โครงสร้าง ของ past simple tense: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
Posted on
763
SHARES
สรุป Tense ทั้ง 12 อย่างละเอียดทุกแง่มุมครอบคลุมเนื้อหาทั้งหมด ได้แก่ ความหมาย, โครงสร้าง tense ต่างๆ นะครับ
ในบทเรียนนี้่จะสรุปหลักการใช้ tense ทั้งหมด และตัวอย่างประโยคที่นำมาใช้งานจริงๆ เพื่อให้ผู้เรียนเห็นได้เห็นภาพว่า จริงๆแล้ว 12 tense นี่มันใช้แตกต่างกันอย่างไร
Table of Contents
Table of Content
♦ Tense คืออะไร
♦ โครงสร้าง tense ทั้ง 12 เป็นอย่างไร แตกต่างกันอย่างไร
♦ หลักการใช้ในสถานการณ์ต่างๆ ใช้ต่างกันอย่างไร
♦ ตัวอย่างประโยคของเทนส์ทั้งหมด เพิ่มเติมเสริมความเข้าใจ
♦ บทเรียนเรื่อง tense 12 ฉบับจัดเต็ม
Tense คืออะไร
ความหมายของ Tense คือ รูปแบบของประโยคที่มีคำกริยา แสดงระบุเวลากำกับการกระทำในขณะที่พูด
นี่คือความหมายคร่าวๆนะครับ ถ้าย่นย่อกันจริงๆในการเรียนหลักภาษาแล้ว Tense คือ กาล (เวลา)

โครงสร้างของ 12 Tense และหลักการใช้
ว่ากันไปแล้ว Tense ใหญ่ๆแค่ 3 เท่านั้นเอง แต่แยกย่อยออกอีก 4 จึงรวมกันได้ 12 tense
1. Present Tense (ปัจจุบันกาล) กล่าวถึงเรื่องราวในปัจจุบัน
2. Past Tense (อดีตกาล) กล่าวถึงเรื่องราวในอดีต
3. Future Tense (อนาคตกาล) กล่าวถึงเรื่องราวในอนาคต
PRESENT TENSE
บอกเล่าเรื่องราวในปัจจุบัน
Present Simple Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + V.1(s/es)
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าข้อเท็จจริงทั่วไป ของคน สัตว์ สิ่งของ สถานที่ …
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I eat rice every day. ฉันกินข้าวทุกวัน
- A dog has four legs. สุนัขมีสี่ขา
- Bangkok is the capital city of Thailand. กรุงเทพเป็นเมืองหลวงของประเทศไทย
- My class starts at 9.00 ชั่วโมงเรียนของฉันเริ่มเวลา 9 นาฬิกา

Present Continuous Tense
Tense นี้อีกชื่อหนึ่งคือ Present Progressive Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + is, am, are + Ving
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นขณะนี้
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังจะเกิดในอนาคตแน่ๆ
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I am eating rice now. ฉันกำลังกินข้าวอยู่ตอนนี้
- A dog is walking. สุนัขกำลังเดิน
- I’m going to London next week. ฉันกำลังจะไปลอนดอนสัปดาห์หน้า
- We are visiting our granddad tomorrow. พวกเรากำลังจะไปเยี่ยมปู่พรุ่งนี้

Present Perfect Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + has, have + V3
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่ดำเนินเสร็จแล้ว
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่ดำเนินมาได้ในระยะเวลาหนึ่งจนถึงปัจจุบัน
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I have eaten rice. ผมกินข้าวแล้ว (กินเสร็จแล้ว)
- She has finished her homework. หล่อนทำการบ้านเสร็จแล้ว
- I have eaten rice for 20 minutes. ผมกินข้าวมาแล้ว 20 นาที
- He has lived here since 2000. เขาอาศัยอยู่ที่นี่ตั้งแต่ปี 2000

Present Perfect Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + has, have +been+ Ving
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่ดำเนินมาได้ในระยะเวลาหนึ่งจนถึงปัจจุบันคล้าย present perfect tense แต่เป็นการเน้นย้ำว่าทำอย่างต่อเนื่อง
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I have been playing football since 8 o’clock. ฉันเล่นฟุตบอล (อย่างต่อเนื่อง) ตั้งแต่ 8 โมง
- She has been walking for 30 minutes. หล่อนเดิน (อย่างต่อเนื่อง) เป็นเวลา 30 นาที
- Toon has been running for 4 hours. ตูนวิ่ง (อย่างต่อเนื่อง) เป็นเวลา 4 ชั่วโมง)
- He has been working here since 1999. เขาทำงานที่นี่ (อย่างต่อเนื่อง)ตั้งแต่ปี 1999 (ไม่เคยย้ายไปไหน)
PAST TENSE
บอกเล่าเรื่องราวในอดีต
Past Simple Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + V2
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ในอดีต ที่เกิดขึ้น ณ จุดเวลาใดเวลาหนึ่ง
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I went to school yesterday. ฉันไปโรงเรียนเมื่อวานนี้
- I ate bananas last week. ฉันกินกล้วยเมื่อสัปดาห์ที่แล้ว
- My dad washed his car last Sunday. พ่อของผมล้างรถของเขาเมื่อวันอาทิตย์ที่แล้ว
- She watched this movie last year. หล่อนดูหนังเรื่องนี้ปีที่แล้ว
- Sam visited his parents five years ago. แซมไปเยี่ยมพ่อแม่ของเขาเมื่อห้าปีที่แล้ว

Past Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + was, were + Ving
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นในอดีต แล้วมีอีกเหตุการณ์หนึ่งแทรกขึ้นมา
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I saw a big elephant while I was walking to school. ฉันเห็นช้างตัวหนึ่งขณะที่ฉันกำลังเดินไปโรงเรียน
- We were eating dinner when dad came home. พวกเรากำลังกินข้าวเย็นอยู่ ตอนที่พ่อมาถึงบ้าน
- The light went out when they were watching TV. ไฟดับตอนที่พวกเขากำลังดูทีวีอยู่
- She was taking a bath when I called her. หล่อนกำลังอาบน้ำอยู่ ตอนที่ผมโทรหาหล่อน
- Sam was driving home when it started to rain. แซมกำลังขับรถกลับบ้าน ตอนที่ฝนเริ่มตก

Past Perfect Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + had + V3
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่สิ้นสุดแล้วในอดีต ก่อนจะมีอีกเหตุการณ์ตามมา
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I had eaten a pizza before I went to bed.ฉันได้กินพิซซ่า ก่อนที่ฉันเข้านอน (กินก่อน )
- John called me after I had left. จอห์นโทรหาฉัน หลังจากที่ฉันได้ออกจากบ้านแล้ว
- All people had gone home when we reached the cinema. คนได้กลับบ้านหมดแล้ว เมือเราไปถึงโรงหนัง
- They had had dinner before they did homework. พวกเขาได้เขากินข้าว ก่อนพวกเขาทำการบ้าน
- The train had left when we got to the station. รถไฟออกไปแล้ว ตอนที่เราไปถึงสถานี

Past Perfect Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + had + been + ฺฺ Ving
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต และดำเนินมาเป็นระยะเวลาหนึ่ง เน้นการบอกเวลามากกว่าการกระทำ
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I had been waiting for the train for three hours before it arrived. ฉันได้รอคอยรถไฟเป็นเวลา(ตั้ง) 3 ชั่วโมง (นะ) ก่อนที่มันจะมาถึง
- We had been walking for one hour when we saw that bird.
พวกเราได้เดิน (ตั้ง) 1 ชั่วโมง (แน่ะ) ตอนที่พวกเราเห็นนกตัวนั้น - They had been playing football for four hours when it started to rain.
พวกเขาได้เล่นฟุตบอล (ตั้ง) 4 ชั่วโมง ก่อนที่ฝนเริ่มตก (วันนี้เล่นได้นาน ปกติไม่เกินชั่วโมงก็ตกแล้ว)
FUTURE TENSE
บอกเล่าเรื่องราวในอนาคต

Future Simple Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + will + ฺฺ V1
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่า คาดการณ์เหตุการที่จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคต
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I will go to school tomorrow. ฉันจะไปโรงเรียนพรุ่งนี้ (คิดว่าต้องไป เดี๋ยวหมดสิทธิ์สอบ)
- I will watch Chin Jang this evening. ฉันจะดูชินจังเย็นนี้ (เพื่อนบอกว่าสนุก จะลองดูหน่อย)
- You will eat papaya salad tonight. คุณจะกินส้มตำคืนนี้ (คุณเคยบอกไว้ ว่าจะกินคืนนี้)
- He will clean the car next week. เขาจะล้างรถสัปดาห์หน้า (เขาบอกมา ว่าจะล้าง)
- She will buy a bike next month. หล่อนจะซื้อจักรยานเดือนหน้า (หล่อนว่าเดินไปเรียนแล้วเหนี่อย)

Future Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + will + ฺฺ be + Ving
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่กำลังเกิดขึ้นอยู่ในอนาคต
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I will be reading books at 8 o’clock tomorrow. ฉันจะกำลังอ่านหนังสือเวลา 8 นาฬิกา วันพรุ่งนี้
- At nine o’clock tomorrow, we will be working on the farm.พรุ่งนี้เวลา 9 นาฬิกา พวกเราจะกำลังทำงานในฟาร์ม
- At six o’clock, we will be eating dinner with our granddad. เวลา 6 นาฬิกา พวกเราจะกำลังกินข้าวกับปู่ของพวกเรา
- She will be waiting when you arrive. หล่อนจะกำลังรอคอย เมื่อคุณมาถึง

Future Perfect Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + will + ฺฺ have + V3
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่สิ้นสุดแล้วในอนาคต
ตัวอย่างประโยค:
- I will have eaten breakfast at 8 o’clock tomorrow. ฉันจะกินข้าวเช้าเรียบร้อยแล้ว เวลา 8 นาฬิกา วันพรุ่งนี้
- Tomorrow morning, we will have finished our project. พรุ่งนี้เช้า พวกเราจะดำเนินโครงการของพวกเราเสร็จแล้ว
- She will have gone when you arrive. หล่อน(คง)จะไปแล้ว เมื่อคุณมาถึง
- I will have cleaned the floor when my mom gets home. ฉัน(คง)จะทำความสะอาดพื้นเรียบร้อยแล้ว ตอนที่แม่มาถึง

Future Perfect Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง: S. + will + ฺฺ have + been + Ving
หลักการใช้:
- บอกเล่าเหตุการณ์ที่ดำเนิมมาได้ระยะเวลาหนึ่งในอนาคต ก่อนมีอีกเหตุการณ์หนึ่งแทรกเข้ามา
ตัวอย่างประโยค
- I will have been eating breakfast for 30 minutes at 8 o’clock tomorrow.
ฉันจะได้กำลังกินข้าวเช้าเป็นเวลา 30 นาทีแล้ว ณ เวลา 8 นาฬิกา วันพรุ่งนี้ - At 10 o’clock tomorrow, we will have been working on the farm for two hours.
เวลา 10 นาฬิกาพรุ่งนี้ พวกเราจะได้กำลังทำงานในฟาร์ม เป็นเวลา 2 ชั่วโมงแล้ว - You will have been waiting for two hours when the plane arrives.
คุณจะได้กำลังรอ เป็นเวลาสองชั่วโมง เมื่อเครื่องบินมาถึง
ถึงแม้ว่า Tense ทั้งหมดจะมี 12 Tense ก็จริง แต่สรุปว่าจริงๆใช้บ่อยก็มีดังต่อไปนี้
- Present Continuous
- Present Simple
- Present Perfect
- Past simple
- Future Simple
นอกนั้นไม่ค่อยได้ใช้เท่าไหร่หรอกครับ
ขอ 5 ดาวให้บทเรียนด้วยครับผม…
คลิกดาวดวงที่ขวามือสุดเลยครับครับ…
[Update] หลักการใช้ Past Simple Tense ง่ายมากๆ ใช้กริยาเดียวกันหมดเลย – NSRU BLOG | โครงสร้าง ของ past simple tense – NATAVIGUIDES
Past Simple Tense คืออะไร มีหลักการใช้อย่างไร และโครงสร้างของประโยคเป็นอย่างไร : Past Simple Tense คือ อดีตกาลธรรมดา เอาไว้เล่าเรื่องราวหรือเหตุการณ์ในอดีต โครงสร้างของประโยคก็ง่ายๆคือ ประธานตามด้วยกริยาช่อง 2 ไม่ว่าประธานตัวใดก็ตาม

past simple tense คืออะไร
- Past พาสท แปลว่า อดีต
- Simple ซิ๊มเพิล แปลว่า ธรรมดา
- Tense เท็นส์ แปลว่า กาล
- Past Simple Tense คือ อดีตกาลธรรมดา บ้างก็เรียก Simple Past
โครงสร้าง past simple tense
- S + V 2 (Subject + Verb ช่อง 2)
- ประธาน + กริยาช่อง 2
SubjectVerb (2)I, You, He, She, It, We,theyatewentdrank
หลักการใช้ past simple tense
Past Simple Tense ถือว่าง่ายที่สุดเลยเพราะการเล่าเรื่องในอดีต ภาษาอังกฤษนั้น ประธานทุกตัวใช้กริยาช่องสองเหมือนกัน (เว้น was ใช้กับประธานเอกพจน์, were ใช้กับประธานพหูพจน์) ให้จำหลักสำคัญของ Tense นี้ไว้ว่า เป็นการเล่าเรื่องราวที่เกิดขึ้นในอดีต และก็จบลงไปแล้วด้วย ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับปัจจุบัน
1. ใช้เล่าเหตุการณ์ในอดีต ที่จะระบุเวลากำกับ หรือรู้กันดีว่ามันเกิดในอดีต
1.1 เล่าเหตุการณ์ที่มีเวลากำกับ คำกำกับเวลาที่พบบ่อย ได้แก่
– yesterday เย็สเตอเด เมื่อวาน
– last + เวลา/ วัน/ สัปดาห์/ เดือน/ฤดู/ ปี เช่น
- last hour ลาสท เอาเวอะ ชั่วโมงที่แล้ว
- last night ลาสทไนท คืนที่แล้ว
- last Monday ลาสท มันเด จันทร์ที่แล้ว last Tuesday อังคารที่แล้ว……
- last month ลาสท มันธ เดือนที่แล้ว
- last Christmas ลาสท คริสมัส คริสต์มาสที่แล้ว
- last Summer ลาสท ซัมเมอะ หน้าร้อนที่แล้ว Last winter ลาสท วินเทอะ หน้าหนาวที่แล้ว
- last year ลาสท เยีย ปีที่แล้ว
– วินาที / นาที/ ชั่วโมง/ วัน/ สัปดาห์/ เดือน/ ปี + ago เช่น
- ten seconds ago เท็น เซเคินส อะโก สิบวินาทีที่แล้ว
- Five minutes ago ไฟฟ มินนิทส อะโก ห้านาทีที่แล้ว
- Three day ago ธรีเดส อะโก สามวันที่แล้ว
- Two weeks ago สองสัปดาห์ที่แล้ว
- one month ago หนึ่งเดือนที่แล้ว (เท่ากับ last month)
- four years agoฟอเยียส อะโก สี่ปีที่แล้ว
ตัวอย่างประโยค past simple tense
ประโยคบอกเล่า
ประโยคบอกเล่าใน past simple tense คือ ประธานตามด้วยกริยาช่อง 2 กับประธานทุกตัว
I saw Jane at the bank yesterday. ฉันพบเจนที่ธนาคารเมื่อวาน
I went to Jim’s party lastnight. ฉันไปงานเลี้ยงของจิมคืนที่แล้ว
We studied math last Friday. พวกเราเรียนคณิตวันศุกร์ที่แล้ว
He bought a radio last month. เขาซื้อวิทยุเดือนที่แล้ว
She came to my house last year. หล่อนมาบ้านฉันปีที่แล้ว
It rained two days ago. ฝนตกสองวันที่แล้วThey ate dinner two hours ago.
พวกเขากินอาหารเย็นสองชั่วโมงที่แล้วJane met Jo ten days ago. เจนพบโจสิบวันที่แล้ว
The bus arrived thirty minutes ago. รถบัสมาถึงสิบนาทีที่แล้ว
I cleaned my room two weeks ago. ผมทำความสะอาดห้องสองสัปสัปดาห์ที่แล้ว
My dog died two years ago. หมาฉันตายสองปีที่แล้ว
I was at school yesterday. ฉันอยู่ที่โรงเรียนเมื่อวาน
They were at home last weekend. พวกเขาอยู่บ้านเมื่อวันอยุดสุดสัปดาที่แล้ว
We had two cups of coffee this morning. พวกเราดื่มกาแฟสองถ้วยเมื่อเช้านี้
ประโยคปฏิเสธ
ประโยคปฏิเสธใน past simple tense ให้เอา did not หรือ didn’t นำหน้ากริยาหลัก และกริยาหลักให้เปลี่ยเป็นช่องที่ 1 โดยไม่ต้องเติม s หรือ es
I din’t see Jane at the bank yesterday. ฉันไม่ได้พบเจนที่ธนาคารเมื่อวาน
I didn’t go to Jim’s party lastnight. ฉันไม่ได้ไปงานเลี้ยงของจิมคืนที่แล้ว
We did not study math last Friday. พวกเราไม่ได้เรียนคณิตวันศุกร์ที่แล้ว
He did not buy a radio last month. เขาไม่ได้ซื้อวิทยุเดือนที่แล้ว
She didn’t come to my house last year. หล่อนไม่ได้มาบ้านฉันปีที่แล้ว
ประโยคคำถาม
ประโยคคำถามใน past simple tense ให้เอา Did น้ำหน้าประโยค หรือ Didn’t ถ้าเป็นคำถามแบบปฏิเสธ และกริยาหลักให้ใช้ช่องที่ 1 โดยไม่ต้องเติม s หรือ es
Did you see Jane at the bank yesterday. คุณได้พบเจนที่ธนาคารเมื่อวานไหม
Yes, I did. ใช่่ ฉันได้พบ
Did you go to Jim’s party lastnight. คุณได้ไปงานเลี้ยงของจิมคืนที่แล้วไหม
No, I didn’t. ไม่ ฉันไม่ได้ไป
Did they study math last Friday. พวกเราได้เรียนคณิตวันศุกร์ที่แล้วไหม
Yes, they did. ใช่ พวกเขาเรียน
Didn’t he not buy a radio last month. เขาไม่ได้ซื้อวิทยุเดือนที่แล้วใช่ไหม
Yes, he did. ใช่ เขาซื้อ
Didn’t she come to my house last year. หล่อนไม่ได้มาบ้านฉันปีที่แล้วใช่ไหม
No, she didn’t. ไม่หล่อนไม่ได้มา
1.2 เล่าเหตุการณ์ที่ไม่มีเวลากำกับก็ได้แต่รู้กันดีว่าพูดถึงเรื่องในอดีต เช่น
Sam : Did you go to the party lastnight. คุณไปงานปาร์ตี้ใช่ไหมคืนที่แล้ว (มีคำว่า last อดีตแน่นอน)
Sim: Yes. It was the great party. I saw Jim and Jo. I drank a lot of cola and ate lots of pizza.
ใช่ มันเป็นปาร์ตี้ที่ยอดเยี่ยม ฉันเห็นจิมและโจ ฉันดื่มน้ำอัดลมเยอะมาก และฉันกินพิซซ่าเยอะมาก
จากตัวอย่างจะเห็นได้ว่าซิมไม่ได้ใช้เวลาระบุเหตุการณ์ในอดีตเลย ทั้งนี้คนถามได้ระบุแล้วเรียบร้อยนั่นเอง
คำบ่งบอกความถี่ เช่น always, sometimes, never เป็นต้น
- She always went to school late last month.
หล่อน ไป โรงเรียน สาย เสมอ เมื่อเดือน ที่แล้ว (เดือนนี้ไม่มาสายแล้ว) - We sometimes watched movies at home last year.
เรา ดู หนัง ที่ บ้าน เป็นบางครั้ง เมื่อปี ที่แล้ว (ปีนี้ไปดูที่โรงหนังอย่างเดียว) - I never read books in the evening last month.
ฉัน ไม่เคย อ่าน หนังสือ ใน ตอนค่ำ เมื่อเดือน ที่แล้ว (เดือนนี้ต้องอ่านเพราะใกล้สอบแล้ว)
3. ใช้เล่านิทาน ส่วนใหญ่จะมีคำว่า Long time ago หรือ Once upon a time (นานมาแล้ว)
ตัวอย่างการใช้ Past Simple Tense ในนิทาน
THE LITTLE MERMAID ตำนานรักธิดาสมุทร
The sea king lived in under the sea.
ราชาแห่งท้องทะเลอาศัยอยู่ในทะเล
His palace was made of shells and sparkling stones.
ปราสาทของเขาทำจากเปลือกหอยและที่ที่เปล่งประกายแวววับ
His mother and six daughters also lived with him.
แม่และลูกสาวของเขาก็อาศัยอยู่กับเขาด้วย
All his daughters were beautiful but his young daughter was the most beautiful.
ลูกสาวทุกคนของเขาสวย แต่ลูกสาวคนเล็กสวยที่สุด
She was not like the others. Her sisters liked to play.
เธอไม่เหมือนคนอื่น พี่ๆของเธอชอบเล่น
But she liked to listen to stories.
JACK AND THE BEANSTALK แจ๊คผู้ฆ่ายักษ์
Once upon a time there was a boy called Jack.
กาลครั้งหนึ่งนานมาแล้ว มี เด็กชาย คนหนึ่ง ชื่อว่า แจ๊ค
He lived with his mother.
เขา อาศัยอยู่ กับ แม่ ของเขา
They were very poor.
พวกเขา จน มาก
All they had was a cow.
สิ่งที่ พวกเขา มี คือ วัว หนึ่งตัว
One morning, Jack’s mother told Jack to take their cow to market and sell her.
เช้าวันหนึ่ง แม่ของแจ็ค บอก แจ็ค ให้ เอา วัว ไปตลาด และขาย มัน
On the way, Jack met a man. He gave Jack some magic beans for the cow.
ขณะเดินทาง แจ็ค พบ ชาย คนหนึ่ง เขา ให้ เมล็ดถั่ว วิเศษ แก่แจ็ค เพื่อแลก วัว
Jack took the beans and went back home.
Time Line เส้นเวลา ใน Past Simple Tense
มาดูไทม์ไลน์กันเลยครับ ที่บอกว่า present simple tense ใช้ “บอกกล่าวเหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึนในอดีต” นั้นเป็นเช่นไร
- สีดำคือ อดีตที่หมองหม่น
- สีส้มคือปัจจุบันที่สดใส
- สีชมพู คือ อนาคตที่เรืองรองผ่องอำไพ
- ลูกศรสีขาวไซร้คือเหตุการณ์
- จุดสีแดงคือ เวลาในอดีต สังเกตจุดสีแดงให้ดีนะครับ มันมีแค่จุดเดียว และมันจะอยู่ตรงไหนก็ได้ ขอให้เป็นอดีต นับตั้งแต่เสี้ยววินาทีที่แล้วเป็นต้นไป และไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับปัจจุบันแล้วเด็ดขาด
สรุปว่าถ้านักเรียนต้องการสื่อเรื่องราวอะไรสักอย่าง ที่มันเป็น “เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้น ณ จุดใดจุดหนึ่งในอดีต” ให้ใช้ Past Siple Tense อดีตกาลธรรมดา
ขอขอบคุณบทความดีๆ จาก: https://ภาษาอังกฤษออนไลน์.com/หลักการใช้-past-simple-tense/
Simple past tense cartoon
This is for learning purposes. No credits will be taken.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

Talking about Your Home in English
Improve your vocabulary and learn how to talk about your home in English.
https://www.kidspages.com/flashcards.htm

Past Simple Tense – Song
A nice song using many verbs in past simple tense.

What are they doing? Present Continuous Tense
Learn how to use the present continuous tense in this video through a short story.

Past Simple Tense be – was / were: Fun \u0026 Interactive English Grammar ESL Video
Teach your beginner students the past simple tense be: was/were with this original \u0026 innovative video and introduce your learners to timelines.
If you love our videos, please support us at Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/oomongzu
WEBSITE: http://oomongzu.com
For more creative, engaging and interactive animated grammar teaching ESL videos, please visit our website.
For the “No Music” version of this ESL video, please click here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9TYJn8v9dr8
Title of English / ESL Video:
Past Simple Tense be: was/were
Target English Grammar:
Past simple tense be: was/were
Student Proficiency Level:
Beginner level grammar
Suggested Courses:
General English
Instructions:
– Play the video in class after delivering a warmup activity first.
– Pause the video whenever the narrator asks students a question to give students time to answer. For example, after elicitations and concept checking questions (CCQs).
Summary of English Grammar: Past Simple Tense be – was/were
Approximate chronological order:
Rules and Explanation:
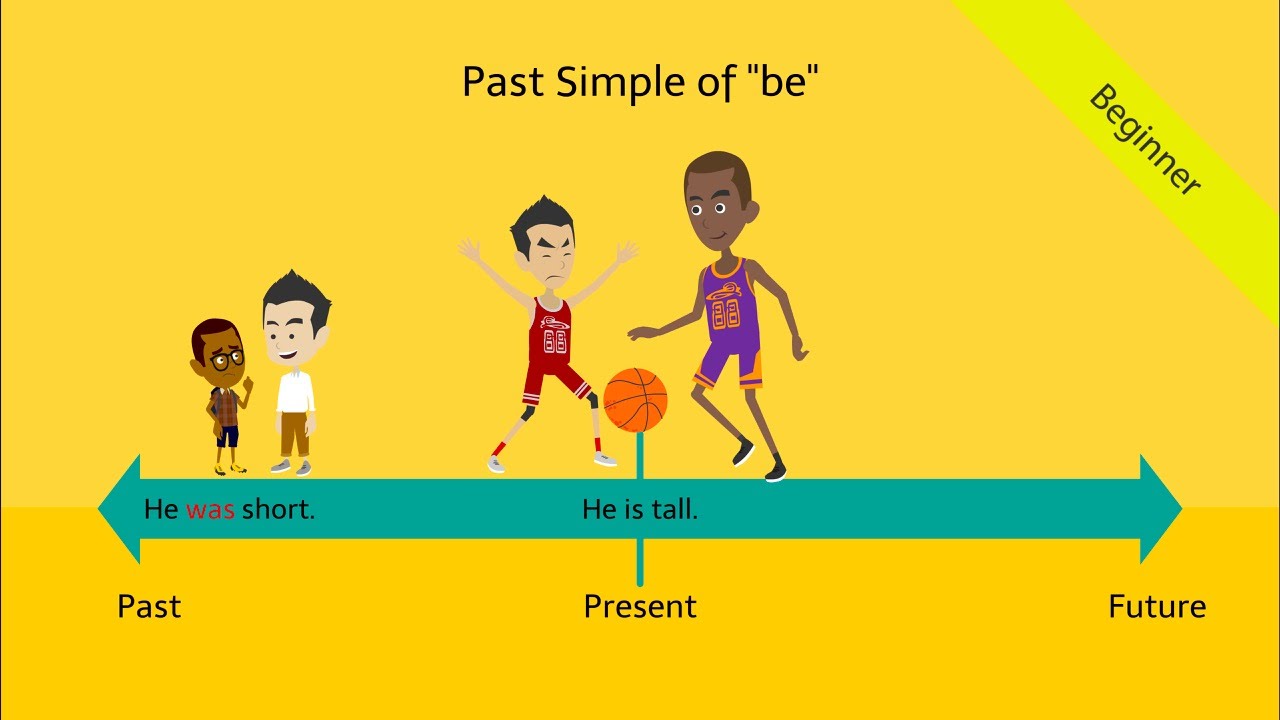
Elicitation of positive example sentence: He was short.
Elicitation of negative example sentence: He wasn’t short.
Pause the video after the question to give students time to answer.
Meaning / Function (Definition):
We use the simple past to talk about the past.
Affirmative and Negative Sentences:
wasn’t = was not (contraction)
Positive and Negative Examples:
– Positive example sentence: I was a police officer.
Negative example question: I wasn’t a police officer.
– Positive example sentence: She was beautiful.
Negative example question: She wasn’t beautiful.
– Positive example sentence: It was expensive!
Negative example question: It wasn’t expensive!
– Positive example sentence: We were at home.
Negative example question: We weren’t at home.
– Positive example sentence: They were in Russia.
Negative example question: They weren’t in Thailand
Form / Structure:
Singular vs. Plural:
The simple past of “be” has two forms: was and were.
Elicit from students: Which one is singular and which one is plural? (Was is singular and were is plural.)
But sometimes English doesn’t always follow the rules. The pronoun you can be singular or plural, but we use were for both singular you and plural you.
– Positive example sentence: You were late to school.
Negative example question: You weren’t late to school.
Wh Question:
– Example question: Why were you late to school?
Yes/No Question Form:
– Example question: Were you late to school?
The short answer for a yes/no question is:
Yes, I was.
No, I wasn’t.
Further Example Wh Questions and Yes/No Questions:
When were they in Russia?
Were they in Russia?
The short answers are:
Yes, they were.
No, they weren’t.
How much was it?
Was it expensive?
(Elicit) And what are the short answers?
Yes, it was.
No, it wasn’t.
Summary:
The negatives are:
was = wasn’t
were = weren’t
was is singular.
were is plural and for you.
The short answers to yes/no questions are:
Yes, + subject + was/were.
No, + subject + wasn’t/weren’t.
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆMAKE MONEY ONLINE
ขอบคุณที่รับชมกระทู้ครับ โครงสร้าง ของ past simple tense

