make to order คือ: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
SAP คือโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์ตัวหนึ่ง ที่ทำหน้าที่จัดการเกี่ยวกับทรัพยากรขององค์เพื่อให้เกิดประโยชน์สูงสุด ซึ่ง SAP จัดเป็น ERP ประเภทหนึ่งนั้นเอง การทำงานในปัจจุบันจะเป็น R/3 (ทำงานแบบ Client/Server) โดย
ในส่วน Application ทั้งหมดของระบบ SAPนั้น ถูกพัฒนาขึ้นด้วยภาษา ABAP หรือ Advance Business Application Programming (ABAP/4 ซึ่งเป็นภาษาโปรแกรมในยุคที่ 4 หรือ 4GL เป็นคำที่เรียกใน SAP Release 3.0 ส่วนใน SAP Release 4.0 เป็นต้นไป จะเรียกว่า ABAP เนื่องจากมีการพัฒนาภาษาโปรแกรม ABAP เป็นแบบObject-Oriented มากขึ้น) ในส่วนของ Run Time หรือ Kernel ของระบบ SAP นั้นถูกพัฒนามาจากภาษา C/C++ ในส่วนของการ Implement ระบบ SAP นั้น จะมีการทำ Customization หรือ Configuration (จริงๆแล้วก็คือการกำหนดค่า Parameter ต่างๆ) ผ่านทาง Implementation Guide (IMG) เพื่อให้ระบบงาน SAP ทำงานได้กับองค์กรนั้นๆซึ่งก็คือ SAP เป็น ERP Software Package ที่มีการทำงานในส่วนของ Customization ในระบบ SAP ให้เข้ากับหน่วยงานนั้นๆได้
Module ต่างๆของ SAP
ใน SAP 4.7 Enterprise ลงไป เค้าจะเรียกว่า SAP R/3 ซึ่งหมายถึง โครงสร้าง 3-tier client/server ซึ่งประกอบด้วย
1. Presentation Server (เป็น GUI คือฝั่ง client นั่นเอง)
2. Application Server
3. Database Server
ใน SAP 4.7 Enterprise ลงไปนั้น เราจะแบ่ง SAP เป็น module ต่างๆ ดังรูป
จากภาพเป็นการแสดงถึงระบบจำลองของ SAP ซึ่งประกอบไปด้วยโมดูลมากมาย ซึ่งแต่ละโมดูลมีฟังก์ชั่นการทำงาน และหน้าที่ต่างกันออกไปตามสายงาน โดยมี ABAP เป็นตัวเชื่อมโมดูลต่างๆ เข้าไว้ด้วยกัน
โมดูลของ SAP มีดังนี้
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING (Fl) – ระบบบัญชีไฟแนนซ์

เป็นระบบบัญชีแยกประเภทซึ่งง่ายและสะดวกในการใช้งาน เช่น สามารถกลับรายการให้อัตโนมัติ
(Reversing Voucher) และยังสามารถรองรับรายการที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำทุกเดือน เช่น รายการชำระค่างวดต่าง ๆ(Recurring Voucher) รวมถึงยังสามารถกำหนดสูตรในการทำการจัดสรรบัญชีต่าง ๆได้อัตโนมัติ สามารถทำงานร่วมกันหลายๆ บริษัทฯ หรือ หลายๆ หน่วยงาน สามารถกำหนดรายงานได้ตามความต้องการ (Report Writer)เพื่อจัดทำงบการเงินและรายงานอื่นๆ ได้ตามต้องการ
ระบบบัญชีมีอยู่หลายระบบ คือ
• General ledger
• Book close
• Tax
• Accounts receivable
• Accounts payable
• Consolidation
• Special ledgers
CONTROLLING (CO) – ระบบควบคุมต้นทุน

โปรแกรมจัดการเกี่ยวกับระบบต้นทุนการผลิต (Job Cost ) ช่วยในการจัดการบริหารการทำงานให้มีประสิทธิภาพมากยิ่งขึ้น ซึ่งระบบต้นทุนการผลิตสามารถควบคุมต้นทุนการผลิตสินค้าได้อย่างถูกต้อง เพราะสามารถที่จะกำหนดสูตรการผลิตสินค้าได้ เพื่อเพิ่มการควบคุมวัตถุดิบให้เป็นมาตรฐานเดียวกันในการผลิต สามารถประมาณการผลิตล่วงหน้าได้ก่อนที่จะมีการผลิตจริงเพื่อใช้ในการ วิเคราะห์ต้นทุนในการผลิต การจัดสรรเกี่ยวกับค่าใช้จ่ายต่าง ๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการผลิต เช่น แรงงาน วัตถุดิบ และค่าใช้จ่ายต่าง ๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการผลิต โปรแกรมสามารถอ้างอิงเอกสารจากระบบขายสินค้าได้ในกรณีที่มีการผลิตตามใบสั่งซื้อของลูกค้า เพื่อความถูกต้องในการอ้างอิงข้อมูลมาเพื่อทำการผลิตสินค้า และสามารถสร้างเอกสารใบขอซื้อให้อัตโนมัติในกรณีที่ไม่มีสินค้าในคลัง และตัดยอดสินค้าให้ในกรณีที่มีการเบิกวัตถุดิบไปผลิต ในระหว่างการผลิตหากมีการเบิกวัตถุดิบเพิ่ม, การส่งคืนวัถตุดิบ และมีค่าใช้จ่ายเพิ่มเติมจากประมาณการผลิตก็สามารถบันทึกรายการตามที่ เกิดขิ้นจริงได้ เมื่อผลิตสินค้าเสร็จ โปรแกรมจะมีระบบตรวจสอบสินค้าของสินค้าที่ผลิต (QC) เพื่อพิจารณาของดีหรือของเสียเพื่อนำเข้าคลังสินค้า ในกรณีที่มีของเสียก็สามารถนำไปผลิตใหม่ได้ และสามารถปันส่วนโสหุ้ยการผลิตได้ในกรณีค่าใช้จ่ายอื่น ๆ ที่ต้องการเพิ่มเป็นต้นทุนของสินค้า สิ่งที่สำคัญของการผลิตสินค้า คือการรับรู้ต้นทุนการผลิตที่ประมาณการไว้กับต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นจริง โดยโปรแกรมจะสรุปต้นทุนการผลิตที่เกิดขึ้นจริงจากการปิดใบสั่งผลิตเพื่อ เปรียบเทียบกับยอดประมาณการผลิตที่ตั้งไว้ และนำมาพิจารณาเพื่อปรับวิธีการทำงานหรือขั้นตอนการผลิต สามารถลดค่าใช้จ่ายและเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพในการทำงานให้มากยิ่งขึ้น
ระบบควบคุมต้นทุนมีอยู่หลายระบบ คือ
• Cost elements
• Cost centres
• Profit centres
• Internal orders
• Activity based costing
• Product costing
มีโมดูลย่อยได้แก่
Overhead Cost Controlling (CO-OM)
• Cost and Revenue Element Accounting (CO-OM-CEL)
• Cost Center Accounting (CO-OM-CCA)
• Overhead Orders (CO-OM-OPA)
• Activity-Based Costing (CO-OM-ABC)
Product Cost Controlling (CO-PC)
• Product Cost Controlling (CO-PC)
• Product Cost Planning (CO-PC-PRD)
• Cost Object Controlling (CO-PC-OBJ)
Profitability Analyses (CO-PA)
ASSET MANAGEMENT (AM) – ระบบการบริหารจัดการทรัพย์สิน

เป็นระบบที่ช่วยในการบริหารจัดการสินทรัพย์ที่มีอยู่ให้เกิดประสิทธิภาพสูงสุดในการใช้งาน นอกจากคำนวณค่าเสื่อมราคาแล้ว ยังมีระบบทะเบียนทรัพย์สินที่ช่วยอำนวยความสะดวกในการติดตามประวัติการใช้งานและค้นหาตำแหน่งที่ตั้งของสินทรัยพ์แต่ละตัว สามารถพิมพ์บาร์โค้ดเพื่อนำไปติดอยู่บนสินทรัพย์แต่ละชิ้น สามารถใช้งานร่วมกับ Barcode Scanner, Barcode Reader, Handheld PC และอุปกรณ์อื่นๆ
- รหัสทรัพย์สินสามารถแจกแจงได้เป็น Asset Group, Asset Sub-Group
- GL Transaction แยกตาม Asset Group และ ตาม Cost Center
- หน่วยงานที่รับผิดชอบทรัพย์สินสามารถบันทึกรายละเอียดตามสถานที่ตั้ง(Location),พนักงานที่ดูแลทรัพย์สิน
- กำหนดรหัสของทรัพย์สินหลัก (Parent Asset Code) ได้ และสามารถรายงานโดย Sort ตาม รหัสทรัพย์สินหลักได้
- กำหนดวิธีการคำนวณค่าเสื่อมราคาของแต่ละทรัพย์สิน มีให้เลือก 4 วิธี 1.Straight Line 2.Declining 3.Double Declining 4.None (สำหรับทรัพย์สินที่กฏหมายกำหนดไว้ว่าไม่ต้องคำนวณค่าเสื่อมราคา เช่น ที่ดิน เป็นต้น)
- บันทึกรายละเอียดต้นทุนของทรัพย์สินแต่ละตัว เช่น ราคาทรัพย์สิน, ค่าติดตั้ง, ค่าขนส่ง ,ค่าภาษี เป็นต้น
- สามารถบันทึกรายการซื้อย้อนหลังโดยให้ระบบคำนวณค่าเสื่อมราคาตั้งแต่วันที่ซื้อ บันทึกเป็นค่าเสื่อมราคาในงวดปัจจุบันได้
- บันทึกประวัติรายละเอียดการซ่อมแต่ละครั้งได้
- บันทึกการโอนย้ายทรัพย์สินระหว่าง หน่วยงาน,สถานที่ตั้ง,ผู้ดูแล พร้อมรายงานตรวจสอบความถูกต้องก่อนยืนยันการโอน
- บันทึกการขายทรัพย์สินหรือหยุดคำนวณค่าเสื่อม พร้อมรายงานเพื่อให้อนุมัติการตัดจำหน่าย
- มีรายงานทะเบียนทรัพย์สินพร้อมค่าเสื่อมราคา โดยแยกตามหน่วยงาน, โครงการ
- มีรายงานค่าเสื่อมราคา ประจำเดือนแบบสรุป สามารถแสดงทั้งยอดยกมา,รายการที่ตัดจำหน่วยในงวด,รายการที่ซื้อมาใหม่ในงวด และค่าเสื่อมของงวดปัจจุบัน
- มีรายงานวางแผนการจัดซื้อหรือตัดจำหน่ายล่วงหน้า 5 ปี (Planing Report)
- มีรายงานทรัพย์สินที่ต้องเสียภาษีโรงเรือน (Property Tax)
- รายงานการตรวจนับทรัพย์สิน สามารถสั่งให้ Sort ตาม Location ก่อนได้ เนื่องจากทรัพย์สินบางตัวถูกคำนวณค่าเสื่อมราคาของหน่วยงานใดหน่วยงานหนึ่ง แต่ตัวทรัพย์สินไม่ได้ตั้งอยู่ที่หน่วยงานนั้น
- รายงานทรัพย์สินที่เข้ามาระหว่าง งวด สามารถแยกเป็นทรัพย์สินที่เริ่มใช้งานแล้วหรืออยู่ระหว่างการติดตั้ง สามารถเลือกรายงานได้ทั้ง Monthly และ Yearly
- มีรายงานทรัพย์สินที่จำหน่ายไปหรือตัดบัญชีไประหว่างงวด สามารถเลือกรายงานได้ทั้ง Monthly และ Yearly
PROJECT SYSTEMS (PS) – ระบบบริหารโปรเจ็กต์งาน
• Make to order
• Plant shut downs (as a project)
• Third party billing (on the back of a project)
SALES AND DISTRIBUTION (SD) – ระบบการขาย และการจัดจำหน่าย

ระบบบริหารการขายมีอยุ่หลายระบบ คือ
• RFQ
• Sales orders
• Pricing
• Picking (and other warehouse processes)
• Packing
• Shipping
MATERIAL MANAGEMENT (MM) – ระบบบริหารวัสดุอุปกรณ์

โปรแกรมสินค้าคงคลัง PDP คือเครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการบริหารจัดการการเคลื่อนไหวของสินค้าสำเร็จรูป วัตถุดิบ เครื่องมืออุปกรณ์ วัสดุสินเปลือง เครื่องใช้สำนักงาน ฯลฯ ซึ่งสิ่งเหล่านี้ล้วนมีผลโดยตรงกับผลการดำเนินงานของธุรกิจว่าจะมีกำไรหรือขาดทุน โปรแกรมสต็อคยังช่วยในการควบคุมวัตถุดิบให้พอเหมาะต่อการใช้งานเพื่อไม่ให้มากเกินไป (ทำให้ต้นทุนสินค้าที่ผลิตสูงขึ้น) หรือน้อยเกินไป (ทำให้เสียโอกาสในการขายเพราะผลิตสินค้าไม่ทัน)
ระบบการบริหารวัสดุอื่นๆ มีดังนี้
• Requisitions
• Purchase orders
• Goods receipts
• Accounts payable
• Inventory management
• BOM’s
• Master raw materials, finished goods etc
PRODUCTION PLANNING (PP) – ระบบวางแผนการผลิต

เป็นระบบงานที่ใช้จัดทำแผนการผลิตทั้งระยะสั้นและระยะยาว โดยรองรับการจัดทำ Sales Forecast และProduction Forecastได้2ปีล่วงหน้า หรือตามที่กำหนด
สามารถจัดทำแผนการผลิตหลัก (MPS) ของสินค้าสำเร็จรูปได้ตามนโยบายการผลิตที่กำหนด ทั้งในกรณีผลิตตามคำสั่งซื้อของลูกค้า และผลิตเป็น Stock เผื่อขาย ซึ่งแผนการผลิตที่ได้จะถูกส่งไปเป็นคำสั่งผลิต ในระบบควบคุมการผลิตได้อัตโนมัติ
สามารถคำนวณความต้องการใช้วัตถุดิบ (MRP)ได้ตามสูตรการผลิต ซึ่งหลังจากประมวลผล ระบบจะสร้างแผนการผลิต และแผนการสั่งซื้อให้ตามความต้องการ และ Lead Time ที่กำหนด ซึ่งสามารถนำผลของการ
RUN MRP ไปสร้างคำสั่งผลิตในระบบควบคุมการผลิต และเปิดใบสั่งซื้อในระบบควบคุมการจัดซื้อได้ทันที
สามารถจัดทำแผนความต้องการกำลังการผลิต (CRP)ในแต่ละศูนย์การผลิตได้ โดยพิจารณาจาก Loading Order และ กำลังการผลิตสูงสุดของแต่ละศูนย์การผลิต
• Capacity planning
• Master production scheduling
• Material requirements planning
• Shop floor
QUALITY MANAGEMENT (QM) – ระบบควบคุมคุณภาพ

เป็นระบบงานที่ใช้สำหรับบันทึกข้อมูลการตรวจสอบคุณภาพของวัตถุดิบ(Incoming), สินค้าระหว่างผลิต(In Process) และสินค้าสำเร็จรูป (Final Inspection) ซึ่งสามารถสร้างข้อกำหนดที่ต้องการจะตรวจสอบสินค้าและวิธีการสุ่มตัวอย่างได้เอง ทั้งที่เป็นตัววัดเชิงปริมาณ(วัดค่าได้) และเชิงคุณภาพ (วัดค่าไม่ได้) สามารถบันทึกผลการตรวจสอบได้ทั้งแบบละเอียด และแบบสรุป มีการระบุสาเหตุของเสียหรือข้อบกพร่องที่ตรวจพบ สามารถออกรายงานทางสถิติต่างๆ เพื่อใช้ในการวิเคราะห์ผลของการตรวจสอบ และวัดระดับคุณภาพของสินค้าตลอดกระบวนการ อีกทั้งยังเชื่อมโยงกับระบบงานการควบคุมสินค้าคงคลัง เพื่อแสดงสถานะของสินค้าในคลังได้
• Planning
• Execution
• Inspections
• Certificates
PLANT MANAGEMENT (PM) – ระบบซ่อมบำรุง และงานดูแลต่างๆ
• Labour
• Material
• Down time and outages
HUMAN RESOURCE (HR) – ระบบบริหารงานบุคคล

• Employment history
• Payroll
• Training
• Career management
• Succession planning
มีโมดูลย่อยได้แก่
• Personnel Management (HR-PM)
• Organizational Management (HR-OM)
• Payroll Accounting (HR-PA)
• Time Management (HR-TM)
– Shift Planning
– Work Schedules
– Time Recording
– Absence Determination
– Error handling
• Personnel Development (HR-PD)
TREASURY (TR) – ระบบคลังสินค้า
มีโมดูลย่อยได้แก่
• Cash Management (TR-CM)
• Treasury Management (TR-TM)
• Funds Management (TR-FM)
• Market Risk Management (TR-MRM)
Workflow (WF) – ระบบกระบวนการทำงาน
INSDUSTRY SOLUTIONS (IS) – ระบบจัดการอุตสหกรรม
AP ย่อมาจาก System Application and Product in Data Processing
SAP เกิดขึ้นที่ประเทศเยอรมันในปี 1974 ถูกพัฒนาโดยการใช้โปรแกรม Program ABAP/4 หรือ Advance business application programming โดยปัจจุบันนี้ได้มีการพัฒนาระบบ SAP ให้สามารถใช้งานได้บนมือถือแล้วเรียกว่า SAP Unwire นั่นเอง
SAP เป็นโปรแกรมสำเร็จรูปทางธุรกิจประเภท ERP ที่ใช้งานอย่างแพร่หลายทั่วโลกโดยใช้ควบคุมทุกสายงานของบริษัท และสามารถรองรับธุรกิจได้หลายประเภท
จุดเด่นของระบบคือ เป็นระบบที่สามารถทำงานเชื่อมโยงกันแบบ Online และ realtime ซึ่งช่วยลดความซ้ำซ้อนในการบันทึกข้อมูลเเละเพิ่มความถูกต้องของข้อมูลด้วย
SAP มีหลายส่วน(ในขณะนี้เป็นเวอร์ชั่น 6) โดยแบ่งได้คร่าวๆดังนี้
SAP for industry
SAP xApps
mySAP Business Suite
SAP Smart Business Solution
SAP Netweaver สามารถเชื่อมต่อกับระบบอื่นได้
การจะศึกษา SAP นั้นมีหลาย Module ครับซึ่งผู้ที่จะศึกษาส่วนใหญ่จะเน้นไปแต่ละ Module จนเชี่ยวชาญ ซึ่ง Module แบ่งได้หลากหลายดังนี้
FI – โมดูลทางด้านบัญชีการเงิน
CO – โมดูลทางด้านบัญชีจัดการหรือบัญชีบริหาร
AM – โมดูลทางด้านการจัดการสินทรัพย์
SD – โมดูลทางด้านการขายและกระจายสินค้า
MM – โมดูทางด้านการจัดการวัตถุดิบ
PP – โมดูลทางด้านการวางแผนการผลิต
QM – โมดูลทางด้านการวางแผนคุณภาพ
PM – โมดูลทางด้านการซ่อมบำรุงโรงงาน
HR – โมดูลทางด้านการจัดการทรัพยากรบุคคล
WF – โมดูทางด้าน Flow การทำงาน
IS – เป็นส่วนงานเฉพาะกิจ ไม่ใช่โมดูลมาตรฐาน
Project Systems –
System Management – BASIS
Advanced Business Application Programming – ABAP

การทำงานของระบบ SAP จะทำงานแบบ 3-tiers คือ Database Server Layer, Application Server Layer และ Presentation Layer โดยการทำงานจะมี Dispatcher เป็นตัวติดต่อกับ SAP GUI และคอยกระจายงานให้กับ Work Process โดยตัว Dispatcher จะคอยตรวจสอบว่า Work Process ตัวใดว่างก็จะส่งงานให้ทำ จากนั้น Work Process ก็จะเข้าติดต่อกับ DB Process เพื่อนำข้อมูลออกมา
Work Process นั้นมี 5 ตัว ดังนี้
1. Enqueue – จะทำหน้า lock ข้อมูลเพื่อไม่ป้องกันไม่ให้ process เข้ามาทำงานทับซ้อนได้ในขณะที่ process ใด process หนึ่งทำงานอยู่
2. Dialog – เป็นส่วนที่ติดต่อกับ User
3. Background – เป็น process ที่ถูกรันอยู่ข้างหลังตลอดเวลา เช่น เราตั้งเวลาให้ process นี้ทำการตัดยอดทุกเที่ยงคืนเป็นต้น
4. Spool – เป็น process ที่ควบคุมการทำงานของเครื่องพิมพ์ โดยทำหน้าที่เก็บ log file ต่างๆ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นผู้สั่งพิมพ์ เวลาพิมพ์ พิมพ์จากเครื่องใด เป็นต้น
5. Update V1, V2 – เป็น process ที่คอยทำงานกับข้อมูลที่มีขนาดใหญ่ (Mass Data) โดย process จะแบ่ง priority เป็น 2 ระดับคือ V1 และ V2 โดยเราสามารถกำหนดให้ work process ทำงานแบบนี้ เช่น V1 > V2 นั่นหมายถึง V2 จะมี priority ในการทำงานต่ำกว่า V1 เป็นต้น
ภายใน Work Process แต่ละอัน จะประกอบด้วยส่วนต่างๆดังนี้
ส่วนที่ 1 Dialog Work Process ประกอบด้วย
Task Handler
ABAP Processor
DYNPRO Processor – ทำหน้าที่ประมวลผลบนหน้าจอ
DB Interface – เป็นตัวแปลคำสั่ง Database
ส่วนที่ 2 Local Memory ประกอบด้วย
User Context
Memory Space
List buffer
ส่วนประกอบของ work process
ระบบ SAP สามารถติดต่อฐานข้อมูลกับค่ายอื่นๆได้หลากหลาย แต่ที่นิยมมีอยู่ 5 ค่ายดังนี้
1. Informix
2. DB2
3. DB4
4. MSSQL
5. Oracle
การ Implement ระบบ SAP ส่วนใหญ่แบ่งเป็น 2 แบบคือ
1. 2 System Landscape
จากรูปการ Implement ลักษณะนี้จะมีข้อดีคือประหยัดค่าใช้จ่ายทางด้าน Hardware เพราะเราไม่ต้องเพิ่ม Server เพื่อทำการทดสอบ Production ก่อนขึ้นจริง แต่ก็จะมีข้อเสียคือ เสี่ยงหาก Production เกิดข้อผิดพลาด ถ้างานไม่สมบูรณ์ ซึ่งวิธีนี้ทาง SAP ไม่แนะนำ
2. 3 System Landscape
จากรูป การ Implement ลักษณะนี้จะมีข้อดี คือได้มีการทดลองงานต่างๆ ก่อนขึ้น production จริง ทำให้งานมีประสิทธิภาพ แต่ ข้อเสีย ก็คือ ต้องมีค่าใช้จ่ายเพื่อวาง server เพิ่ม แต่
คำศัพท์ที่ควรรู้ในระบบงาน SAP
– Module/Sub-Module คือ ระบบงาน/ระบบงานย่อย เช่น FI, AP, AM Submodule เป็นต้น
– Configuration – คือการกำหนดค่าให้ระบบสามารถทำงานตามที่วางแผนไว้ได้ตามผู้ใช้งาน
– System Parameter คือค่าที่ต้องระบุให้ระบบสามารถทำงานได้
– Session คือ หน้าจอการทำงานของระบบ SAP ซึ่งปกติระบบจะอนุญาติให้ทำงานได้พร้อมกัน 6 session
– Transaction Code คือ รหัสหมายเลขของหน้าจอการทำงาน เช่น หน้าจอการสร้างรหัสบัญชี คือ FSS0
การทำงานในระบบ SAP แบ่งออกเป็น 3 ทีม ดังนี้
1. ทีม Consult
2. ทีม Configuration
3. ทีม ABAP
คำสั่งใน SAPGUI
/o – open session ใหม่
/n – ปิด program
/nex – logoff จากระบบ SAP
/i – ลบ session ที่ทำงานอยู่ปัจจุบัน
/bend
/nSkip
Table of Contents
ตัวอย่างผลิตภัณฑ์ของ SAP
ขอขอบคุณ
ที่มา http://www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/ASIN/0471179965/sapinformation0e/102-4244053-0591316
ที่มา http://www.apacsoftware.co.th/modules.php?name=InventoryControl
http://mybi-dw.blogspot.com/2011/10/sap.html
ที่มา http://www.bbs.co.th/Manufacturing_SF.html
ที่มา http://www.crystalsoftwaregroup.com/pageconfig/viewcontent/viewcontent1.asp?pageid=1187&directory=8473&contents=3330
ที่มา http://www.prosoft.co.th/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=486&Itemid=815
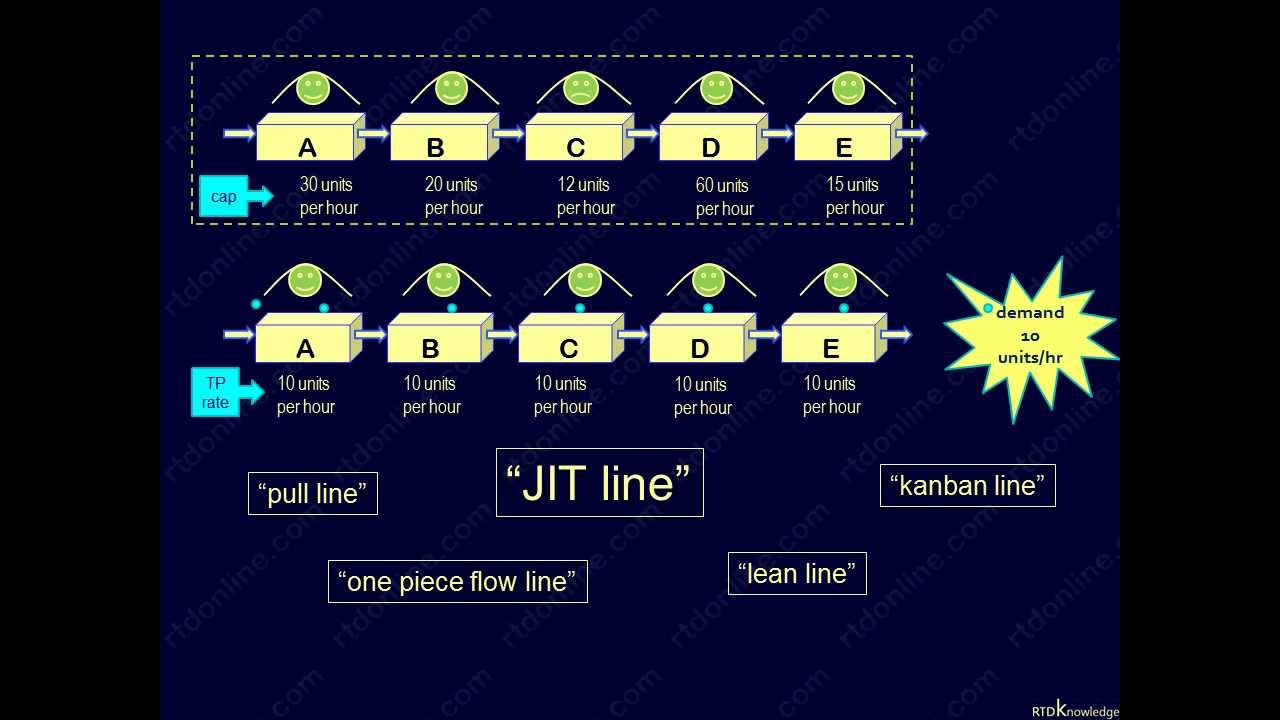
[NEW] Make to order (MTO) vs make to stock (MTS) — Katana | make to order คือ – NATAVIGUIDES
What are the advantages of make to stock?
As already stated before, this might be a viable method for you, depending on your type of business.
But we’ll still look at the advantages and disadvantages to understand if make to stock is a strategy you should incorporate. Three advantages are:
1. Spread resources and production
As you’ll be manufacturing your products ready for the customer’s demand, you can properly and carefully organize your resources and production that will be carried out to maximize your efficiency.
2. Make to stock scheduling
Using this method means that you’ll be able to design a master production schedule to make sure your workflow is as smooth as it can possibly be. It allows you and your employees to know where they need to be and what is left to do.
3. Minimize customer wait times
Finally, your products will be waiting for your customers – obviously if everything is completed on time. As soon as your customers have placed their order, their product can be shipped out to them, reducing the customers waiting time by a huge amount.
Using a make to stock method seems like a dream come true for someone who values organization and has complete control of their business’s workflow.
The best defense is a strong offense, so to speak.
What are the disadvantages of make to stock?
However, this tactic can also come with some disadvantages as, for the most obvious reason, this type of manufacturing process relies heavily on the assumption of the industry.
Let’s take a look at three disadvantages that could affect you and your business:
1. Unpredictable nature of consumer trends
You forecast by analyzing historical sales and seasonal spikes, but even though you’ve made it as completely accurate as you can and with correct assumptions, your products, unfortunately, aren’t selling as well as you originally predicted.
Or the other extreme, a sudden boom that you weren’t prepared for. It’s just the nature of the beast.
2. Inventory levels
You can technically be in a perpetual state of either having too much or not enough stock.
3. The difficulty making accurate sales forecasts
The industry can be complex and affected by a ton of variables, so that already makes it difficult to forecast your sales. However, one little mistake or miscalculation means you could end up with too little or an excess of stock, which will cost your business.
There are pros and cons to following either workflow — make to stock vs make to order.
However, you should know that if you decide to organize production following one of these tactics, that doesn’t have to be your final choice. You can experiment and switch between the two, or it might even be beneficial for your business to switch completely over to a different workflow. It all depends on your business’s needs.
But, either way, you probably realize that there is a lot of work needing to be done, regardless of choice.
And when it comes down to brass tacks, successful implementation is what’s key here.
But, how?
Make-to-stock vs. Make-to-order (Push vs. Pull)
Maketostock vs. Maketoorder (Push vs. Pull)
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่
How to Order Food in an American Restaurant – Travel English
Learn the insider vocabulary you need to order food in an American restaurant like a local!
Decode authentic, unscripted conversations by fasttalking Americans with my American Accent Survival Kit. It’s free at https://christinarebuffet.com/americanaccentsurvivalkit2/
Complete transcript of this episode \u0026 vocabulary at https://christinarebuffet.com/blog/orderfoodinanamericanrestaurant/
MORE FUN ENGLISH LESSONS!
How much to tip in the USA: http://bit.ly/2ue1cnE
Getting through US customs at the airport: http://bit.ly/2tEXGTt
How to rent a car in the USA: http://bit.ly/2taibqg
Become fluent in English and have fun learning with my weekly video lessons on American English.
You’ll increase your vocabulary in English, improve your pronunciation, boost your Business English, and become fluent faster.
Become a Speak English Ambassador and receive a new English lesson every week: http://bit.ly/SEwCjoin
PRACTICE ENGLISH EVERY DAY WITH ME ON SOCIAL MEDIA:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/SpeakEnglishWithChristina/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/christinarebuffetbroadus
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/speakenglishwithchristina/

เป็นหยังยังฮักอยู่ – มีนตรา อินทิรา【LYRIC VIDEO】
เพลง : เป็นหยังยังฮักอยู่
ศิลปิน : มีนตรา อินทิรา
อัลบั้ม : อินทิรา
IG : ms.meentra
FB : https://www.facebook.com/meentraintira/
Line : https://line.me/ti/g2/OolIN5AZJdWfblaEcEyYw/
TikTok : https://www.tiktok.com/@ms.meentra
ติดต่องานจ้าง โทร.0854847345
คำร้อง/ทำนอง : ภานุวัฒน์ วิเศษวงษา
เรียบเรียง : จินนี่ ภูไท
Executive Producer \u0026 Strategic Planner : พิชญ์ ทอมมัส
Producer : จินนี่ ภูไท
Vocal Director : กริช ทอมมัส
Mixed \u0026 Mastered : จินนี่ ภูไท
Creative Director : ธิดารัตน์ ชูรัตน์
Art Creator : กิตติพันธุ์ มหากิจกำพล
Music Video : Kick the Dust
อาจสิเห็นว่าเค้าบ่เป็นหยัง
อยู่ลำพังคนเดียวกะไหว
อาจสิบ่แสดงอาการเสียใจ
คือจั่งคนถืกถิ่มมา
แต่ในใจมีไผสิฮู้
ว่าซุมื้อต้องอยู่กับน้ำตา
ตั้งแต่มื้อที่เธอถิ่มป๋า
ความเจ็บบ่เคยจางหาย
คือมื้อที่เธอนั้นมีคนใหม่
คือมื้อที่เค้าบ่อยากหายใจ
บ่ฮู้มื้อได๋ความเจ็บจั่งสิตาย
ไปจากหัวใจ
เป็นหยังยังฮักเธออยู่
เป็นหยังยังคิดฮอดอยู่
เป็นหยังยังอยากเห็นหน้าเธออยู่
สิล้มสิตาย
ทั้งที่มันกะโดนเติบแล้ว
ที่เธอถิ่มเค้าไป
แต่ความเจ็บกะยังบ่เคยไปไส
ใจยังฮักคนที่มันหลายใจ คือเก่า
อาจสิเห็นว่าเค้าเก่งคือหยัง
กินข้าวเบิ่งหนังคนเดียวกะได้
อาจสิเห็นว่ามื้อที่บ่มีไผ
กะอยู่ได้บ่มีปัญหา
แต่ในใจมีไผไผสิฮู้
ว่าซุมื้อเขาอยู่กับน้ำตา
ตั้งแต่มื้อที่เธอถิ่มป๋า
ความเจ็บบ่เคยจางหาย
ใจยังฮักคนที่มันหลายใจ บ่เคยสร่างซา
เป็นหยังยังฮักอยู่ มีนตราอินทิรา
❤︎ ติดตามอัพเดทผลงานศิลปิน Grammy Gold ได้ที่
Line@ : http://bit.ly/LineGold
IG : Grammygold_Official
YouTube : http://bit.ly/GrammyGoldOfficial
Twitter : http://bit.ly/TwitGold
Facebook : http://bit.ly/FBgmmGold
☎ ติดต่องานจ้างศิลปิน แกรมมี่โกลด์ โทร.0854847345

Here’s How Professional Models Are Made (Very Satisfying)
This video takes us inside a professional modelbuilding shop in Chicago called Presentation Studios International (PSI). They make models for all kinds of clients, but mostly for developers and architects. We get a tour of the shop from Robert Becker, an architectural designer and former employee. He helps us understand how models are conceptualized a little differently here than within an architectural office or in school. Here, they are almost strictly miniature buildings with the job of faithfully depicting a building design and serving as a persuasive tool to motivate investment. Then, we hear from Martin Chadwick, a lifelong model builder to talk through the process of making highquality miniature buildings and landscapes.
__Membership__
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCYAm24PkejQR2xMgJgn7xwg/join
__About the Channel__
Architecture with Stewart is a YouTube journey exploring architecture’s deep and enduring stories in all their bewildering glory. Weekly videos and occasional live events breakdown a wide range of topics related to the built environment in order to increase their general understanding and advocate their importance in shaping the world we inhabit.
__About Me__
Stewart Hicks is an architectural design educator that leads studios and lecture courses as an Associate Professor in the School of Architecture at the University of Illinois at Chicago. He also serves as an Associate Dean in the College of Architecture, Design, and the Arts and is the cofounder of the practice Design With Company. His work has earned awards such as the Architecture Record Design Vanguard Award or the Young Architect’s Forum Award and has been featured in exhibitions such as the Chicago Architecture Biennial and Design Miami, as well as at the V\u0026A Museum and Tate Modern in London. His writings can be found in the coauthored book Misguided Tactics for Propriety Calibration, published with the Graham Foundation, as well as essays in MONU magazine, the AIA Journal Manifest, Log, bracket, and the guestedited issue of MAS Context on the topic of character architecture.
__Contact__
FOLLOW me on instagram: @stewart_hicks \u0026 @designwithco
Design With Company: https://designwith.co
University of Illinois at Chicago School of Architecture: https://arch.uic.edu/

Luyện nghe tiếng Anh thụ động-IELTS|I’m Mary
luyệnnghe nghetiếnganh ielts nghethụđộng
Luyện nghe tiếng Anh thụ độngIELTS|I’m Mary
Luyện nghe tiếng anh thụ động trong khi làm việc nhà sẽ giúp bạn vừa cải thiện kĩ năng nghe tiếng anh vừa tiết kiệm thời gian.
Learn English with me!!! I’m Mary.
♥♥♥Các bạn nhớ ấn Đăng Ký mình để nhận videos mới mỗi ngày nhé ♥♥♥
Love all.
Cre: Collins Listening for IELTS
Edit: by me
Những Track trong video này:
Track 1 [ 00:00 ]
Track 2 [00:52]
Track 3 [ 2:12 ]
Track 4 [ 3:15 ]
Track 5 [ 4:02 ]
Track 6 [ 5:17 ]
Track 7 [ 7:07 ]
Track 8 [ 9:52 ]
Track 9 [ 11:24 ]
Track 10 [ 13:13 ]
Track 11 [ 14:05 ]
Track 12 [ 15:40 ]
Track 13 [ 17:31 ]
Track 15 [ 19:49 ]
Track 16 [ 20:21 ]
Track 17 [ 22:12 ]
Track 18 [ 24:42 ]
Track 19 [ 27:24 ]
Track 20 [ 29:18 ]
Track 21 [ 30:41 ]
Track 22 [ 31:36 ]
Track 23 [ 33:19 ]
Track 24 [ 35:58 ]
Track 25 [ 37:27 ]

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่LEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ make to order คือ