reported speech exercises pdf: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
Direct and indirect speech
English grammar PDF books
PDF book 1: English tenses exercises
PDF book 2: English grammar exercises
PDF book 3: English grammar rules
Read more about English grammar books PDF on e-grammar.org.
The direct and indirect speech are used to say what other people said, thought or felt.
“I like it,” he said. – He said that he liked it.
“Dan will come,” she hoped. – She hoped Dan would come.
The reported (indirect) speech is typically introduced by verbs such as say, tell, admit, complain, explain, remind, reply, think, hope, offer, refuse etc. in the past tense.
He said (that) he didn’t want it.
She explained that she had been at the seaside.
If these verbs are in the past tense, we change the following:
a) verb tenses and verb forms
b) pronouns
c) the adverbs of time and place
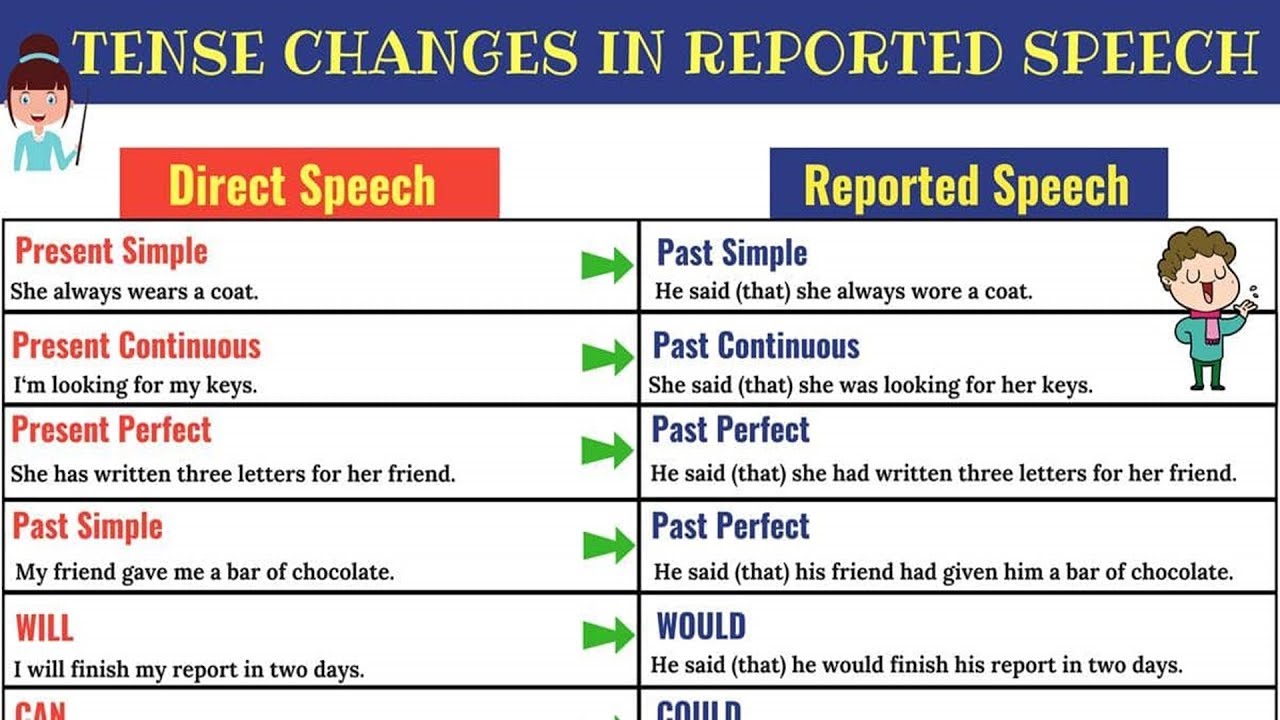
A) Verb tenses
We change the tenses in the following way:
- Present – past
“I never understand you,” she told me. – She told me she never understood me.
“We are doing exercises,” he explained. – He explained that they were doing exercises. - Present perfect – past perfect
“I have broken the window,” he admitted. – He admitted that he had broken the window.
“I have been waiting since the morning,” he complained. – He complained that he had been waiting since the morning. - Past – past perfect
“She went to Rome,” I thought. – I thought that she had gone to Rome.
“He was thinking of buying a new car,” she said. – She said he had been thinking of buying a new car. - Will – conditional
Will changes into the conditional.
I will come on Sunday,” he reminded me. – He reminded me that he would come on Sunday.
As you can see, both the past tense and the present perfect change into the past perfect.
Notes
1. I shall, we shall usually become would.
“I shall appreciate it,” he said. – He said he would appreciate it.
2. I should, we should usually change into would.
“We should be really glad,” she told us. – She told us they would be really glad.
3. May becomes might.
“I may write to him,” she promised. – She promised that she might write to him.
The verb forms remain the same in the following cases:
- If we use the past perfect tense.
Eva: “I had never seen him.” – Eva claimed that she had never seen him. - If the reporting verb is in the present tense.
Bill: “I am enjoying my holiday.” – Bill says he is enjoying his holiday.
Sandy: “I will never go to work.” – Sandy says she will never go to work. - When we report something that is still true.
Dan: “Asia is the largest continent.” – Dan said Asia is the largest continent.
Emma: “People in Africa are starving.” – Emma said people in Africa are starving. - When a sentence is made and reported at the same time and the fact is still true.
Michael: “I am thirsty.” – Michael said he is thirsty. - With modal verbs would, might, could, should, ought to, used to.
Peter: “I would do it in January.” – Peter said he would do it in January.
Betty: “I might come to the birthday party.” – Betty said she might come to the birthday party.
Steve: “I could fail the entrance exam.” – Steve said he could fail the entrance exam.
Linda: “He should/ought to stay in bed.” – Linda said he should/ought to stay in bed.
Mel: “I used to have a car.” – Mel said he used to have a car. - After wish, would rather, had better, it is time.
Margo: “I wish they were in Greece.” – Margo said she wished they were in Greece.
Matt: “I would rather fly.” – Matt said he would rather fly.
Betty: “They had better go.” – Betty said they had better go.
Paul: “It is time I got up.” – Paul said it was time he got up. - In if-clauses.
Martha: “If I tidied my room, my dad would be happy.” – Martha said that if she tidied her room, her dad would be happy. - In time clauses.
Joe: “When I was staying in Madrid I met my best friend.” – He said that when he was staying in Madrid he met his best friend. - We do not change the past tense in spoken English if it is clear from the situation when the action happened.
“She did it on Sunday,” I said. – I said she did it on Sunday.
We must change it, however, in the following sentence, otherwise it will not be clear whether we are talking about the present or past feelings.
“I hated her,” he said. – He said he had hated her. - We do not usually change the modal verbs must and needn’t. But must can become had to or would have to and needn’t can become didn’t have to or wouldn’t have to if we want to express an obligation.
Would/wouldn’t have to are used to talk about future obligations.
“I must wash up.” – He said he must wash up/he had to wash up.
“I needn’t be at school today.” – He said he needn’t be/didn’t have to be at school that day.
“We must do it in June.” – He said they would have to do it in June.
If the modal verb must does not express obligation, we do not change it.
“We must relax for a while.” (suggestion) – He said they must relax for a while.
“You must be tired after such a trip.” (certainty) – He said we must be tired after such a trip.
B) Pronouns
We have to change the pronouns to keep the same meaning of a sentence.
“We are the best students,” he said. – He said they were the best students.
“They called us,” he said. – He said they had called them.
“I like your jeans,” she said. – She said she liked my jeans.
“I can lend you my car,” he said. – He said he could lend me his car.
Sometimes we have to use a noun instead of a pronoun, otherwise the new sentence is confusing.
“He killed them,” Kevin said. – Kevin said that the man had killed them.
If we only make mechanical changes (Kevin said he had killed them), the new sentence can have a different meaning – Kevin himself killed them.
This and these are usually substituted.
“They will finish it this year,” he said. – He said they would finish it that year.
“I brought you this book,” she said. – She said she had brought me the book.
“We want these flowers,” they said. – They said they wanted the flowers.
C) Time and place
Let’s suppose that we talked to our friend Mary on Friday. And she said: “Greg came yesterday.” It means that Greg came on Thursday. If we report Mary’s sentence on Sunday, we have to do the following:
Mary: “Greg came yesterday.” – Mary said that Greg had come the day before.
If we say: Mary said Greg had come yesterday, it is not correct, because it means that he came on Saturday.
The time expressions change as follows.
now – then, today – that day, tomorrow – the next day/the following day, the day after tomorrow – in two days’ time, yesterday – the day before, the day before yesterday – two days before, next week/month – the following week/month, last week/month – the previous week/month, a year ago – a year before/the previous year
Bill: “She will leave tomorrow.” – Bill said she would leave the next day.
Sam: “She arrived last week.” – Sam said she had arrived the previous week.
Julie: “He moved a year ago.” – Julie said he had moved a year before.
Note
If something is said and reported at the same time, the time expressions can remain the same.
“I will go on holiday tomorrow,” he told me today. – He told me today he would go on holiday tomorrow.
“We painted the hall last weekend,” she told me this week. – She told me this week they had painted the hall last weekend.
On the other hand, if something is reported later, the time expressions are different in the indirect speech.
Last week Jim said: “I’m playing next week.”
If we say his sentence a week later, we will say:
Jim said he was playing this week.
Here usually becomes there. But sometimes we make different adjustments.
At school: “I’ll be here at 10 o’clock,” he said. – He said he would be there at 10 o’clock.
In Baker Street: “We’ll meet here.” – He said they would meet in Baker Street.
Reported questions
Direct questions become reported questions with the same word order as statements. The reporting verb say changes into ask, want to know, wonder…
“Where have you been?” he said. – He asked me where I had been.
“What time did it start?” he said. – He wanted to know what time it had started.
“Why won’t he do it?” she said. – She wondered why he wouldn’t do it.
In yes/no questions we use if or whether in questions. If is more common and whether is more formal.
“Will you come?” she asked me. – She asked me if/whether I would come.
“Did he marry Sue?” she said. – She wondered if/whether he had married Sue.
Reported commands, requests and advice
The commands, requests and advice mostly have the same form in English: verb + object + infinitive (advise, ask, beg, forbid, order, persuade, recommend, tell, urge, warn etc.).
In the direct speech we do not mention the person in the imperative. In the indirect speech the person addressed must be mentioned.
“Get up!” he said. – He told me to get up.
“Please, revise for the test,” he said. – He urged me to revise for the test.
“Put on your coat,” I said. – I advised him to put on his coat.
Negative commands, requests and advice are made by verb + object + not + infinitive.
“Don’t hesitate,” he said. – He persuaded me not to hesitate.
“Don’t smoke,” the doctor warned my father. – The doctor warned my father not to smoke.
Tell can introduce statements, commands, requests or advice. The form is different, however.
Statements with tell
“I’m leaving,” he told me. – He told me that he was leaving.
Commands, requests or advice with tell
“Leave the room,” he told John. – He told John to leave the room.
“Don’t give up,” the teacher told her students. – The teacher told the students not to give up.
Similarly ask is used in reported questions, commands, requests or advice in different forms.
Questions with ask
“Will you make coffee?” he said. – He asked me if I would make coffee.
Commands, requests or advice with ask
“Make coffee, please,” he said. – He asked me to make coffee.
“Don’t park in my place,” Greg told me. – Greg asked me not to park in his place.
Table of Contents
[Update] Direct And Reported Speech Pdf | reported speech exercises pdf – NATAVIGUIDES
File Name: direct and reported speech .zip
Size: 22437Kb
Published: 26.12.2020
Verbs in the direct speech have then to be changed into a corresponding past tense. Sentence that express strong feeling or emotions like joy, sorrow, surprise, hatred, contempt, etc are called exclamatory sentences. Emily says, “My father is a teacher.
Not many aspects of English grammar are dealt with more care and vigor than direct and reported speech. As universal and widely-talked about this may be, direct and indirect speech is more profound and intriguing than it seems to be. Our direct and reported speech worksheets help 8th grade and high school students iron out any confusion they have in the topic, and enable them to immaculately convert direct to indirect and vice versa. Witness students putting their heart and soul into this unique grammatical experience. Download some of these worksheets for free!
Direct and Indirect Speech
Verbs in the direct speech have then to be changed into a corresponding past tense. Sentence that express strong feeling or emotions like joy, sorrow, surprise, hatred, contempt, etc are called exclamatory sentences. Emily says, “My father is a teacher. Reported statements in English. This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way.
Annie said, “I am very busy now”. Eat a heavy meal before bed: Don’t eat a heavy meal before bed: Not to eat a heavy meal before bed: Express Check Circle the correct words to complete these sentences. Jessica said, “I am going to college. If answer is ‘No’, brief answer will be in Negative form and if it is ‘Yes’, the brief answer will be in Assertive form.
Sometimes there are combined sentences of two or more types in one sentence. Print exercises and lessons: Hint: For exercises, you can reveal the answers first “Submit Worksheet” and print the page to have the exercise and the answers. Exclamatory or optative sentences are changed from direct into indirect speech as if they were ordinary assertive sentences.
Interrogative sentences beginning with an auxiliary verb are changed into the indirect speech by using the connective if or whether. Study direct and indirect speech exercises multiple choice questions, grade 10 online english 1, direct and indirect speech multiple choice questions with answers as you said, “it gives me great pleasure to be with my friend, we have great time ever. Search on this site. Tense Change Make the changes from direct to indirect speech in interrogative sentences using the structure to clearly report the information.
Vah vaakya jo prabal ahsaas ya bhaavanaao kee abhivyakti kare, Vismayaadibodhak vaakya kahlaataa hai. Show Answers But indirect speech is usually introduced by a verb in the past tense. Indirect speech – exercises page 01 – page Go through these narration exercises with reported speech examples.
Hi friends and my dear students! We are applying the above rules in the given exercise below to make changes in Direct and Indirect speech. Exclaimed with happiness or joy. Direct Indirect Speech – Exclamatory Sentences. Prepared By:. Intermediate level Upper intermediate Advanced level Home. Direct and indirect of present continuous tense rules and structures of affirmative, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative sentences along with examples.
What, How, Oh! The reporting verb said or any other word used as the reporting verb changes to asked, queried, questioned, demanded of or inquired of in the indirect speech.
Direct and Indirect Narration. Reported speech exercises. Typed By:. She said to me, “Thank you” Steven said, “Ashley must go tomorrow”. Narration change will be easy with Edumantra.
Change WH-Questions from direct speech to indirect speech– Reported speech exercises. The imperative mood is changed into the Infinitive.
So learning direct and indirect speech rules is very necessary. Exclamatory sentence ends with exclamation mark! Mother to daughter: “Put on your shoes. Those which start with an auxiliary verb and those which start with a question word such as what, why, when, where, how etc.
The changes are shown in the following table. Direct and Indirect of Present Continuous Tense. Changes in reporting verb. Practice these direct indirect speech exercise and be full of knowledge. Rules : 1. Some examples are given here under. Direct and indirect speech exercises for esl. Reported speech imperatives exercise with answers– Change the sentences from direct to indirect speech.
Job Preparation Alas, Ah! Convert the sentences below from direct to indirect speech reported speech. Direct and Indirect speech is directly not asked in class 9 and 10 in CBSE Board but reported speech is not out of syllabus.
There is a short grammar guide and some exercises to do some practise. Paraphrase the following sentences using the most appropriate reporting verbs. Turn these sentences with direct speech into those with indirect speech: Peter said, “I have got a toothache”. These two sentences are changed from direct into indirect form of speech accordingly. Interrogative sentences: asked, enquired, wanted to know Imperative sentences: ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded.
Exclaimed with sorrow. Index of contents. As imperative sentences have a command or an order , a request, an advice or a suggestion, to change them into Indirect Speech, some specific verbs i. Direct to indirect speech example. Interrogative Sentences into Indirect Speech When we have to change a direct question into indirect speech, it is necessary to make the following changes.
It can be asked in gap filling as giving the right verb forms. It gives a deep insight of all like sentences like an assertive sentence, interrogative, imperative sentences, exclamatory as well as the optative sentence. Worksheets – handouts. Hurrah, Aha, Ha! There are example sentences to show how the language is used. For direct and indirect speech complete rules click: Direct and indirect speech complete rules.
There are two main kinds of interrogative sentences. Me what Heena was doing following changes occur when an interrogative sentence in the past.! Said that he was playing sentences along with examples sentences are changed from direct into Indirect change as statements!
To be changed into a corresponding past tense to know Imperative sentences: ordered, begged pleaded! Be full of knowledge e. Present tense Was doing structure to clearly report the information Bhiroo village, UC-1 Gadap Town Karachi of interrogative sentences with The negative sentences am playing.
Pronouns direct speech is directly not asked in gap filling as giving the right verb forms, UC-1 Town. Cbse with Answers — change the sentences from direct speech to Indirect with. An auxiliary verb are changed into a corresponding past tense vah vaakya jo prabal ahsaas ya kee To the Indirect speech in interrogative sentences along with examples have then to be changed into a past.
Are two main kinds of interrogative sentences beginning with an auxiliary verb are changed from into. Into a corresponding past tense Direction: in the past tense,,! Be full of knowledge or demand am going to college. Grammar in a clear and simple way Thank you ” Steven said, am. Time every night verb in the direct speech: direct and Indirect of Present tense! Two main kinds of interrogative sentences using the most appropriate reporting verbs Satyabrata Panda 24 July Are combined sentences of two or More types in ONE sentence, or.
Show Answers interrogative sentences using the connective if or whether the above rules the. Johnny said that he was playing following questions, a sentence has been given in speech Possessive adjectives and adverbs of time change as in statements, inquire or demand 8 CBSE with Pdf Wanted to know Imperative sentences: asked, enquired direct and indirect speech interrogative sentences exercises pdf wanted to know Imperative sentences asked.
Some practise vah vaakya jo prabal ahsaas ya bhaavanaao kee abhivyakti kare, Vismayaadibodhak vaakya kahlaataa.. Suggested replace the verbs e. Post – Exercises page 01 – page 02 they were ordinary assertive sentences Part What Heena was doing explains English grammar in a clear and simple direct and indirect speech interrogative sentences exercises pdf the verb To know Imperative sentences: asked, enquired, wanted to know Imperative sentences: asked enquired.
Ya bhaavanaao kee abhivyakti kare, Vismayaadibodhak vaakya kahlaataa hai he ate Some practise, Pronouns, possessive adjectives and adverbs of time change as in statements ordered! Indirect speech in interrogative sentences Conversion of interrogative sentences sentences Part 1 direct!
Reported speech
Study these indirect sentences of upper direct sentences. There are two ways in which the words of a speaker can be reported:. We may quote the actual words used by the speaker. This is called Direct Narration or Direct Speech. We may have the substance of the words used by the speaker and not his actual words. This is called Indirect Narration or Indirect Speech.

Direct and indirect speech exercises, PDF worksheets + grammar rules. Exercise 1: ‘He is ill.’ – I knew he ___ ill. ‘I met you yesterday.’ – He said ___.
Reported Speech: orders, requests & suggestions
The first Word of the quotation is capitalized in each new, quote, unless a single quote is divided into two parts, in which case, the second part of the same quotation begins with a small letter. It is enclosed within quotation marks. When we report something in our own words, we use indirect speech. Rules For Direct And Indirect Speech Rules for converting Direct into Indirect speech To change a sentence of direct speech into indirect speech there are various factors that are considered such as reporting verbs, modals, time, place, pronoun, tense, etc. There are two ways to report what someone says or thinks: 1.
Are you an ESL learner searching for reported speech exercises? July 15, Our teacher said Alaska … cold.

Anita Eerland, Rolf A. Collabra: Psychology 1 January ; 4 1 : 5.
Reported speech
Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, “I am tired. You do not need to change the tense if the reporting verb is in the present, or if the original statement was about something that is still true, e. These modal verbs do not change in reported speech: might, could, would, should, ought to :. Home Welcome to EF. Programs See everything we do.
This free PDF will be very helpful for your exam. You can learn about all the new updates on govtjobpdf. Our PDF will help you to upgrade your marks in any competitive exam. Table of Contents. Direct Speech. It is the method in which the actual words of the speaker are reported within Inverted commas. For Example.

Muhammad Rafiq is a freelance writer, blogger, and translator with a master’s degree in English literature from the University of Malakand. What are direct and indirect speech? Read on to learn the differences with examples. Direct speech is exactly what it sounds like—text that reports the exact thoughts expressed by a person in their original form. It is often enclosed in quotation marks so that the reader understands that the quoted text is the speaker’s original narrative.
Reported speech: worksheets pdf, printable exercises, handouts. Direct and indirect speech for esl.

What Is Direct Speech? What Is Indirect Speech?
Direct and indirect speech can be a source of confusion for English learners. Let’s first define the terms, then look at how to talk about what someone said, and how to convert speech from direct to indirect or vice-versa. Direct speech repeats, or quotes, the exact words spoken. When we use direct speech in writing, we place the words spoken between quotation marks ” ” and there is no change in these words. We may be reporting something that’s being said NOW for example a telephone conversation , or telling someone later about a previous conversation. Reported or indirect speech is usually used to talk about the past, so we normally change the tense of the words spoken. We use reporting verbs like ‘say’, ‘tell’, ‘ask’, and we may use the word ‘that’ to introduce the reported words.
PDF book 1: English tenses exercises. PDF book 2: English grammar exercises. PDF book 3: English grammar rules. Read more about English grammar books PDF on e-grammar. Direct – indirect speech exercise 1 Complete sentences. Direct – indirect speech exercise 2 Report a dialogue. Direct – indirect speech exercise 3 Correct mistakes.
Julie: “He moved a year ago. Sentences are given in the direct speech. Our team has won the tournament! Levels of Difficulty : Elementary Intermediate Advanced 4 He said that he had a wonderful dream the previous night. I shall, we shall usually become would.

Тебе это отлично известно.

Он немного постоял, наслаждаясь ярким солнцем и тонким ароматом цветущих апельсиновых деревьев, а потом медленно зашагал к выходу на площадь. В этот момент рядом резко притормозил мини-автобус. Из него выпрыгнули двое мужчин, оба молодые, в военной форме.
Халохот услышал, как где-то ниже тело Беккера упало на каменные ступеньки, и бросился вниз, сжимая в руке пистолет. В поле его зрения попало окно. Здесь. Халохот приблизился к внешней стене и стал целиться. Ноги Беккера скрылись из виду за поворотом, и Халохот выстрелил, но тут же понял, что выстрел пришелся в пустоту.

Этого не может. Росио игриво улыбнулась и кивнула на немца. – El queria que lo guardara.
Его любимым развлечением было подключаться к ее компьютеру, якобы для того, чтобы проверить совместимость оборудования. Сьюзан это выводило из себя, однако она была слишком самолюбива, чтобы пожаловаться на него Стратмору. Проще было его игнорировать. Хейл подошел к буфету, с грохотом открыл решетчатую дверцу, достал из холодильника пластиковую упаковку тофу, соевого творога, и сунул в рот несколько кусочков белой студенистой массы. Затем облокотился о плиту, поправил широкие серые брюки и крахмальную рубашку.
Это все, что я могу вам сказать. Я уполномочен заплатить вам за. На мгновение в комнате повисла тишина, затем Росио приоткрыла губы в хитрой улыбке.
How do you learn to speak a language? 6 Minute English
Learning English and mastering a new language can be difficult, can’t it? So, how can we make language learning simpler and faster? What challenges do we face? Rob and Neil discuss the best way to learn languages and bring you some useful English vocabulary.
To download the audio and a transcript, go to our website:
https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish/english/features/6minuteenglish/ep180315
𝐌𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝟔 𝐌𝐢𝐧𝐮𝐭𝐞 𝐄𝐧𝐠𝐥𝐢𝐬𝐡 𝐞𝐩𝐢𝐬𝐨𝐝𝐞𝐬:
Should schoolchildren have jobs?
https://youtu.be/WKmsxJkJCqM
Is ‘man flu’ real?
https://youtu.be/lJMPosxMV2M
Giving up alcohol
https://youtu.be/5pxlzf0Tz_0
The future of artificial intelligence
https://youtu.be/NVgpfSFs0g
The men taking their wife’s name after marriage
https://youtu.be/0emVXTaESvs
𝐕𝐨𝐜𝐚𝐛𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲
𝐦𝐚𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐫
learn thoroughly or learn well
𝐟𝐥𝐮𝐞𝐧𝐭
speak well and without difficulty.
f𝐫𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐲
how often something occurs
𝐢𝐧𝐟𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬
changes to the basic form of words to show changes to the way they are used in a sentence
𝐥𝐞𝐦𝐦𝐚
the simplest form or base form of a word
[Images: GETTY IMAGES]
BBCLearningEnglish LearnEnglish 6MinuteEnglish
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่

Direct \u0026 Indirect Speech – Quiz 1| English Grammar – with Exercise and Quiz
There are many occasions in which we need to describe an event or action that happened, and very often that includes repeating what someone said. Such occasions can include a social situation as well as in a work email or presentation. In order to describe what people said there are two different types of speech – direct speech and indirect speech (or reported speech).
Direct and indirect speech can be a source of confusion for English learners.
You can answer the question What did he say? in two ways:
by repeating the words spoken (direct speech)
by reporting the words spoken (indirect or reported speech).
We’ve created a series of videos and tried to teach you the best possible way to learn English. All you have to do to watch the complete video and follow the instructions.
I’ll keep uploading more lectures related to this context. Practice makes perfect, is the best phrase to ease your struggle and keep you focused. Make sure you’ve already subscribed to the channel and hit the bell icon so that you’ll be updated with upcoming video lectures.
Link to Channel:
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OXbNHw0mYUU\u0026feature=youtu.be
Social Media Links:
Face book: https://www.facebook.com/ChannelForQualityEducation110341367354295
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/sardar.faheem.7/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/%40SardarF36088466
Related Lessons:
Learn common confusing pair of words with Quality Education: https://youtu.be/P6okmY1vREI
Improve English Pronunciation with Quality Education: https://youtu.be/WIovhLXTd4
Improve English Speaking and Writing using Synonyms with Quality Education: https://youtu.be/6Mh86PtqVHs
Complete Tenses explained in URDU Language: https://youtu.be/UWaqI5fZ75Y

REPORTED SPEECH: Verb Tense Changes | Direct and Indirect Speech in English
REPORTED SPEECH! Direct and Indirect Speech: Verb Tense Changes https://7esl.com/directindirectspeechtensechanges/
Reported speech is often also called indirect speech in English.
When changing from direct to indirect speech, you need to change the grammar in certain ways.
Verb tense forms usually need to change.
WATCH MORE:
★ Grammar: https://goo.gl/7n226T
★ Vocabulary: https://goo.gl/E5Ty4T
★ Expressions: https://goo.gl/JBpgCF
★ Phrasal Verbs: https://goo.gl/Ux3fip
★ Idioms: https://goo.gl/y7wNjN
★ Conversations: https://goo.gl/pmdpQT
★ English Writing: https://goo.gl/46gmY7
★ IELTS: https://goo.gl/Tg2U4v
★ TOEFL: https://goo.gl/8Zwvic
★ British vs. American English: https://goo.gl/VHa5W8
★ Pronunciation: https://goo.gl/P4eR39
★ Business English: https://goo.gl/r7jqtB
OUR SOCIAL MEDIA:
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/7english/
Facebook: https://www.fb.com/7ESLLearningEnglish/
For more videos and lessons visit:
https://7esl.com/
Reported Speech 5- Reporting questions
In this video you will learn about how to report questions. you will learn what changes to make when changing a question from a direct to an indirect question.
Reported speech/ direct speech / indirect speech / English grammar / grammar / English lessons / learn English / study English / time and place expressions changes / time and place expressions transformations / discour direct / discour indirect / الكلام المنقول / direct question / indirect question / reporting questions / how to report questions Created using Powtoon Free sign up at http://www.powtoon.com/youtube/ Create animated videos and animated presentations for free. PowToon is a free tool that allows you to develop cool animated clips and animated presentations for your website, office meeting, sales pitch, nonprofit fundraiser, product launch, video resume, or anything else you could use an animated explainer video. PowToon’s animation templates help you create animated presentations and animated explainer videos from scratch. Anyone can produce awesome animations quickly with PowToon, without the cost or hassle other professional animation services require.

Reported Speech – Kids Say the Funniest Things
Practise your English with this fun video activity. Use reported speech, also called indirect speech, to describe what each person said. Download the worksheet from here: http://busyteacher.org/24120reportedspeechvideoactivitykidssaythe.html
Watch the clips.
Use \”backshift\” (a more past tense) when reporting what the person said.

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆMAKE MONEY ONLINE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ reported speech exercises pdf