talking about Your Family in English
Teach and learn the names of the family members in English and learn how to talk about your family.
https://www.kidspages.com

TẠI SAO HỌC MÃI MÀ KHÔNG GIỎI TIẾNG ANH??? 3 bí quyết luyện nói tiếng Anh tại nhà
Update: Mã trên video đã hết hạn nhưng mình sẽ vẫn làm việc với Cambly để có mã giảm giá thường xuyên cho các bạn khán giả The Present Writer. Các bạn có thể cập nhật trong post này: https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=355462699277078\u0026set=pb.100044400520488.2207520000..\u0026type=3
📱Tải Cambly trên smartphone tại đây:
► APPSTORE: https://apps.apple.com/us/app/camblyenglishteacher/id564024107
► GOOGLE PLAY: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.cambly.cambly
📌Honest Review của mình về Cambly: https://www.facebook.com/photo?fbid=329757321847616\u0026set=a.223753215781361
📌Để tiết kiệm và tận dụng triệt để Cambly: https://www.facebook.com/photo?fbid=330891665067515\u0026set=a.223753215781361
Tại sao học mãi mà tiếng Anh vẫn không được cải thiện? Video nói về một sai lầm \”chí mạng\” khi học tiếng Anh mà nhiều người gặp phải, trong đó có mình trước đây. Đồng thời, mình chia sẻ 3 cách để luyện nói tiếng Anh ngay tại nhà.
TIMESTAMP:
00:00 Mở đầu
00:41 Lý do học mãi mà không giỏi tiếng Anh
01:42 Ba cách luyện nói tiếng Anh tại nhà
01:49 1 Tự nói một mình
02:54 2 Thu âm/Ghi hình khi nói và xem lại
04:17 3 Nói với người bản ngữ
05:08 Cambly | 60% Off
08:26 Kết
THAM KHẢO THÊM:
🎥 Các video về học tiếng Anh: https://bit.ly/3ycnyHp
🎥 Các video về kỹ năng học tập: https://bit.ly/3tKejuM
BLOG:
https://thepresentwriter.com/blog/
📌Khoá học làm blog MIỄN PHÍ: https://www.subscribepage.com/a1z5x3
PODCAST:
https://thepresentwriter.com/podcast
INSTAGRAM:
https://www.instagram.com/thepresentwriter/
FACEBOOK:
https://www.facebook.com/PresentWriter
EMAIL:
[email protected] (cá nhân)
[email protected] (công việc)
THEO DÕI:
Đăng ký nhận newsletter miễn phí: https://thepresentwriter.com/theodoi/
BUY ME A COFFEE:
https://thepresentwriter.com/ungho/
//CÔNG CỤ:
🎥 CANON EOS M50 (camera): https://amzn.to/3hyzBVR
🎥 CANON EF 50mm (lens): https://amzn.to/3c5nsqb
🎙BLUE YETI NANO (microphone): https://amzn.to/3iM7RyB
💻 CANVA (thiết kế): https://bit.ly/3mcXQfK (30day free trial)
🎼EPIDEMIC SOUND (âm nhạc): http://share.epidemicsound.com/tpw (30day free trial)
🎬TUBEBUDDY (Youtube SEO): https://bit.ly/3c5m8nd
🖥 Vieo được biên tập với FINAL CUT PRO X
Disclosure: Video được tài trợ bởi Cambly. Một số đường link phía trên là affiliate link. Nếu bạn đăng ký sử dụng dịch vụ hoặc mua sản phẩm qua link này (chi phí không đổi cho bạn), The Present Writer sẽ nhận được khoản hoa hồng nhỏ để tiếp tục hoạt động và phát triển bền vững. Cảm ơn mọi người đã ủng hộ Chi và The Present Writer!
Special thanks to all the Cambly teachers who gave me their permission to share our conversations publicly!

Sara’s Day – featuring the Present Simple
What do you do EVERY DAY?
Wake up, go to work, have lunch, go home…
Watch this video about Sara’s day.
There are lots of examples of the PRESENT SIMPLE tense.
We use the Present Simple for repeated action, things that we always do.
Find out more about learning English with us:
Visit http://bigbusinessenglish.com/

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆMAKE MONEY ONLINE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ simple present