reported speech คือ: คุณกำลังดูกระทู้
ในบางครั้ง เรามีความจำเป็นต้องยกคำพูดของบางคนขึ้นมา หากเป็นการยกมาตรงๆ โดยไม่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะโครงสร้างใดๆ เราเรียกว่า Direct Speech (ไดเร็กทฺ สปีช) หรือบางคนเรียกว่า Quoted Speech (โควทิด สปีช) แต่หากเป็นการยกโดยมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะโครงสร้าง หรือโดยอ้อม เราเรียกว่า Indirect Speech (อินไดเร็กทฺ สปีช) หรือบางคนเรียกว่า Reported Speech (ริพอทิด สปีช)
ข้อสังเกตของ Direct Speech คือ คำพูดดังกล่าวของบุคคลนั้น จะอยู่ภายในเครื่องหมายคำพูดที่เรียกว่า Quotation marks (โควเทเชิ่น มาคสฺ)
ตัวอย่าง คำพูดของบุคคลต่อไปนี้
Jane. My brother is a student.
Mary. So is mine. He’s studying at Trium Udom School.
Where’s your brother studying?
ลักษณะโครงสร้างแบบ Direct/Quoted Speech อาจจะเป็น ดังนี้ก็ได้ คือ
(1) Jane said, “My brother is a student.”
Mary said, “So is mine. He’s studying at Trium Udom School.”
หรืออาจจะยกคำพูดของบุคคลนั้นขึ้นมาก่อน แล้วจึงบอกว่าใคร เป็นผู้พูดเช่นนั้น ดังนี้
(2) “My brother is a student,” Jane said.
“So is mine. He’s studying at Trium Udom School,”
Mary said.
ข้อสังเกต ใน (1) ลักษณะโครงสร้างของ Direct/Quoted Speech เป็นดังนี้
1.1 ใส่ comma หลัง said เช่น Jane said,
1.2 ใส่ quotation marks หลัง comma เช่น Jane said,”
1.3 หลัง quotation marks เริ่มด้วยอักษรใหญ่ เช่น Jane said, “M…
1.4 คำพูดของผู้พูดถูกยกมาทั้งหมด มิได้เปลี่ยนแปลงใดๆ ทั้งสิ้น แล้วใส่เครื่องหมาย full stop หรือ period เช่น Jane said, “My brother is a student.”
1.5 ใส่ quotation marks ปิดท้าย เช่น Jane said, “My brother is a student.”
ใน (2) ลักษณะโครงสร้างของ Direct/Quoted Speech เป็นดังนี้
2.1 ใส่ quotation marks เช่น “
2.2 เริ่มด้วยอักษรใหญ่หลัง Quotation marks rfu “M
2.3 คำพูดของผู้พูดถูกยกมาทั้งหมด มิได้เปลี่ยนแปลงใดๆ ทั้งสิ้น แล้ว ใส่เครื่องหมาย comma เช่น “My brother is a student,
2.4 ใส่ Quotation marks ท้ายคำพูด เช่น “My brother is a student,”
2.5 ยกชื่อผู้พูด ก่อนจะปิดท้ายด้วยคำว่า said และเครื่องหมาย period เช่น “My brother is a student,” Jane said.
ส่วน Indirect/Reported Speecli ซึ่งเป็นการยกคำพูดมาโดยอ้อม จึงมีการเปลี่ยนด้านรูปของคำกริยา (verb forms) สรรพนาม (pronouns) รวมทั้งไม่มี quotation marks
ตัวอย่าง
Jane said (that) her brother was a student.
Mary said (that) her brother was a student.
He’s studying at Trium Udom School.
Where’s your brother studying?
หาก ใช้คำว่า tell/told แทน say/said จะต้องใช้โครงสร้างต่างกันไปดังนี้
Say + something tell + someone + something
แสดงว่า เมื่อใดก็ตามที่ใช้คำว่า say/said จะไม่มีกรรม (object) รองรับ แต่ถ้าใช้ tell/told จะต้องมีกรรมรองรับ แต่ถ้าใช้ say/said ตามด้วยบุพบท to ต้องมีกรรมรองรับ เช่น said to me
ตัวอย่าง
Direct Speech
Jane said, “My brother is a student.”
Jane said to me, “My brother is a student.”
Jane told me, “My brother is a student.”
Indirect Speech
Jane said (that) her brother was a student.
Jane told me (that) her brother was a student.
หมายเหตุ จะใส่หรือไม่ใส่คำว่า that หลัง say/said ma tell/told เมื่อเป็น Indirect Speech ก็ได้
ต่อไปนี้ จะขอกล่าวถึงเรื่อง indirect/Reported Speech ไปตามลำดับทีละเรื่องดังนี้
1. Reported Speech (statements)
2. Reported Speech (questions)
3. Reported Speech (imperatives)
4. Reported Speech (exclamations)
1. Reported Speech (statements)
ในประโยคปกติทั่วไป (statements สเตทเม้นสฺ) จะประกอบด้วย ภาคประธาน + กริยา + กรรม หรือส่วนขยาย เมื่อแปรเปลี่ยนจาก Direct/quoted Speech ไปเป็น Indirect/Reported Speech จะมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้างบางอย่าง ส่วนใหญ่มักเป็นการเปลี่ยนแปลงสรรพนาม และรูปคำกริยา แต่มีบางครั้งที่เปลี่ยนแปลงรูป adverbs of time & place ด้วย
ตัวอย่าง
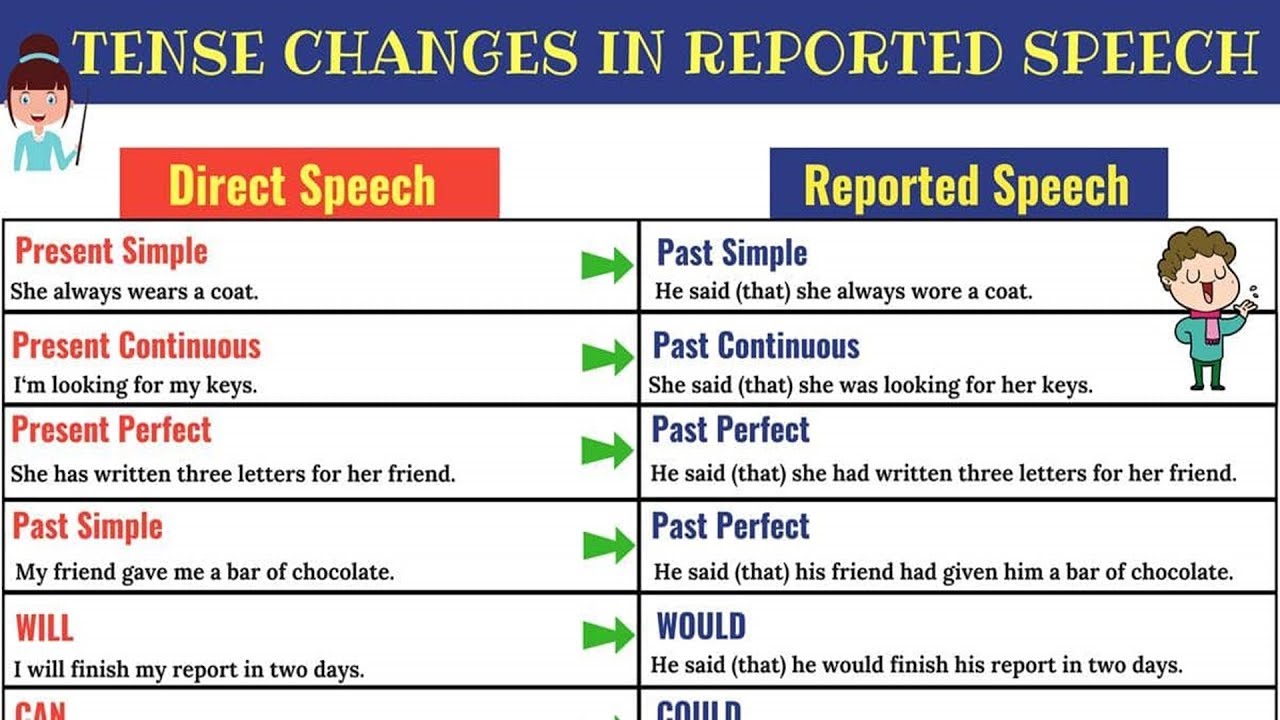
(1) Present Simple→ Past Simple
D:“I can’t stand him” Sue said.
R : Sue said (that) she couldn’t stand him.
(2) Present Continuous →Past Continuous
D : Sue said, “I am having an ice-cream.”
R : Sue said (that) she was having an ice-cream.
(3) Present Perfect → Past Perfect
D : “I have cooked a delicious meal,” Sue said.
R : Sue said (that) she had cooked a delicious meal.
(4) Present Perfect Continuous → Past Perfect Continuous
D : Sue said, “I have been watching TV all day.”
R : Sue said (that) she had been watching TV all day.
(5) Past Simple → Past Perfect
D : Sue said to her mother, “I passed the entrance exam.”
R : Sue told her mother (that) she had passed the entrance exam.
(6) Future Simple → Conditional
D : They said, “We will do it tomorrow.”
R : They said (that) they would do it the next day.
(7) Future Continuous →Conditional Continuous
D : They said, “We will be studying here next year.”
R : They said they would be studying there the following year.
จะเห็นได้ว่า เมื่อมีการเปลี่ยนจาก Direct/Quoted Speech เป็น Reported/Indirect Speech จะมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงสรรพนาม (pronouns) และคำกริยา (verbs) ดังตัวอย่างที่ 1-5 และนอกจากจะมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงดังกล่าวแล้ว ยังมีการเปลี่ยน adverbs of time ดังตัวอย่างที่ 6-7 และ adverbs of place ดังตัวอย่างที่ 7
การเปลี่ยนแปลงของ adverbs of time & adverbs of place จาก Direct Speech เป็น Reported Speech มีตังนี้
Direct Speech → Reported Speech
here there
now then
yesterday → the day before
this that
next week the following week
ago before
today that day
tonight that night
tomorrow the next day / the following day
next Monday the following Monday
last Monday the previous Monday
ลองดูตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม
D : “I’m here on holiday,” Patricia said.
R : Patricia said (that) she was there on holiday.
D : “I’ll see you next Tuesday,” Patricia said to me.
R : Patricia told me (that) she would see me the following Tuesday.
อย่างไรก็ตาม บางทีนักเรียนอาจจะเคยได้ยินเจ้าของภาษาอังกฤษพูดคุยกัน โดยไม่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดๆ เกี่ยวกับ adverbs of time & place เหล่านี้ ก็ถือว่าไม่ผิดอะไร เพราะนั่นเป็นภาษาพูด (spoken language) สำหรับภาษาเขียน ที่เป็นมาตรฐาน (standard written language) แล้ว มีความจำเป็นที่จะต้องปฏิบัติตามหลักการที่กล่าวมาข้างต้น
2. Reported Speech (questions)
ประโยคคำถาม (questions เควสเชิ่นสฺ) อาจแบ่งได้เป็น 2 ประเภทใหญ่ๆ คือ Yes-No Questions หรือ คำถามที่ผู้ตอบจะตอบรับว่า Yes/No และ Wh-word Questions หรือคำถามที่ขึ้นต้นด้วย Wh-words ดังนั้นการจะเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของประโยคลักษณะดังกล่าวนี้เป็น Reported Speech จึงจำเป็นต้องกล่าวถึงทีละประเภทคือ
2.1 Yes-No Questions
ประโยคคำถามประเภทนี้ จะขึ้นต้นด้วยคำกริยาช่วย (helping verbs) อาทิ Do, Does, Did, Will, Would, Shall, Should, May, Might, Must, Have, Has, Is, Am, Are เป็นต้น
ตัวอย่าง
Jane: Are you cold?
Do you want some hot drink?
May I bring you a blanket?
ลักษณะโครงสร้าง Direct/Quoted Speech อาจจะเป็นดังนี้ก็ได้คือJane asked, “Are you cold?”
Jane asked, “Do you want some hot drink?”
Jane asked, “May I bring you a blanket?”
เมื่อต้องการจะเปลี่ยน Direct Speech ของประโยคแบบ Yes-No Questions ดังกล่าว เป็น Reported Speech จำเป็นจะต้องทดแทนการถามว่า “ใช่ไหม” ด้วยคำว่า if/whether ฉะนั้นจากตัวอย่างของ Direct Speech ที่เห็นข้างบน เมื่อสักครู่ จึงเขียนแบบ Reported Speech ได้ดังนี้
ตัวอย่าง
Jane asked Tom if (OR whether) he was cold.
เจนถามทอมว่าเขาหนาวไหม
Jane asked Tom if (OR whether) he wanted some hot drink.
เจนถามทอมว่าเขาต้องการเครื่องดื่มร้อนๆ บ้างไหม
Jane asked Tom if (OR whether) she might bring him a blanket.
เจนถามทอมว่าเธอจะนำเอาผ้าห่มมาให้เอาไหม
นอกจากจะสามารถใช้คำว่า ask/asked ใน Reported Speech แล้วยังมีคำและวลีอื่นที่ใช้ได้ด้วยเช่นกัน ที่พบบ่อยคือ wonder/wondered และ want/ wanted to know เป็นต้น
ในด้านของการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้าง อาทิ สรรพนาม กริยา ฯลฯ จาก Direct Speech เป็น Reported Speech ก็เป็นไปในลักษณะเดียวกันกับที่ได้กล่าวมาแล้วใน Reported Statements ข้อ 1 ลองดูตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม
D : Jane asked, “Have you seen my dog?”
R : Jane wondered if he had seen her dog.
D : He asked, “Did she do it by herself?”
R : He wanted to know whether she had done it by herself.
D : Mary asked, “Will you arrive here on time?”
R : Mary asked Peter if he would arrive there on time.
2.2 Wh-word Questions
ประโยคคำถามแบบนี้ขึ้นต้นด้วย Wh-words อาทิ What, When, Where, Why, How, Who, Whom, How long. … เป็นต้น
ตัวอย่าง
Jane : What do you want to buy?
Which book have you seen?
How much does it cost?
ลักษณะโครงสร้างแบบ Direct/Quoted Speech อาจจะเป็นดังนี้ก็ได้ คือ
Jane asked, “What do you want to buy?”
Jane asked, “Which book have you seen?”
Jane asked, “How much does it cost?”
เมื่อต้องการจะเปลี่ยน Direct Speech ของประโยคแบบ Wh-word Questions ดังกล่าวเป็น Reported Speech จะต้องคง Wh-words ไว้ แล้วจึงตามด้วยภาคประธานของประโยคดังกล่าว จากนั้นจึงตามด้วย กริยาช่วย (ถ้ามี) และกริยาแท้ ส่วนขยายหรือกรรมที่เหลือก็ลอกไปเหมือนเดิม ฉะนั้นจากตัวอย่างของ Direct Speech ที่เห็นข้างบน จึงเขียนแบบ Reported speech ได้ดังนี้
ตัวอย่าง
Jane asked Tom what he wanted to buy.
เจนถามทอมว่าเขาต้องการซื้ออะไร
Jane asked Tom which book he had seen.
เจนถามทอมว่าเขาเห็นหนังสือเล่มไหน
Jane asked how much it cost.
เจนถามว่าราคาเท่าไร
นอกจากจะสามารถใช้คำว่า ask/asked ใน Reported Speech แล้วยัง สามารถใช้คำหรือวลีต่อไปนี้ได้ด้วยคือ wonder/wondered และ want/wanted to know เป็นต้น
ในด้านของการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้าง อาทิ สรรพนาม กริยา ฯลฯ จาก Direct Speech เป็น Reported Speech ก็เป็นไปในลักษณะเดียวกับที่ได้กล่าวมาแล้วใน Reported statements ข้อ 1
ลองดูตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม
D : Jane asked, “How long have you been in San Francisco?”
R : Jane asked him how long he had been in San Francisco.
D : He asked, “What part did you play in the robbery?”
R : He wanted to know what part she had played in the robbery, D : Jane asked, “Where were you last weekend?”
R : Jane wondered where he had been the previous weekend.
3. Reported Speech (imperatives)
imperatives (อิมเพอระทิฟสฺ) หมายถึง ประโยคคำสั่ง ซึ่งสามารถสังเกตได้ง่ายคือ ประโยคลักษณะนี้จะขึ้นต้นประโยคด้วยคำกริยา (verbs) ทันที
ตัวอย่าง
Jane : Go away!
Come here!
Don’t wrap it up in a piece of paper!
ลักษณะโครงสร้างแบบ Direct/Quoted Speech อาจจะเป็นดังนี้ก็ได้ คือ
Jane ordered the children, “Go away.”
Jane said to me, “Come on Monday.”
“Don’t wrap it up in a piece of paper,” Jane asked him.
เมื่อต้องการจะเปลี่ยน Direct Speech ของประโยคลักษณะดังกล่าวเป็น Reported speech จะต้องใช้ to-infinitive นั่นคือ วางบุพบท to ไว้หน้าคำกริยาของประโยคคำสั่ง หากเป็นคำสั่งห้ามที่ขึ้นต้นด้วย Don’t หรือ Never ให้เพิ่มคำว่า not หน้าบุพบท to แล้วจึงลอกส่วนที่เหลือ หากมี adverbs of time & place ตามที่ระบุไว้ใน Direct Speech ก็ต้องเปลี่ยนเมื่อเป็น Reported Speech ฉะนั้น จากตัวอย่าง Direct Speech ที่เห็นข้างบนเมื่อสักครู่ จึงเขียนแบน Reported Speech ได้ดังนี้
ตัวอย่าง
Jane ordered the children to go away.
เจนสั่งให้เด็กๆ ไปให้พ้น
Jane told me to come on Monday.
เจนบอกให้ผมมาวันจันทร์
Jane asked him not to wrap it up in a piece of paper.
เจนขอร้องเขาไม่ให้พับมันในกระดาษ
คำกริยาที่สามารถใช้ใน Direct Speech และ Reported Speech ของประโยคคำสั่ง สามารถใช้ได้หลายคำ แล้วแต่ลักษณะความรุนแรงของการสั่งการ อาทิ ask (ขอร้อง) request (ขอร้อง) invite (เชื้อเชิญ) tell (บอก) remind (เตือน) demand (เรียกร้อง) order (สั่ง) และ command (สั่งการ) เป็นต้น ส่วนโครงสร้างของคำสรรพนาม รวมทั้ง adverbs of time & place ก็เปลี่ยนแปลงไปตามกฎเกณฑ์ที่ได้กล่าวมาแล้วตั้งแต่ต้นใน Reported statements ข้อ 1 สำหรับ กรรมที่จะรองรับท้ายคำกริยาที่ระบุมา หากข้อความใน Direct Speech ไม่ได้ให้ไว้ ก็กำหนดเอาเองตามสะดวก
ลองดูตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม
D : “Don’t interrupt me,” she said to them.
R : She told them not to interrupt her.
D : The manager requested, “Sit down, please.”
R : The manager requested me to sit down.
D : “Don’t go out without your keys,” she reminded me.
R : She reminded me not to go out without my keys.
4. Reported Speech (exclamations)
exclamations (เอ็กซฺคลาเมเชิ่นสฺ) คือ ประโยคหรือข้อความอุทาน ซึ่งอาจจะมีรูปลักษณะคล้ายๆ กับคำถาม แต่ลงท้ายด้วยเครื่องหมาย! (ไม่ใช้เครื่องหมาย ?) หรืออาจจะคล้ายกับคำสั่ง คำกริยาที่ใช้ในรูปแบบประโยคดังกล่าวนี้มักจะได้แก่ remark (กล่าว/บอก) greet (ทักทาย) exclaim (อุทาน) ask (ถาม) say (พูด) เป็นต้น
ตัวอย่าง
Jane : What a lovely garden!
Hello! Where are you going?
Oh dear! I’ve tom my clothes.
ลักษณะโครงสร้างแบบ Direct/Quoted Speech อาจจะเป็นดังนี้ก็ได้ คือ
“What a lovely garden!,” Jane remarked.
He said, “Hello!” and asked, “Where are you going?”
“Oh dear! I’ve tom my clothes,” she said.
เมื่อต้องการจะเปลี่ยน Direct Speech ดังกล่าวเป็น Reported Speech ก็จะต้องพิจารณาตามความเหมาะสมว่าจะใช้คำกริยาใด และต้องคำนึงถึงลักษณะคำถาม (หากมี) รวมทั้งบางทีอาจจะจำเป็นต้องเพิ่มคำบางคำเข้าไปด้วย ฉะนั้นจากตัวอย่างของ Direct Speech ที่เห็นข้างบนนี้ จึงเขียนแบบ Reported speech ได้ดังนี้
ตัวอย่าง
Jane remarked what a lovely garden it was.
เจนพูดว่าสวนดังกล่าวช่างสวยงามจริงๆ
He greeted me and asked where I was going.
เขาทักทายผมและถามว่าผมจะไปไหน
She exclaimed and said (that) she had torn her clothes.
เธออุทานและพูดว่าเธอทำเสื้อผ้าของเธอขาด
ในด้านการเปลี่ยนแปลงโครงสร้าง อาทิ สรรพนาม กริยา ฯลฯ จาก Direct Speech เป็น Reported Speech ก็เป็นไปตามที่ได้กล่าวมาแล้วใน Reported statements ข้อ 1
ลองดูตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติม
D : Mary remarked, “What a terrible noise!”
R : Mary remarked what a terrible noise it was.
D : “Oh dear! I’ve spilt my coffee,” Jane said.
R : Jane exclaimed and said she had spilt her coffee
D : “Look out! There’s a car coming.” he warned me.
R : He warned me to look out and said there was a car coming.
ที่มา:รองศาสตราจารย์ทณุ เตียวรัตนกุล
(Visited 37,789 times, 1 visits today)
Table of Contents
[NEW] ประโยค Reported Speech | reported speech คือ – NATAVIGUIDES
ประโยค Reported Speech & Indirect Speech คืออะไร
Reported แปลว่า รายงาน Speech แปลว่า คำพูด สองคำนี้แปลว่า คำพูดที่นำมารายงาน จะพูดให้เข้าใจเป็นภาษาง่ายๆคือ การนำคำพูดของคนอื่นมารายงานให้คนอื่นทราบ หรือการเอาคำพูดคนอื่นมาเล่าต่อนั้นเอง ตัวอย่างเช่น
- แซมพูดว่า “คุณสวยที่สุดในโลก” เราก็เอามาเล่าต่อว่า “แซมบอกว่า ฉันสวยที่สุดในโลก”
- แม่ร้องขึ้นว่า “ล้างจานให้หมด” เราก็มาเล่าต่อว่า “แม่สั่งให้ฉันล้างจานให้หมด”
- สมศรีถามว่า “คุณชอบกินอะไร” เราก็มาเล่าต่อว่า “สมศรีถามฉันว่าฉันชอบกินอะไร”
Direct speech และ Indirect speech
Direct speech คำพูดแบบตรง หมายถึง การนำคำพูดคนอื่นมาพูดต่อ เช่น โจพูดว่า “ฉันชอบแมว” เราก็เอามาเล่าต่อว่า “โจบอกว่า ฉันชอบแมว” ถ้าเอาคำพูดนี้มาเล่าต่อ คนฟังจะเข้าใจว่าอย่างไร โจหรือฉันที่ชอบแมว แน่นอนว่าคนฟังต้องคิดว่า ฉันที่ชอบแมว ไม่ใช่โจ
Indirect speech หรือ Reported speech คำพูดแบบอ้อม หมายถึงการนำคำพูดคนอื่นมาเปลี่ยนเสียก่อนที่จะนำไปพูดบอกคนอื่น เช่น โจพูดว่า “ฉันชอบแมว” เราก็เอามาแปลงเป็น “โจบอกว่า เขาชอบแมว” แบบนี้คนฟังก็จะรู้เลยว่าคนที่ชอบแมวคือโจ
หลักการเปลี่ยน Direct speech เป็น Indirect speech
1. เปลี่ยนคำพูดของคนอื่นให้อยู่ในรูปของอดีตกาล หรือ Past Tense นั่นเอง (ถ้าจะศึกษาเรื่องนี้ต้องผ่านด่านเรื่อง Tense มาแล้วนะครับ)
2. เปลี่ยนแปลงเวลาและคำแวดล้อมให้ถูกต้องกับความเป็นจริงในปัจจุบันที่พูด
3. เปลี่ยนสรรพนามจาก I เป็น He/She จาก We เป็น They / you จาก me เป็น her/ him แล้วแต่สถานการณ์
4. คำพูดที่อยู่ในรูปของประโยคคำถาม ให้แปลงเป็นประโยคบอกเล่า
ประโยค Reported Speech หรือ Indirect Speech มีกี่ประเภท
มี 3 ประเภทด้วยกัน
1. Indirect Speech – Statement ประโยคบอกเล่า
2. Indirect Speech – Commands, Requests or Suggestions ประโยค คำสั่ง แนะนำ ขอร้อง
3. Indirect Speech – Question ประโยคคำถาม
1. Indirect Speech – Statement ประโยคบอกเล่า
ขอให้จำกฎง่ายๆว่า ต้องเปลี่ยนคำกริยาปัจจุบันให้เป็นอดีต และเปลี่ยนคำที่เป็นบริบทให้ตรงกับความเป็นจริง
ในประโยคบอกเล่านี้ เราจะใช้คำว่า said that (พูดว่า…) หรือ told….that (บอก…ว่า) ก็ได้ คำว่า that จะละไว้ก็ได้
Present Simple Tense เปลี่ยนเป็น Past Simple tense
- โจพูดกับฉัน ” I am tired.” ฉันเหนื่อย
Jo told me that he was tired. โจบอกฉันว่าเขาเหนือย
Jo said he was tired. โจพูดว่าเขาเหนื่อย - เจนพูดกับโจ ” I love you very much.” ฉันรักคุณมาก
Jane said that she loved Jo very much. เจนพูดว่าหล่อนรักโจมาก
Jane told Jo that she loved Jo very much. เจนบอกโจว่าหล่อนรักโจมาก - โจพูดกับเจน ” I love you too.” ผมรักคุณเช่นกัน
Jo said that he loved Jane too. โจพูดว่าเขารักเจนเช่นกัน
Jo told Jane that he loved her too. โจบอกเจนว่าเขารักหล่อนเช่นกัน - เด็กน้อยพูดกับแม่ ” I want to eat pizza every day.” หนูอยากกินพิซซ่าทุกวัน
The little girl said that she wanted to eat pizza every day. หนูน้อยพูดว่าเธออยากกินพิซซ่าทุกวัน
The little girl told her mum that she wanted to eat pizza every day. หนูน้อยพูดว่าเธออยากกินพิซซ่าทุกวัน - พวกเขา(บรรดานักบอลที่ได้แชมป์)พูดกับแฟนๆว่า ” We are so happy.” พวกเรามีความสุขมาก
They said they were so happy. พวกเขาพูดว่าพวกเขามีความสุขมาก
They told their fans that they were so happy. พวกเขาบอกกับแฟนๆว่าพวกเขามีความสุขมาก
ปล. ไม่จำเป็นต้องเปลี่ยนกริยาให้เป็นรูปอดีตก็ได้ ถ้าความนั้นเป็นข้อเท็จจริงทั่วไป เช่น
- โจพูดกับฉันว่า I am a teacher. ผมเป็นครู (อันนี้เป็นข้อเท็จริง ตลอดกาล)
- Jo said that he is a teacher. จะเห็นว่า ใช้กริยา is โดยที่ไม้ต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น was
เที่ยบกับ
- โจพูดกับฉัน ” I am tired.” ฉันเหนื่อย
Jo told me that he was tired. โจบอกฉันว่าเขาเหนือย
อันนี้ไม่ใช่ข้อเท็จจริง เขาแค่เหนื่อยในขณะนั้นในอดีต ซึ่งตอนนี้อาจจไม่ใช่แล้ว ส่วนประโยคอื่นๆก็เทียบเคียงกัน
Present Continuous Tense เปลี่ยนเป็น Past Continuous tense
- โจพูดกับฉัน ” I am eating dinner.” ฉันกำลังกินข้าวเย็นอยู่
Jo said that he was eating dinner. โจพูดว่าเขากำลังกินข้าวเย็นอยู่
Jo told me that he was eating dinner. โจบอกฉันว่าเขากำลังกินข้าวเย็นอยู่ - เจนพูดกับโจ ” I am taking a bath.” ฉันกำลังอาบน้ำอยู่
Jane said that she was taking a bath. เจนพูดว่าหล่อนกำลังอาบน้ำอยู่
Jane told Jo that she was taking a bath. เจนบอกโจว่าว่าหล่อนกำลังอาบน้ำอยู่ - พวกเขา(บรรดานักบอลที่กำลังลงสนาม)พูดกับแฟนๆว่า ” We are playing against Leeds United.” พวกเรากำลังจะลงแข่งกับลีดส์ยูไนเต็ด
They said they were playing against Leeds United. พวกเราพูดว่า พวกเขากำลังจะลงแข่งกับลีดส์ยูไนเต็ด
They told their fans that they were playing against Leeds United. พวกเราบอกกับแฟนๆของพวกเขาว่า พวกเขากำลังจะลงแข่งกับลีดส์ยูไนเต็ด
Present Perfect Tense เปลี่ยนเป็น Past Perfect tense
- โจพูดกับฉัน ” I have eaten dinner.” ฉันกินข้าวเย็นแล้ว
Jo said that he had eaten dinner. โจพูดว่าเขากินข้าวเย็นแล้ว
Jo told me that he had eaten dinner. โจบอกฉันว่าเขากินข้าวเย็นแล้ว - เจนพูดกับโจ ” I have taken a bath.” ฉันอาบน้ำแล้ว
Jane said that she had taken a bath. เจนพูดว่าหล่อนอาบน้ำแล้ว
Jane told Jo that she had taken a bath. เจนบอกโจว่าว่าหล่อนอาบน้ำแล้ว
Present Perfect Continuous Tense เปลี่ยนเป็น Past Perfect Continuous tense
- โจพูดกับฉัน ” I have been eating dinner for 30 munites.” ฉันกินข้าวเย็นมาเป็นเวลา 30 นาทีแล้ว
Jo said that he had been eating dinner for 30 munites.. โจพูดว่าเขากินข้าวเย็นมาเป็นเวลา 30 นาทีแล้ว
Jo told me that he had been eating dinner for 30 munites.. โจบอกฉันว่าเขากินข้าวเย็นมาเป็นเวลา 30 นาทีแล้ว
ทีนี้ถ้ามันเป็นเหตุการณ์ในอดีตล่ะ….ถ้าเป็นเหตุการณ์ในอดีตเอาสูตรง่ายๆไปใช้คือ คงเดิมไว้ เปลี่ยนแค่ตัวประธานให้ตรงกับสถานการณ์ก็พอ
Past Simple Tense เปลี่ยนเป็น Past Perfect tense หรือ คง Tense ไว้
- โจพูดกับฉัน ” I ate dinner with Jenny yesterday.” ฉันกินข้าวเย็นกับเจนเมื่อวาน
Jo told me that he ate dinner with Jenny the day befor yesterday. โจบอกฉันว่าเขากินข้าวเย็นกับเจนเมื่อวานก่อน
Past Continuous Tense ก็ให้คงไว้
- โจพูดกับฉัน ” While I was walking to school, I saw a long snake. ขณะที่ฉันกำลังเดินไปโรงเรียน ฉันเห็นงูตัวยาว
Jo said while he was walking to school, he saw a long snake. โจพูดว่าขณะที่เขากำลังเดินไปโรงเรียน เขาเห็นงูตัวยาว
ประโยคที่มี auxiliary verb ให้เปลี่ยนดังนี้
- can > could
- may > might
- will > would
- shall > should
- must > must, had to
- โจพูดกับฉัน ” I can run fast.
- Jo said that he could run fast. โจพูดว่าเขาสามารถวิ่งได้เร็ว
- เจนพูดว่า ” I will go to London next month.
Jane said she would go to London next month.
2. Indirect Speech – Commands, Requests or Suggestions ประโยค คำสั่ง แนะนำ ขอร้อง
การสั่งจะใช้คำว่า ordered, commanded
การแนะนำจะใช้ advised, suggested, recommended, told..
การของร้องจะใช้ asked
ส่วนคำสั่ง คำแนะนำ และคำขอร้องจะใช้ infinitive with to (มี to นำหน้า)
- นายพลสั่งลูกน้อง ” Jump into the sea now!” กระโดดลงทะเลยเดี๋ยวนี้
The general ordered his soldiers to jump into the sea then. - ตำรวจสั่งชายผู้ต้องสงสัยบนถนน ” Put you hands on your head!” เอามือวางไว้บนหัวของคุณ!
The police ordered the man to put his hand on his head. ตำรวจสั่งให้ชายหนุ่มเอามือของเขาวางไว้บนหัวของเขา - ผมป่วยอยู่บ้าน เจนมาหา ” You should see the doctor. ” คุณควรพบหมอนะ
Jane advised me to see the doctor. เจนบอกว่าให้ฉันไปพบหมอ
“Why don’t you go to see the doctor.” ทำไมคุณไม่ไปพบหมอล่ะ
Jane told me to see the doctor. เจนบอกให้ผมไปพบหมอ - เจนขอให้เราปิดประตูให้ ” Open the door, please.” ช่วยปิดหน้าต่างให้หน่อยค่ะ
Jane asked me to open the door.
3. Indirect Speech – Question ประโยคคำถาม
ถ้าคำถามใช้ modal auxiliary verb ให้ใช้ if หรือ wether นำหน้า ซึ่งแปลว่า “ว่า” และ เรียงประโยคในรูแบบ ประธาน + modal verb + กริยาหลัก
- เจนถามว่า ” Can you swim?” คุณว่ายน้ำเป็นไหม
Jane asked me if I could swim. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันว่ายน้ำเป็นใช่ไหม - เจนถามว่า ” Will you go tomorrow?” คุณจะไปพรุ่งนี้ใช่ไหม
Jane asked me if I would go tomorrow. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันจะไปพรุ่งนี้ใช่ไหม - เจนถามว่า “Shall I go tomorrow?” ฉันควรไปพบหมอไหม
Jane asked me if she should go tomorrow. เจนถามฉันว่าหล่อนควรไปพรุ่งนี้ใช่ไหม - เจนถามว่า ” Will you go tomorrow?” คุณจะไปพรุ่งนี้ใช่ไหม
Jane asked me if I would go tomorrow. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันจะไปพรุ่งนี้ใช่ไหม
**คำถาม do, does, did ให้ตัด do, does, did**
- เจนถามว่า ” Do you like cats?” คุณชอบแมวไหม
Jane asked me if I liked cats. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันชอบแมวใช่ไหม - เจนถามว่า ” Did you eat my cake?” คุณกินเค้กฉันใช่ไหม
Jane asked me if I ate her cake. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันกินเค้กของหล่อนใช่ไหม
คำถาม Verb to be (is, am, are, was, were + ประธาน) ให้เรียงเป็นประโยคบอกเล่า (ประธาน + verb to be)
- เจนถามว่า “Are you a doctor?” คุณชอบแมวไหม
Jane asked me if I was a doctor. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันเป็นหมอใช่ไหม - เจนถามว่า “Were you a doctor at ABC Hospital?” คุณเคยเป็นหมออยู่ที่โรงพยาบาลเอบีซีใช่ไหม
Jane asked me if I was a doctor at ABC Hospital. เจนถามฉันว่าเคยเป็นหมออยู่ที่โรงพยาบาลเอบีซีใช่ไหม
คำถาม Wh Questions (who, what, where, when, why และ how) ให้ใช้ wh question นำหน้า และเรียงเป็นประโยคบอกเล่า ประธาน + กริยา
- เจนถามว่า “Where are you from?” คุณมาจากไหน
Jane asked me where I was from. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันมาจากไหน - เจนถามว่า “Who do you love?” คุณรักใคร
Jane asked me who I loved. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันรักใคร - เจนถามว่า “What will you do?” คุณจะทำอะไร
Jane asked me what I would do. เจนถามฉันว่าฉันจะทำอะไร - เจนถามว่า “When is your birthday?” วันเกิดของคุณเมื่อไหร่
Jane asked me when my birthday was. เจนถามฉันว่าวันเกิดของฉันเมื่อไหร่ - เจนถามว่า “Why is Jo crying?” ทำไหมโจร้องให้
Jane asked me why Jo was crying. เจนถามฉันว่าทำไมโจร้องให้
Share this:
Like this:
ถูกใจ
กำลังโหลด…
Related
Reported Speech
Reported Speech or Indirect speech is the exact meaning of what someone said, but not their exact words. We use reporting verbs like say, tell, ask, admit, promise, explain, announce, invite, etc.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

Reported Speech
Learn all about reported speech or indirect speech!
Reported speech or indirect speech is used to report something that someone said in the past.
Practice here: http://www.teacherdiane.com/youtube/page/1
Learn English on Skype: http://www.teacherdiane.com
Follow Teacher Diane on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/teacherdianeESL

Câu Tường Thuật ( lý thuyết)
►Đăng Ký theo dõi (Subscribe): https://goo.gl/PGHQeq
► Trang web: http://mrstranganh.edu.vn/
Liên hệ:
► Facebook cô Trang Anh: https://goo.gl/PJXUgE
►Fanpage học Tiếng Anh: https://goo.gl/TQ9hV8
►Cảm ơn đã xem video của tôi.
© Bản quyền thuộc về Trang Anh English
© Copyright by Trang Anh English ☞ Do not Reup

REPORTED SPEECH: Verb Tense Changes | Direct and Indirect Speech in English
REPORTED SPEECH! Direct and Indirect Speech: Verb Tense Changes https://7esl.com/directindirectspeechtensechanges/
Reported speech is often also called indirect speech in English.
When changing from direct to indirect speech, you need to change the grammar in certain ways.
Verb tense forms usually need to change.
WATCH MORE:
★ Grammar: https://goo.gl/7n226T
★ Vocabulary: https://goo.gl/E5Ty4T
★ Expressions: https://goo.gl/JBpgCF
★ Phrasal Verbs: https://goo.gl/Ux3fip
★ Idioms: https://goo.gl/y7wNjN
★ Conversations: https://goo.gl/pmdpQT
★ English Writing: https://goo.gl/46gmY7
★ IELTS: https://goo.gl/Tg2U4v
★ TOEFL: https://goo.gl/8Zwvic
★ British vs. American English: https://goo.gl/VHa5W8
★ Pronunciation: https://goo.gl/P4eR39
★ Business English: https://goo.gl/r7jqtB
OUR SOCIAL MEDIA:
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/7english/
Facebook: https://www.fb.com/7ESLLearningEnglish/
For more videos and lessons visit:
https://7esl.com/
I Asked Bill Gates What’s The Next Crisis?
I got the chance to interview Bill Gates so I asked him: Will Covid19 be the last pandemic? How does he deal with misinformation and conspiracy theories? And what is the next disaster? The Foundation Letter is here: https://ve42.co/BG21
Special thanks to Patreon supporters:
Ludovic Robillard, jim buckmaster, Robert, fanime96, Marc Forand, Juan Benet, Robert Blum, Grace O’Maille KRON x Arc iOS, Richard Sundvall, Lee Redden, Vincent, Lyvann Ferrusca, Alfred Wallace, Arjun Chakroborty, Joar Wandborg, Clayton Greenwell, Pindex , Michael Krugman, Cy ‘kkm’ K’Nelson, Sam Lutfi, Ron Neal
Thanks to Petr Lebedev for the thumbnail, early edits and Jonny Hyman for feedback

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่LEARN FOREIGN LANGUAGE
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ reported speech คือ
